Winter Hazards
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
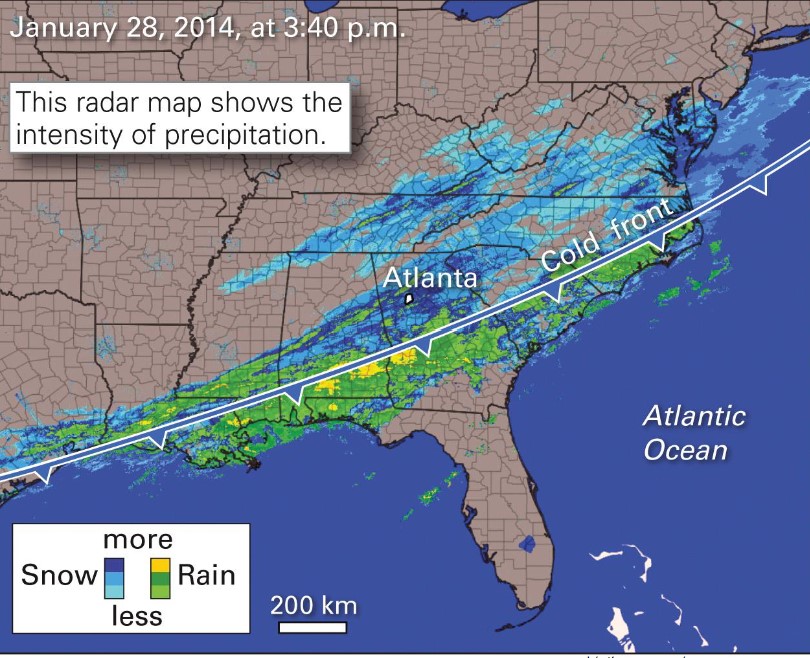
Case Study: Atlanta Snowpocalypse
* Jan 2014, Atlanta Georgia experienced ‘snowpocalypse” when \~ 5 cm snow fell
* Drivers lacked experience driving in snow and icea
* accidents halt traffic flow
* poor emergency response:
* many municipalities sprawl across the region
* no comprehensive, regional emergency coordination
* 1200 traffic accidents
* 2000 children had to sleep on buses or in police stations
* several deaths
* commerce disruption
* airport shut down
* Drivers lacked experience driving in snow and icea
* accidents halt traffic flow
* poor emergency response:
* many municipalities sprawl across the region
* no comprehensive, regional emergency coordination
* 1200 traffic accidents
* 2000 children had to sleep on buses or in police stations
* several deaths
* commerce disruption
* airport shut down
2
New cards
what temperature must body maintain?
* 37ºC
3
New cards
what is hypothermia?
* when core temperature drops below safe range
* mild, then severe, shivering
* death results if core stays below 33.3ºC
* mild, then severe, shivering
* death results if core stays below 33.3ºC
4
New cards
what is frostbite?
* occurs when body tissue freezes
5
New cards
what is wind chill?
* your body creates a thin layer of warm air next to your skin
* wind strips away warm layer, causing you to lose heat
* wet skin cools faster than dry skin due to evaporation
* faster moving wind = faster layer striped away
* wind strips away warm layer, causing you to lose heat
* wet skin cools faster than dry skin due to evaporation
* faster moving wind = faster layer striped away
6
New cards
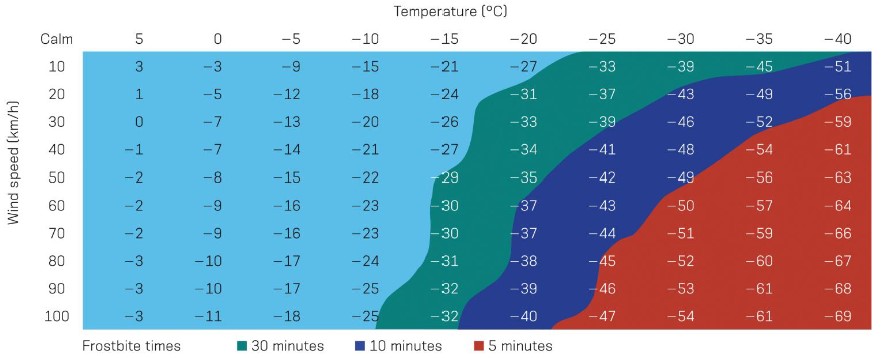
what is wind chill temp?
* represents heats loss when dry skin is exposed to wind
* depicts exposure time that leads to frostbite
* depicts exposure time that leads to frostbite
7
New cards
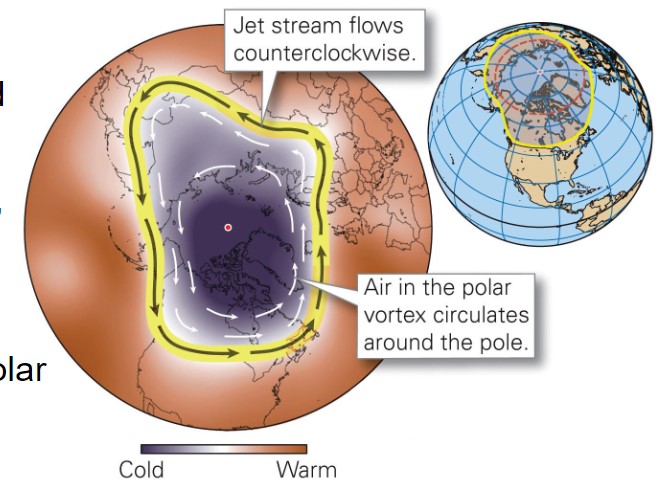
what is a polar front?
* the boundary between cold polar air and warmer air
* stretches around the globe, normally at high latitude
* can sometimes stretch far south
* may persists for weeks
* creates hazards for people living in temperate climates
* stretches around the globe, normally at high latitude
* can sometimes stretch far south
* may persists for weeks
* creates hazards for people living in temperate climates
8
New cards
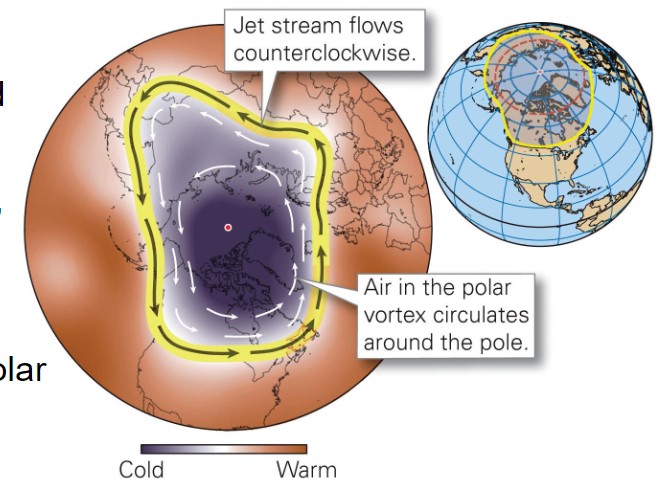
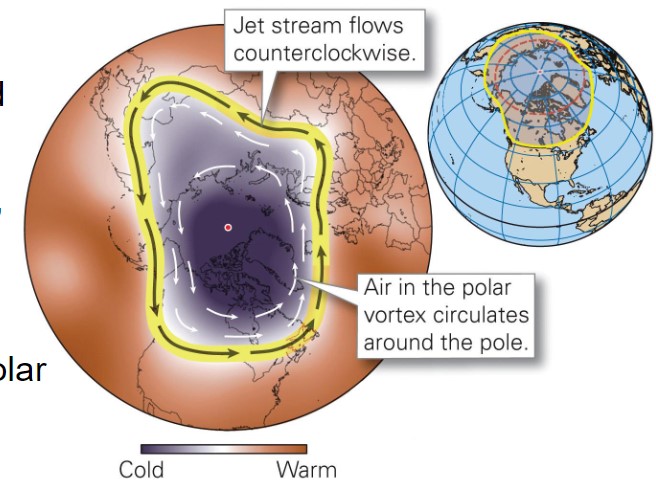
what is a polar vortex?
* counterclockwise flow of polar air
* circulates around the North Pole
* circulates around the North Pole
9
New cards
what is a polar jet stream?
* traces out the southern edge of the polar vortex
10
New cards
what are cold waves?
* defined relatively to normal, expected conditions
* requires society to take precautions against cold
* requires society to take precautions against cold
11
New cards
what does snowfall intensity depend on?
* visibility
* light: visibility > 1 km
* moderate: visibility 1-0.5 km
* heavy: visibility < 0.5 km
* light: visibility > 1 km
* moderate: visibility 1-0.5 km
* heavy: visibility < 0.5 km
12
New cards
heavy snow may accumulate at _________ cm/hr
* \~2.5
* occurs rapidly
* occurs rapidly
13
New cards
melting snowpack may cause?
* flooding
14
New cards
why is snow important for?
* groundwater recharge
* insulating soil
* insulating soil
15
New cards
what is a blizzard based on?
1. winds>56 km/h
2. visibility
16
New cards
what are whiteout conditions?
* visibility reduced to 0 km
* people cannot distinguish between the ground n sky
* snowdrifts may grow to several meters deep
* people cannot distinguish between the ground n sky
* snowdrifts may grow to several meters deep
17
New cards
what are ground blizzars?
* occurs in clear weather
* wind blows dry snow \~15 meters high
* wind blows dry snow \~15 meters high
18
New cards
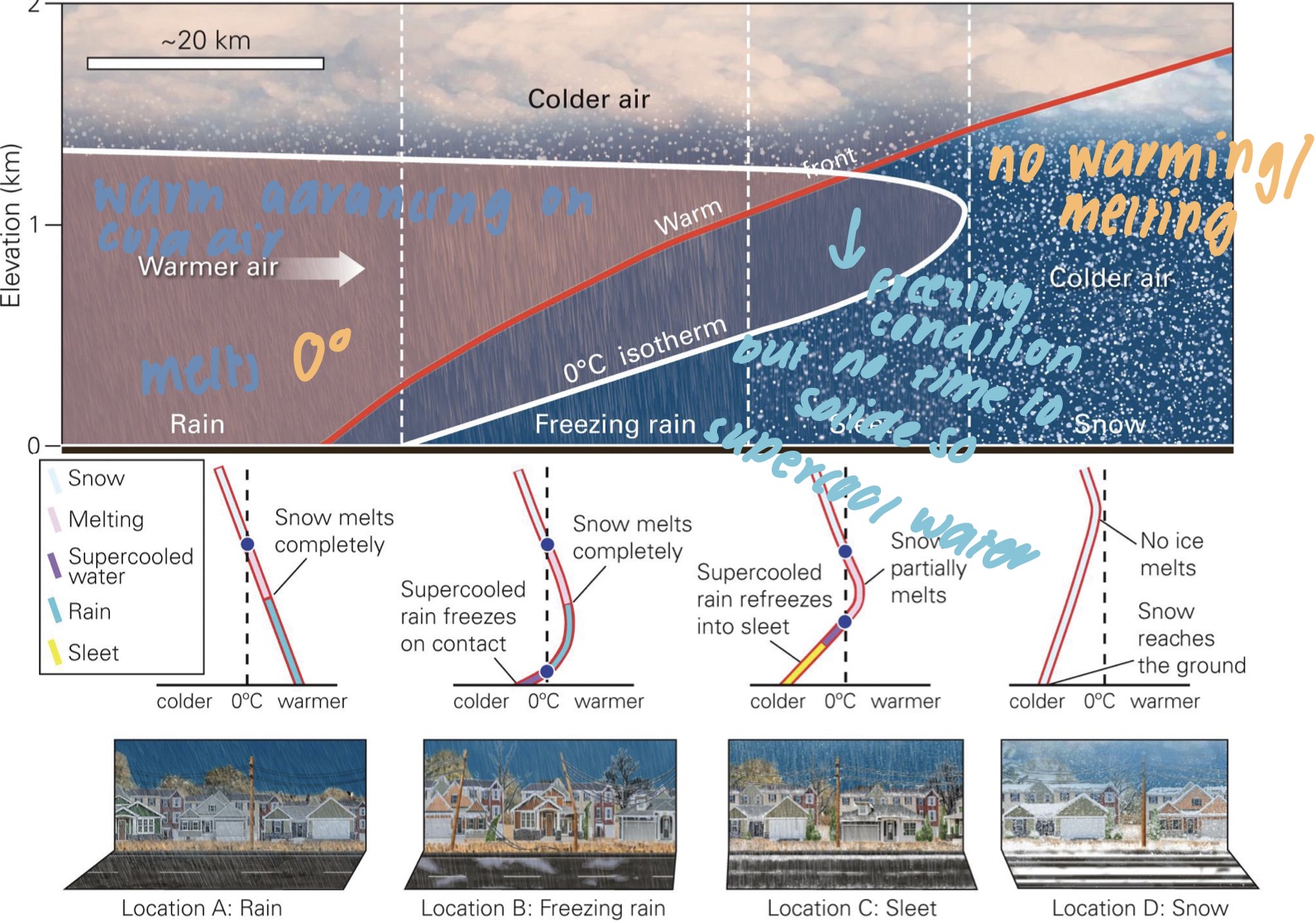
winter precipitation
19
New cards
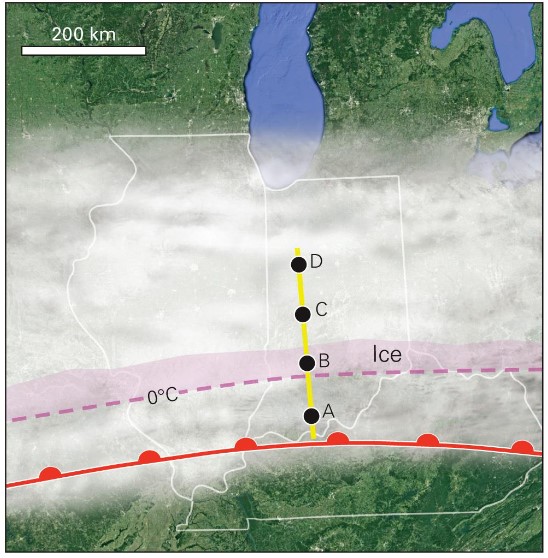
winter precipitation
* Location A: Rain
* Air is above-freezing
* Location B: Freezing rain
* 0ºC isotherm is near ground
* rain falls n is supercooled
* supercooled rain freezes on contact w/ surfaces
* Location C: Sleet
* Warm air wedge is not vv deep, nor vv warm
* snow falling thry warm air wedge partially melts
* Location D: Snow
* air is below freezing
* Air is above-freezing
* Location B: Freezing rain
* 0ºC isotherm is near ground
* rain falls n is supercooled
* supercooled rain freezes on contact w/ surfaces
* Location C: Sleet
* Warm air wedge is not vv deep, nor vv warm
* snow falling thry warm air wedge partially melts
* Location D: Snow
* air is below freezing
20
New cards
Great Ice Storm 1998
* Montreal n Ottawa shut down due to ice hazards
* Ice snapped tress, power lines, and transmission towers
* Millions w/o power
* 30 fatalities from hypothermia
* Livestock and wild animals perished
* Industries shut down
* Total damage> $6 billion
* Ice snapped tress, power lines, and transmission towers
* Millions w/o power
* 30 fatalities from hypothermia
* Livestock and wild animals perished
* Industries shut down
* Total damage> $6 billion
21
New cards
other hazards winter hazards may bring?
* transportation closures; Traffic accidents
* Heart attack from shoveling
* falls on slippery surfaces
* carbon monoxide poisoning
* ice accumulation can be a danger to aircrafts
* water mains may burst
* electric grid may fail
* deaths of livestock and crops; can lead to famine
* Heart attack from shoveling
* falls on slippery surfaces
* carbon monoxide poisoning
* ice accumulation can be a danger to aircrafts
* water mains may burst
* electric grid may fail
* deaths of livestock and crops; can lead to famine
22
New cards
what are causes of winter storms?
* mid latitude cyclones
* oceanic cyclones
* lake-effect snow
* mountain snowstorms
* oceanic cyclones
* lake-effect snow
* mountain snowstorms
23
New cards
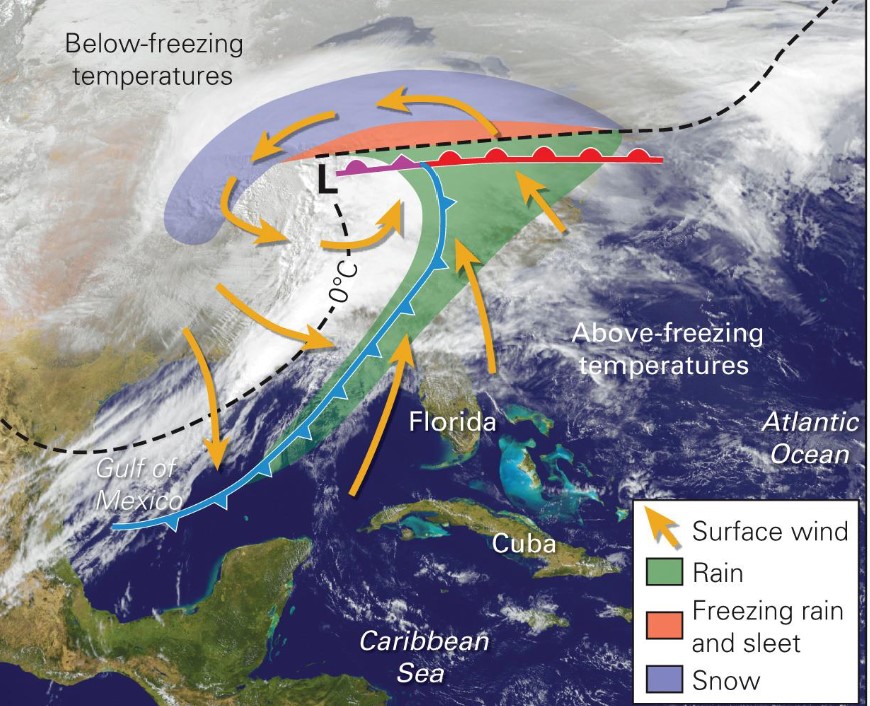
mid-latitude cyclones - Nor’easters
* Mid-latitude cyclones on east coast
* warm coastal waters provide moisture for precipitation
* storms with strong winds blowing from the NE
* create severe storms along east coast of N. America
* they can create a storm surge, blizzards, and ice storms
* warm coastal waters provide moisture for precipitation
* storms with strong winds blowing from the NE
* create severe storms along east coast of N. America
* they can create a storm surge, blizzards, and ice storms
24
New cards
what are oceanic cyclones?
* wintertime mid-latitude cyclones over the ocean
* stronger than continental ones:
* warm water provides energy for the storm
* wind has no barrier to block or slow its flow
* create intense storms when making landfall
* stronger than continental ones:
* warm water provides energy for the storm
* wind has no barrier to block or slow its flow
* create intense storms when making landfall
25
New cards
lake-effect snow
* the great lakes retain the moisture late into the yr which adds moisture to passing cold air
* land cools faster than water
* clouds form and precipitate snow on downside shores
* common in late Nov and early Jan
* Impact zone is \~50 –80 km from shore
* they dev after a mid-latitude cyclone’s cold front has passed
* high snow removal costs r common
* land cools faster than water
* clouds form and precipitate snow on downside shores
* common in late Nov and early Jan
* Impact zone is \~50 –80 km from shore
* they dev after a mid-latitude cyclone’s cold front has passed
* high snow removal costs r common
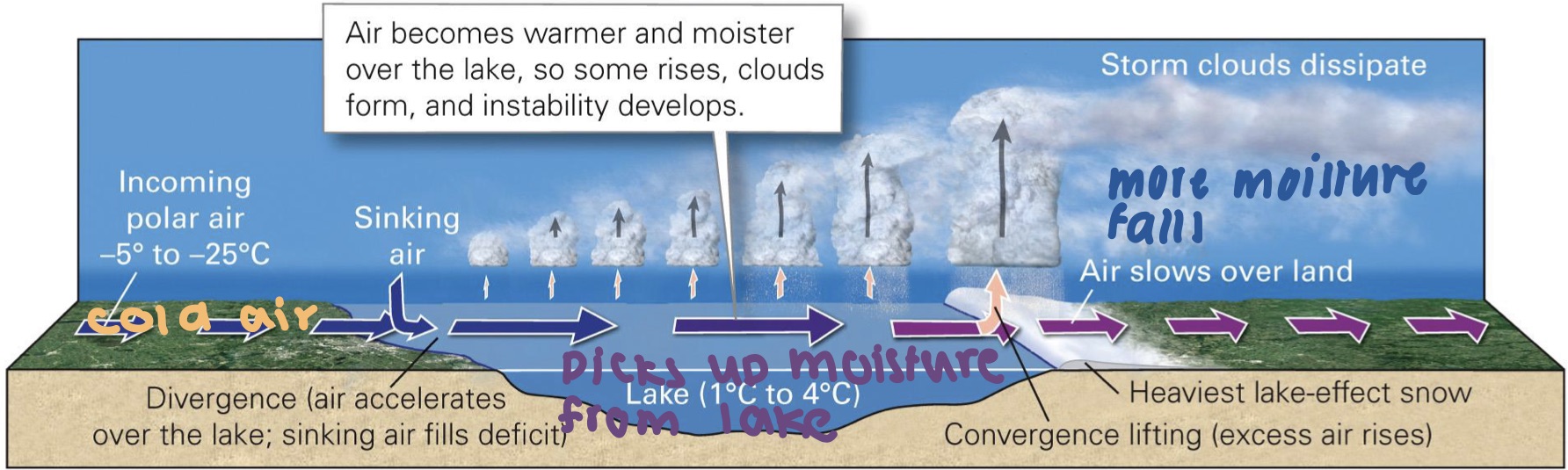
26
New cards
mountain snowstorms
* orographic uplift creates clouds on windward flanks
* clouds precipitate snow during winter months
* create the heaviest snowstorms and snowpacks in the world
* common in Rocky Mountains, Ca
* melting snowpacks provides drinking water, power generation and irrigation
* clouds precipitate snow during winter months
* create the heaviest snowstorms and snowpacks in the world
* common in Rocky Mountains, Ca
* melting snowpacks provides drinking water, power generation and irrigation
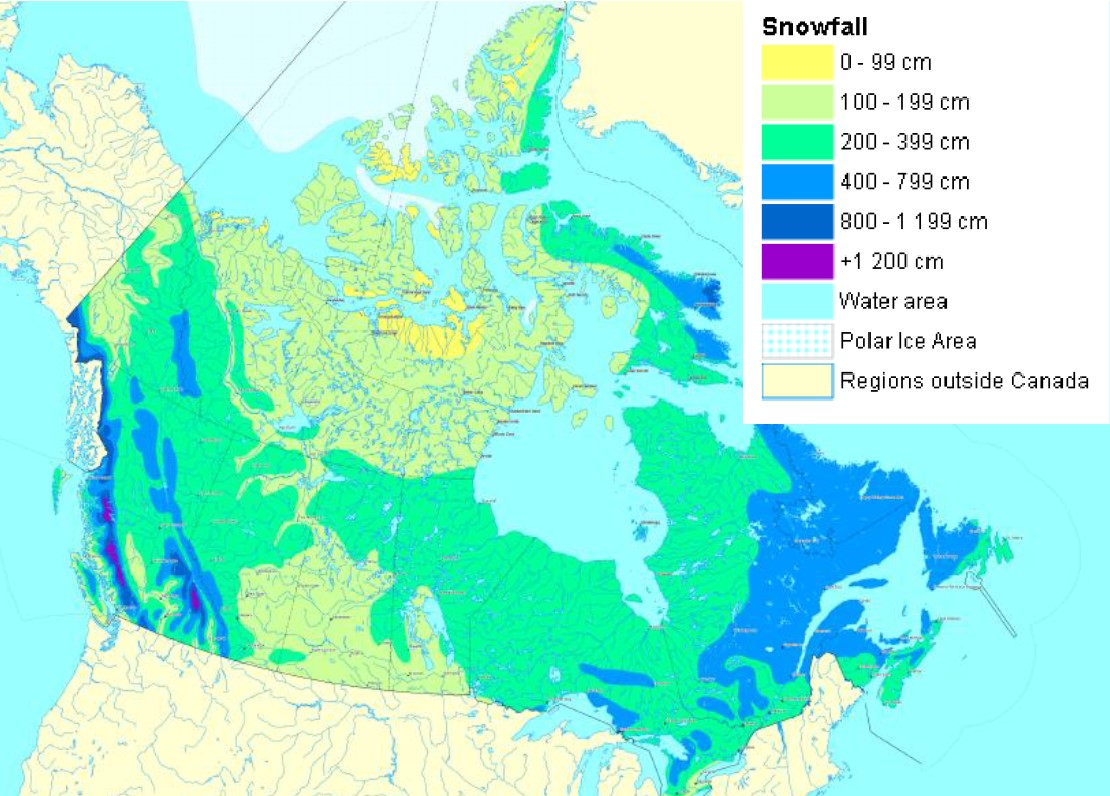
27
New cards
hazardous winter weather in Asia
* frigid, dangerously cold may flow east into China
* may encounter warm, moist air from Indian Ocean
* Creates hazards for densely pop chinese cities
* may encounter warm, moist air from Indian Ocean
* Creates hazards for densely pop chinese cities
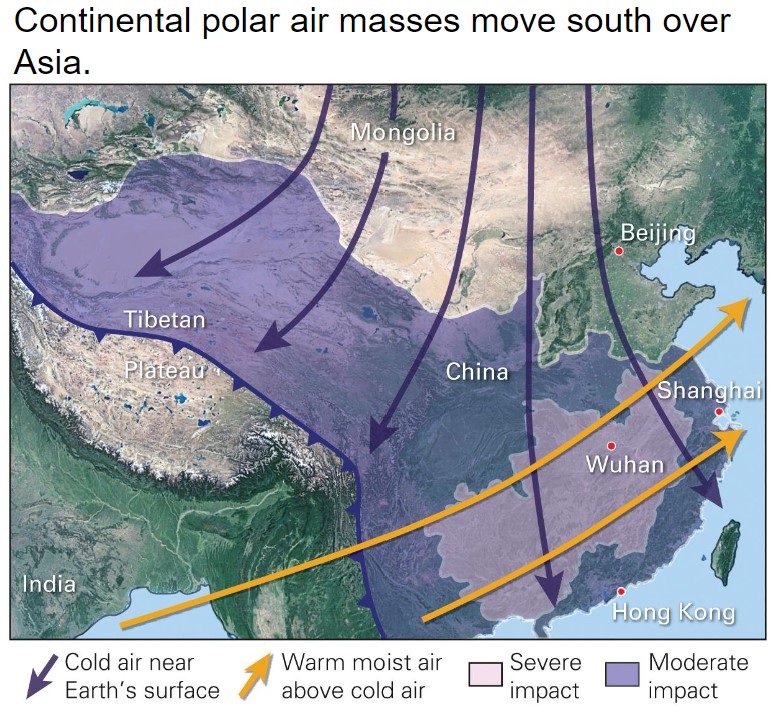
28
New cards
China worst winter; feb 2008
* primary disaster:
* burst water pipes flooded thousands of homes
* elec grid failed
* snow and ice collapsed roods
* over 1M livestock died
* 10% forest damaged or killed
* 40% winter crops destroyed
* Secondary disasters:
* Erosion
* landslides
* insect infestations
* wildfires
* Economic loss>$22.3B
* burst water pipes flooded thousands of homes
* elec grid failed
* snow and ice collapsed roods
* over 1M livestock died
* 10% forest damaged or killed
* 40% winter crops destroyed
* Secondary disasters:
* Erosion
* landslides
* insect infestations
* wildfires
* Economic loss>$22.3B
29
New cards
what are avalanches?
* rapid downslope movement of snow as flow
30
New cards
what factors contribute to avalanche formations?
* alternating times of freezing n thawing
* a min of 30cm of snow
* slopes of 20-40 degrees
* sun exposure can promote partial melting
* recent precipitation
* strong winds
* added weight
* a min of 30cm of snow
* slopes of 20-40 degrees
* sun exposure can promote partial melting
* recent precipitation
* strong winds
* added weight
31
New cards
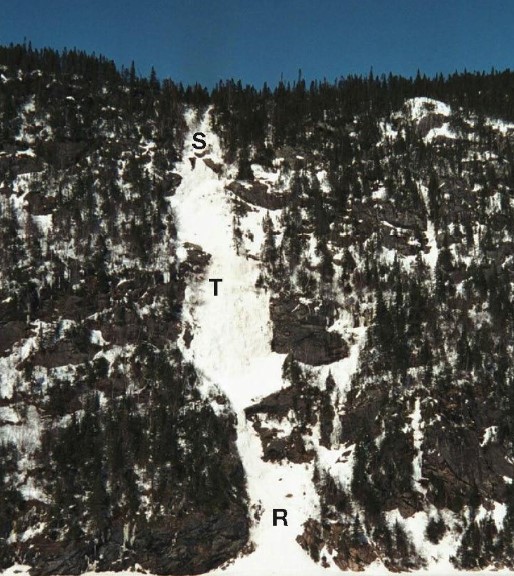
what are the 3 main parts of avalanches?
1. motion is initially in the Start Zone (S)
2. moves downslope forming a track (T)
3. as it loses momentum it spreads n slows in the run-out zone (R)

32
New cards
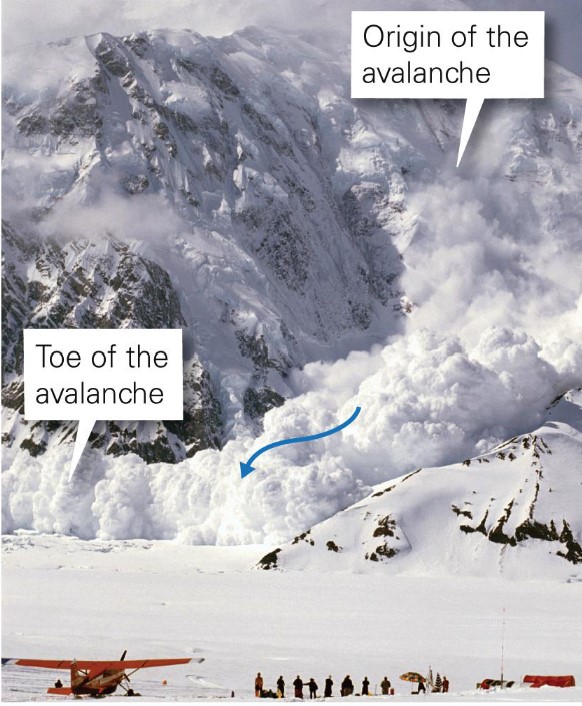
what do dry avalanche involve?
* the movement of powdery or granular snow forming loose, turbulent flows down slope
* speed : 60-200 km/hr
* compressed air forms wind gusts capable of knocking down trees
* speed : 60-200 km/hr
* compressed air forms wind gusts capable of knocking down trees

33
New cards
what are wet avalanches?
* composed of loose wet or moist snow
* higher density than dry - can be more deadly
* occur during periods of prolonged melting - usually in later winter/spring
* higher density than dry - can be more deadly
* occur during periods of prolonged melting - usually in later winter/spring
34
New cards
what are slab avalaches?
* involves detachment of blocks of snow
* most common
* contain greater vol of snow than powder avalanches n there is a high probability for burial
* most common
* contain greater vol of snow than powder avalanches n there is a high probability for burial
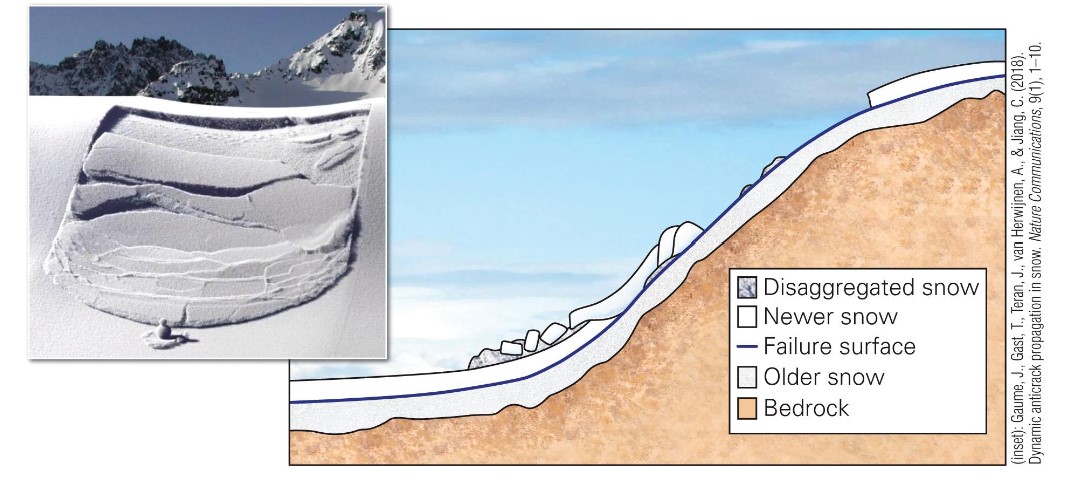
35
New cards
avalanche as a hazard
* kills approx 200 peep/yr
* in Ca, 10-15 peep die due to avalanche activity
* most avalanches in Ca r associated w/ recreational accidents
* in Ca, 10-15 peep die due to avalanche activity
* most avalanches in Ca r associated w/ recreational accidents