exam 3 pt 8 (character displacement -> commensalism)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
character displacement
tendency for characteristics to be more divergent in sympatric populations of two species than in allopatric populations of the same two species
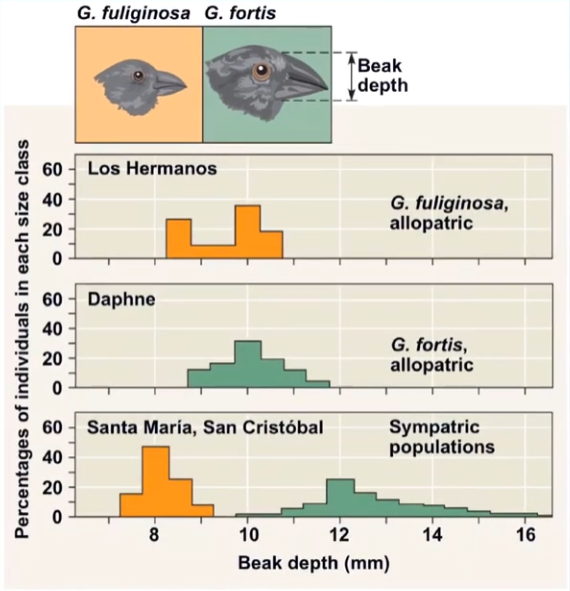
what is this an example of?
character displacement
predation
refers to interaction where the predators kills and eats the prey
(±)
→ predator benefits, prey loses
what are some feeding adaptations of predators?
claws, teeth, fangs, stingers, poisons
what are some adaptations of prey?
hiding, feeling, forming herds/schools, self-defense, alarm calls
cryptic coloration/camouflage
makes prey difficult to spot
what morphological/physiological defense adaptations can animals have?
A) cryptic coloration
B) aposematic coloration
aposematic coloration
warning coloration → predators get scared of bright coloration and will usually leave them alone
batesian mimicry
species that are edible + harmless/chill MIMICKING species that are inedible harmful/unpalatable
→ makes predators not want to eat them
mullerian mimicry
two or more unpalatable species resembling each other → it is easier for a predator to learn 1 type of coloration to stay away from than rather than trying to remember a bunch of patterns
difference between batesian/mullerian mimicry?
batesian: inedible mimicking edible
mullerian: harmful species resembling each other
herbivory
refers to an interaction in which an herbivore eats parts of a plant or alga
(±)
→ good for the herbivore, bad for the plant
symbiosis
relationship where two or more species live in direct + intimate contact with one another
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
parasitism
parasite derives nourishment from host that is harmed in the process
(±)
→ parasite gets nutrients, host gets harmed
mutualism
interspecific interaction that benefits both species; can be obligate or facultative
(+/+)
→ both species gain something from sharing
obligate mutualism
one species cannot survive without the other
facultative mutualism
where both species could survive alone
commensalism
one species benefits and the other is apparently unaffected
(+/0)
→ i.e. birds that do not eat bugs or parasites chilling on the backs of cattle because cattle cause bugs to come up out of the grass by walking through—the birds benefit, but they are not helping/hurting the cattle