chapter 23 - redox and electrochemical cells
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Rules for oxidation numbers
O→ -2 (except in peroxides)
H → +1 (except in metal hydride)
G1 → +1
Elements = 0
Oxidising agent definition
oxidise something else and is reduced gains electrons and decreases in oxidation number
Reducing agent definition
reduces something else and is oxidised so lose electrons and increase in oxidation number
Constructing redux equation using half equations
number of electrons must balance

Steps to writing half equations
1)workout oxidation states
2) balance the elements which change oxidation states
3) balance electrons
4)balance oxygens with
5) balance Hs with H plus
6) check half equation by checking total charge on both sides equations are the same
what are common redox titrations?
Potassium manganate seven under acidic conditions and sodium thiosulphate for determination of I2
What’s the colour change in a manganate seven titration?
Pink to Colourless, end point is judged as first permanent pink colour in conical flask
Why must the other chemical in a manganate seven titration be a reducing agent?
MnO4- are reduced to Mn2+ so other chemical must be oxidised
How is a manganate titration set up?
KMNO4 in burette, solution being analysed in conical flask along with hydrogen ions ( sulphuric acid)
Where is meniscus read from in a Manganate titration?
Read from the top rather than at the bottom
What is reduced and what is Oxidised in thiosulphate redox titration?
Thiosulfate ions are oxidised and iodine is reduced
What are the half equations and full equations for iodine and thiosulphate redox titration
Equations
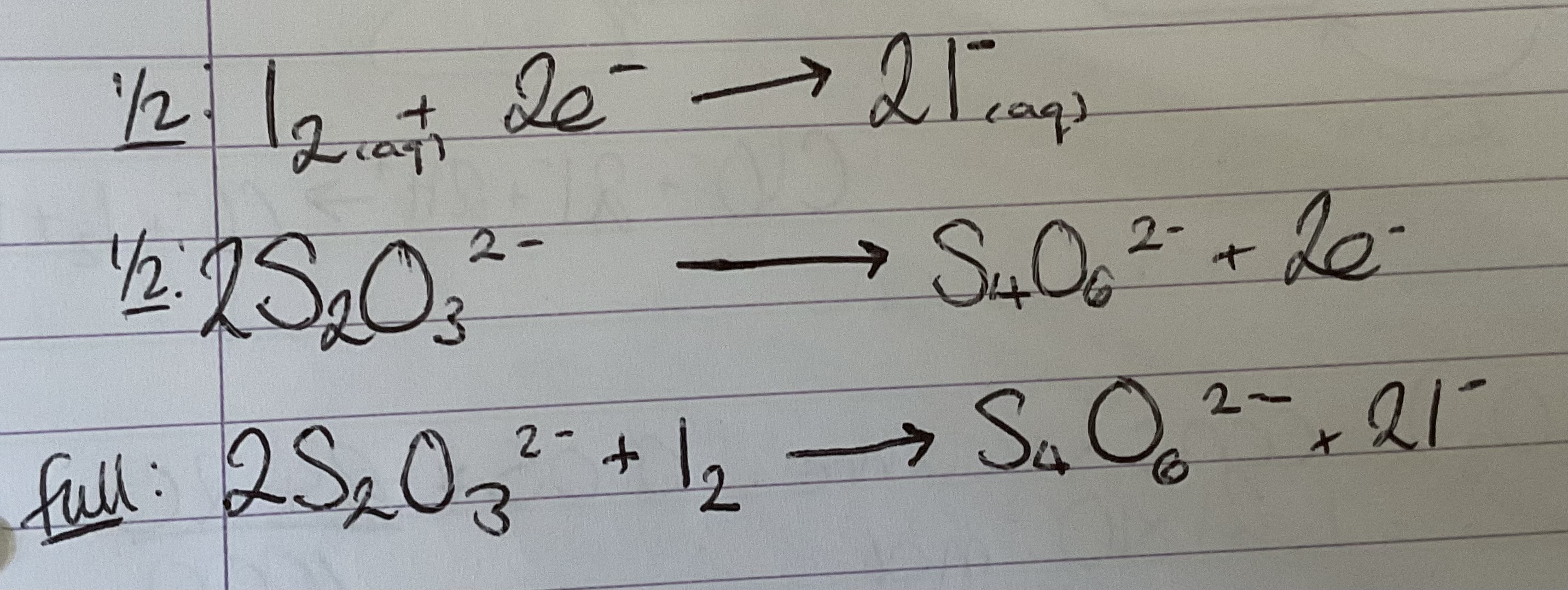
How can you change the procedure of an iodine thiosulphate redox titration to make it possible to analyse a wide range of oxidising agents?
React oxidising agent with excess KI
I- Plus oxidising agent → I2
Titrate with Thiosulphate ions to work out moles of I2
Work Out moles of oxidising agent
Colour change: brown (I2)→ fade → add starch (blue black) → blue back disappears (end point)
Wait to fade to add starch so does an oxidise ,if didn’t add starch colour change would be too difficult to see
What is a voltaic cell
type of electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical. involves using redox reactions as a movement of electrons which results in electrical energy.
What are half cells?
Contains the species that are present in the redux half equations
What is a Voltaic cell made of?
2 cells that kept separate to allow electrons to flow in a controlled manner
How are metal/metal ion half cell set up?
Metal rod dipped into a solution of the aqueous ions

How are ion/ion half cell set up?
Ions of the same element in different oxidation states, there’s no metal to transfer electrons so need an inert metal electrode made from platinum

What happens when 2 half cells are connected together?
One will gain electrons one will lose electrons
What do electrode potentials allow us to see?
Which half cell is more likely to gain electrons or lose electrons
Standard electrode potential definition
The tendency to be reduced is measured by the standard electrode potential
How are standard electrode potentials measured?
Measured using the standard lecture potential for hydrogen E = 0.0 0V

What is the forward reaction for a standard electrode potential?
Reduction
What does it mean if a standard electro potential is more negative?
Great attendance to lose electrons and be oxidised
What does it mean if standard electrode potential is more positive?
Great tendency to gain electrons and be reduced
How is the standard electro pencil of a cell calculated?
More positive takeaway more negative
What are the limitations of predictions from electrode potential?
Gives idea of thermodynamic visibility but not rate of reaction may have a very large EA
If concentration is not exactly 1moldm-3 the electrode potential will change
Other conditions may not be standard
What’s the three types of cells?
Primary secondary fuel
What’s a primary Cell
Non-rechargeable And are designed to only be used once reaction not can be reversed E.G AA batteries
What is a secondary cell?
Rechargeable and the reaction can be reversed during recharging E.G a laptop or phone
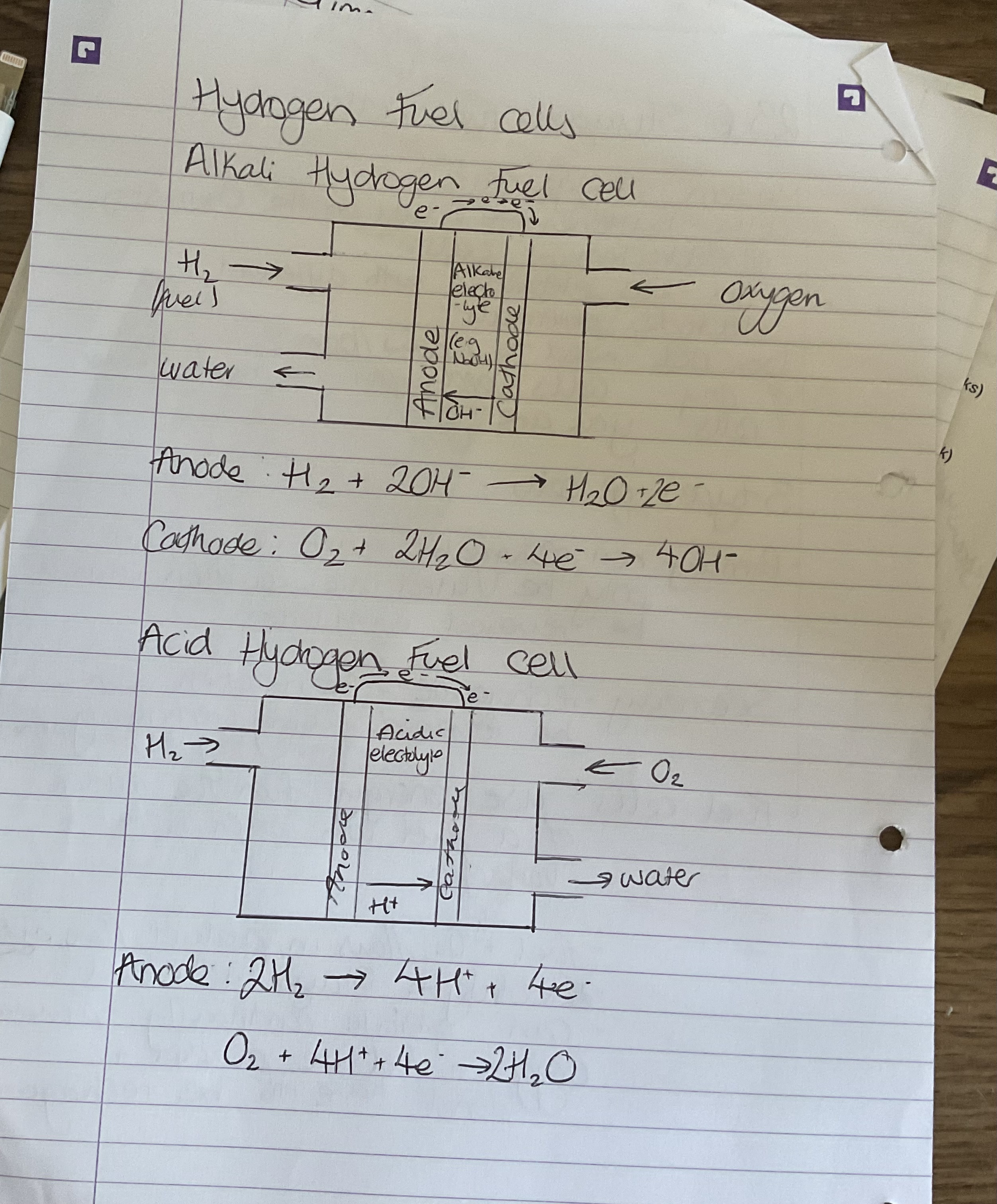
What’s a fuel Cell
Use energy from the reaction of a fuel with oxygen to create a voltage
Fuel and oxygen flows in product flows out and the electrolyte stays in the cell can operate continuously provided oxygen and fuel are provided
do not have to be recharged
What are the two types of hydrogen fuel cell
Acid and alkali Hydrogen fuel cells