Carbohydrates
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This deck contains content from 3.1.2 Carbohydrates.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the biological name for carbohydrates?
Polysaccharides
What are the monomers for polysaccharides?
Monosaccharides
What bonds join monosaccharides together?
Glycosidic bonds
What elements are within carbohydrates?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
What is the general formula of a monosaccharide?
(CH2O)n
What are two properties of monosaccharides?
Sweet-tasting
Soluble
What are 3 examples of monosaccharides?
Glucose
Galactose
Fructose
What is the difference between hexose & pentose?
A hexose is a 6-carbon sugar, a pentose is a 5-carbon sugar
What is an isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but with a different arrangement of atoms
What is an example of 2 isomers?
a - glucose & B - glucose
What is the main difference between alpha & beta glucose?
The hydroxyl group on each is swapped, so on alpha, it is on the bottom and on beta, it is on the top
What is a disaccharide & how are they formed?
Two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond, and they are formed by the condensation of two monosaccharides
What is maltose made of?
Glucose + Glucose
What is Sucrose made of?
Glucose + Fructose
What is lactose made of?
Glucose + Galactose
What is the test for reducing sugars called?
Benedict’s Test
What are some examples of reducing sugars?
All monosaccharides
Some disaccharides(maltose)
What is reduction?
A chemical reaction that involves the gain of electrons/hydrogen
What is a reducing sugar?
A sugar that can donate electrons to another chemical( e.g. Benedict’s reagent)
What is Benedict’s Reagent?
An alkaline solution of copper(II)sulphate (CuSO4)
What is the method for the test for reducing sugars?
Add 2cm3 of the food sample to a test tube
Add an equal volume of Benedict’s
Heat the mixture gently in a water bath for 5 min
What is the positive result for the test for reducing sugars?
A colour change from blue to green/yellow/orange/red
What type of test is Benedict’s test?
Semi-quantitative
What is an example of a non-reducing sugar?
The rest of the disaccharides, such as sucrose
What is the method for the test for non-reducing sugars?
Perform Benedict’s test & obtain a negative result
Boil with HCl & neutralise with NaHCO3 alkali
Heat with Benedict’s again & obtain a red precipitate.
Give 3 examples of polysaccharides…
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
What is starch made up of?
Chains of alpha-glucose
What bonds link the monomers in starch?
1,4 and some 1,6 glycosidic bonds
What are 1,6 glycosidic bonds responsible for?
Branching of polysaccharides
Where is starch found?
In plants as small grains
What are the chains in starch?
Branched
Unbranched
So is a tight coil, making it highly compact
Where is starch never found?
Animal cells
What does starch look like?
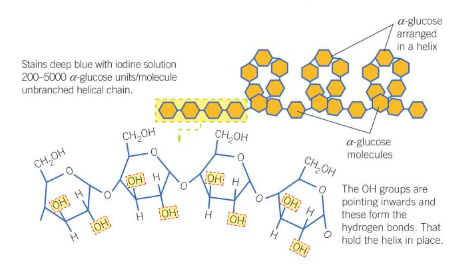
What are the 5 features of starch that make it a good storage molecule?
Insoluble, so does NOT affect water potential
Branched, so molecule is compact
Polymer of glucose, so provides glucose for respiration
Branched, so more ends for fast hydrolysis
Large molecule, so CANNOT cross the cell membrane
How do we test for starch?
Add 2cm3 of food sample into a test tube and add 2 drops of iodine.
Shake/stir.
The positive result is a colour change from orange to blue/black.
What is glycogen made up of?
Chains of alpha glucose molecules
What bonds link the monomers in glycogen?
1,4 & 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Where is glycogen found?
In animal and bacterial cells
What is the main difference between starch & glycogen?
Starch is a longer molecule and less branched than glycogen
What is glycogen stored as?
Small granules in the muscles and liver
What are the 5 points where the structure of glycogen relates to its function?
Helical/coiled so is compact
Polymer of glucose, so glucose is easily released for respiration
Polymer of glucose, so easily hydrolysed
Highly branched, so more ends, for faster hydrolysis
Insoluble, so does not affect water potential
What is cellulose made up of?
Chains of beta glucose molecules
What bonds link the monomers in cellulose?
Only 1,4 glycosidic bonds
What do the type of bonds in cellulose mean for it’s structure?
It is a straight molecule
How does cellulose look?
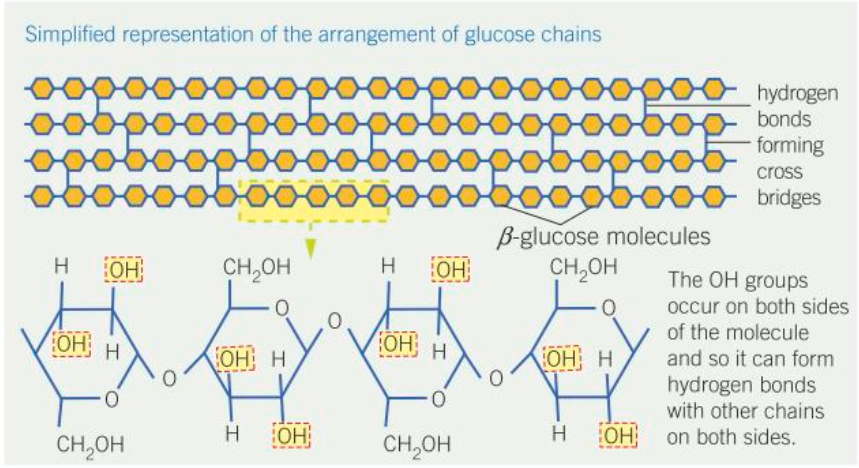
How are alternate monomers in cellulose arranged?
They are flipped by 180 degrees
What is formed when cellulose molecules are grouped together?
Microfibrils
How are microfibrils arranged?
They run parallel to one another
Why do alternate monomers in cellulose flip?
To allow the hydroxyl groups of C1 & C4 to become adjacent and form a glycosidic bond
What is the purpose of hydrogen bonds in cellulose?
To form cross-linkages between adjacent chains
What helps to strengthen cellulose?
The many hydrogen bonds
What are microfibrils grouped together to form?
Fibres
How does cellulose look with hydrogen bonds included?
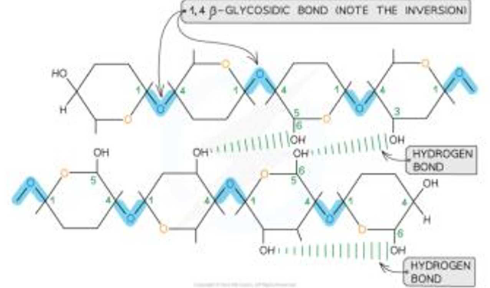
What is the relationship of cellulose’s structure to it’s function?
It has long, straight/unbranched chains of beta-glucose;
Joined by hydrogen bonding;
To form microfibrils; SO
Provides rigidity/strength.