intro bacteriology
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Who is the father of microbio?
Van Leeuwenhoek
Do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have DNA with a nuclear membrane?
only eukaryotic
Describe cell division in prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells
prokaryotic: binary fission
eukaryotic: mitosis
Describe chromosome number in prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells
prokaryotic: single circular
eukaryotic: 23 pairs
Do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles?
only eukaryotes
Describe the ribosomes in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
prokaryotes: 70S (50 + 30)
eukaryotes: 80S (70S in organelles)
Describe cell walls in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
prokaryotes: usually present, complex
eukaryotes: not in human cells, simple (chitin, cellulose)
T/F bacteria are prokaryotic multicellular organisms
F, unicellular
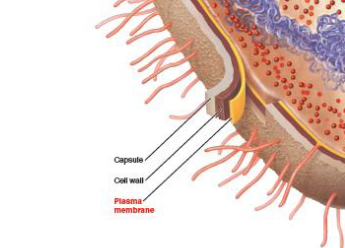
Going from innermost to outermost, describe the layers of the bacterial outer membrane. Are these found in ALL bacteria?
plasma membrane → cell wall → capsule
no, only plasma membrane is in all
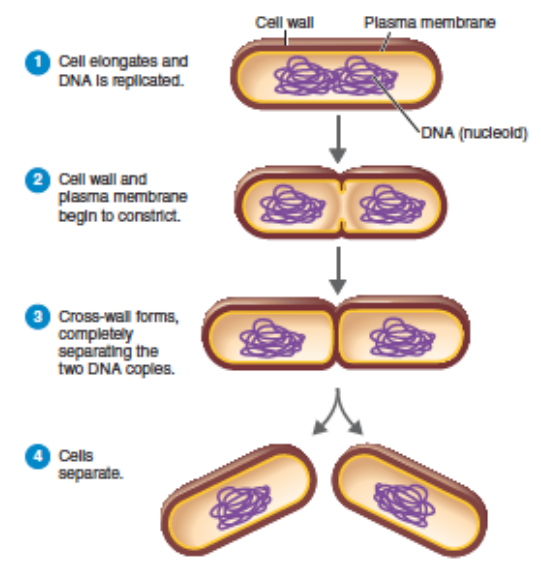
Briefly describe binary fission.
cell elongates, DNA replicated, cell constricts then splits
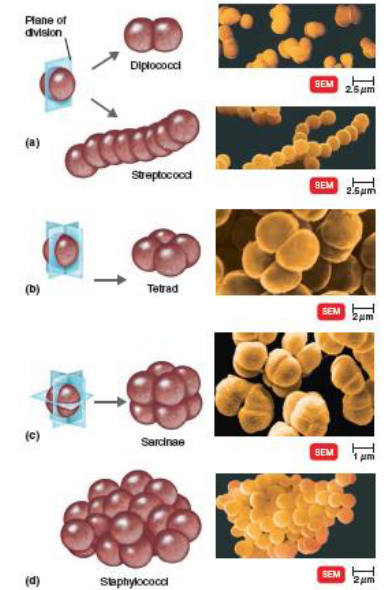
What 3 shapes do bacteria come in?
cocci (sphere)
bacilli (rod)
spiral
What does it mean when a bacteria is pleomorphic?
vary in shape and size
Describe cocci shape:
diplococci
streptococci
tetrad
sarcinae
staphylococci
diplo: pair
strepto: chain
tetrad: group of 4
sarcinae: cube of 8
staphylo: grape
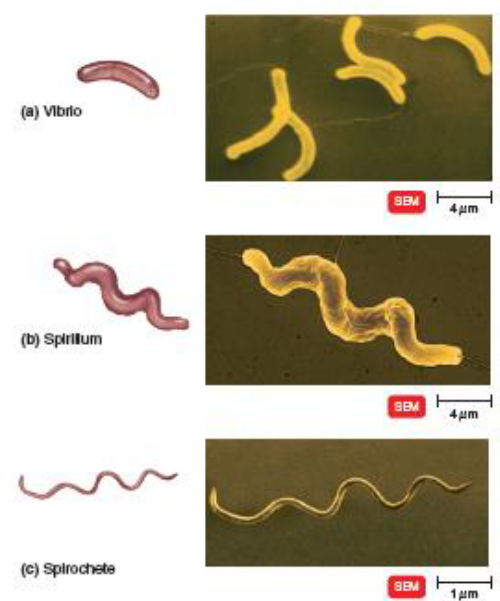
Describe spiral bacteria: vibrio, spirillum, and spirochete
vibrio: curved rod, resemble comma
spirillum: corkscrew + rigid
spirochete: thin + flexible
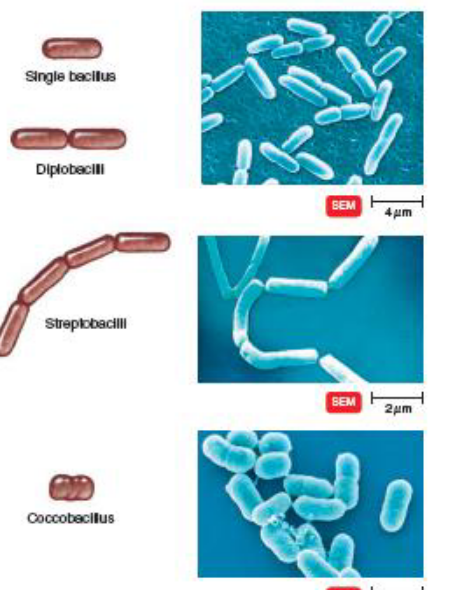
Describe bacilli: single, diplobacilli, streptobacilli, and coccobacillus
single: one rod
diplo: pair of rods
strepto: chain
cocco: short oval rods, resemble cocci
T/F both gram positive and negative bacteria have outer membrane and periplasm
F, gram negative
Describe peptidoglycan in gram positive and negative bacteria
positive: thick
negative: thin
How does the cell envelope differ in gram positive and negative bacteria?
+: peptidoglycan, plasma membrane
-: outer membrane, peptidoglycan, plasma membrane
In the cell wall, peptidoglycan is composed of
alternating NAG and NAM
What is the difference between NAG and NAM?
NAM has tetrapeptide
What major surface antigens are found in gram positive cell wall?
lipoteichoic acid and wall tectonic acid
T/F gram negative outer membrane is unilayered and includes lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
F, bilayered
In LPS, what gives it toxic properties that allow it to be an endotoxin in gram negative?
Lipid A
What major surface antigens is found in LPS and contributes to endotoxin properties?
Ompolysaccharide
The outer membrane of gram negative bacteria have special channels called
Poring
What molecules can pass through porins?
low MW and hydrophilic
T/F different bacteria species have different types and number of porins
T
Do gram negative bacteria have high antibiotic resistance? If so, why?
Yes
Large ABX cannot penetrate outer membrane, need to use specialized ABX
What are the 4 functions of the bacterial cell wall?
Protection
Cell division
Shape
Target site (ABX, lysozymes, bacteriophages)
The gram staining procedure classifies bacteria based on what property?
Amount of peptidoglycan cell wall
Briefly describe the steps of gram staining.
Crystal violet dye
Iodine (mordant)
Alcohol wash
Counterstain (safranin)
How do gram negative vs positive bacteria differ in the alcohol wash step?
-: dye washes off
+: dye stays
At the end of gram staining, describe the colour of gram positive vs negative bacteria
+: purple (crystal violet dye trapped)
-: pink (counterstain)
How can you remove bacteria cell wall?
may remove spontaneously or in presence of penicillin
What is the difference between spheroplasts and protoplasts?
Spheroplasts: from gram -
Protoplasts: from gram +
What are L forms?
bacteria without cell wall that can still grow and divide
What are the 2 types of L forms?
unstable: revert back once penicillin removed
stable: no revert
What is mycoplasma?
naturally occurring bacteria without cell wall
What is the cytoplasmic membrane?
deepest layer of plasma membrane
thin and semipermeable
What are the functions of the cytoplasmic membrane?
permeability/transport
biosynthetic function
electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation (energy)
chemotactic systems (respond to envir., how bacteria communicate)
T/F in an electron microscope, you will see an inner nucleoid region composed of DNA and mitochondria
F, no mitochondria
What are ribosomes for?
protein synthesis, sense mRNA
What is the nucleoid?
DNA core
What are plasmids?
carry non essential genes
application in biotech and ABX resistance transfer
What is glycocalyx?
capsule/slimy layer, surrounds cell wall
What are the functions of glycocalyx?
adherence (cause infection)
virulence
biofilm formation
What are flagella?
organ of locomotion, have characteristic patterns of distribution
Describe the following bacterial flagella:
peritrichous
monotrichous
lophotrichous
amphitrichous
peri: multiple, around cell
mono: single
loph: tuft at one end
amphi: at both ends
What are pili and fimbriae?
thin short filamentous appendages, mostly in gram -, made of pilin
What are fimbriae for?
adherence
biofilm formation (adhere to one another)
What are pili for?
twitch/glide motility
conjugation sex pili (transfer DNA; ex: ABX resistance)
adherence
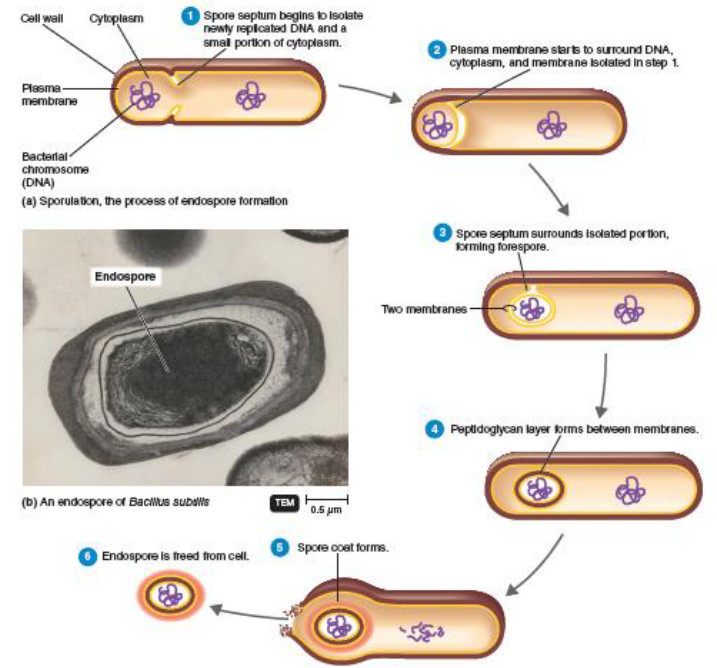
What are bacterial endospores?
gram +, highly resistant dormant stage during unfavourable conditions (starvation) to protect
Briefly describe endospore formation (sporulation)
initiated by clear portion of cytoplasm at one end of cell
membrane grows inward forming double layer (forespore)
spore wall forms thick covering layer
T/F endospores are highly resistant to high temps and boiling
T
What makes endospores so resistant to heating and drying?
outer coat, low H2O content, low metabolic activity, high [calcium dipicolinic acid]
What is germination?
endospore → vegetative cell
3 stages: activation, initiation, outgrowth
What is the susceptibility of gram - vs + bacteria to penicillin and sulfonamide?
-: low, hard to penetrate outer membrane
+: high, can penetrate peptidoglycan
What is the susceptibility of gram - vs + bacteria to streptomycin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline?
-: high, target porins and ion channels
+: low, no ion channels or porins
What factors impact bacterial growth?
O2 requirements
temp
pH
H2O
What are obligate aerobes?
need O2
What are obligate anaerobes?
cannot use O2
What are facultative anaerobes?
can live aerobic or anaerobically
What are aerotolerant anaerobes?
has some enzymes that detoxify O2 (ferment)
What are microaerophiles?
require specific O2 level (2-10%)
In a tube of growth medium, how would obligate aerobes grow?
at top, need O2
catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) neutralize O2

In a tube of growth medium, how would facultative anaerobes grow?
throughout tube, mostly at top
catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) neutralize O2

In a tube of growth medium, how would obligate anaerobes grow?
bottom of tube, no O2
lack enzymes to neutralize O2

In a tube of growth medium, how would aerotolerant anaerobes grow?
evenly distributed in tube
SOD neutralizes O2

In a tube of growth medium, how would microaerophiles grow?
middle of tube, need specific O2 level

How does temperature impact bacteria and bacterial growth?
low = rigid and fragile
high = flexible
use fridge to control bacterial growth
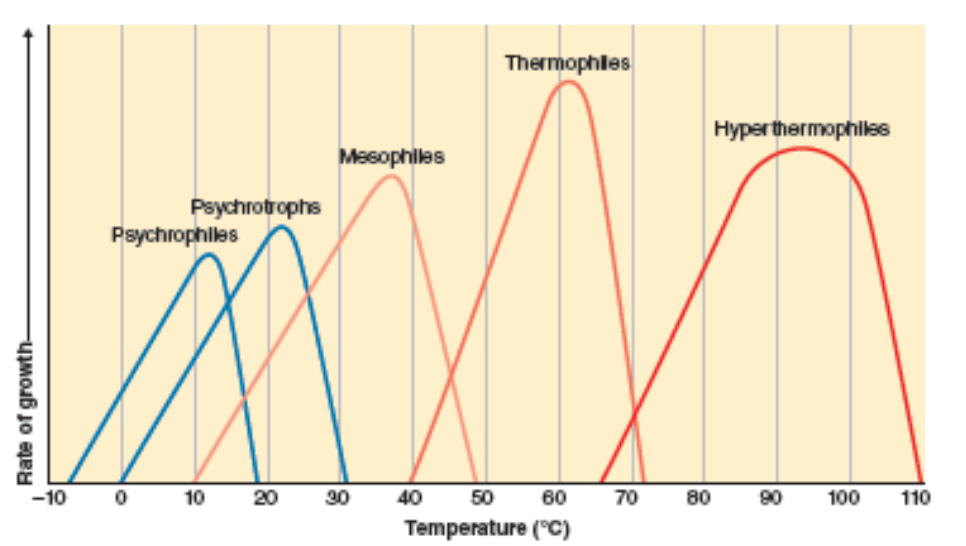
What are psychorophiles an psychorotrophs?
grow at low temps (<37*C)
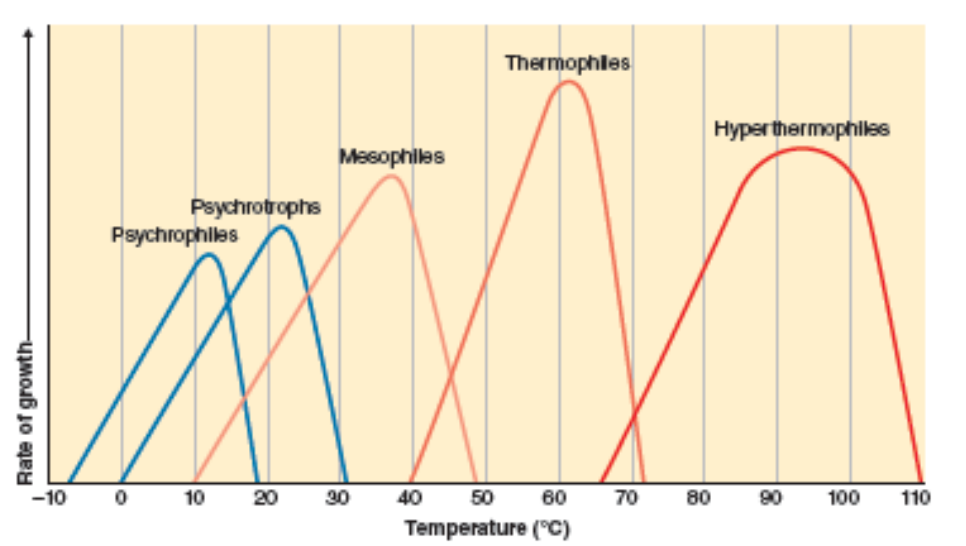
What are mesophiles?
most bacteria
grow at 37*C
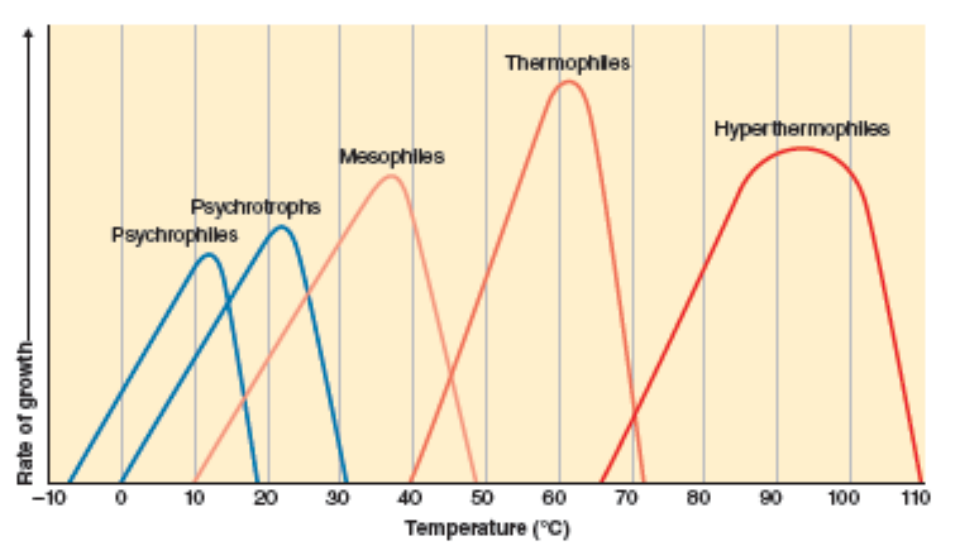
What are thermophiles and hyperthermophiles?
grow at high temps (>37*C)
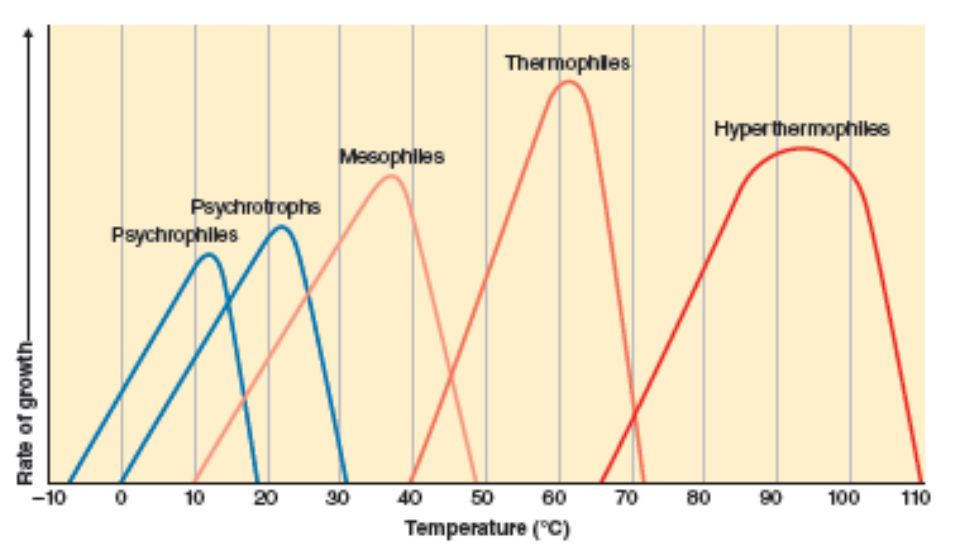
Given a temp vs rate of growth curve, where is the optimal growth temperature?
peak of curve
What are neutrophiles?
most bacteria
grow at pH 6-8
What are acidophiles?
grow at pH <4
high [H+]
What are alkaphiles?
grow at pH up to 11.5
high [OH-]
What do microbes use H2O for?
dissolve enzymes, nutrients, metabolic rxns
T/F endospores can survive in dry environments
T
What is generation time?
time required for bacteria to divide
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the cause of TB, why is it hard to diagnose?
long doubling time (can use qPCR)
Most bacteria have a doubling/generation time of
1-3h
What are the phases of the growth curve?
lag phase
exponential phase
stationary phase
death phase
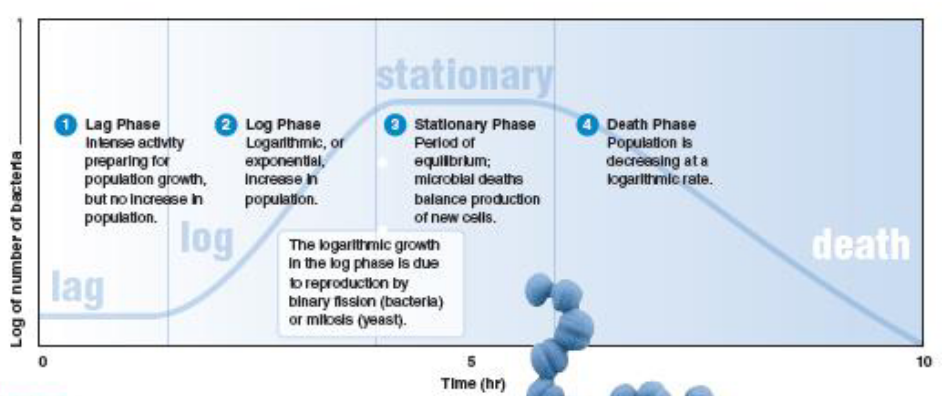
What happens during the lag phase?
prep for growth/log phase
accumulate nutrients
What happens during the log phase?
cells divide and grow, most susceptible to antimicrobials
binary fission and double time calculated from this phase
What happens during the stationary phase?
equilibrium (# new cells = # cells dying)
nutrient depletion
What happens during the death phase?
no growth or nutrients
What is a pathogen?
microorganism that can cause disease
What are opportunistic pathogens?
rarely cause disease except in immunocompromised
What is virulence?
ability of agent to cause disease
involve adherence, invasion and toxigenicity
From an organism’s pov, what factors influence infection?
# organisms and virulence
From a host’s pov, what factors influence infection?
host defense (innate and acquired immunity)
What determines bacterial pathogenesis?
transmission
adherence
invasion and intracellular survival
toxins
intracellular pathogenecity
Why is it important to know the mode of transmission?
know how to prevent spread
What are some major adherence factors?
capsule/slime layer
adherence proteins
lipoteichoic acid
fimbriae (pili)
Provide an example of capsule/slime layer and how it helps in adherence
E coli capsule promotes adherence to intestinal villi
Provide an example of adherence proteins and how it helps in adherence
N gonorrhea have Opa proteins that bind receptors to prevent endocytosis
Provide an example of lipoteichoic acid and how it helps in adherence
S pyogenes lipoteichoic acid helps bind to respiratory receptor and M protein in host cell
Provide an example of fimbriae/pili and how it helps in adherence
N gonorrhea pili help bind to epithelium
What are adhesins?
surface molecule on pathogen binds host cell to open channel and let pathogen into host