AP Biology Unit 7
1/83
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Define natural selection.
A major mechanism of evolution
Define evolution.
The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is supported by multiple lines of evidence
What are the requirements for evolution by natural selection?
-Limited resources
-Competition
Define variation.
Genetic differences within a population
Define adaptations.
Traits that provide an advantage in a particular environment
How is reproductive success measured?
By evolutionary fitness
Define fitness.
The ability of an organism to survive and produce fertile offspring
Define reproductive success.
Refers to the production of offspring
Define heritability.
Ability to pass on adaptations to successive generations
A stable environment results in ___ evolution.
Slow
An unstable environment results in ___ evolution.
Fast
Define genetic variation.
Genotypic and phenotypic differences in a population.
Define selective pressures.
Any biotic or abiotic factors influencing survivability
Define artificial selection.
Process by which humans select desirable traits in other species and selectively breed individuals with desirable traits
Define convergent evolution.
The process by which similar environmental conditions select similar traits in different populations or different species over time
Define analogous structures.
Structures evolved independently in different species due to similar environment/selective pressures
What is evolution driven by?
By random occurrances
Reduction of genetic variation can ___ the differences between populations of the same species.
Increase
Define genetic drift.
Random change in the frequency of a particular allele within a population
What size population does genetic drift/non-selective processes occur in?
Small population
Define bottleneck events.
Population sharply decreases due to a catastrophe
Define the founder's effect.
Refers to a random process that reduces genetic variation within a small population (Polydactyly)
What are examples of the founder's effect?
-Migration
-Geological events
Continued migration leads to ___ genetic diversity between populations over time
Less
Define null hypothesis.
Hypothesis which states experimental variables have no relationship and experimental observations are the result of chance
Define alternative hypothesis.
One of several hypotheses stating experimental variables have a relationship and the experimental observations are a result of nonrandom cause
Define Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium.
A model for describing and predicting allele frequencies in a non evolving population
What are the 5 requirements to use the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
-Large population (no genetic drift)
-Absence of migration (no gene flow)
-No net mutation (no modified gene flow)
-Random mating (no sexual selection)
-Absence of selection (no natural selection)
Define gene flow.
The movement of individuals between populations causing an exchange of alleles between population
What is the equation to calculate genotype?
p^2 + 2pq + q^2=1
What is the equation to calculate an allele
p + q=1
What is p in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
Dominant allele
What is q in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
Recessive allele
When using the Hardy-Weinberg equation, do we calculate the dominate or recessive allele first?
Recessive
What evidence is used to indicate evolution?
-Geographical
-Geological
-Physical
-Biochemical
-Mathematical
Define geographical evidence.
Evidence based on characteristics of habitat or land area
Define geological evidence.
Evidence based on environmental features over the earth over time (fossils)
Define physical evidence.
Evidence based on phenotypes of species
Define biochemical evidence.
Evidence based on the chemical composition of living things (DNA)
Define mathematical evidence.
Evidence based on calculation and statistics
Define morphological homologies.
Modified traits shared among differential species
Define homologous structures.
Structure that is derived from a common ancestor (one bone, two bones, little bones, digits)
Define vestigial structures.
Reduced features that serve no purpose for an organism
When looking at DNA for evolution, the more amino acid difference the ___ time has passed between organisms' divergence.
More
What evidence supports common ancestry for all eukaryotes?
-Membrane bound organelles
-Linear chromosomes
-Genes that contain introns
What at the mechanisms of genetic change?
-Changes in DNA
-Cell division (crossing over)
-Environmental disruptions
Define phylogenetic/cladogram tree.
Changes over time and is a branch diagram showing the evolutionary relationships amongst species
Define the out-group.
Lineage that is least closely related to the remainder of the organisms
Define node.
Where 2 lines meet
Define derived character.
A trait in a recent species having evolved for an ancestral trait
Define speciation.
Occurs when organisms are reproductively isolated from each other and new species form
What do biological barriers prevent species from?
-Interbreeding
-Producing fertile offspring
How does reproductive isolation prevent gene flow?
-Prezygotic barriers
-Postzygotic barriers
What are prezygotic barriers?
-Habitat isolation
-Temporal isolation
-Behavioral isolation
-Mechanical isolation
-Gamete isolation
Define habitat isolation.
Different habitats
Define temporal isolation.
Species breed at different times
Define behavioral isolation.
Different mate/courtship preferences
Define mechanical isolation.
Reproductive structures prevent "baby making"
Define gamete isolation.
Sperm doesn't fertilize egg
What are postzygotic barriers?
-Hybrid inviability
-Hybrid sterility
-Hybrid breakdown
Define hybrid inviability.
Incompatibility stops development of zygote (miscarriage)
Define hybrid sterility.
Hybrid is healthy but sterile
Define hybrid breakdown.
First-generation hybrids are fertile, second-generation are sterile
Genetically diverse populations are ___ ___ to environmental change
More resilliant
Define extinction.
The disappearance of a species from Earth
Define niche.
An organism's role in an environment
Define deleterious.
Traits are those that reduce the chance of survival
Define adaptive.
Traits that increase the chance of survival
What is the RNA world hypothesis?
The hypothesis that RNA was the first nucleic acid to evolve and early life was based on RNA rather than DNA or proteins
Define allopatric speciation.
Evolution of new species due to individuals for the same species being geographically isolation
Define sympatric speciation.
Evolution of new species due to individuals being reproductively isolated from a surviving ancestral population
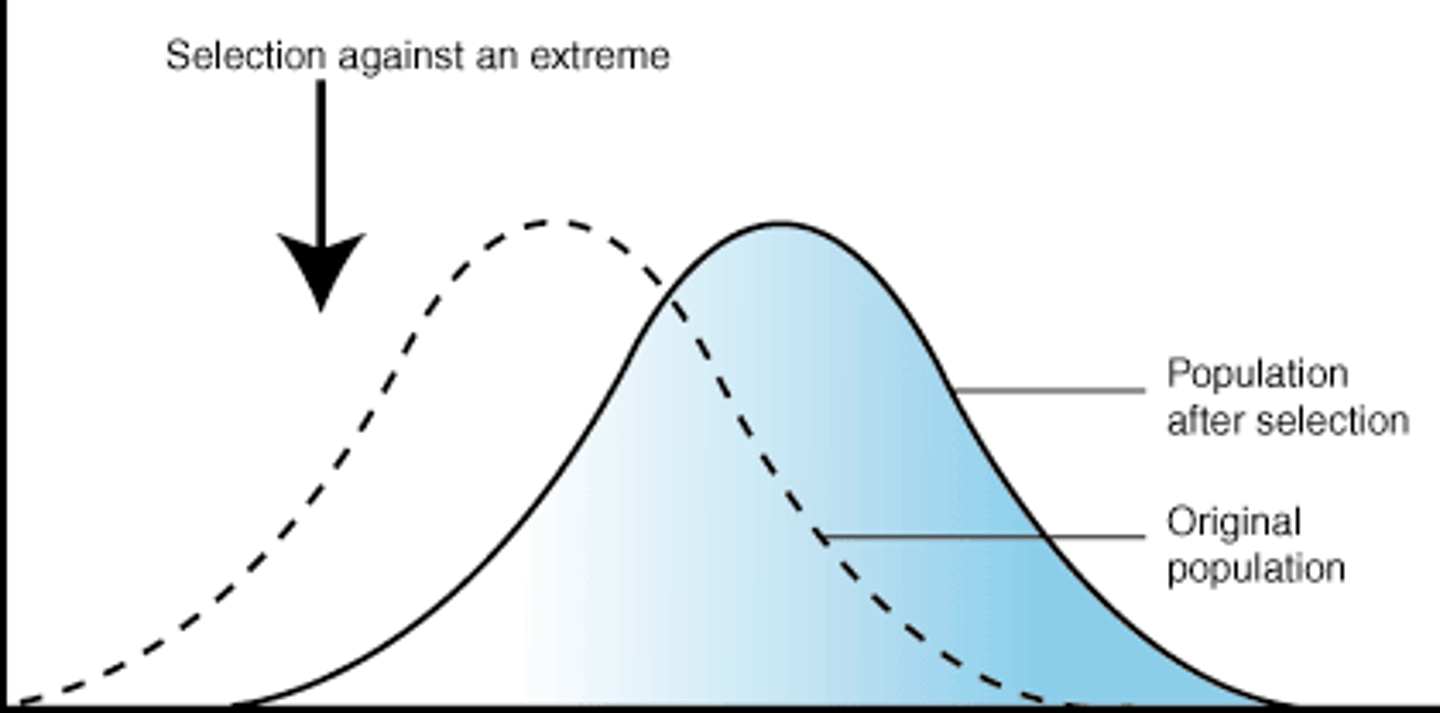
Define directional selection.
Favors individuals at one end of the phenotypic range
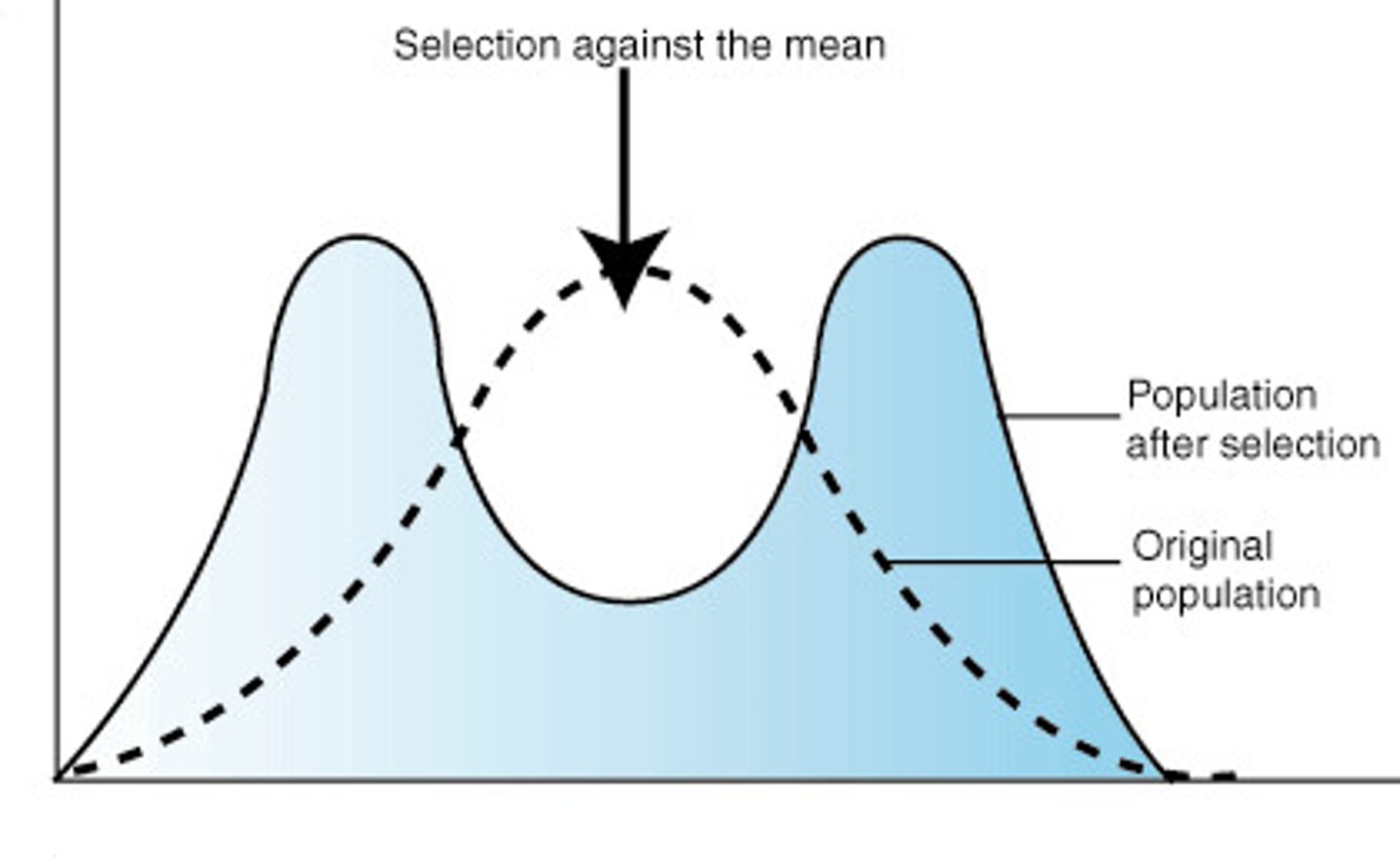
Define disruptive selection.
Favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
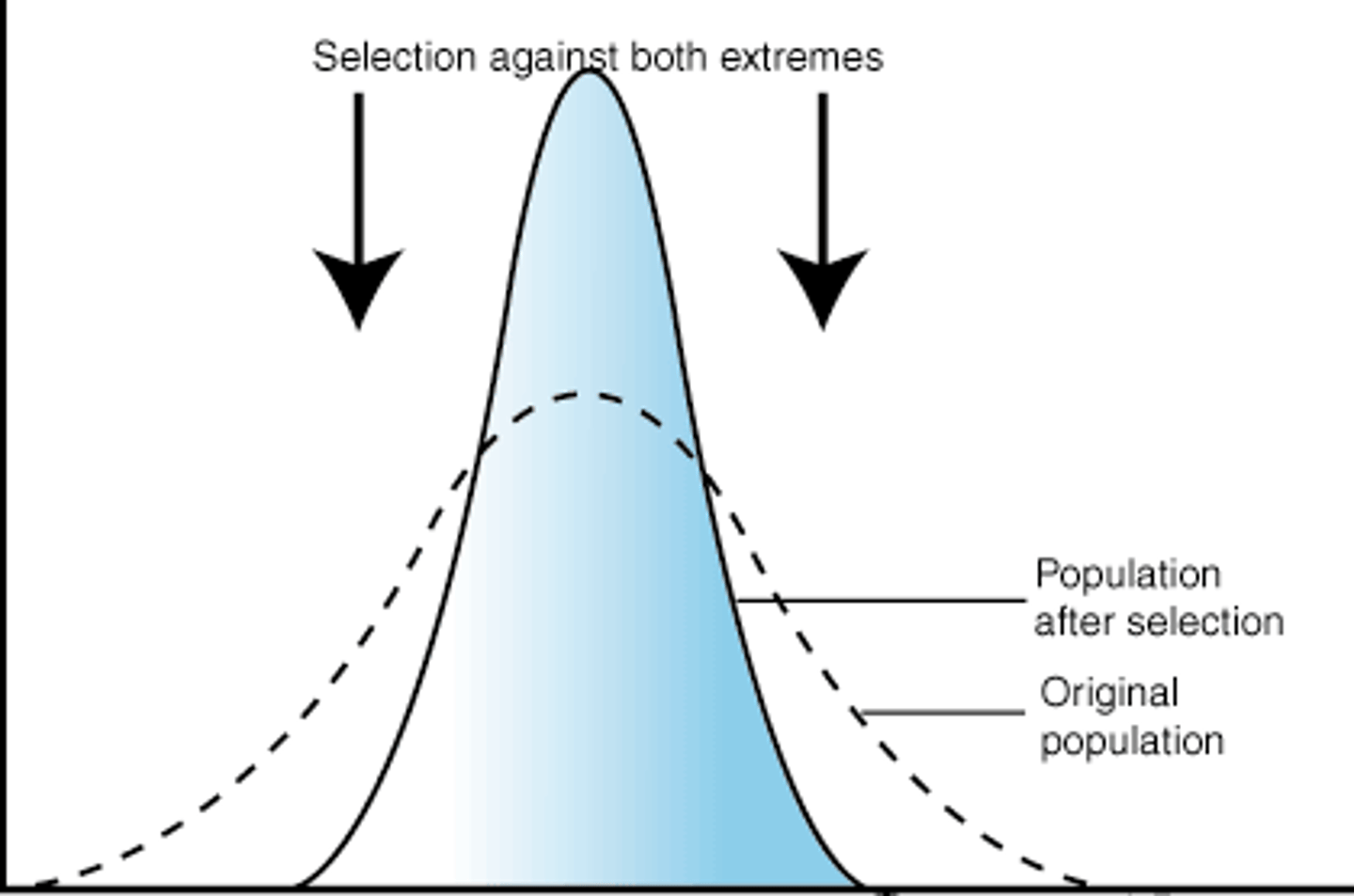
Define stabilizing selection.
Favors intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes
Define microevolution.
Change in allele frequencies in a population over generations
Define survival of the fittest.
Individuals with certain heritable adaptive characteristics
Does natural selection create new traits?
No, it edits or selects for traits already present in the population.
When constructing a phylogeny, what is maximum parsimony?
The simplest explanation that is consistent with the facts
When constructing a phylogeny, what is maximum likelihood?
The one that reflects the most likely sequence of evolutionary events, given certain rules about how DNA changes over time.
Define monophyletic group.
Consists of an ancestor and all of its descendants.
Define paraphyletic group.
Includes the most recent common ancestor of the group, but not all its descendants
Define polyphyletic group.
Does not have common ancestors for all decendents
Define endosymbiosis.
A process by which the mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells probably evolved from symbiotic associations between small prokaryotic cells living inside larger cells.
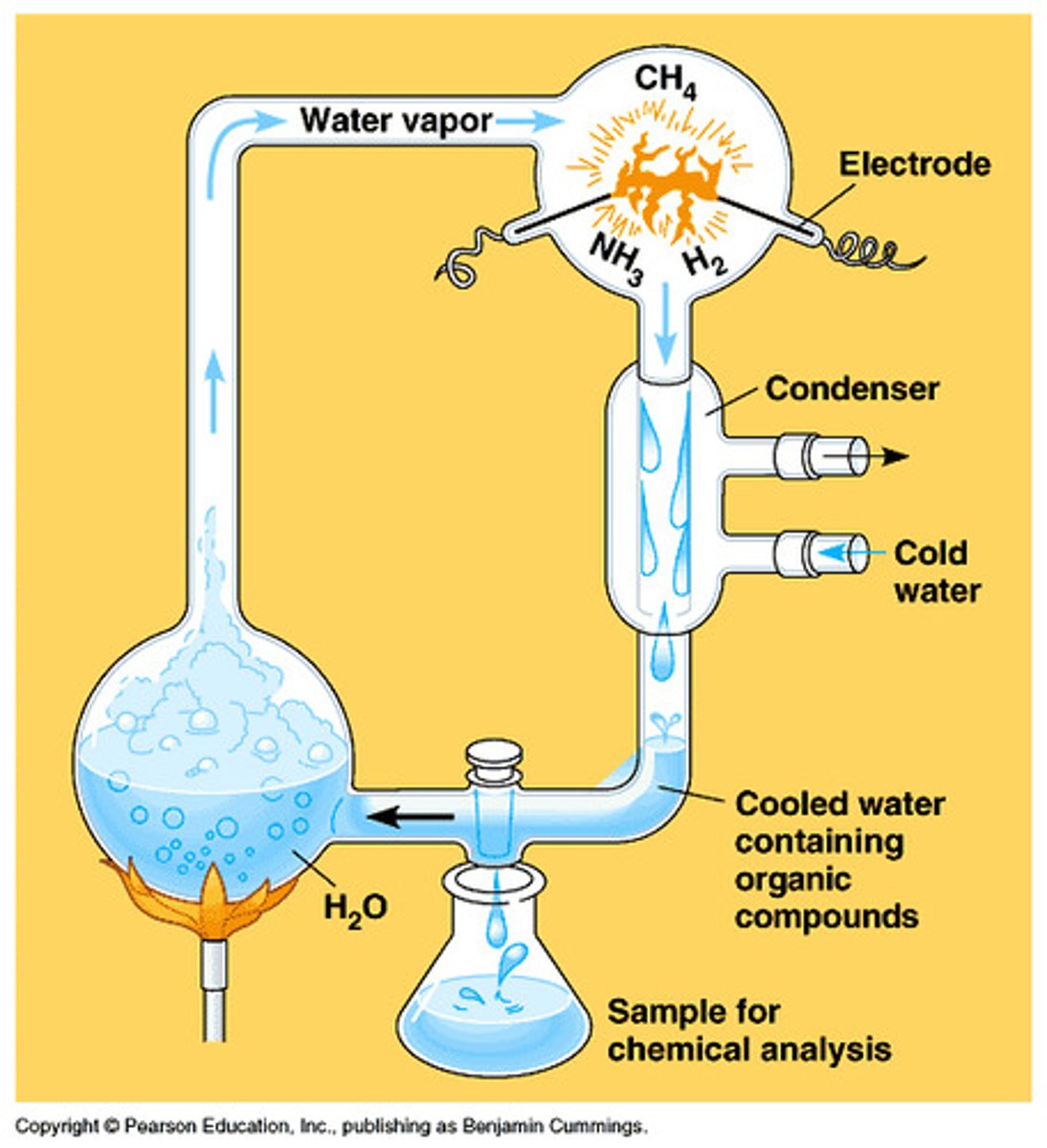
What was the Miller-Urey experiment?
An experiment to show if the hypothesis of lighting led to the formation of organic molecules from inorganic molecules present in the atmosphere of the early earth.