Igneous Rocks
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the two main types of igneous rocks based on where they solidify?
The two main types are intrusive igneous rocks (solidify beneath Earth's surface from magma) and extrusive igneous rocks (solidify above Earth's surface from lava or pyroclastic debris)
Define magma and lava.
Magma is molten (liquid) rock material below Earth's surface, while lava is molten rock material at or above Earth's surface
List and briefly explain the three main causes of melting in the Earth's mantle
The three main causes are:
◦Decompression melting
◦Melting due to volatile addition (flux melting)
◦Melting due to heat transfer
Decompression melting
Melting due to a decrease in pressure
Melting due to volatile addition (flux melting)
Volatiles like H2O and CO2 lower the melting point of rocks
Melting due to heat transfer
Rising magma can melt surrounding rock
How does partial melting affect the composition of magma relative to its source rock?
Partial melting typically results in magma that is more silica-rich (felsic) than the original source rock, leaving behind a more mafic solid residue
Define viscosity. What are the main factors that control the viscosity of magma?
Viscosity is a fluid's resistance to flow . Magma viscosity is primarily controlled by temperature (higher temp = lower viscosity), volatile content (higher volatiles = lower viscosity), and silica content (higher silica = higher viscosity)
What are the two primary reasons why magma rises towards the Earth's surface?
Magma rises due to its lower density (buoyancy) compared to surrounding rocks (due to heat) and the pressure exerted by overlying rocks squeezing it upwards
What are the two main processes that cause magma or lava to freeze and become igneous rock?
Magma or lava freezes due to loss of volatiles and cooling
What factors influence the cooling rate of magma and lava?
The cooling rate of magma is influenced by depth, shape and size of the magma body, and the presence/absence of groundwater .... The cooling rate of lava is influenced by the shape and size of the erupted material and the presence/absence of water
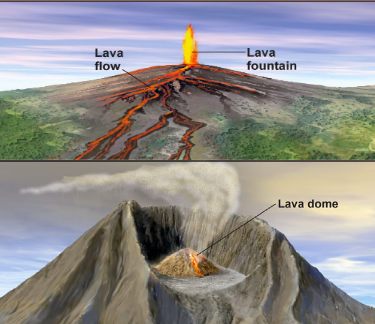
Which eruption is felsic? Which is mafic
1st) Mafic (low Si, low viscosity)
2nd) Felsic (high Si, high viscosity)