A & P 2 exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:28 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
1
New cards
Lymphatic system
protects us against disease from pathogens, transports materials (hormones, wastes and nutrients), returns excess fluid to bloodstream, and maintains normal blood volume
**Composed of:**
\-lymph
\-Lymph vessels
\-lymphoid tissue and organs
\-lymphoid cells (lymphocytes, phagocytes, ect)
**Composed of:**
\-lymph
\-Lymph vessels
\-lymphoid tissue and organs
\-lymphoid cells (lymphocytes, phagocytes, ect)
2
New cards
three categories lymphatic cells respond to?
1\.) environmental pathogens (bacteria, viruses, ect)
2\.)Toxins (poisons, venom)
3\.)Abnormal body cells (cancer)
2\.)Toxins (poisons, venom)
3\.)Abnormal body cells (cancer)
3
New cards
Immunity
the ability to resist infections and disease
4
New cards
primary lymphoid tissue
Place where lymphocytes are produced
\-include the red bone marrow and thymus
\-include the red bone marrow and thymus
5
New cards
secondary lymphoid tissue
Place where lymphocytes are activated
\-Include tonsils, lymph nodes, spleen and MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue)(aka mucus membranes)
\-Include tonsils, lymph nodes, spleen and MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue)(aka mucus membranes)
6
New cards
lymphatic vessels
carry lymph-interstitial fluid from peripheral tissue to venous return
\-contain minimal pressure
\-rely on valves to prevent backflow of lymph
\-contraction of SM aid flow
\-contain minimal pressure
\-rely on valves to prevent backflow of lymph
\-contraction of SM aid flow
7
New cards
Lymphatic capillaries
tiny vessels that transports and filters lymphatic fluid (lymph) from your body's cells and tissues into lymphatic vessels
8
New cards
lymphatic vessels vs blood capillaries
**Lymphatic vessels are:**
\-Closed at one end
\-contain larger luminal diameters
\-have thinner walls
\-irregular outline in sectional view
\-Closed at one end
\-contain larger luminal diameters
\-have thinner walls
\-irregular outline in sectional view
9
New cards
Flow of fluid in lymphatic vessels
Overlap of endothelial cells act as one way valves. This prevents the return of things such as fluids, solutes, viruses, bacteria, ect from leaving the vessel once inside
(acts as a one way door where it can only open inward, not outward)
(acts as a one way door where it can only open inward, not outward)
10
New cards
Lacteals
special lymphatic capillaries found in small intestine
\-transports lipids from Digestive tract
\-transports lipids from Digestive tract
11
New cards
lymphedema
blockage of lymph drainage in limbs
\-results in severe swelling
\-results in severe swelling
12
New cards
where are lymphatic vessels located in the body?
in the peripheral tissues of the throat, armpits, chest, abdomen and groin (almost everywhere)
13
New cards
Lymphoid tissue
connective tissue dominated by lymphocytes
14
New cards
lymphoid nodules
areolar tissue with densely packed areas of lymphocytes
\-Found in lymph nodes, spleen, respiratory tract (tonsils), along reproductive, digestive and urinary tracts
\-Found in lymph nodes, spleen, respiratory tract (tonsils), along reproductive, digestive and urinary tracts
15
New cards
germinal centers
central zone of each nodule, contains dividing lymphocytes
16
New cards
Lymphoid organs
Include lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen
17
New cards
Lymph nodes
small lymphoid organs that:
\- filter substances in lymph (purifies lymph before it reaches veins)
\-acts as early defense system (antigens in lymph stimulate macrophages and lymphocytes in nearby nodes)
\-monitor peripheral infections (respond before infection reaches vital organs)
\
\*greatest amount found in neck, axillae and groin
\*largest nodes found in groin, axillae and base of neck
\*Nodes in gut, trachea and thoracic duct protect digest. and resp. tract
\*swells in response to infection
\- filter substances in lymph (purifies lymph before it reaches veins)
\-acts as early defense system (antigens in lymph stimulate macrophages and lymphocytes in nearby nodes)
\-monitor peripheral infections (respond before infection reaches vital organs)
\
\*greatest amount found in neck, axillae and groin
\*largest nodes found in groin, axillae and base of neck
\*Nodes in gut, trachea and thoracic duct protect digest. and resp. tract
\*swells in response to infection
18
New cards
Trabeculae
bundles of collagen fibers which extend into the interior of nodes
19
New cards
Hilum
shallow indentation where blood and nervous vessels reach nodes
20
New cards
Afferent lymphatics
bring lymph to the lymph node from peripheral tissues
21
New cards
efferent lymphatics
vessels that carry lymph away from the lymph node and towards venous circulation
22
New cards
lymphadenopathy
excessive enlargement of nodes
23
New cards
thymus
located in mediastinum (where t cells are produced)
\-Atrophies after puberty
**thymic lobule**:
\-contains a dense outer cortex and pale central medulla
\-lymphocytes divide in cortex and migrate into medulla (this is where t cells leave)
\-Atrophies after puberty
**thymic lobule**:
\-contains a dense outer cortex and pale central medulla
\-lymphocytes divide in cortex and migrate into medulla (this is where t cells leave)
24
New cards
what is/ the function of the spleen
the spleen is a specialized filter
* removes abnormal BC and other blood components
* stores iron recycles from ruptures RBC
* initiation of immune response by b and t cells
* removes abnormal BC and other blood components
* stores iron recycles from ruptures RBC
* initiation of immune response by b and t cells
25
New cards
types of immunity
Innate: always works the same
adaptive: specialized responses depending on for antigen (develops after exposure)
adaptive: specialized responses depending on for antigen (develops after exposure)
26
New cards
lymphoid stem cells
**group 1 (lymphoid stem cells in bone marrow)**
\-produce B and NK cells
\
**Group 2 (lymphoid stem cells migrates to thymus)**
\-produce t cells
\
\*T cells differ in response to hormones while B cells differ in response to interleukins-7 (cytokines)
\-produce B and NK cells
\
**Group 2 (lymphoid stem cells migrates to thymus)**
\-produce t cells
\
\*T cells differ in response to hormones while B cells differ in response to interleukins-7 (cytokines)
27
New cards
T cells
engage in cell mediated immunity (cell to cell combat)
28
New cards
types of T cells
1\.) cytotoxic T cells: attacks antigens physically and chemically
2\.)Helper T cells: stimulate responses of T and B cells
3\.)regulatory T cells: moderate immune responses
4\.) memory t cells: keeps record of previous encounters with pathogens (allows for quicker responses upon re-exposure)
2\.)Helper T cells: stimulate responses of T and B cells
3\.)regulatory T cells: moderate immune responses
4\.) memory t cells: keeps record of previous encounters with pathogens (allows for quicker responses upon re-exposure)
29
New cards
Types of regulatory t cells
1\.) Inflammatory t cells: up regulate
2\.)Suppressor t cells: down regulate
2\.)Suppressor t cells: down regulate
30
New cards
B cells
engage in antibody- mediated immunity (defends against antigens and pathogens in body fluid)
\
Types of B Cells:
1\.)Plasma cells; produce antibodies
2\.)Memory b cells: keep record of previous pathogen encounters
\
Types of B Cells:
1\.)Plasma cells; produce antibodies
2\.)Memory b cells: keep record of previous pathogen encounters
31
New cards
Do T and B cells retain their ability to divide?
yes, they maintain their ability to divide. There are allows a small number of lymphocytes (typically memory cells) circulating around the body. When a lymphocyte becomes exposed to the right antigen, it will produce many clones of it itself (with the same specificity)
\-allows for effective fighting against an antigen through combined t and b cell attacks
\-allows for effective fighting against an antigen through combined t and b cell attacks
32
New cards
Clonal selection
the process of an antigen selecting particular lymphocytes for cloning
33
New cards
Innate defenses
block or attack any foreign substance/pathogen
34
New cards
types of Innate defenses
\-Physical barriers (skin, hair, mucous, stomach acid, ect)
\-Phagocytes (monocytes)
\-Immune surveillance (nk)
\-Interferons
\-complement
\-Inflammation
\-fever
\-Phagocytes (monocytes)
\-Immune surveillance (nk)
\-Interferons
\-complement
\-Inflammation
\-fever
35
New cards
Fixed macrophages (histiocytes)
stay in specific tissues and organs
36
New cards
Microglia
macrophages in CNS
37
New cards
Stellate macrophages
located on luminal surface of liver sinusoids
38
New cards
free macrophages
travel throughout the body
39
New cards
alveolar macrophages
monitor epithelial surfaces of lungs
40
New cards
what’s the Complement system?
system which enhances the action of antibodies and phagocytes (involves complement proteins in plasma)
\
\-complement proteins work in groups that can aid in pathogen destruction, opinization or histamine release
\
\-complement proteins work in groups that can aid in pathogen destruction, opinization or histamine release
41
New cards
NK cells
take part in immune surveillance
\-secrete chemicals which lyse the plasma membrane of abnormal cells
\-secrete chemicals which lyse the plasma membrane of abnormal cells
42
New cards
Interferons (INFs)
small proteins released by activated lymphocytes, macrophages and infected tissues
\-they trigger the release of antiviral proteins by cells which block viral replication
\-they trigger the release of antiviral proteins by cells which block viral replication
43
New cards
Inflammation
localized immune response caused by damaged cells, antigens, pathogens, ect (causes vasodilation (heat, edema, redness, pain))
\
\*activation of mast cells results in the release of histamine-→ triggers
\
\*activation of mast cells results in the release of histamine-→ triggers
44
New cards
effects of inflammation
\-Temporary wound repair through clot formation
\-slows spread of pathogens to other areas of the body
\-Mobilizes local, regional and systemic defenses in order to overcome pathogens and facilitate regeneration (removes debris and stim of fibroblasts)
\-slows spread of pathogens to other areas of the body
\-Mobilizes local, regional and systemic defenses in order to overcome pathogens and facilitate regeneration (removes debris and stim of fibroblasts)
45
New cards
Products of inflammation
1\.)Necrosis (local tissue destruction)
2\.)Pus (mix of debris, fluid, cells waste and dying tissue)
3\.)Abscess: collection of pus in an enclosed space
2\.)Pus (mix of debris, fluid, cells waste and dying tissue)
3\.)Abscess: collection of pus in an enclosed space
46
New cards
fever
temp greater than 37.2 degrees C (99 F)
\
**Function:**
\-Increases metabolic rate (more chemical reactions=more release of Energy)
\-accelerates defenses since cells can move faster and enzymatic reactions r faster
\-slows replication of some viruses and bacteria
\
**Function:**
\-Increases metabolic rate (more chemical reactions=more release of Energy)
\-accelerates defenses since cells can move faster and enzymatic reactions r faster
\-slows replication of some viruses and bacteria
47
New cards
Pyrogens
released by bacteria, molds, viruses and yeasts
\-Causes hypothalamus to raise body temp
\
\*endogenous pyrogens are produced internally and include interferons, interleukin-1, ect
\-Causes hypothalamus to raise body temp
\
\*endogenous pyrogens are produced internally and include interferons, interleukin-1, ect
48
New cards
immune surveillance
Carried out by NK cells'
\
Steps:
1\.)Identify and adhere abnormal cells
2\.) Golgi bodies produced vesicles with perforins
3\.)perforins are released by vesicles
4\.) perforins form pores on plasma membrane of abnormal cell=lysis
\
Steps:
1\.)Identify and adhere abnormal cells
2\.) Golgi bodies produced vesicles with perforins
3\.)perforins are released by vesicles
4\.) perforins form pores on plasma membrane of abnormal cell=lysis
49
New cards
cell-mediated immunity
Defends against abnormal cell and pathogens inside cells
\-Achieved through cell-mediated immunity
\-Achieved through cell-mediated immunity
50
New cards
Antibody-mediated immunity
Defends against antigen and pathogens in body fluid (humoral immunity because antibodies are found in body fluid)
51
New cards
Four forms of immunity
1\.)Naturally acquired active immunity: developed in response to antigen exposure (undeliberate)
2\.)Artificially acquired active immunity: deliberate exposure to antigens through medical means (vaccines)
3\.)Naturally acquired passive immunity: antibodies which can be passed between individuals (breast milk, placenta)
4\.) already made antibodies received from an outside source through medical means (anti-venom
2\.)Artificially acquired active immunity: deliberate exposure to antigens through medical means (vaccines)
3\.)Naturally acquired passive immunity: antibodies which can be passed between individuals (breast milk, placenta)
4\.) already made antibodies received from an outside source through medical means (anti-venom
52
New cards
Four general properties of adaptive immunity
1\.) specificity (responds to specific antigens)
2\.)Versatility (many types of lymphocytes)
3.) Memory (memory cells provide protection against re-exposure)
4\.) Tolerance (immune system ignores self antigens)
2\.)Versatility (many types of lymphocytes)
3.) Memory (memory cells provide protection against re-exposure)
4\.) Tolerance (immune system ignores self antigens)
53
New cards
MHC proteins
Membrane glycoproteins which bind to antigens (displays abnormal peptide on cell’s surface for t cell recognition)
54
New cards
class 1 MHC proteins
are in the plasma membrane of all nucleated cells
\-displays abnormal peptide on cell’s surface for t cell recognition= lysis of cell
\-triggered by viral or bacterial infection
\
\*like a little red flag saying “I’m abnormal, kill me”
\-displays abnormal peptide on cell’s surface for t cell recognition= lysis of cell
\-triggered by viral or bacterial infection
\
\*like a little red flag saying “I’m abnormal, kill me”
55
New cards
Class 2 MHC proteins
only present in membranes of APCs (include all monocyte-macrophage types, dendritic cells (Langerhans cells) of skin and those of lymph nodes and spleen
\-Class 2 MHC proteins only appears in plasma membrane during antigen processing (will engulf pathogen, break it down in antigenic fragments, display parts on cell surface for t cells)
\
\*t cell receptors can bind to both 1 and 2 MHC, will only become activated (antigen recognition) for specific antigen
\-Class 2 MHC proteins only appears in plasma membrane during antigen processing (will engulf pathogen, break it down in antigenic fragments, display parts on cell surface for t cells)
\
\*t cell receptors can bind to both 1 and 2 MHC, will only become activated (antigen recognition) for specific antigen
56
New cards
CD markers
cluster of differentiation markers in T cell membranes (reason for t cell specificity to certain antigens)
\-CD8: cytotoxic and regulatory t cells (responds to 1 MHC)
\-CD4: Helper T cells (respond to 2 MHC)
\-CD8: cytotoxic and regulatory t cells (responds to 1 MHC)
\-CD4: Helper T cells (respond to 2 MHC)
57
New cards
How are T cells activated?
T cells are activated by exposure to an antigen
* only recognize antigens presented by APC’s (present antigens to certain lymphocytes for recognition)
* Also need costimulation (secondary signal produced by abnormal target cell to confirm plan of action)
* only recognize antigens presented by APC’s (present antigens to certain lymphocytes for recognition)
* Also need costimulation (secondary signal produced by abnormal target cell to confirm plan of action)
58
New cards
what produces memory t cells?
produced by cytotoxic t cells
* memory t cells can form cytotoxic t cells upon re-exposure to same antigen
* memory t cells can form cytotoxic t cells upon re-exposure to same antigen
59
New cards
How are B cells activated
1\.)Antigens in body fluid bind to receptors on b cell membranes=sensitization (antigen will reappear on b cell surface with 2 MCH
2\.)Helper T cell binds to 1 MHC and secretes cytokines the activate B cell
2\.)Helper T cell binds to 1 MHC and secretes cytokines the activate B cell
60
New cards
Constant segment
Same for all antibodies of that class (determines class of antibody)
\
\*the vertical portion of the Y
\
\*the vertical portion of the Y
61
New cards
Variable segment
part that is antigen specific
\
\*the V portion of a Y
\
\*the V portion of a Y
62
New cards
IgG
Largest and most diverse class of antibodies (part of secondary response because THEY TAKE LONGER TO PRODUCE)
\-can provide maternal immunity (cross the placenta)
\-Produces hemolytic disease
\-can provide maternal immunity (cross the placenta)
\-Produces hemolytic disease
63
New cards
IgE
increases release of histamine and other inflammation chemicals by binding to exposed surfaces on basophils and mast cells
64
New cards
IgM
1st class of antibody secreted after antigen is encountered (part of primary response)
\-Anti A and Anti B antibodies
\-Anti A and Anti B antibodies
65
New cards
IgA
delivered through breast milk
66
New cards
cytokines
chemical messengers released by tissue cells (not hormones because they can be produced by most body cells, not exclusive to endocrine cells)
\
Functions:
\-stimulate T cell division (which produces memory cells or quickens cytotoxic t cell maturation)
\-Attract and stimulate Macrophages
\-Promote activation of B cells
\
ex. INFs
\
Functions:
\-stimulate T cell division (which produces memory cells or quickens cytotoxic t cell maturation)
\-Attract and stimulate Macrophages
\-Promote activation of B cells
\
ex. INFs
67
New cards
Immunocompetence
ability to produce immune response after antigen exposure
\-babies can develop this at 3 to 4 months old
\-babies can develop this at 3 to 4 months old
68
New cards
respiratory system
composed of structures involved in ventilation and gas exchange
69
New cards
functions of respiratory system
\-Provide extensive surface area for gas exchange between air and blood
\-Move air to and from exchange surfaces on lungs
\-Protect resp. surfaces from dehydration, temp changes and pathogens
\-Produce sound
\-Detect odors
\-Move air to and from exchange surfaces on lungs
\-Protect resp. surfaces from dehydration, temp changes and pathogens
\-Produce sound
\-Detect odors
70
New cards
Upper resp. tract
nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and pharynx
71
New cards
Lower resp. tract
Larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli
72
New cards
Alveoli
Air filled pockets within lungs (where gas exchange occurs)
73
New cards
Resp. Mucosa
mucus membrane lining conducting portion of resp. tract (nasal cavity to larger bronchioles)
\
Function:
\-Provides filtration that makes up resp, defense system
\
Function:
\-Provides filtration that makes up resp, defense system
74
New cards
Components of resp. defense system
\-Filtration by nasal cavity removes large particles
\-Cilia sweep mucous and trapped debris to pharynx for swallowing
\-Cilia sweep mucous and trapped debris to pharynx for swallowing
75
New cards
olfactory region
located in superior portion of nasal cavity
\-Provides sense of smell
\-Provides sense of smell
76
New cards
meatuses
narrow passages which produce air turbulence to 1.) warm and humidify incoming air and 2.) bring to olfactory receptors
77
New cards
Lamina propria
underlying layer of areolar tissue that supports resp. epithelium
\
Upper resp.: has mucous glands
Conducting portion of lower resp: smooth muscles
\
Upper resp.: has mucous glands
Conducting portion of lower resp: smooth muscles
78
New cards
Pharynx
chamber shared by digestive and resp. systems (throat)
\
Divided into three parts:
1\.)Nasopharynx (Superior, pharyngeal tonsils and auditory tube openings)
2\.)Oropharynx (connects directly to oral cavity)
3\.)Laryngopharynx (most inferior, between hyoid bone and entrance to larynx and esophagus
\
Divided into three parts:
1\.)Nasopharynx (Superior, pharyngeal tonsils and auditory tube openings)
2\.)Oropharynx (connects directly to oral cavity)
3\.)Laryngopharynx (most inferior, between hyoid bone and entrance to larynx and esophagus
79
New cards
Glottis
slit-like opening between vocal cords (voice box) (where air enters the larynx)
80
New cards
Larynx
a cartilaginous tube that surrounds and protects the glottis
\
Made of three unpaired cartilages:
\-Thyroid cartilage
\-Cricoid cartilage
\-epiglottis cartilage
\
Made of three unpaired cartilages:
\-Thyroid cartilage
\-Cricoid cartilage
\-epiglottis cartilage
81
New cards
epiglottis
structure which prevents food and liquids from entering resp. tract (folds over glottis)
82
New cards
how is sound produced?
air passing through open glottis vibrates vocal cords, producing sound waves
\
\-pitch depends on diameter, tension and length of vocal folds
\
\-pitch depends on diameter, tension and length of vocal folds
83
New cards
Trachea
a tough flexible tube that delivers/takes gases from lungs
\-Splits to form right and left main bronchi in mediastinum
\-Splits to form right and left main bronchi in mediastinum
84
New cards
tracheal cartilage
cartilages that make up the trachea (about 15-20)(stiffens windpipe and protects airway)
Function:
\-prevent collapse and overexpansion of due to pressure changes in resp. tract
Function:
\-prevent collapse and overexpansion of due to pressure changes in resp. tract
85
New cards
Bronchial tree
Right and left main bronchi enter each of their respective lungs, and divide to form lobar bronchi
86
New cards
How many lobes in left and right human lungs (also differences between the two)
**Right lung:**
\-slightly larger (wider due to liver)
\-3 lobes (superior, middle and inferior)
\-3 lobar branches
\-10 bronchopulmonary
\
Left lung:
\-Longer
\-two lobes (superior and inferior)
\-two lobar branches
\-8-9 bronchopulmonary
\-slightly larger (wider due to liver)
\-3 lobes (superior, middle and inferior)
\-3 lobar branches
\-10 bronchopulmonary
\
Left lung:
\-Longer
\-two lobes (superior and inferior)
\-two lobar branches
\-8-9 bronchopulmonary
87
New cards
Division of lungs
Trachea→ main bronchus →lobar branches→ segmental bronchi→ bronchopulmonary segments (each segmental provides air to one bronchopulmonary segment)
88
New cards
bronchopulmonary segments
Branching of segmental bronchi form bronchioles
\-Bronchioles will than divide to form terminal bronchioles (finest conducting branches)
\-Terminal bronchioles branch to form respiratory bronchioles (connected to alveoli via alveolar ducts)
\-Alveolar ducts end in sac (common chambers for many individuals alveoli)
\*bronchioles kind of act like the arterioles of the resp. system
\*have no cartilage, dominated by smooth muscle
\-Bronchioles will than divide to form terminal bronchioles (finest conducting branches)
\-Terminal bronchioles branch to form respiratory bronchioles (connected to alveoli via alveolar ducts)
\-Alveolar ducts end in sac (common chambers for many individuals alveoli)
\*bronchioles kind of act like the arterioles of the resp. system
\*have no cartilage, dominated by smooth muscle
89
New cards
Alveolar cell layer
mainly composed of simple, squamous epithelium
\-pneumonocytes type 1: very thin and are sites of gas diffusion
\-Pneumonocytes type II: produce surfactant (oil secretions)(without things, surface tension would collapse the alveoli)
\-pneumonocytes type 1: very thin and are sites of gas diffusion
\-Pneumonocytes type II: produce surfactant (oil secretions)(without things, surface tension would collapse the alveoli)
90
New cards
Bronchodilation
caused by sympathetic nervous system
\-enlarges diameter of luminal diameter of bronchioles
\-less resistance to flow
\-enlarges diameter of luminal diameter of bronchioles
\-less resistance to flow
91
New cards
Bronchoconstriction
Caused by parasympathetic nervous system and histamine activation
\-reduced luminal diameter
\-more resistance to flow
\-reduced luminal diameter
\-more resistance to flow
92
New cards
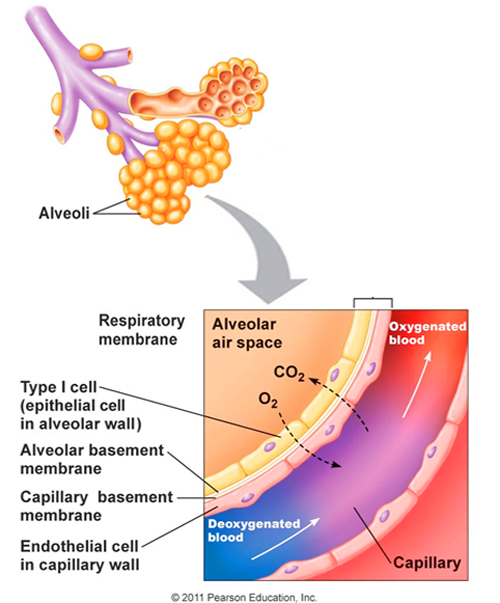
blood air barrier
three layered barrier where gas exchange occurs in alveoli (The barrier between capillary blood and alveolar air)
\
The 3 layers:
\-Alveolar cell layer
\-Capillary endothelial layer
\-Fused basement membrane between them
\
\*very efficient because distance for diffusion is short and CO2/O2 are lipid soluble (can diffuse readily through surfactant & plasma membrane)
\
The 3 layers:
\-Alveolar cell layer
\-Capillary endothelial layer
\-Fused basement membrane between them
\
\*very efficient because distance for diffusion is short and CO2/O2 are lipid soluble (can diffuse readily through surfactant & plasma membrane)
93
New cards
three layers that make up blood air barrier
\-Alveolar cell layer
\-Capillary endothelial layer
\-Fused basement membrane between them
\-Capillary endothelial layer
\-Fused basement membrane between them
94
New cards
Pneumonia
inflammation of lung tissue
95
New cards
pleural cavities
contains the left and right lungs
\-pleura is composed of a parietal pleura (lines outer surface of thoracic wall inner surface) and visceral pleura (covers surface of lungs)
\-Between the two layers is a space filled with pleural fluid
\-pleura is composed of a parietal pleura (lines outer surface of thoracic wall inner surface) and visceral pleura (covers surface of lungs)
\-Between the two layers is a space filled with pleural fluid
96
New cards
External respiration
all processes involved with exchange of O2 and CO2 with external environment (breathing)
97
New cards
Internal respiration
uptake of O2 and release of CO2 by cells (cellular respiration)
98
New cards
Pulmonary ventilation
physical movement of air into and out of resp. tract
99
New cards
Boyles law
Relationship between gas and pressure and volume
\-pressure of a gas increases when volume decreases
(increase V= Decrease P; Decrease V=Increase P)
\-pressure of a gas increases when volume decreases
(increase V= Decrease P; Decrease V=Increase P)
100
New cards
pressure and airflow
Air flows from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure