Renal/GU taxonomy (pathophys)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
prerenal
-before the kidney
-hypoperfusion (volume depletion, 3rd spacing, restricted renal arterial blood flow)
-drop in blood pressure
pre renal disease
prerenal azotemia
prerenal azotemia
-most common acute kidney injury
-most common cause of renal failure (inpatient patients)
-most commonly caused by dehydration
intrarenal
direct damage to the kidneys (inflammation, toxins, drugs, infection, reduced blood supply)
categories of intrarenal diseases
-vascular
-glomerular
-tubular
-interstitial
types of vascular diseases (intrarenal)
-vasculitis
-malignant HTN
-scleroderma
-thromboembolic
types of glomerular diseases (intrarenal)
-acute glomerulonephritis
-chronic glomerulonephritis
types of acute glomerulonephritis (intrarenal, glomerular)
-Anti-GM-associated acute GN
-Goodpasture's syndrome
-IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease)
-Crescentic GN
-post streptococcal GN
types of chronic glomerulonephritis (intrarenal, glomerular)
-diabetic neuropathy
-lupus nephritis
-membranous nephropathy
-focal segmental glomerular sclerosis
-minimal change disease
-membranoproliferative GN
types of tubular disease (intrarenal)
-acute tubular
-chronic tubular
types of acute tubular disease (intrarenal, tubular)
-acute tubular necrosis
-multiple myeloma
-uric acid nephropathy
types of chronic tubular disease (intrarenal, tubular)
-polycystic kidney disease
-medullary sponge kidney
types of interstitial disease (intrarenal)
-acute
-chronic
-renal neoplasias
types of acute interstitial disease (intrarenal, interstitial)
-interstitial nephritis
-acute pyelonephritis
types of chronic interstitial disease (intrarenal, interstitial)
-chronic pyelonephritis
-analgesic nephropathy
-chronic interstitial nephritis
types of renal neoplasias (intrarenal, interstitial)
-renal adenomas
-renal transition cell carcinoma
-renal cell carcinoma
postrenal
-after the kidneys
-obstructive (renal damage by back pressure)
types of post renal disease
-obstructive uropathy
-bladder disorders
-lower urinary tract obstructions
types of obstructive uropathy (postrenal)
-kidney stones
-infection/inflammation
types of bladder disorders (postrenal)
-functional uropathy
-overactive bladder syndrome
-bladder tumors
types of lower urinary tract obstruction (postrenal)
-UTI
-prostate enlargement
-urethral stricture
-severe pelvic organ prolapse
-low bladder wall compliance
how is UTI determined by type:
-complicated (recurrent, difficult to treat)
-uncomplicated (most common)
how is UTI determined by location:
-Urethritis (inflammation in urethra)
-Prostatitis (inflammation in prostate)
-Cystitis (bladder inflammation)
-interstitial cystitis (cystitis with negative urine cultures)
-pyelonephritis (inflammation of upper urinary tract)
vasculitis
-vascular, intrarenal
-inflammation, immune mediated (ANCA)
malignant HTN
-vascular, intrarenal
-thickened, degraded arterioles/tubules/glomeruli from increased pressure in kidneys
scleroderma
-vascular, intrarenal
-systemic disease, progressive
-renal degradation, obliterative vasculopathy
-collagen overproduction, connective tissue disorder
thromboembolic disease
-vascular, intrarenal
-arterial embolus blocks flow to at least a portion of kidney
-local or distant thromboembolitic events
acute glomerulonephritis
-glomerular, intrarenal
-immune mediated
-uncommon
-nephritic or nephrotic
Anti-GBM associated acute glomerulonephritis
-glomerular (acute), intrarenal
-antibodies attack glomerular basement membrane
-variety of disorders associated with it
goodpasture's syndrome
-anti-GBM (acute GN, glomerular, intrarenal)
-sequela of lung infection
-antibodies simultaneously attack lung and kidney basement membrane
IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease)
-IgA associated (acute GN, glomerular, intrarenal)
-most common type
- abnormal IgA to mesangial cells* in the glomerulus, activating a complement pathway → injury and mesangial proliferation
crescentic glomerulonephritis
-may be anti-GBM associated (acute GN, glomerular, intrarenal)
-proliferation of glomerular capillary cells
-rapid loss of renal function
post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
-anti-GBM associated (acute GN, glomerular, intrarenal)
-rarer now due to testing and antibiotics
-immune mediated
-follows group A strep infection
nephritic
-blood in the urine and LITTLE protein
-immune mediated inflammation
-usually less significant
-leads to mild HTN
nephrotic
-blood in the urine with LOTS of protein
-noninflammatory damage
-leads to hyperlipidemia
-usually very serious
diabetic nephropathy
-chronic GN, glomerular, intrarenal
-podocyte injury leads to thickening of glomerular basement membrane
-most common type of chronic GN
lupus nephritis
-chronic GN, glomerular, intrarenal
-systemic condition
-formation of autoantibodies against double stranded DNA
-deposition of immune complexes on GBM
focal segmental glomerular sclerosis
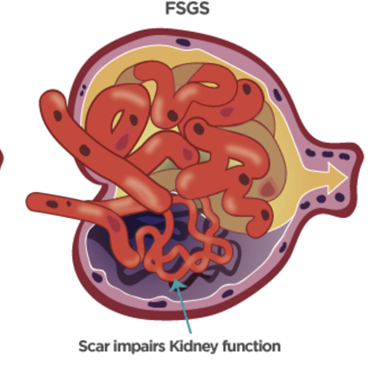
-chronic GN, glomerular, intrarenal
-involves some or parts of glomeruli hardening
-autoimmune plus drugs, infection, Sickle Cell causes
minimal change disease
-chronic GN, glomerular, intrarenal
-most common nephrotic condition in kids
-idiopathic and without major tissue changes
membranoproliferative GN
-chronic GN, glomerular, intrarenal
-abnormal activation of complement cascade in kids and young adults
-can cause renal deposits in eye
-characteristic kidney lesions
acute tubular necrosis
-acute, tubular, intrarenal
-most common cause of intrarenal AKI
-from ischemia, toxins, sepsis (majority= dehydration)
-muddy brown casts
multiple myeloma
-acute, tubular, intrarenal
-large numbers of ineffective antibodies
-can be toxic or obstructive to tubules
-myeloma in kidney= 25% of MM patients
-Bence Jones proteins found in urine
uric acid nephropathy
-acute, tubular, intrarenal
-uric acid overproduction and crystallization causes obstruction
-uric acid= reversible cause of acute renal failure
polycystic kidney disease
-chronic, tubular, intrarenal
-widespread cyst formation from genetic disorders
-can progress to ESRD
medullary sponge kidney
-chronic, tubular, intrarenal
-rare congenital disorder
-small tubular cysts
-usually benign without symptoms

interstitial nephritis
-acute, interstitial, intrarenal
-immune mediated
-often drug induced
-eosinophils in the urine
acute pyelonephritis
-acute, interstitial, intrarenal
-infective
-in blood or upward from bladder
-white blood cell casts
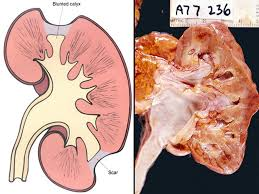
chronic pyelonephritis
-chronic, interstitial, intrarenal
-can become chronic and lead to chronic kidney failure
-persistent, recurrent infections of kidneys
analgesic nephropathy
-chronic, interstitial, intrarenal
-iatrogenic
-chronic use of high dose NSAIDS
-mostly women over age 30
-frequent urinary tract infections
chronic interstitial nephritis
-chronic, interstitial, intrarenal
- immune-mediated, generally drug-induced
-sx: fever, maculopapular rash, eosinophils in urine
-from failure to resolving acute version (drug-induced (NSAIDS, antibiotics, diuretics, allopurinol)
-nonspecific, diagnosed by exclusion
renal adenomas
-renal neoplasia, interstitial, intrarenal
-benign glandular tumor
renal transition cell carcinoma
-renal neoplasia, interstitial, intrarenal
-malignant and rare
renal cell carcinoma
-renal neoplasia, interstitial, intrarenal
-most common type of neoplasia
-malignant
-genetic mutation of tumor suppressor gene (VHL)
kidney stones
-obstructive uropathy, postrenal
-renal calculi or urolithiasis
-Ca oxalate is most common crystal composition
-Staghorn calculi (large, filling calyces, non-obstructive)
functional uropathy
-bladder disorder, postrenal
-neurogenic bladder
-from upper or lower motor neuron defects
overactive bladder syndrome
-bladder disorder, postrenal
-detrusor overactivity
-urinary urgency and urodynamic testing
bladder tumors
-bladder disorder, postrenal
-urothelial transition carcinoma (most common)
-painless microscopic hematuria
urinary tract infection
causes:
-epithelial inflammation (pathogen or not)
-retrograde flow into urethra and bladder
-local obstruction, ascending infection, infective implications
-classified by type (complicated vs uncomplicated)
-classified by location
urethritis
inflammation of urethra
prostatitis
inflammation of prostate
cystitis
bladder inflammation
interstitial cystitis
cystitis with negative urine cultures
pyelonephritis
inflammation of upper urinary tract
other causes of lower urinary tract obstructions
-prostate enlargement
-urethral stricture
-severe pelvic organ prolapse
-low bladder wall compliance
stage 1 kidney disease
-kidney damage with normal or increased GFR
-GFR > or equal to 90
stage 2 kidney disease
-kidney damage with mildly decreased GFR
-GFR= 60-89
stage 3 kidney disease
-moderately decreased GFR
-GFR= 30-59
stage 4 kidney disease
-severely decreased GFR
-GFR= 15-29
stage 5 kidney disease
-kidney failure
GFR < 15 (dialysis)
chronic kidney disease
-defined as either kidney damage or GFR < 60 for 3 months or longer
-kidney damage defined as pathological abnormalities/markers of damage (including urine/blood tests, imaging studies)
what is normal urine flow?
1.2-2 liters/day
adult urine production
0.5-1 mL/kg/hr
polyuria
-excessive urination
more than 2 liters/day
oliguria
-decreased urine output
-less than 500 mL/day
anuria
-absence of urine
-less than 100 mL/day