PHR 936 - Block 1 Sleep
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
functions of sleep
metabolism
learning & memory
cardiovascular health
emotional regulation
immune function
brain health
hippocampal-cortical memory consolidation
occurs during sleep
memories are moved from short-term, low capacity storage into long-term, high capacity storage
- this solidifies memories after learning and opens storage space in the hippocampus for new memories
consequences of sleep deprivation
decreased immune function
- increased risk of infections
- potential increase risk of cancer
- inflammatory neurodegenerative diseases
- autoimmune diseases
- inflammatory metabolic & vascular disease
- decreases vaccine response
- decreased number of NK cells
risk for mental illness
buildup of toxins/ waste products
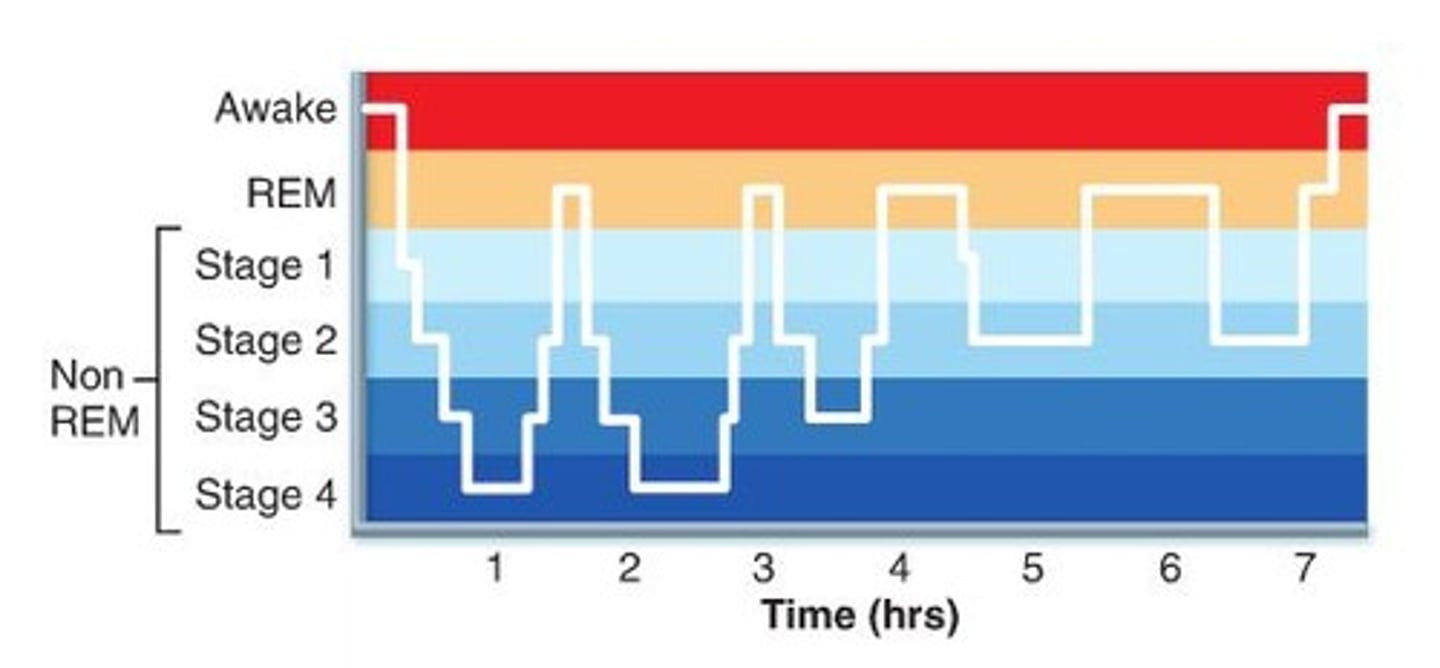
NREM stage 1
the initial stage of NREM sleep, which is characterized by low-amplitude brain waves (4-6 Hz) of irregular frequency, a slow heart rate, and reduced muscle tension
- lasts 5-10 minutes
- transition period between wake and sleep
NREM stage 2
the start of true sleep
body temperature drops & heart rate slows
brain begins to produce sleep spindles
- lasts 20 minutes
NREM stage 3
deepest sleep occurs
muscles relax, breathing rate drops
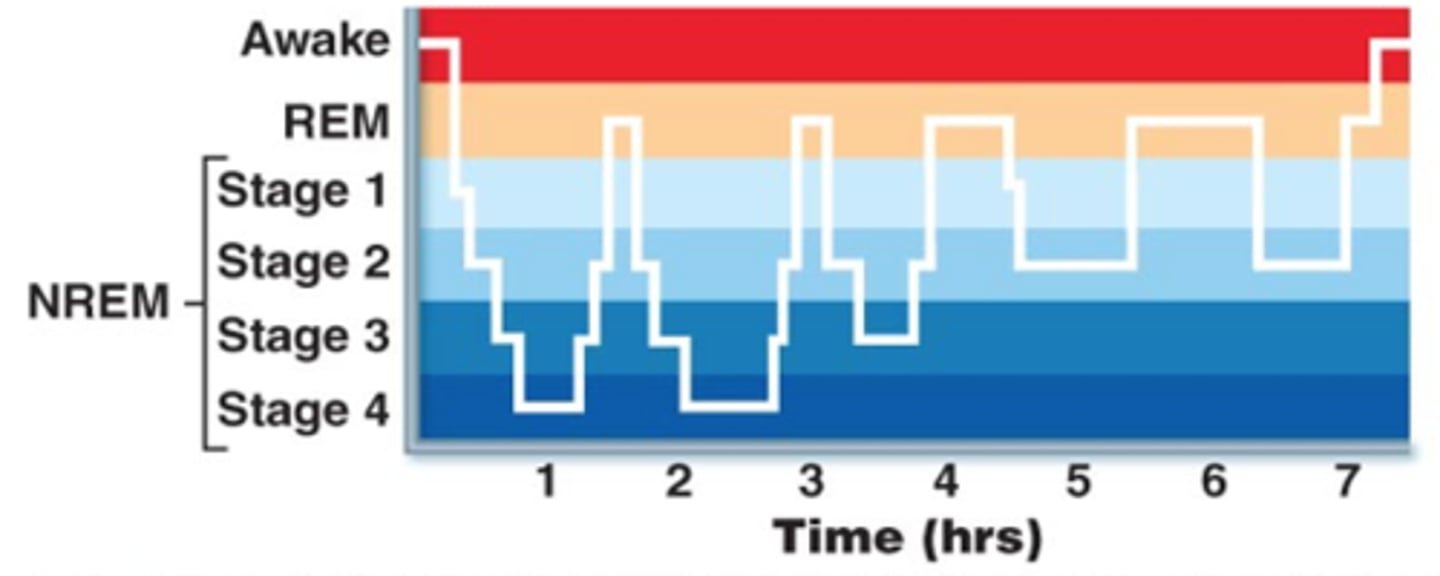
REM sleep
rapid eye movement sleep, a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur
body becomes relaxed & immobilized
brain becomes more active
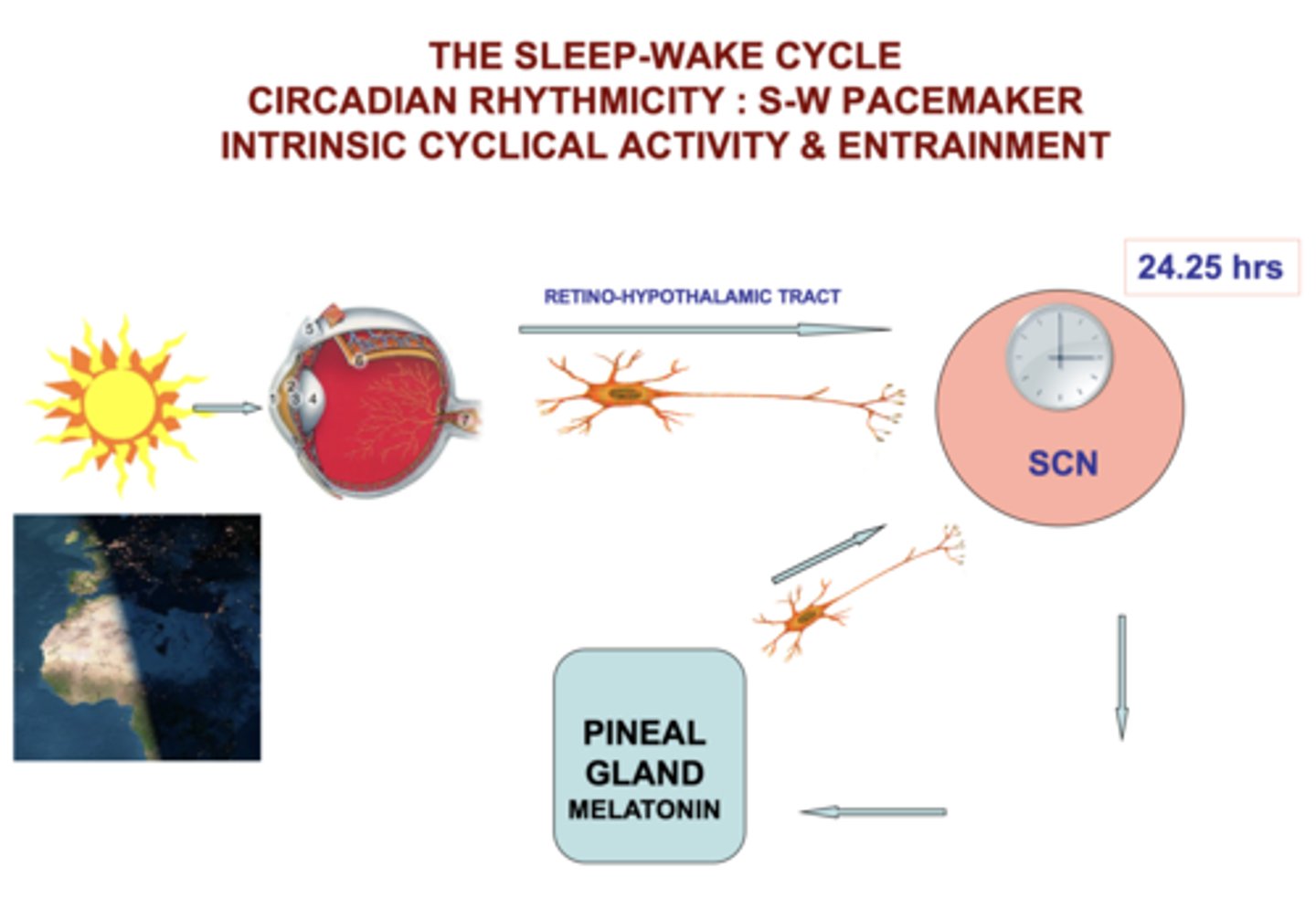
circadian rhythm
Process C
"about a day"
homeostatic process informed by outside environment
melatonin
a hormone secreted by the pineal gland, regulated by the SCN
- MT1 receptors: entrainment to light-dark cycles
- MT2 receptors: phase-shifting
functions in the body:
inflammatory regulation
epigenetic regulation
oxidative stress
glucocorticoid programming
RAS regulation
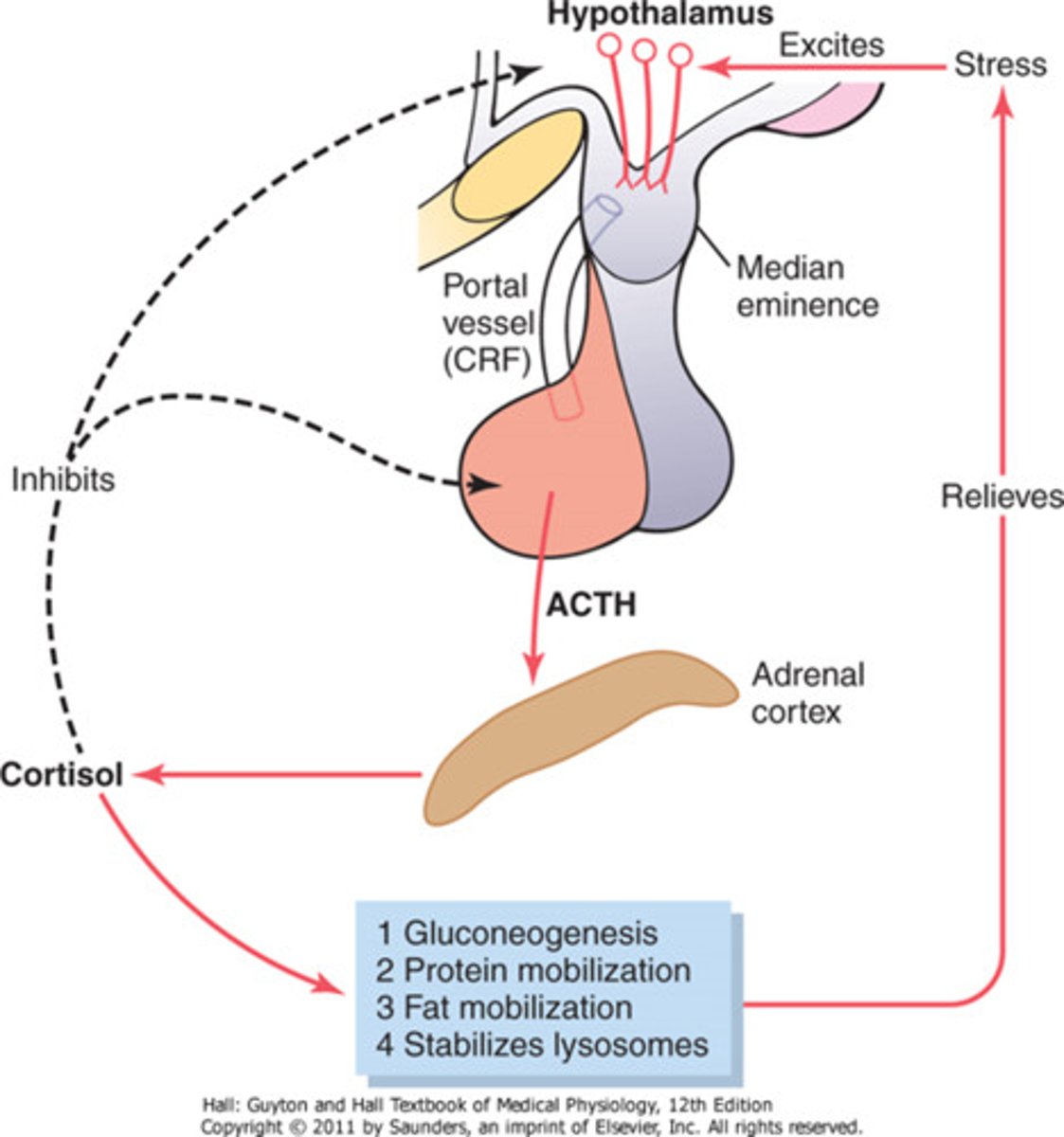
cortisol
stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex
heightens memory and attention
functions in the body:
increases blood pressure
increases blood glucose
decreases pain sensitivity
suppresses immune response
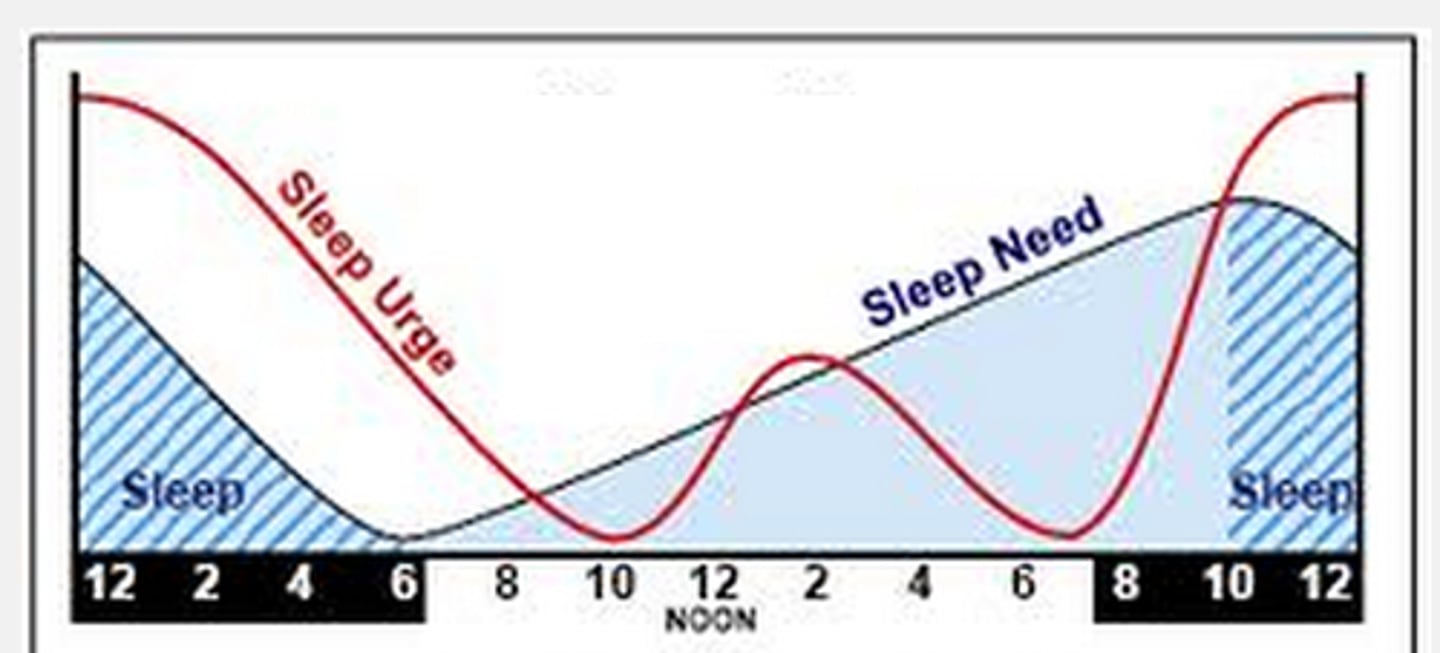
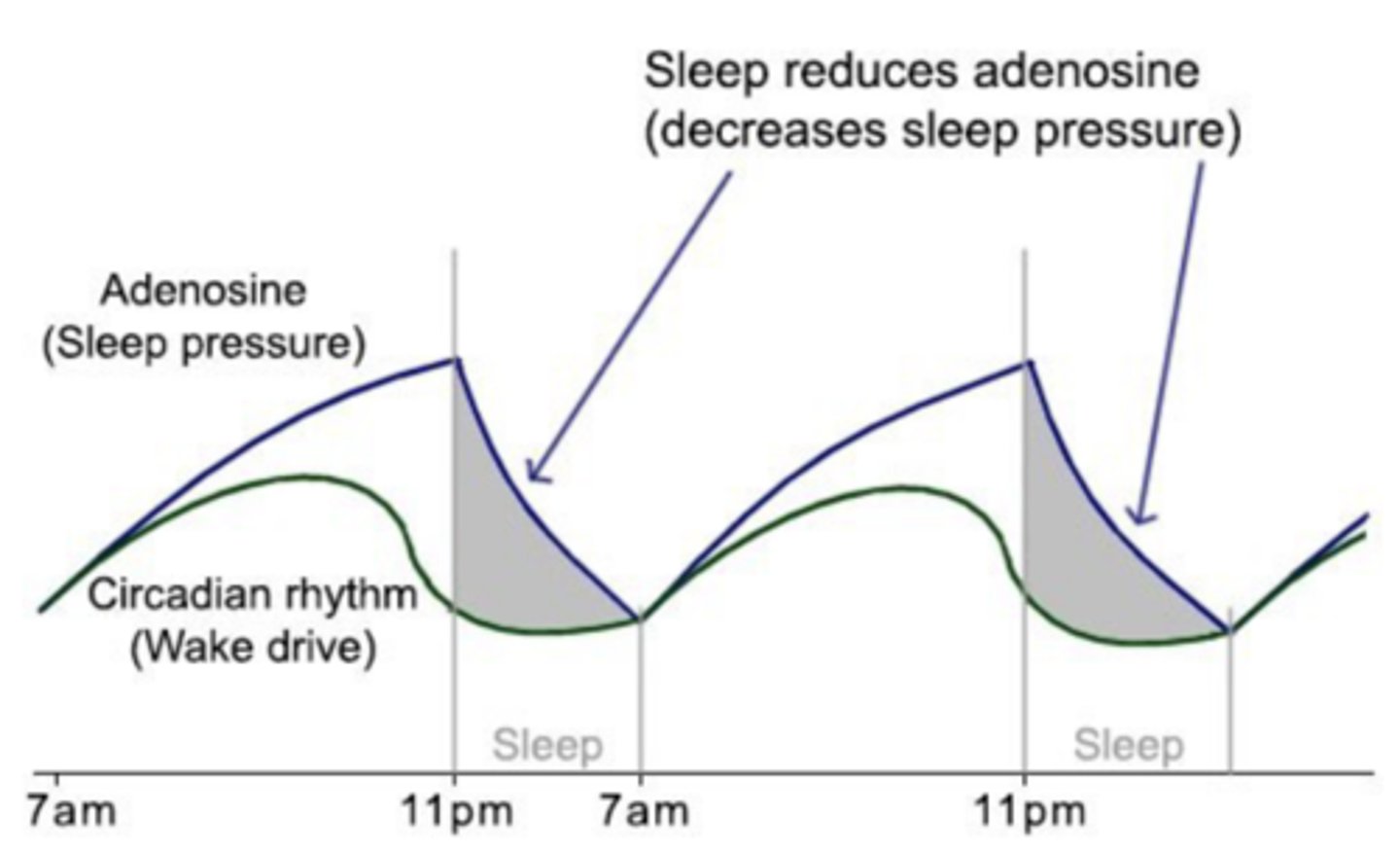
sleep pressure
Process S
driver of sleep
cellular metabolism generates adenosine -> adenosine receptor stimulation promotes sleep
adenosine is recycled in sleep -> improved wakefulness the next day
ATP ⇌ adenosine ⇌ sleep
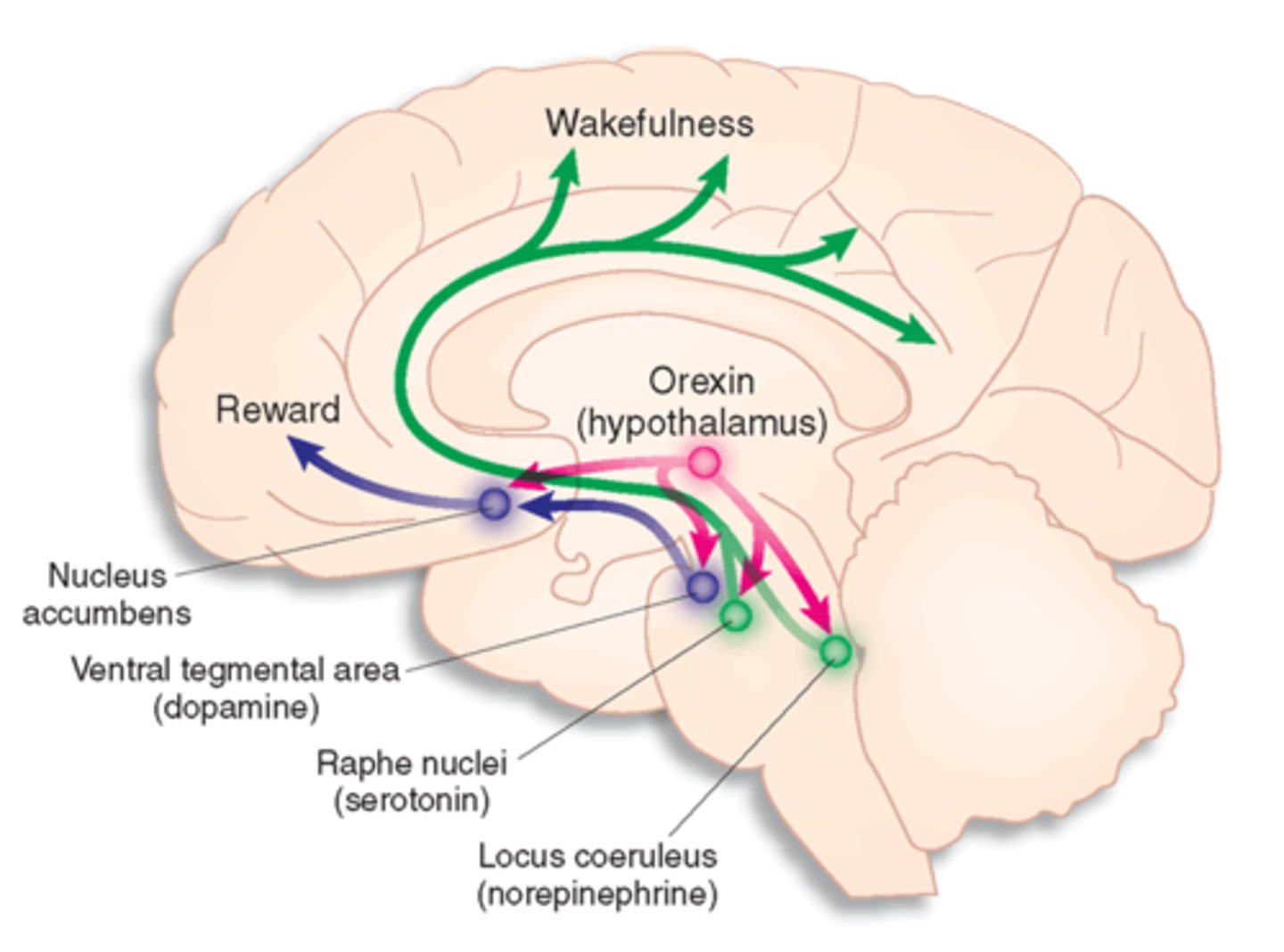
other sleep/ wake promoting neurotransmitters
wake:
acetylcholine
histamine
monoamines (dopamine, norepi, serotonin)
orexin
sleep:
GABA galanin
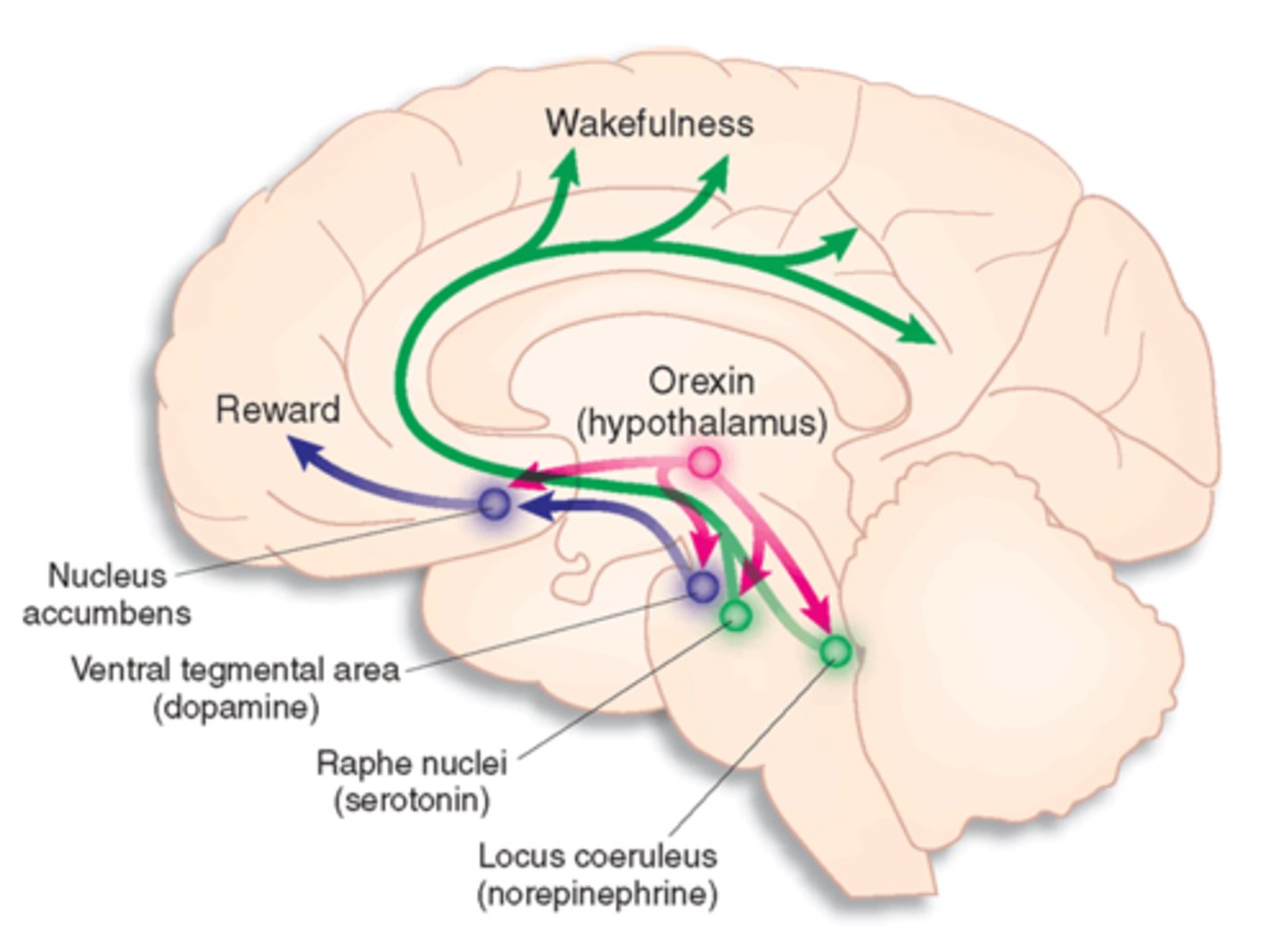
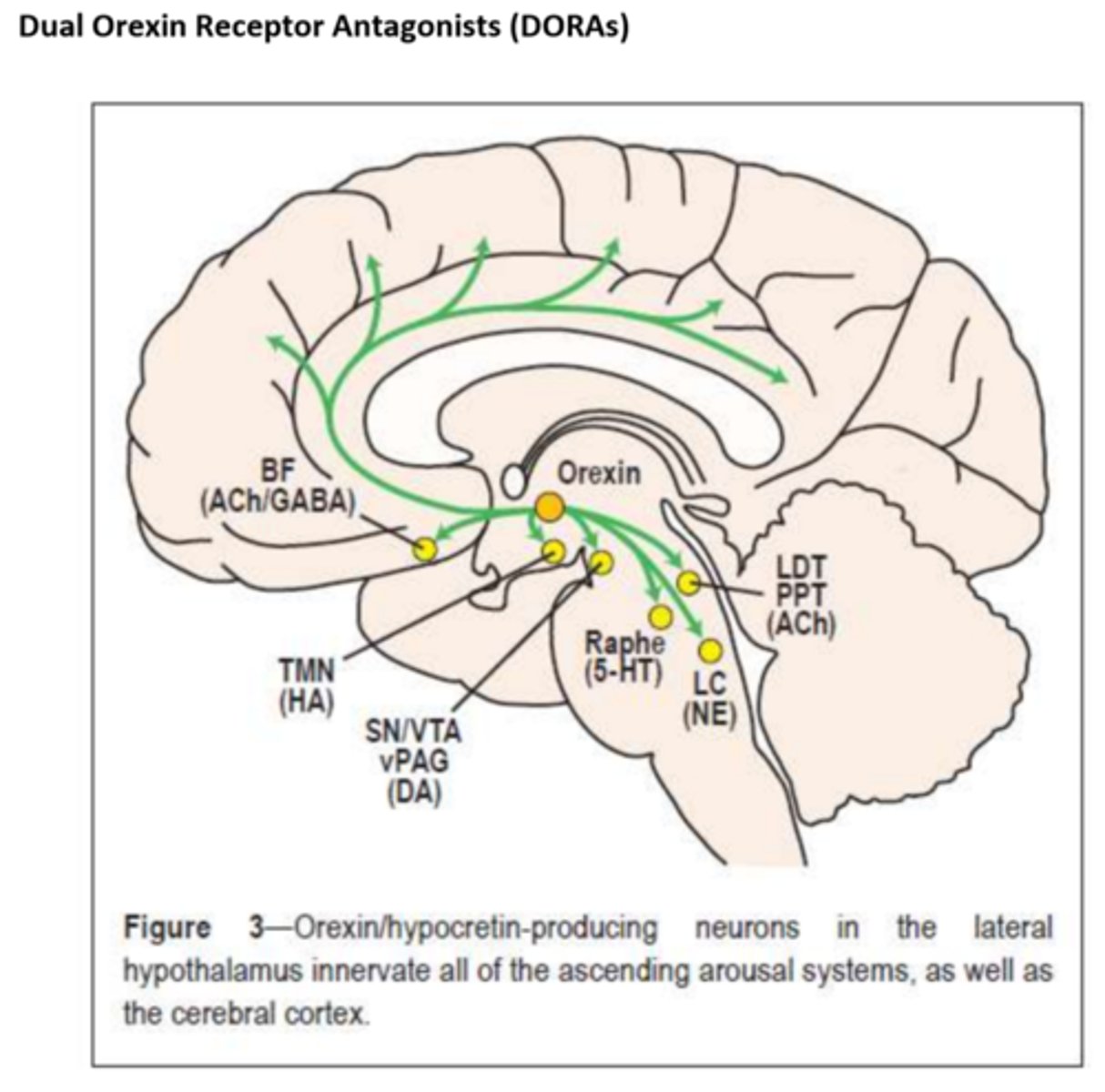
orexin
neuropeptide involved in regulations of feeding behavior, sleep-wake cycles, and autonomic function
- orexin A binds both OXR1 and OXR2
- orexin B is selective for OXR2
- OXR1: wakefulness
- OXR2: sleep, suppresses motor activity during dreams
sleep trends across life
newborns: sleep sporadically throughout the day
1 y/o: SCN is developed, child syncs with circadian rhythm
adolescence: increase in deep NREM sleep for synaptic pruning
midlife/ old age: sleep decreases, but need for sleep does not
- substantial reductions in deep NREM sleep (stage 3&4)
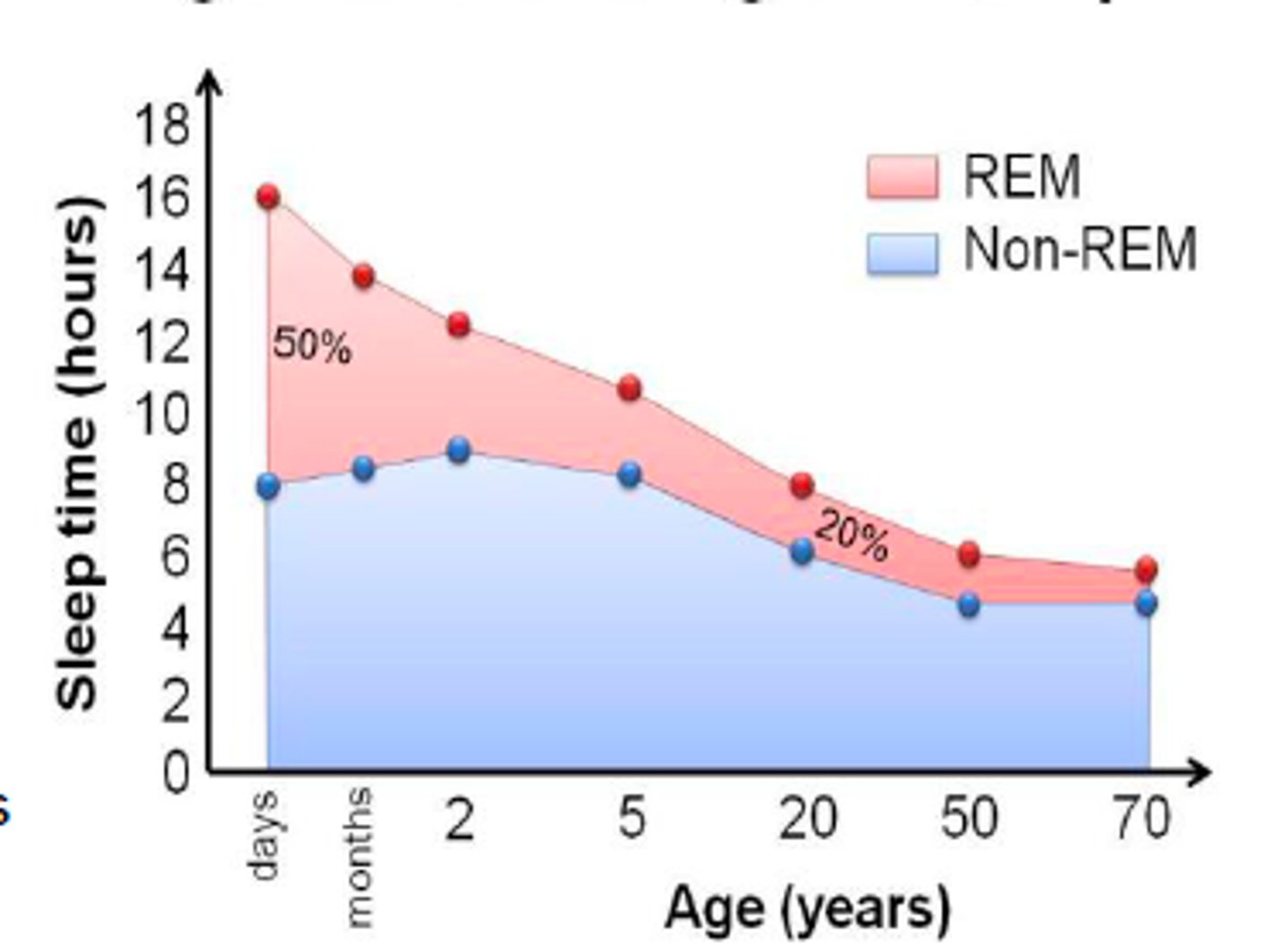
assessing sleep
#1: polysomnography: multi-parameter sleep test
actigraphy: at home device (watch) that estimates sleep stages
- variable reliability
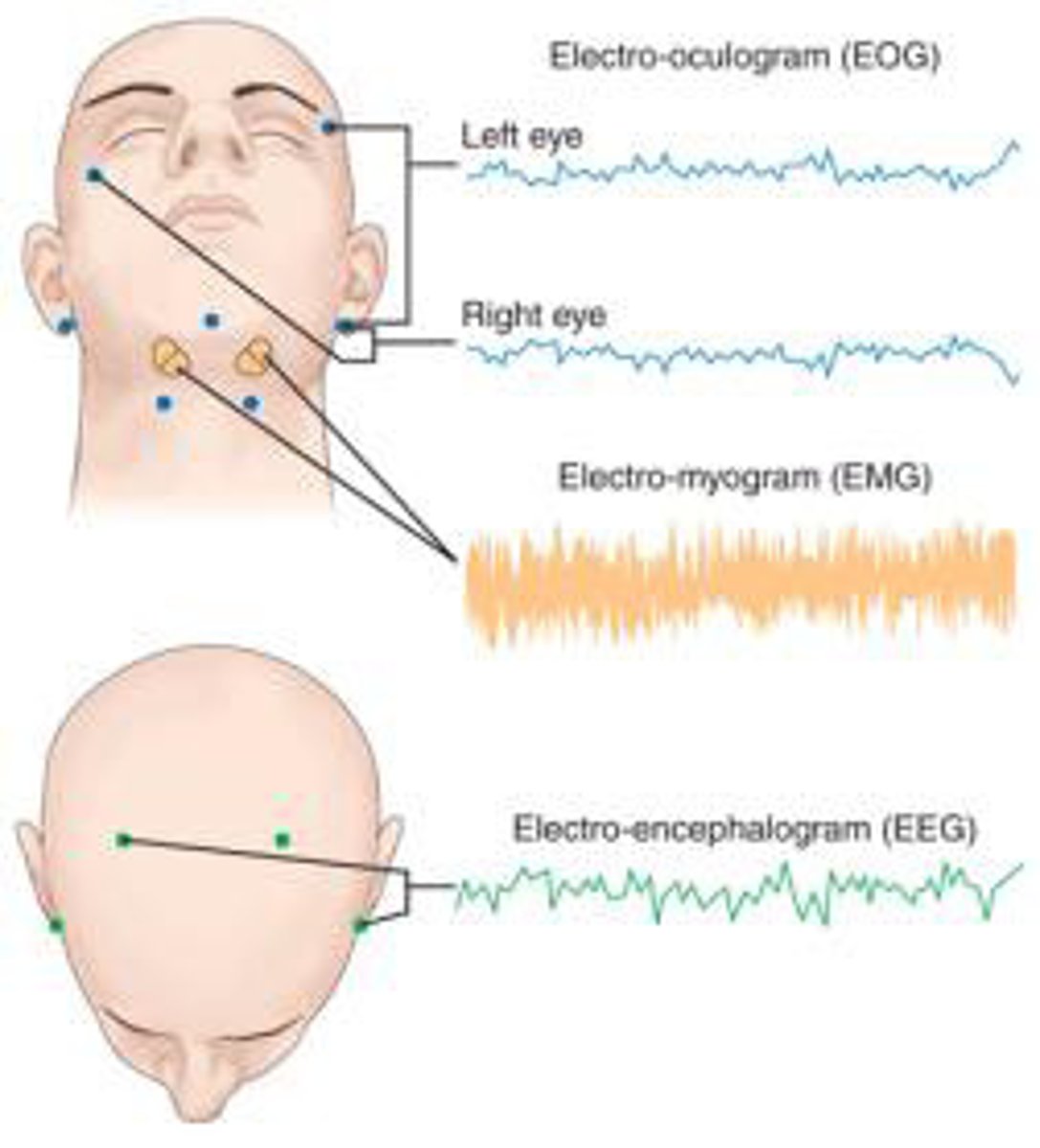
2 categories of sleep disorders
1. dyssomnias
- trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or excessive sleepiness
- insomnia, OSA, narcolepsy, sleep movement disorders
2. parasomnias
- abnormal activities or behaviors during sleep
- nightmares, sleepwalking, sleep paralysis, sleep terrors, bruxism
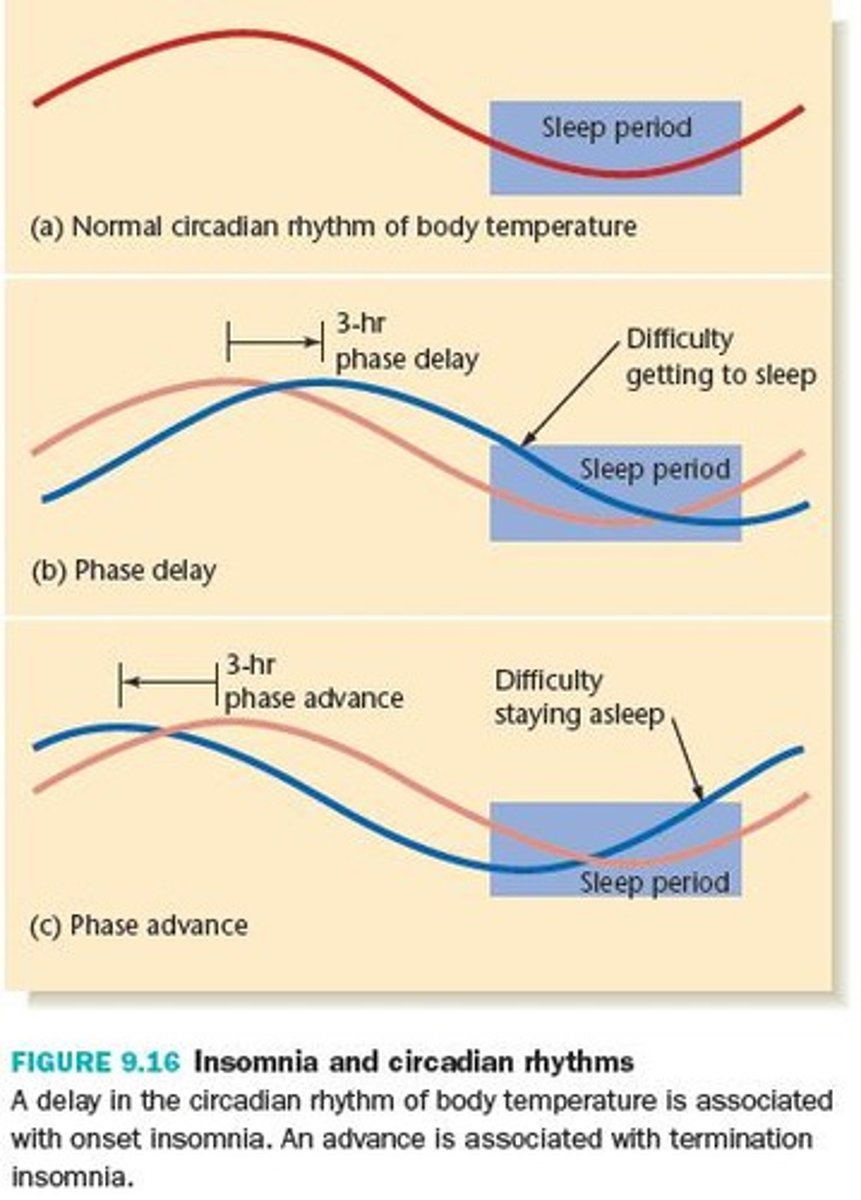
insomnia
dyssomnia
difficulty falling and/or staying asleep
- occurs at least 3 nights per week for at least 3 months (chronic)
- occurs despite adequate sleep opportunity
- most common
- notable in: military/ veterans, psychiatric disorders, eldery

insomnia pathology
genetic vulnerability
+ precipitating event/ stressor and moderators (age, medications, comorbidities)
↓
abnormalities in neurobiological processes
- co-activation of wake and sleep promoting areas
↓
neurophysiological hyperarousal, psychological and behavioral processes
↓
insomnia
↓
adverse health outcomes
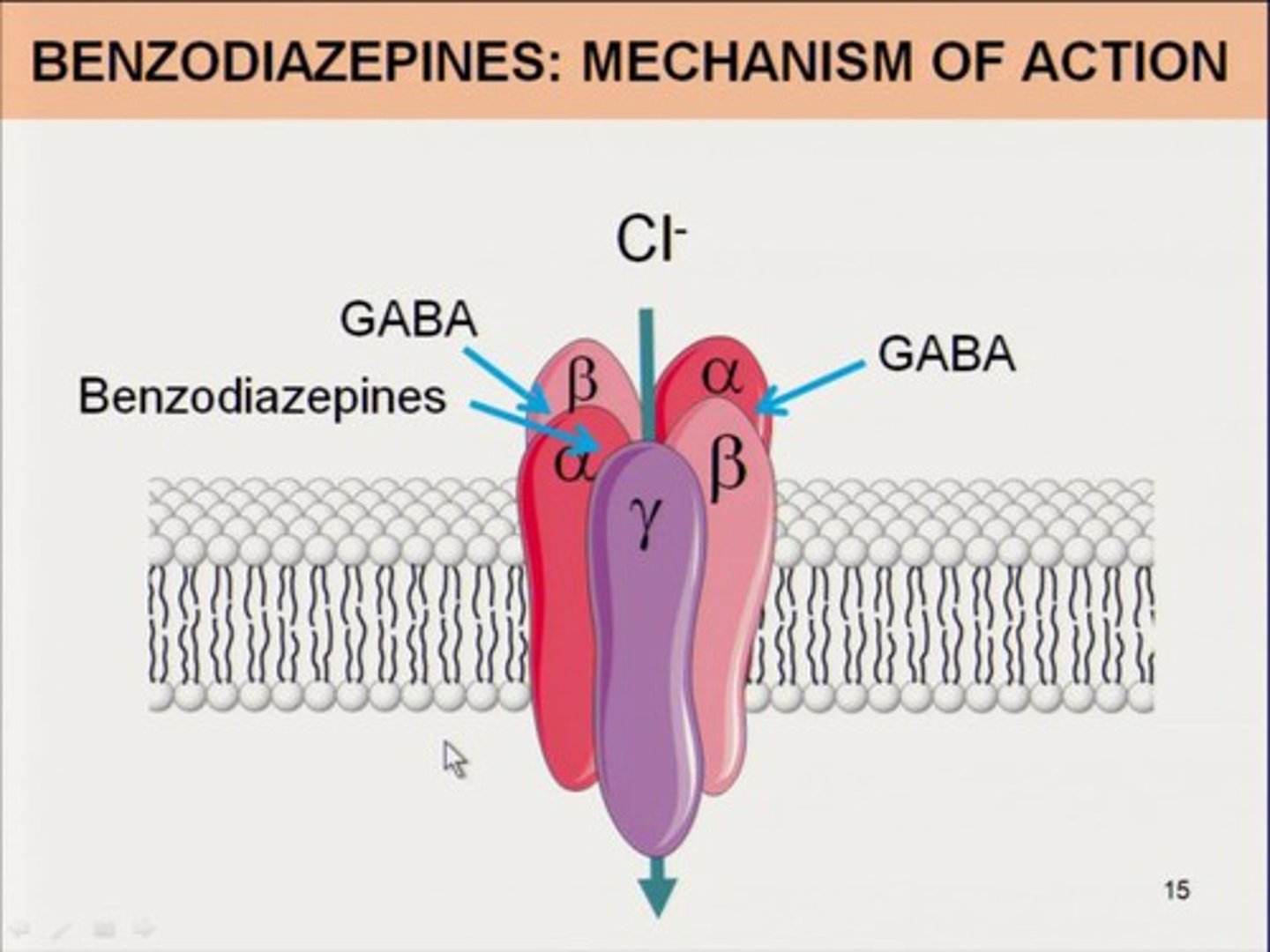
benzodiazepines
oldest class of sleep drugs
positive allosteric modulator of GABAa receptors (inhibitory NT)
- GABA binding -> Cl entry -> decreased likelihood of an action potential
commonly used for insomnia: temazepam (Restoril), triazolam (Halcion)
caution: pregnancy X, causes dizziness/ drowsiness, abuse potential, should be limited to short term use (<2 weeks)
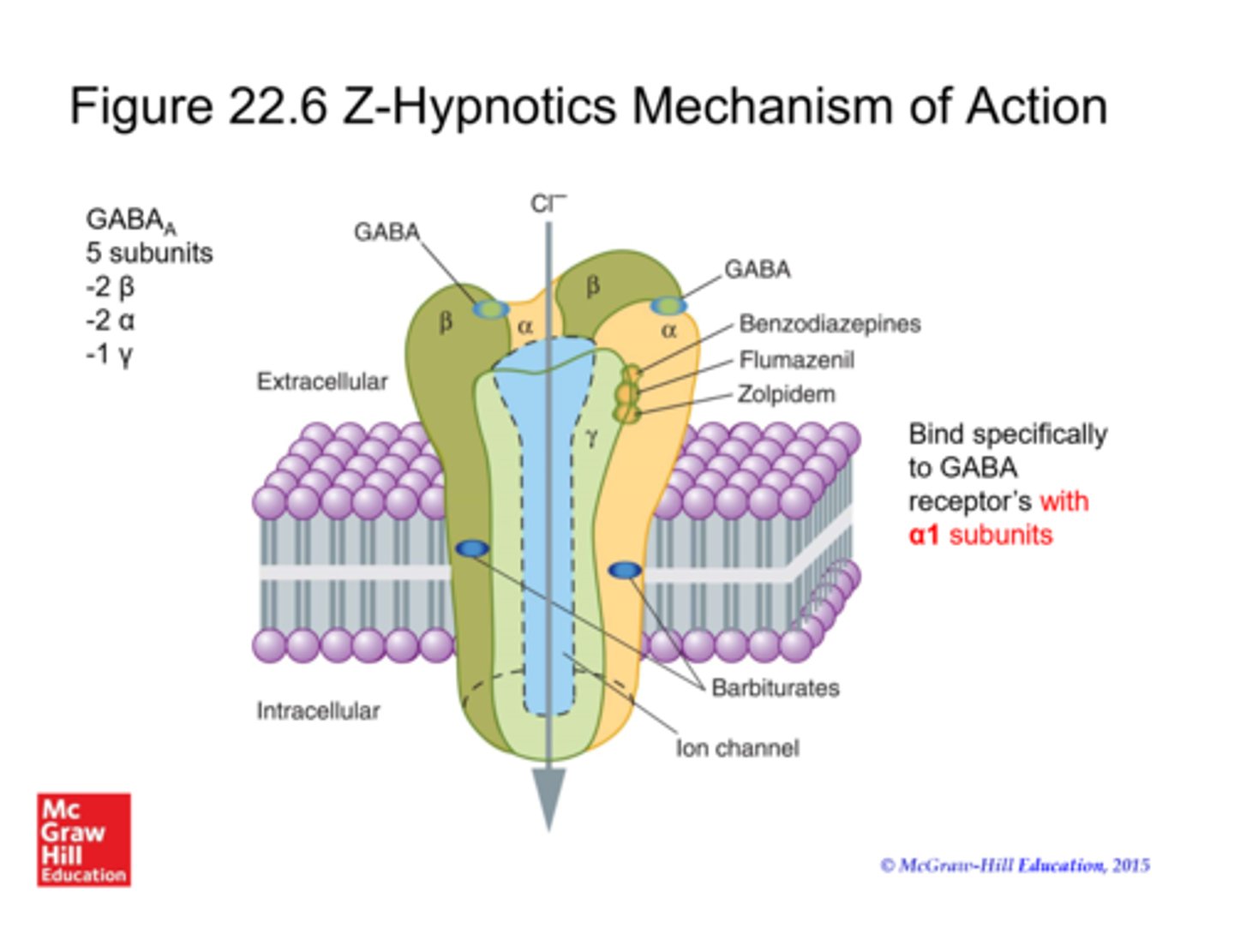
Z-hypnotics
similar to benzos, has increased specificity for GABAa1 receptors and LESS MUSCLE RELAXANT ACTIVITY (=less potential for respiratory depression, the diaphragm is a muscle!!)
commonly used for insomnia: zolpidem (Ambien)
caution: pregnancy C, dizziness/drowsiness, abuse potential, sleep related behaviors (eating, walking, sex)
orexin receptor antagonists
block OXR1 and OXR2
commonly used for insomnia: sucorexant (Belsomra)
caution: pregnancy C, obesity, abnormal dreams
antihistamines & antidepressants
some use in insomnia
antihistamines: MUST cross BBB = 1st generation only
- diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
> short term only
antidepressants: MUST have antihistamine activity
- trazadone (Desyrel), amitriptyline (Elavil), doxepin (Silenor)
> lower dose than for depression
caution: significant anticholinergic effects, including delirium
- activity on the H1 receptor

melatonin (drug)
only appropriate for sleep onset insomnia
- ramelteon (Rozerem): melatonin receptor agonist

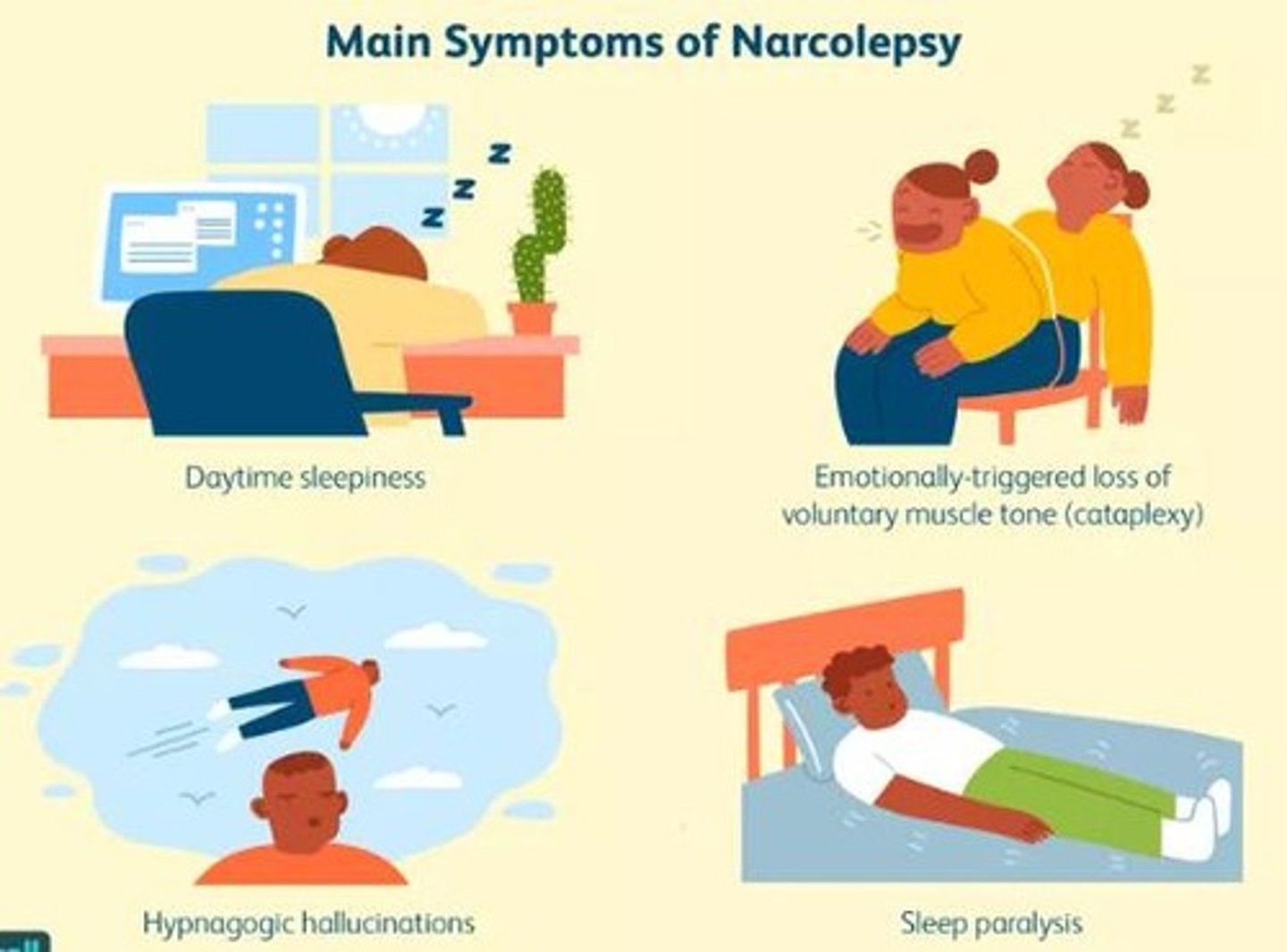
narcolepsy
excessive daytime sleepiness with
- cataplexy: emotionally triggered transient muscle weakness
- hypnagogic hallucinations: vivd, frightening hallucinations occurring at sleep onset
- sleep paralysis: inability to move for 1-2 minutes at sleep onset/waking
diagnosis includes Epworth sleepiness scale: objective questionnaire, asks "how likely are you to fall asleep in these scenarios"
narcolepsy pathophysiology
progressive loss of orexin neurons
> ↓orexin = motor off switch is hit outside of REM sleep
- early = excessive sleepiness
- later = cataplexy, rapid daytime transition into REM sleep
likely other mechanisms related to histamine and other brain areas
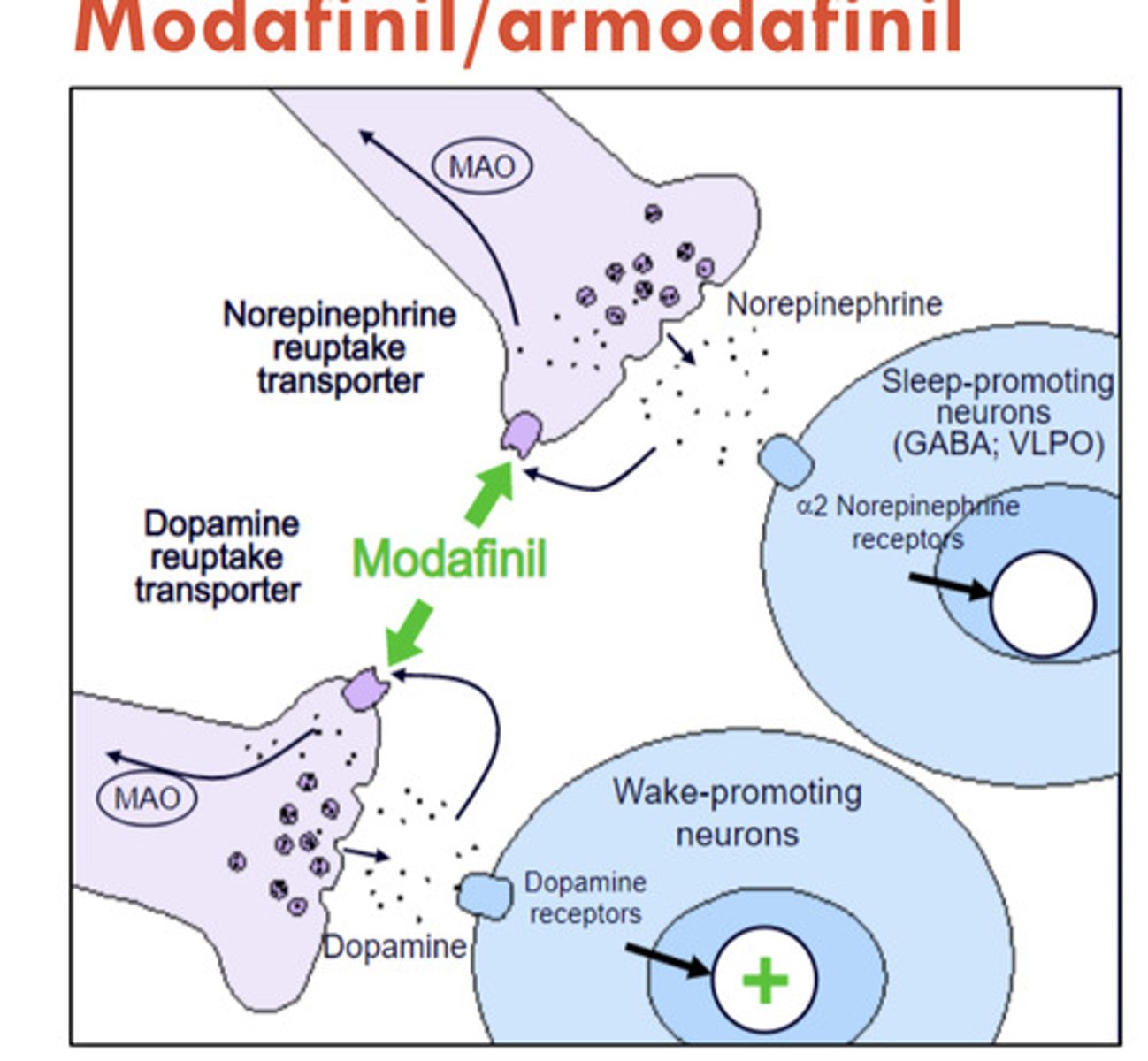
modafinil, armodafinil
Provigil, Nuvigil
CIV CNS stimulants
for narcolepsy
MOA: likely acts via increased dopamine signaling
lower abuse potential than amphetamines
ADE: headache, nausea, dry mouth, anorexia, diarrhea
solriamfetol
Sunosi
CIV CNS stimulant
for narcolepsy
similar to (ar)modafanil in efficacy and ADEs
MOA: dual norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibition
methylphenidate, amphetamines
CII CNS stimulants
for narcolepsy
MOA: increased synaptic dopamine (& norepi)
- methylphenidate: blocks DAT/NET (signal that says to stop releasing DA and NE)
- amphetamines: does what methylphenidate does + reverses DAT/NET to flood system with more DA and NE
- IR and ER formulations
- may reduce cataplexy, hallucinations, and sleep paralysis
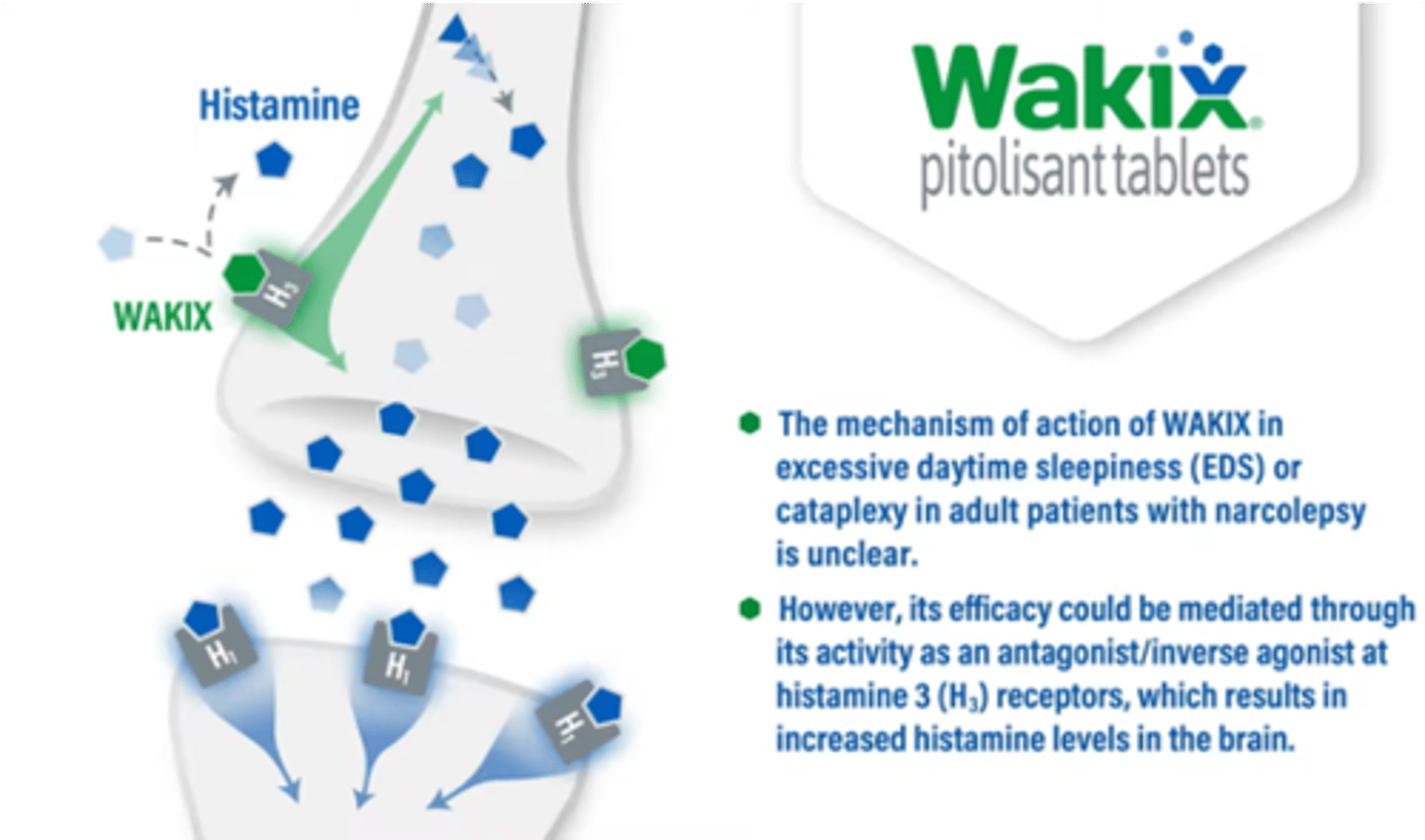
pitolisant
Wakix
for narcolepsy
MOA: H3 receptor antagonist/ inverse agonist
- binds presynaptic H3 receptors, preventing histamine from binding AND increasing histamine release
- basically, blocks signal that says to stop releasing histamine = increased histamine
- may reduce cataplexy
sodium oxybate
Xyrem
CIII for narcolepsy
MOA: gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) -> GABA metabolite
- likely related to GABAb activity to increase REM sleep
[BLACK BOX]: risk of abuse, misue, death; REMS
- must take at bed time and 2.5-4 hours later
- date rape drug
![<p>Xyrem</p><p>CIII for narcolepsy</p><p>MOA: gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) -> GABA metabolite</p><p>- likely related to GABAb activity to increase REM sleep</p><p>[BLACK BOX]: risk of abuse, misue, death; REMS</p><p>- must take at bed time and 2.5-4 hours later</p><p>- date rape drug</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/349eacf7-c261-4d27-9e89-4487e2bb7df4.jpg)
oveporexton
not approved yet, for narcolepsy
MOA: selective OXR2 agonist
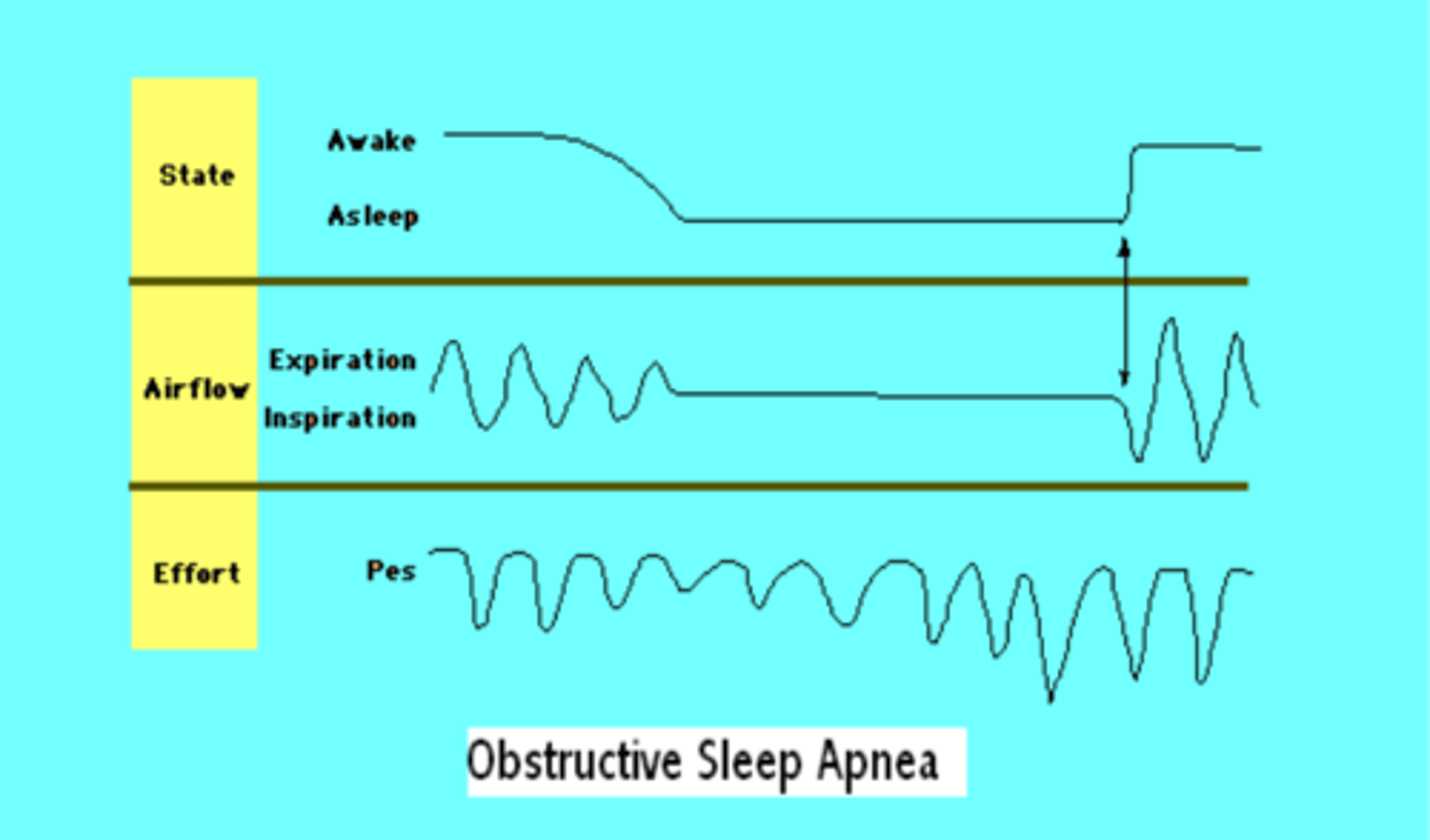
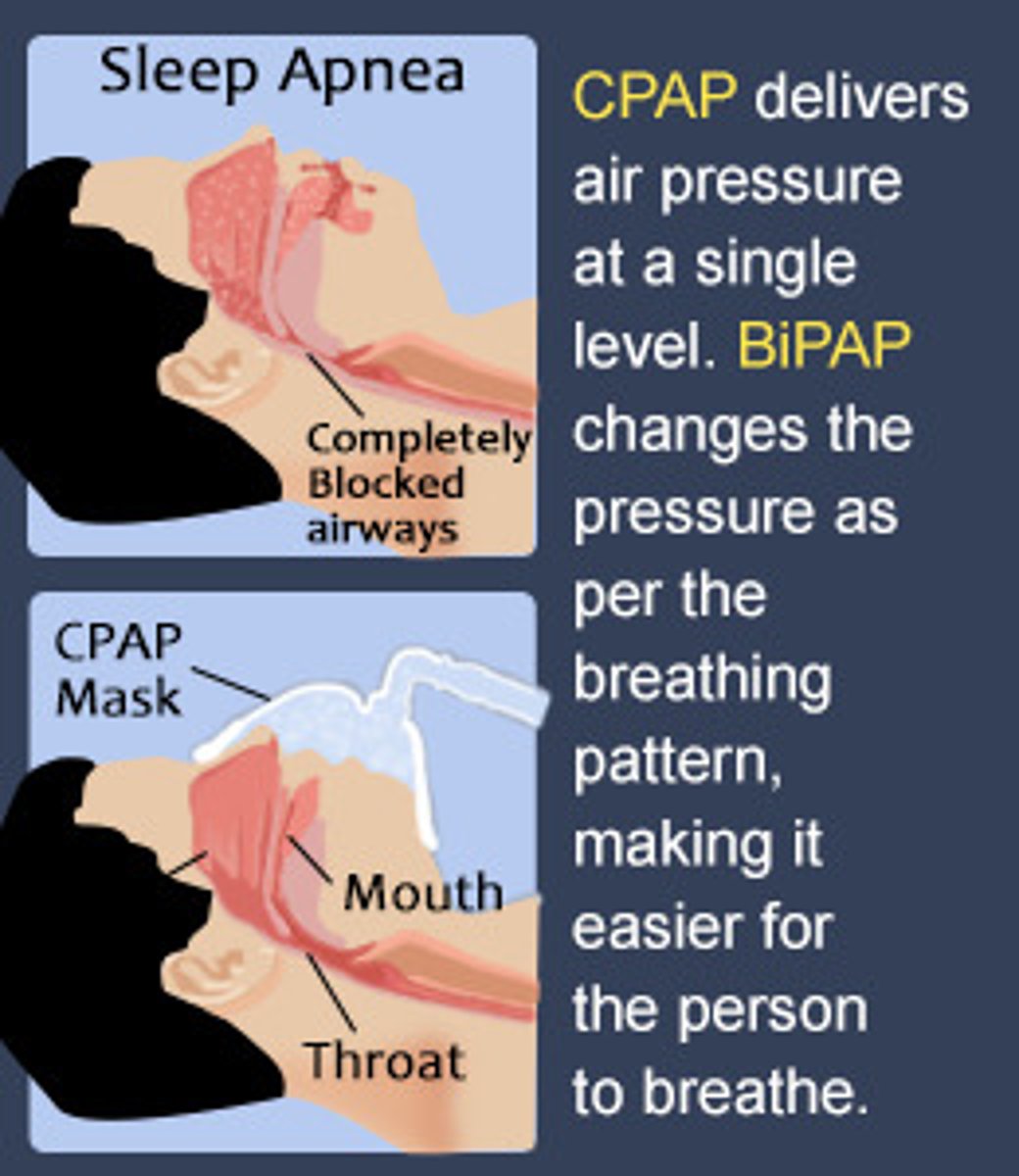
obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
soft palate airway obstruction during sleep
- apnea = no airflow
- hypoapnea = decreased airflow with desaturation
symptoms: snoring/ snorting, EDS, hypertension, morning headaches, depression, anxiety, short term memory loss
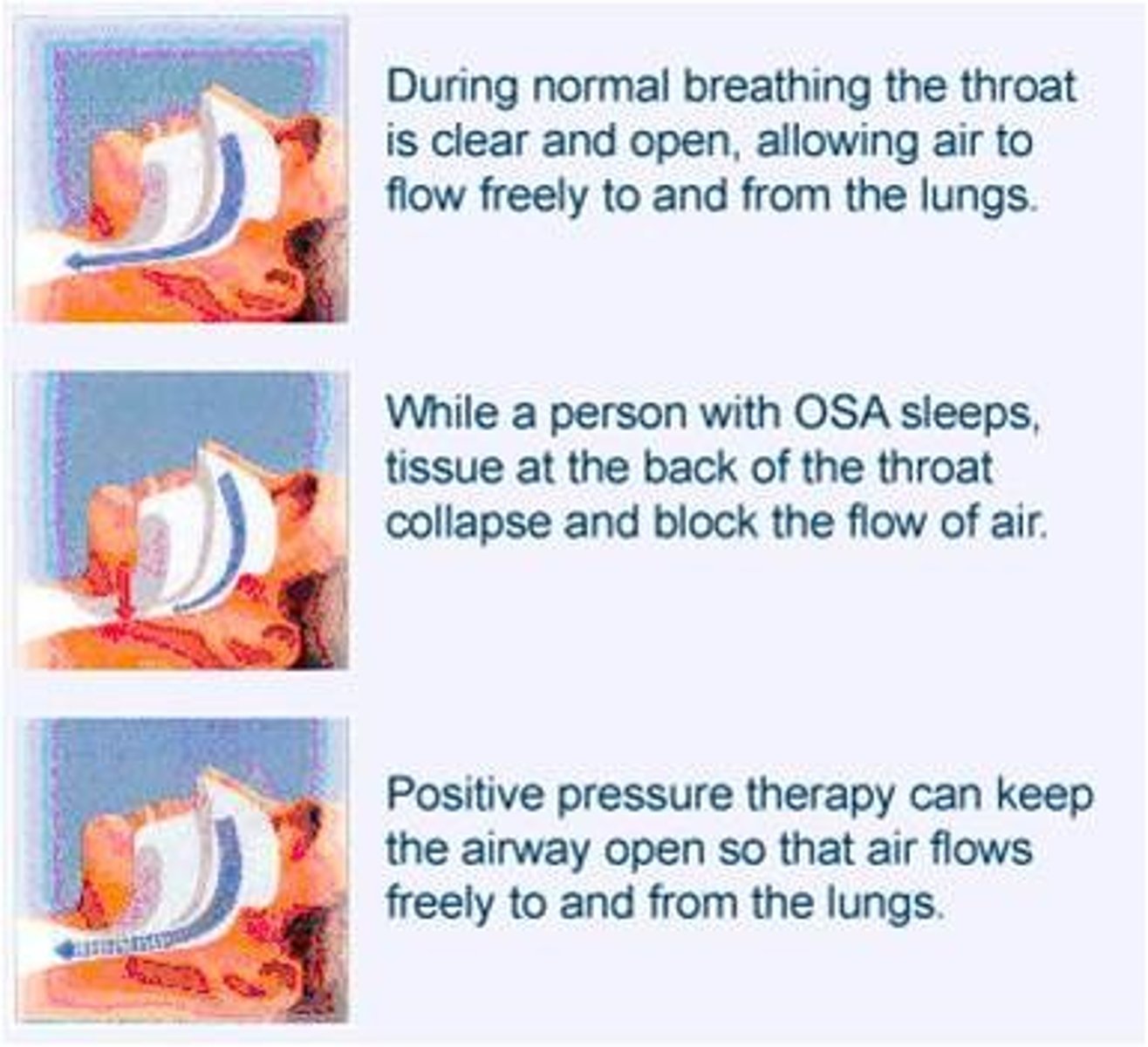
OSA diagnosis
apnea/ hypopnea index (AHI)
- mild = 5-15 events/hr
- moderate = 15-30
- severe = >30
polysomnography used
OSA device based therapy
continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) - forces steady flow of pressurized air into nose/ mouth
mandibular repositioning device - removable device that physically moves the jaw forward
Inspire upper airway stimulation - implamted device that sends electrical signals to hypoglossal nerve
restless leg syndrome (RLS)
the urge to move legs, often accompanied by discomfort
symptoms occur at rest and are relieved by movement
- worsen at night
- more common in: women, 30+

RLS pathophysiology
- brain iron deficiency
genetic predisposition, exposure to certain medications/ withdrawal from anticonvulsants, benzos, barbituates
↓
dopaminergic dysfunction and cortico-striato-spinal dysfunction
↓
RLS
iron replacement
for restless leg syndrome
MOA: iron is a cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase, which is necessary for dopamine creation
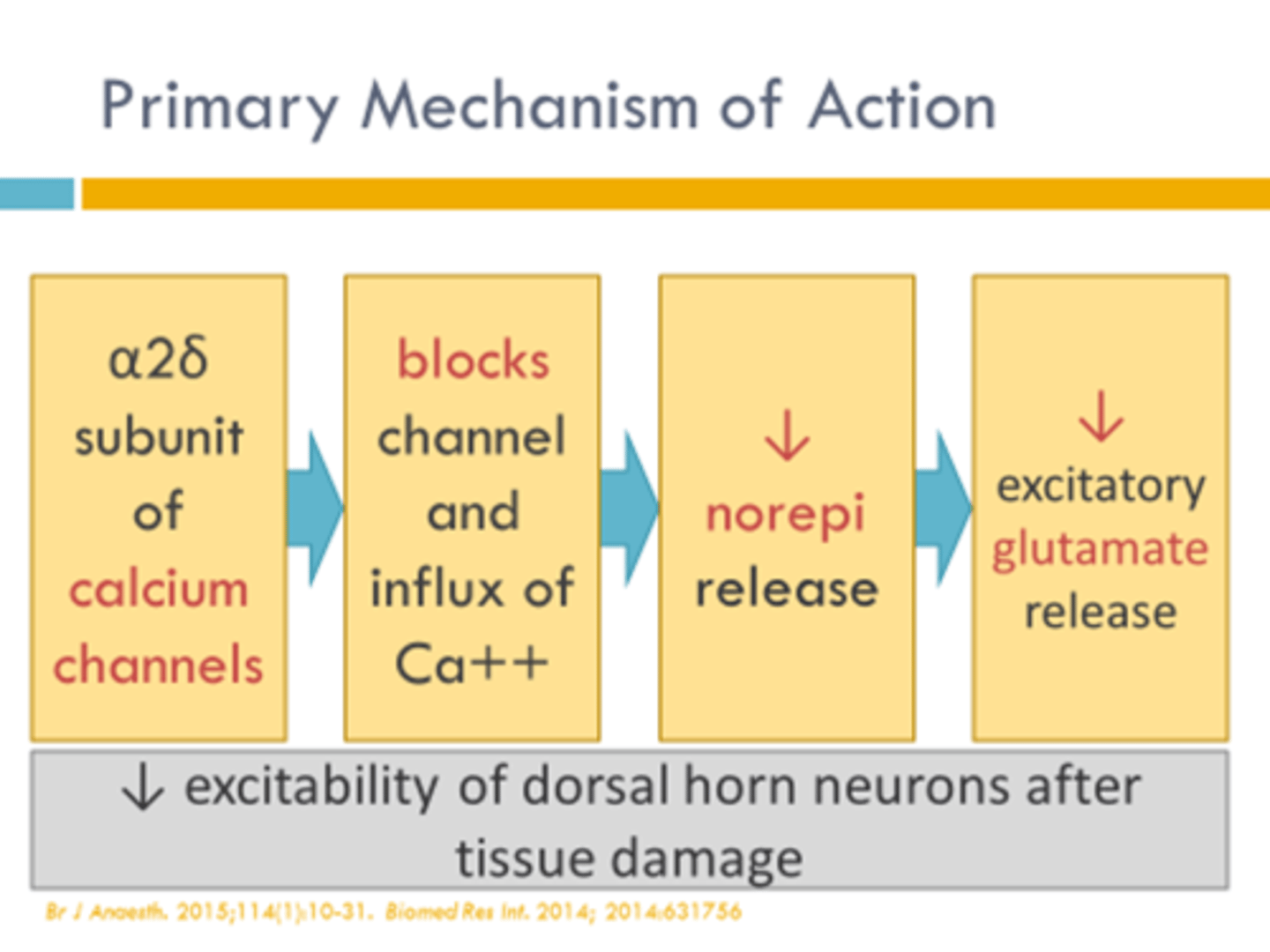
gabapentinoids
gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregablin (Lyrica)
for restless leg syndrome
MOA: bind α2∆ subunit of presynaptic volatge-gated Ca channels (blocks signal) -> destabilization, internalization, and recycling
Horizant: gabapentin encarbil prodrug -> higher levels in the body
dopamine agonists
pramipexole (Mirapex)
for restless leg syndrome
MOA: D2 receptor agonism
ADE: somnolence, dizziness, headache, nausea
caution: augmentation (higher highs & lower lows), have to increase dose as body tolerates, may increase impulsive behaviors
- not a 1st line
