Autonomic and Somatic Nervous Systems
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
what does the autonomic nervous system consist of
motor neurons that innervate visceral effectors
ex: smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, glands
what is the autonomic nervous system responsible for
routine homeostatic activities
examples of routine homeostatic activities
shunting blood to areas that need it
adjusts heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, etc
the autonomic nervous system operates via what type of control?
subconscious (involuntary) control
What are the two major divisions of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system - fight, flight, or freeze
parasympathetic nervous system - rest and digest
The somatic nervous system has what types of neurons
both sensory and motor neurons
motor neurons
innervate skeletal muscles
sensory neurons
touch, pain, temperature, proprioception (sense of self position), sight, hearing, taste, smell, and equilibrium
Both the ANS and Somatic nervous system have
motor fibers
what do the ANS and Somatic nervous system differ in
efferent pathways and ganglia
target organ responses to neurotransmitters
Both the ANS and the somatic nervous system are regulated and coordinated by
higher brain centers
Most spinal and many cranial nerves contain
both somatic and autonomic fibers
Adaptions usually involve
both skeletal muscles and visceral organs
somatic nervous system
one-neuron motor pathway
the somatic nervous system directly synapses with the
effector
which two motor neurons does the autonomic nervous system use in series
preganglionic neuron
postganglionic neuron
preganglionic neuron
cell body in CNS
axon extends to an autonomic ganglion
postganglionic neuron
cell body and dendrites located in an autonomic ganglion
unmyelinated axon extends from ganglion to effector
Where does the postganglionic neuron synapse with preganglionic axons
in an autonomic ganglion
pathway of an autonomic motor neuron in the ANS
preganglionic cell body (CNS) → preganglionic axon → autonomic ganglion (postganglionic dendrites and cell body) → postganglionic axon → effector
effectors in SNS
skeletal muscle
efferent pathways in SNS
one nerve fiber from CNS to effector
no ganglia
neurotransmitters in SNS
acetylcholine
effect on target cells in SNS
always excitatory
effect of denervation in SNS
flaccid paralysis
control of SNS
usually voluntary
effectors in ANS
glands, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle
efferent pathways in ANS
two nerve fibers from CNS to effector
synapse at a ganglion
Neurotransmitters of ANS
ACh and Norepinephrine
ANS’ effect on target cells
excitatory or inhibitory
ANS’ effect of denervation
denervation hypersensitivity
ANS control
usually involuntary
SNS sensory input
from somatic senses and special senses
SNS control of motor output
voluntary control from cerebral cortes
SNS motor neuron pathway
one-neuron pathways
somatic motor neuron extending from CNS synapse directly with effector
SNS response
contraction of skeletal muscle
ANS sensory input
mainly from interoceptors
some from somatic and special senses
ANS control of motor output
involuntary control from hypothalamus, limbic system, brainstem, and spinal cord; limited control from cerebral cortex
ANS motor neuron pathway
usually two-neuron pathway
ANS responses
contraction or relaxation of smooth muscle
increased or decreased rate and force of contraction of cardiac muscle
increased or decreased secretions of glands
divisions of ANS
parasympathetic division
sympathetic division
parasympathetic division
promotes maintenance functions
conserves energy
sympathetic division
mobilizes body during activity
dual innervation
all visceral organs are served by both divisions, but these divisions cause opposite effects
what is the purpose of dynamic antagonism between the two divisions of the ANS
maintains homeostasis
the sympathetic division is referred to as
fight or flight system/ E division
What activates the sympathetic divison
exercise, excitement, emergency, embarrassment
bodily reaction to sympathetic division activation
increased heart rate and blood pressure
dry mouth
cold, sweaty skin
dilated pupils
during vigorous physical activity, the sympathetic division
shunts blood to skeletal muscles and heart
dilates airways
causes liver to release glucose
The parasympathetic division aims to
keep body energy use as low as possible, even while carrying out maintenance activities
what is the parasympathetic division referred to as
rest and digest system
D division
what does the parasympathetic division direct
directs digestion, diuresis, defecation
example of the parasympathetic division - person relaxing and reading after a meal
blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rates are low
GT activity is high - increased salivation, increased secretions and motility
pupils constricted; lenses accommodated for close vision
ganglia
sites of synapses between preganglionic and postganglionic neurons in the PNS
parasympathetic ganglia
terminal ganglia
sympathetic ganglia
sympathetic trunk (paravertebral) ganglia
prevertebral ganglia
sympathetic trunk (paravertebral) ganglia
lie in a vertical row on either side of the vertebral column
prevertebral ganglia
lie anterior to the vertebral column and close to the large abdominal arteries
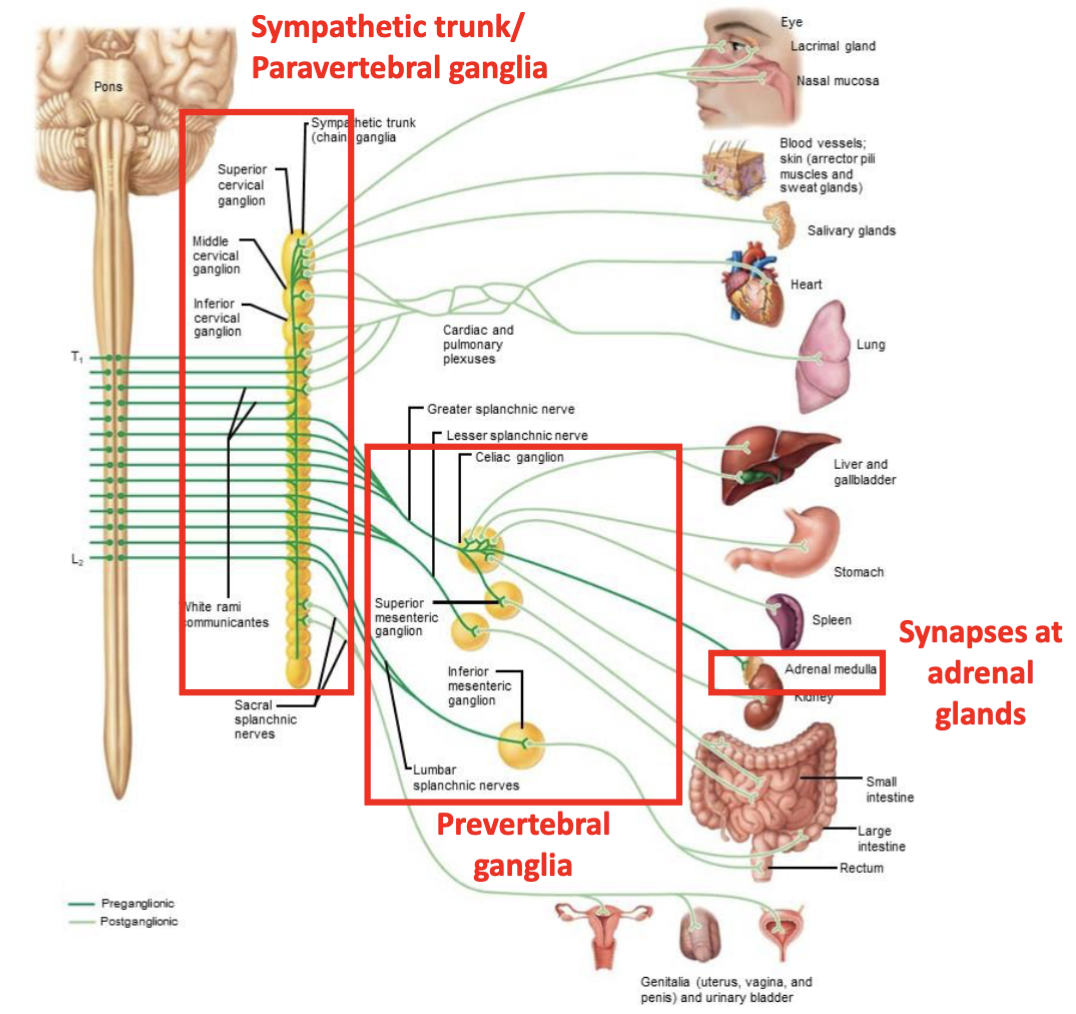
Sympathetic division site of origin
thoracolumbar (T1 - L2/3)
Sympathetic division preganglionic fiber length
short
sympathetic division postganglionic fiber length
long
sympathetic division ganglia location
close to spinal cord
sympathetic division neurotransmitters released
preganglionic - ACh
postganglionic - mostly NE, some ACh
parasympathetic sites of origin
craniosacral (CN III, VII, IX, X, and S2-S4)
Parasympathetic preganglionic fiber length
long
parasympathetic postganglionic fiber length
short
Parasympathetic ganglia location
in or near their visceral effector organ
parasympathetic neurotransmitters released
preganglionic - ACh
postganglionic - ACh
What is the complexity and innervation of the sympathetic division like in comparison to the parasympathetic division
the sympathetic division is more complex and innervates more organs than the parasympathetic division
what structures are innervated only by the sympathetic division
sweat glands
arrector pili muscle
smooth muscles of all blood vessels
The sympathetic division includes which ganglia
sympathetic trunk ganglia and prevertebral ganglia
the sympathetic division innervates which gland
adrenal glands
organization of sympathetic division diagram
what are the two areas of the parasympathetic division
cranial and sacral
In the parasympathetic division, where do the long preganglionic fibers extend from and to
extend from the CNS almost to target organs
in the parasympathetic division, what do the long preganglionic fibers synpase with
synapse with postganglionic neurons in ganglia that are close to (terminal ganglia) or within (intramural ganglia) target organs
in the parasympathetic division, what do short postganglionic fibers synapse with
synapse with effectors
Terminal ganglia of the parasympathetic division
ciliary ganglion
pterygopalatine ganglion
submandibular ganglion
otic ganglion
Where do preganglionic axons branch off of, and what do they form
sacral nerves
form pelvic splanchnic nerves
where are the cell bodies of the parasympathetic division located
the brain stem
Cranial nerves that carry parasympathetic fibers
Oculomotor (III)
Facial (VII)
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Vagus (X)
oculomotor in Parasympathetic division
constrict pupils, adjust lens for focus
Facial nerve in parasympathetic division
stimulate nasal and lacrimal glands
stimulate submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
glossopharyngeal nerve in parasympathetic division
stimulate parotoid salivary glands
vagus nerve in parasympathetic division
90% of all preganglionic parasympathetic fibers
Preganglionic fibers for vagus nerve arise from
the medulla
where do the preganglionic fibers for the vagus nerve synapse in
ganglia in walls of all thoracic and abdominal viscera
functional effects of the vagus nerve in the parasympathetic division
slows heart rate
serves lungs and bronchi
sends branches to stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small intestine, and part of large intestine
Where does the sacral part of the parasympathetic division originate from
neurons in S2-S4
what does the sacral part of the parasympathetic division serve
pelvic organs and distal half of large intestine
where do axons in the sacral part of the parasympathetic division travel
in the ventral root of spinal nerves
they then branch off to form pelvic splanchnic nerves
preganglionic parasympathetic neurons in the sacral part of the parasympathetic division synapse with
ganglia in the pelvic floor
intramural ganglia in walls of distal half of large intestine, urinary bladder, ureters, and reproductive organs