Session 2: Transcription
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Gene expression
Process by which information encoded in a DNA sequence is translated into a product that has some effect on a cell/organism (protein or RNA)
Gene
Basic unit of heredity.
A sequence of nucleotides in DNA that encode the synthesis of a gene product, either protein or RNA.
Most eukaryotic genes contain segments of coding sequences known as ___ interrupted by non-coding sequences called ___
Most eukaryotic genes contain segments of coding sequences known as exons interrupted by non-coding sequences called introns
Introns are removed after transcription in a process called ___ to form mature m-RNA
splicing
Antisense strand of DNA
The noncoding DNA strand, which is complementary to
mRNA and serves as the template for RNA synthesis. Also called the transcribed strand.
Sense strand of DNA
The coding strand of DNA that is read to make mRNA during transcription. Contains the nucleotide sequence of a gene.
Promoter
Specific region of a gene where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription
The ___ site on the prokaryotic RNA polymerase directs the polymerase to the promoter site by binding specifically to the ___ and ___ sequences leading to initiation of prokaryotic transcription
The σ-site on the prokaryotic RNA polymerase directs the polymerase to the promoter site by binding specifically to the -10 and -35 sequences leading to the intitiation of prokaryotic transcription
Prokaryotic promoter sequences are characterised by two sets of sequences located ___ and ___ base pairs upstream of the transcription start site called the ___ and ___ elements and some further upstream elements
Prokaryotic promoter sequences are characterised by two sets of sequences located 10 and 35 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site called the -10 and -35 elements and some further upstream elements
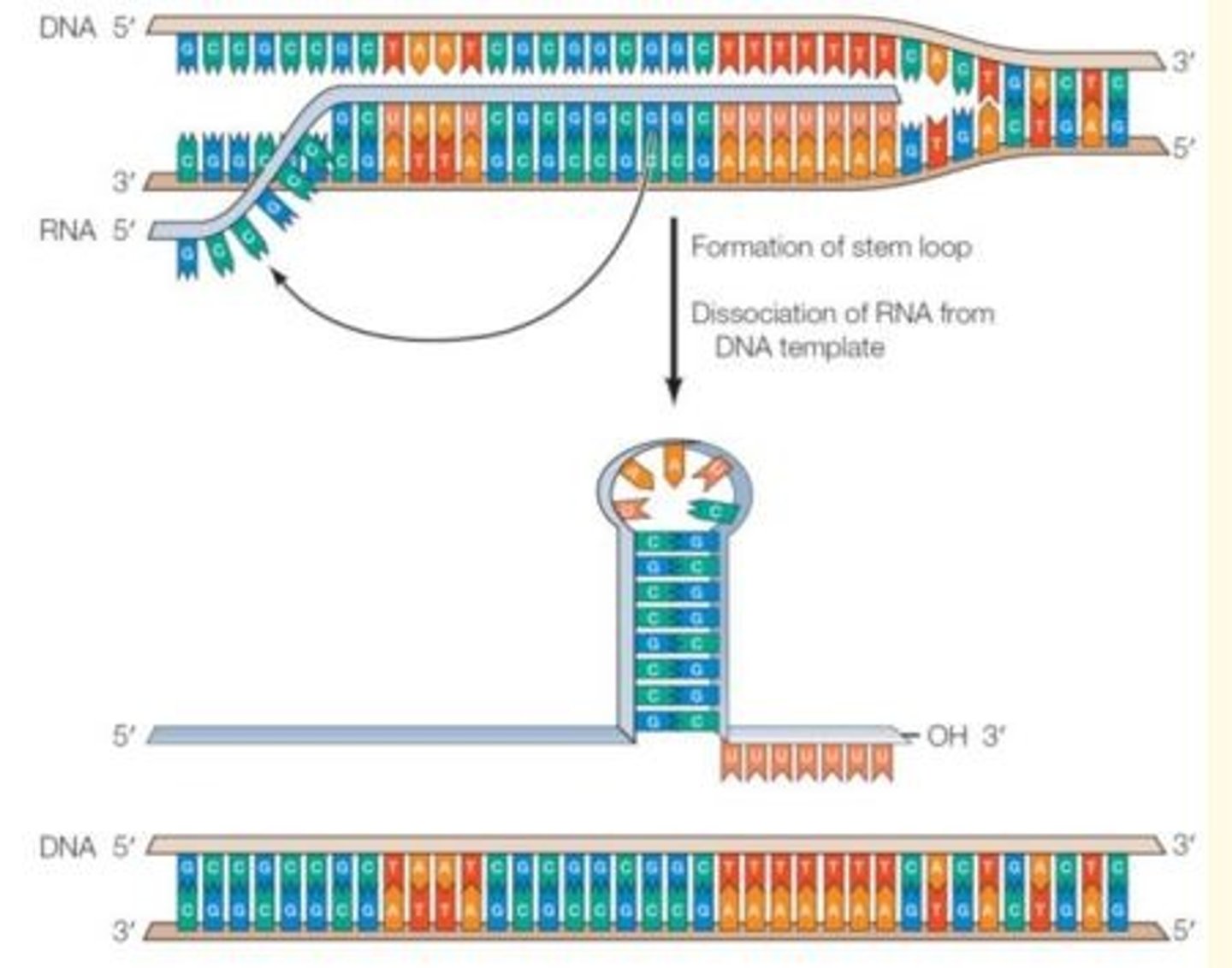
Termination signal
RNA polymerase reaches this when it comes to the end of a sequence during transcription - this terminates transcription process
Most common type of termination signal in prokaryotic transcription
Symmetrical inverted repeat of GC-rich sequences followed by seven A-residues that form a stable stem-loop structure in RNA - terminates transcription
Different types of RNA molecules produced in cells
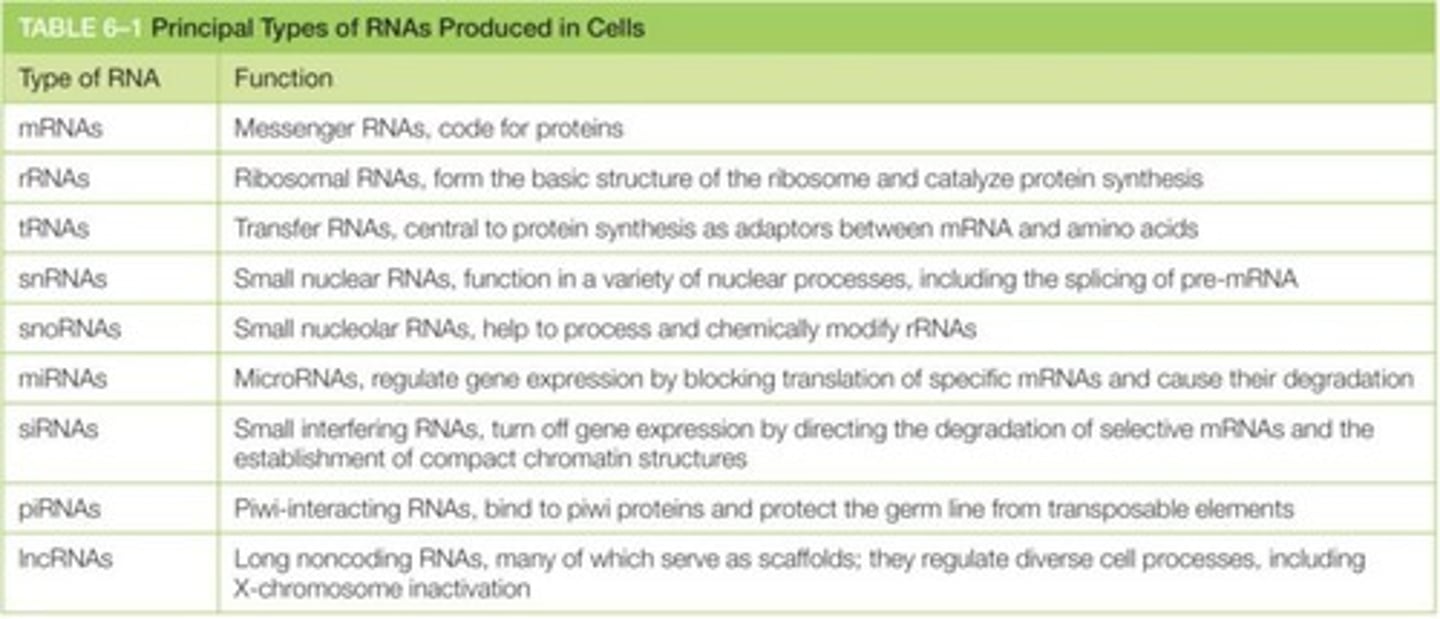
Most of the RNA in a cell is ___ RNA (~80%)
Ribosomal-RNA (r-RNA)
m-RNA comprises ___% of RNA in a cell
3-5%
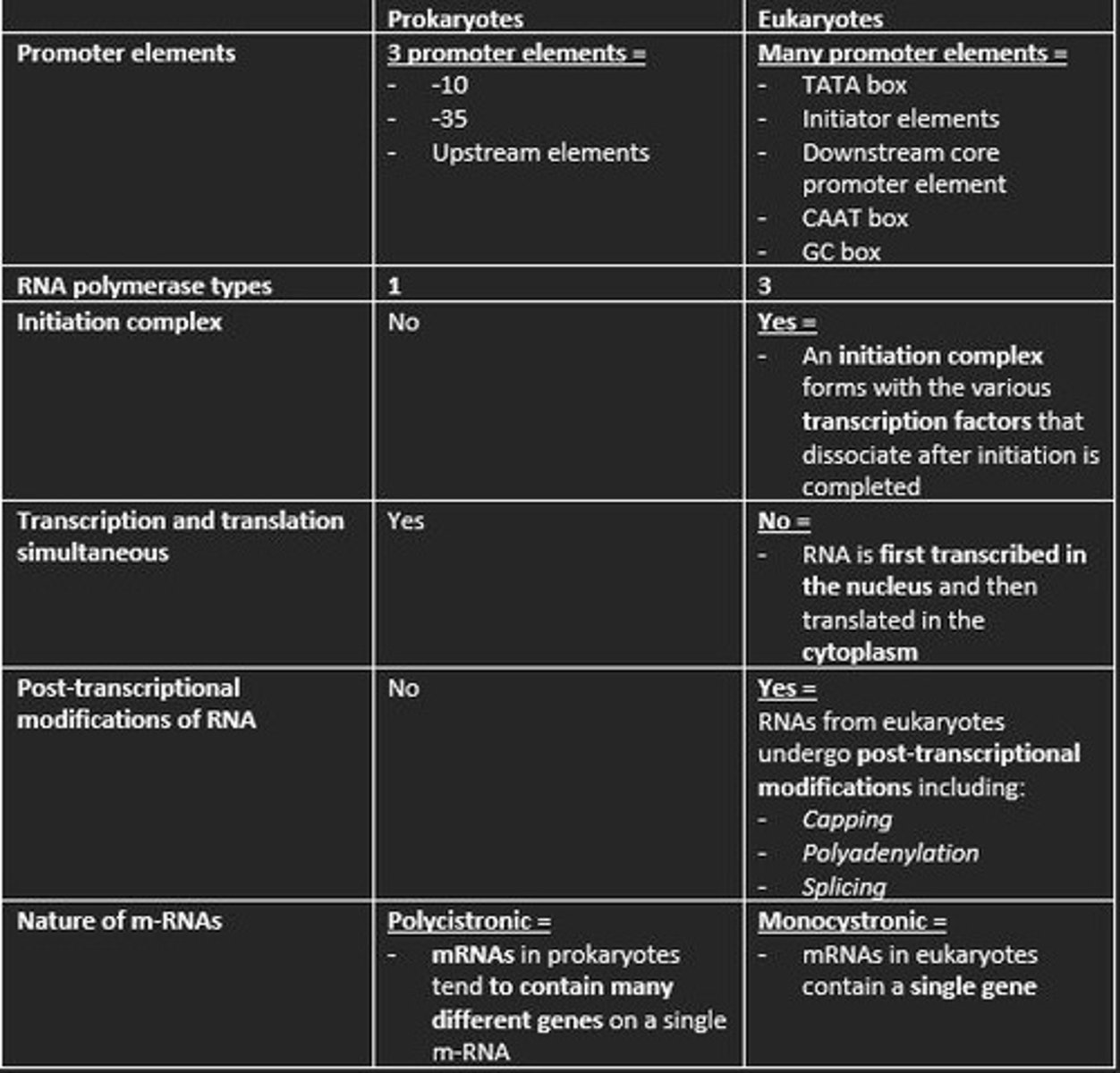
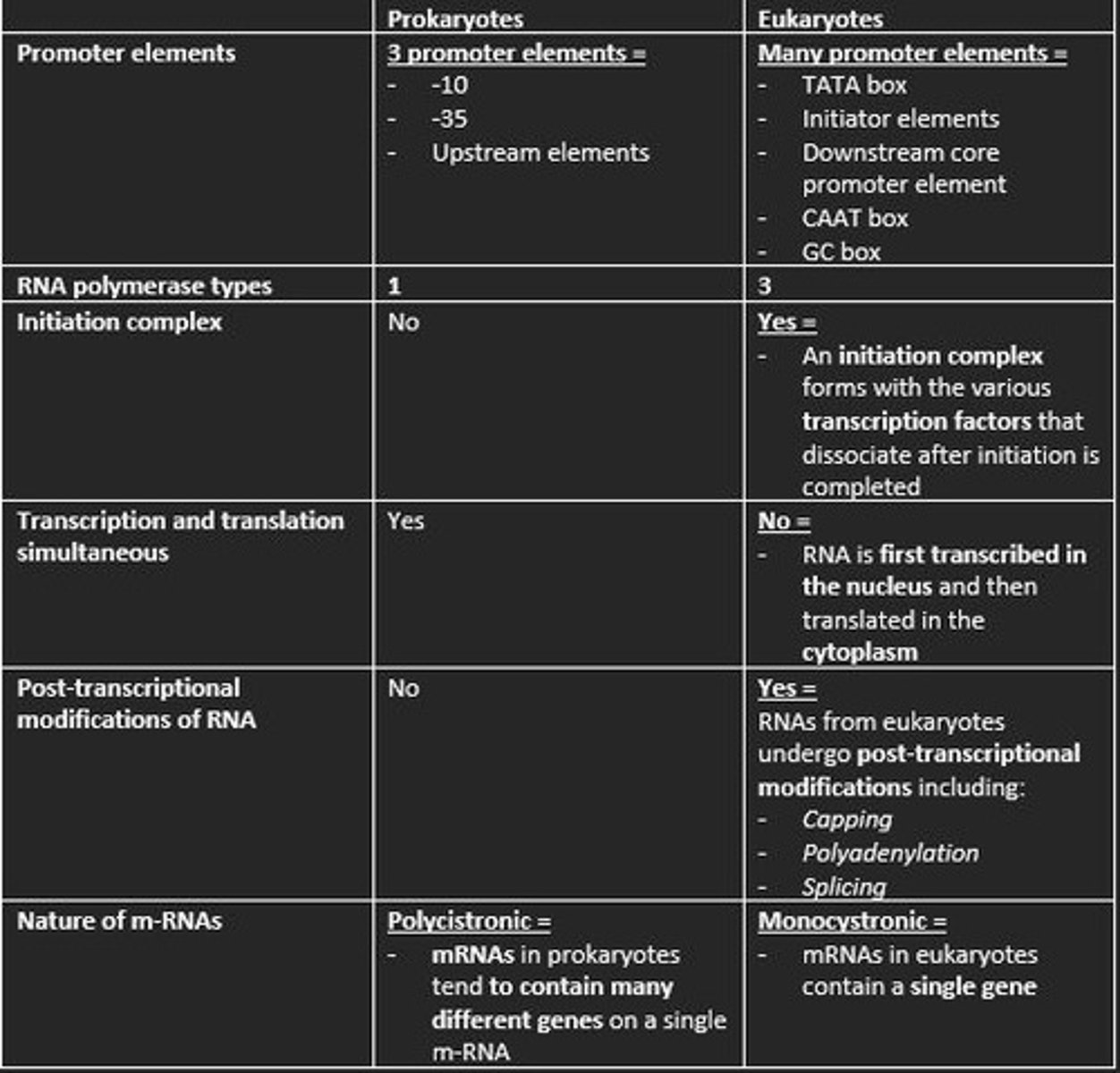
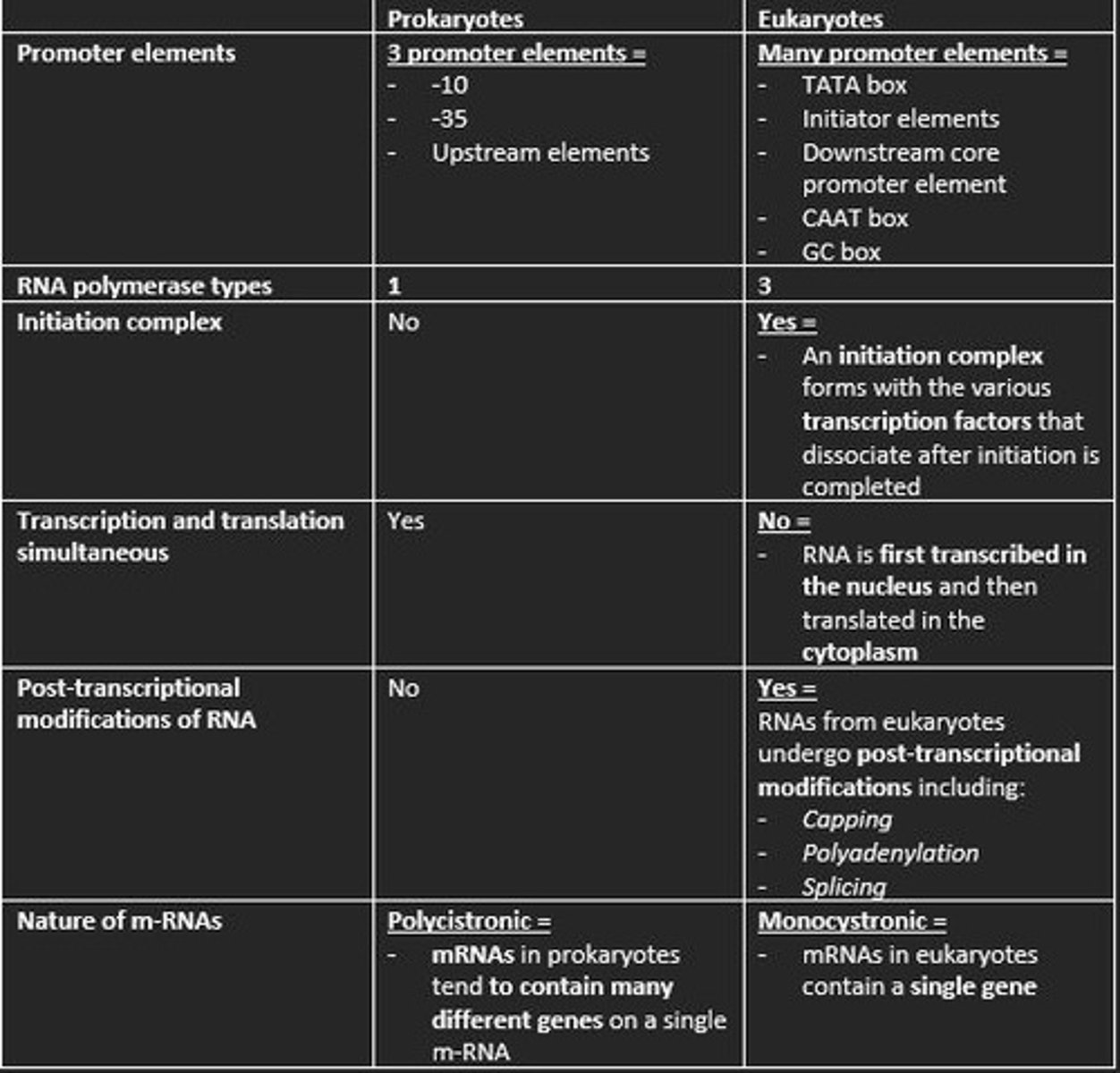
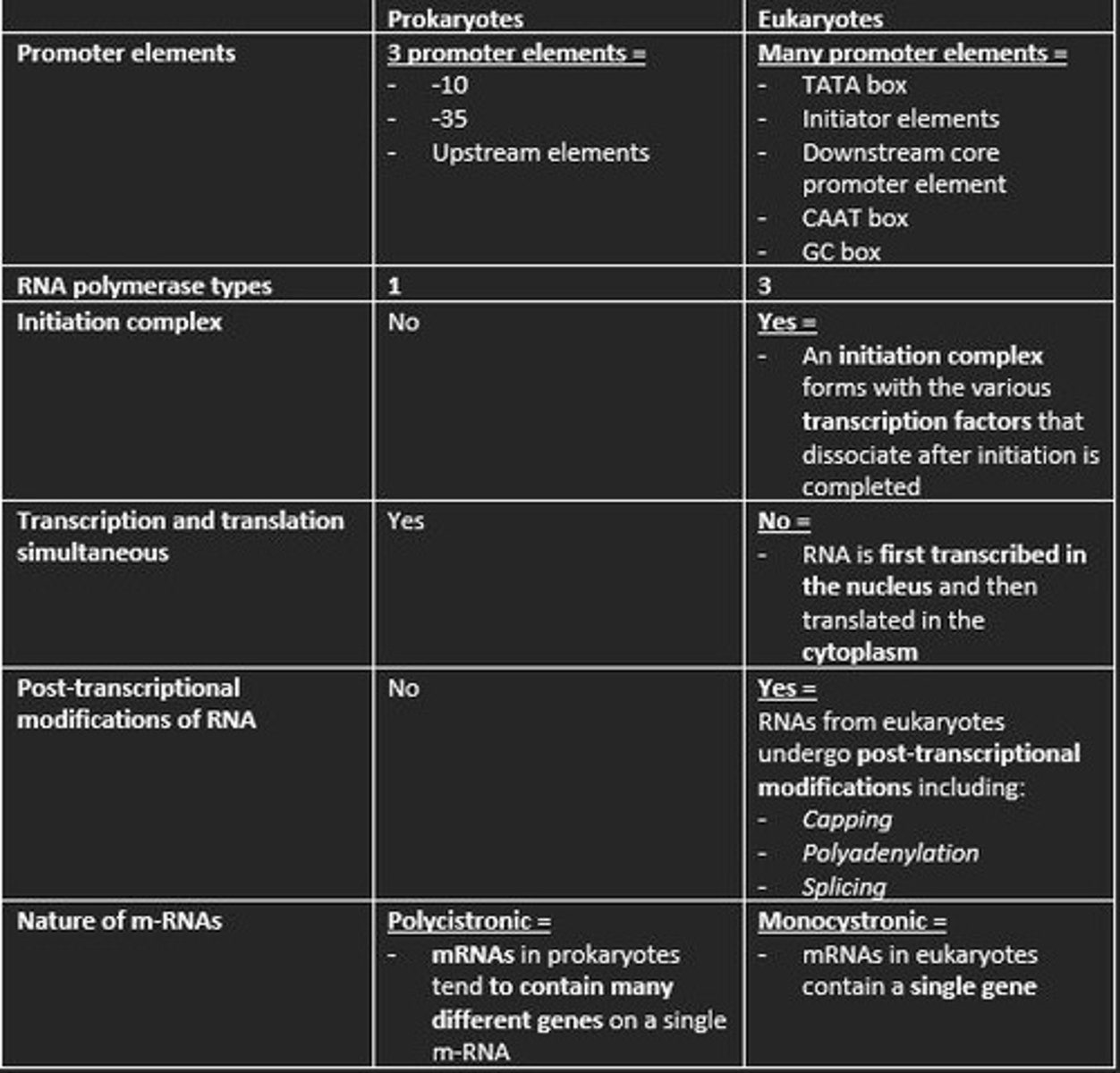
Three promoter elements in prokaryotic transcription
1) -10
2) -35
3) Upstream elements
Is transcription and translation simultaneous in prokaryotes?
Yes
Nature of m-RNA in prokaryotes
Polycistronic
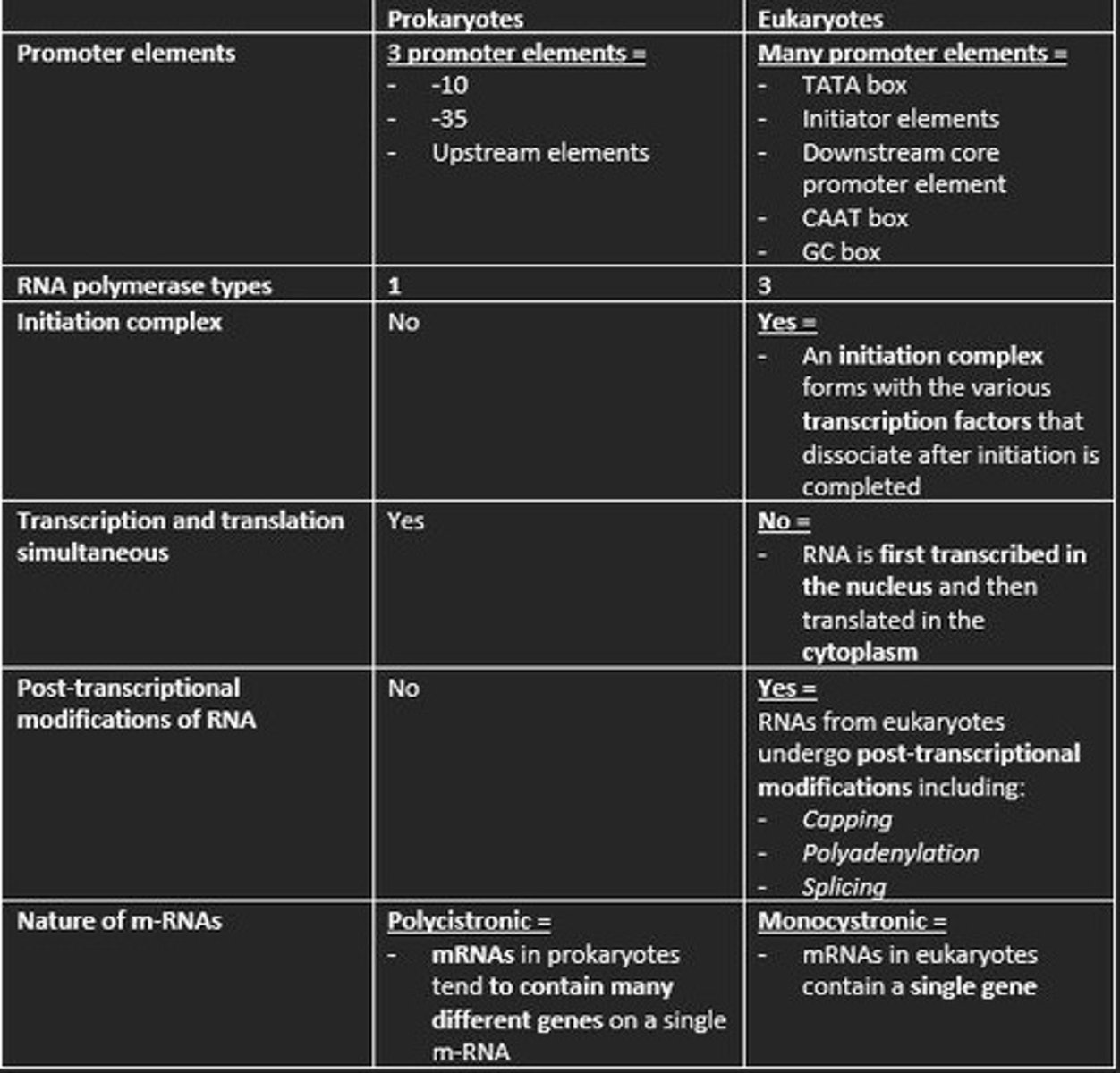
How many types of RNA polymerase in eukaryotic transcription?
3
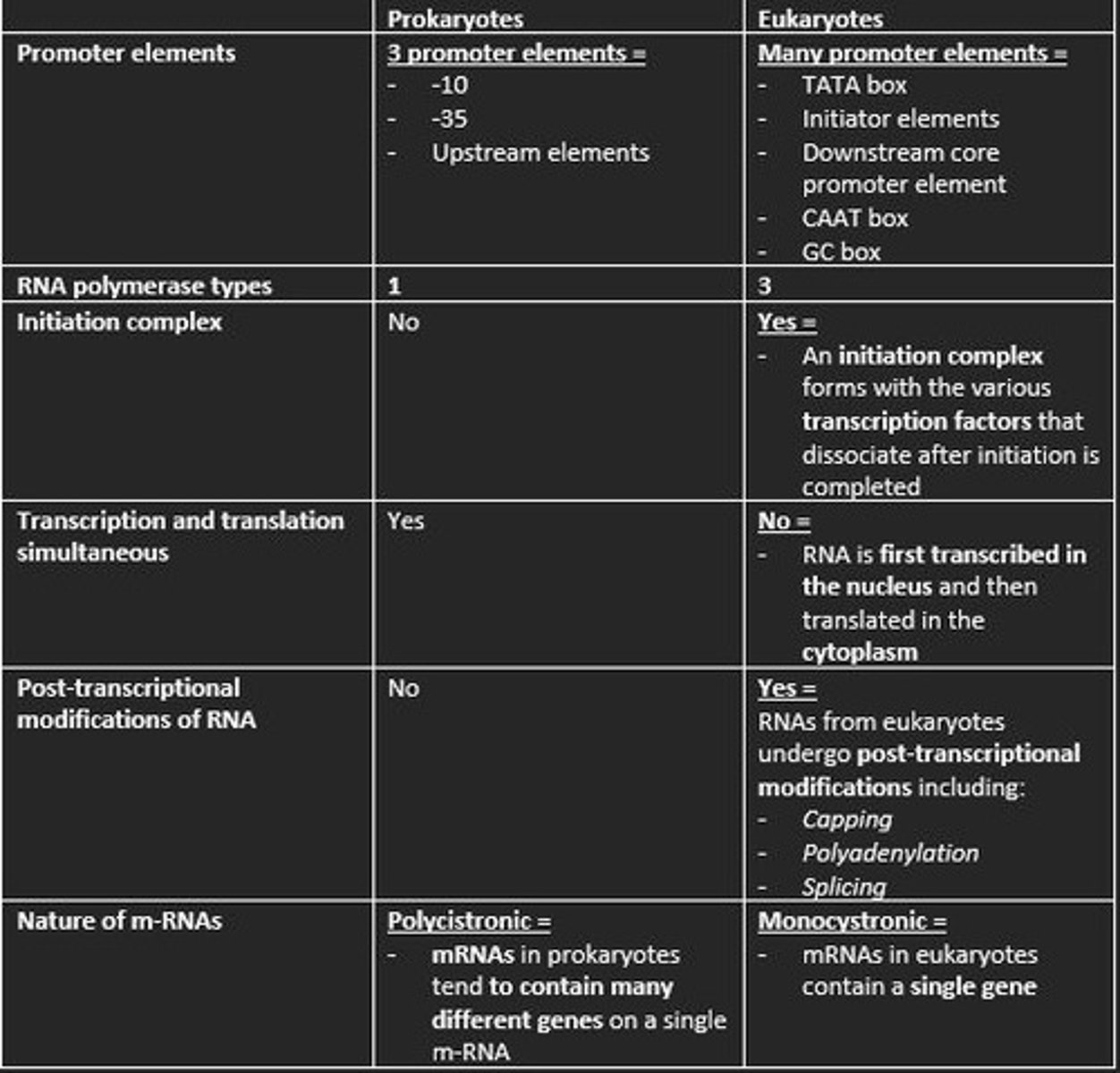
Is an initiation complex formed in either prokaryotic or eukaryotic transcription of m-RNA?
An initiation complex is formed only in eukaryotic transcription. This forms with the various transcription factors that dissociate after initiation is completed.
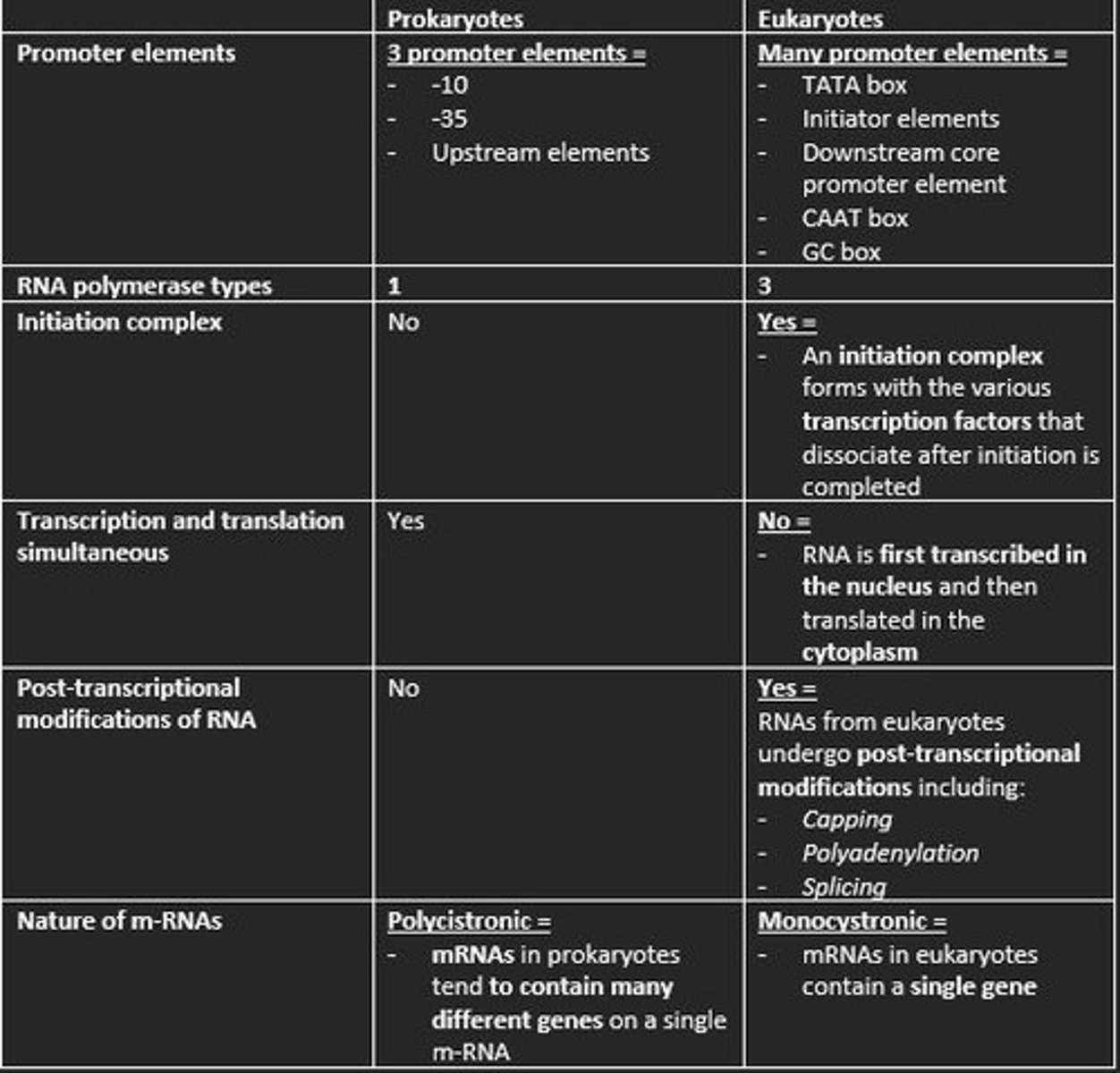
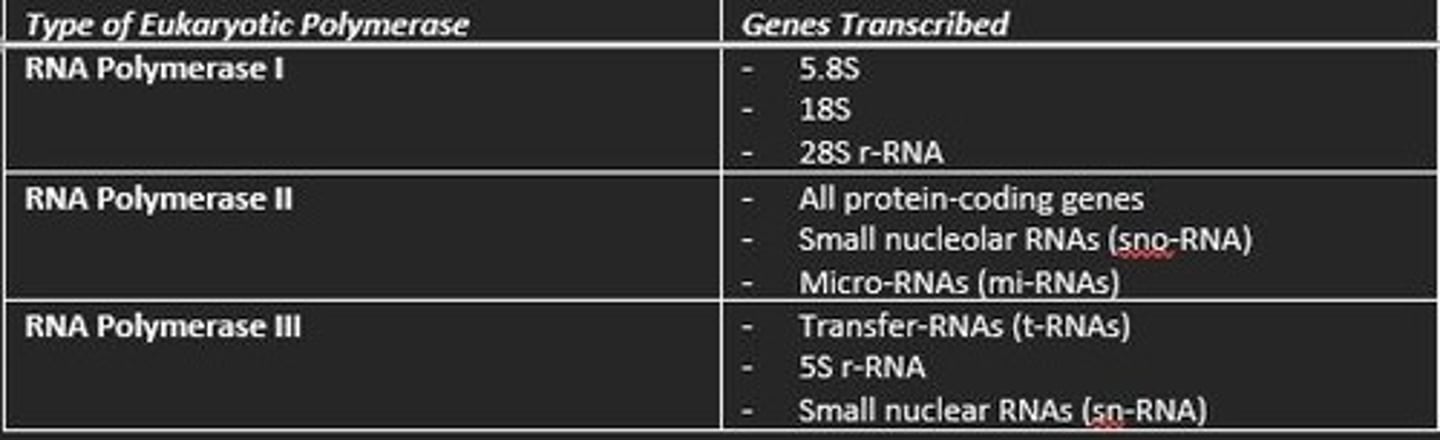
What genes does RNA polymerase II transcribe?
- All protein-coding genes
- snoRNA genes
- miRNA genes
- siRNA genes
- IncRNA genes
- snRNA genes
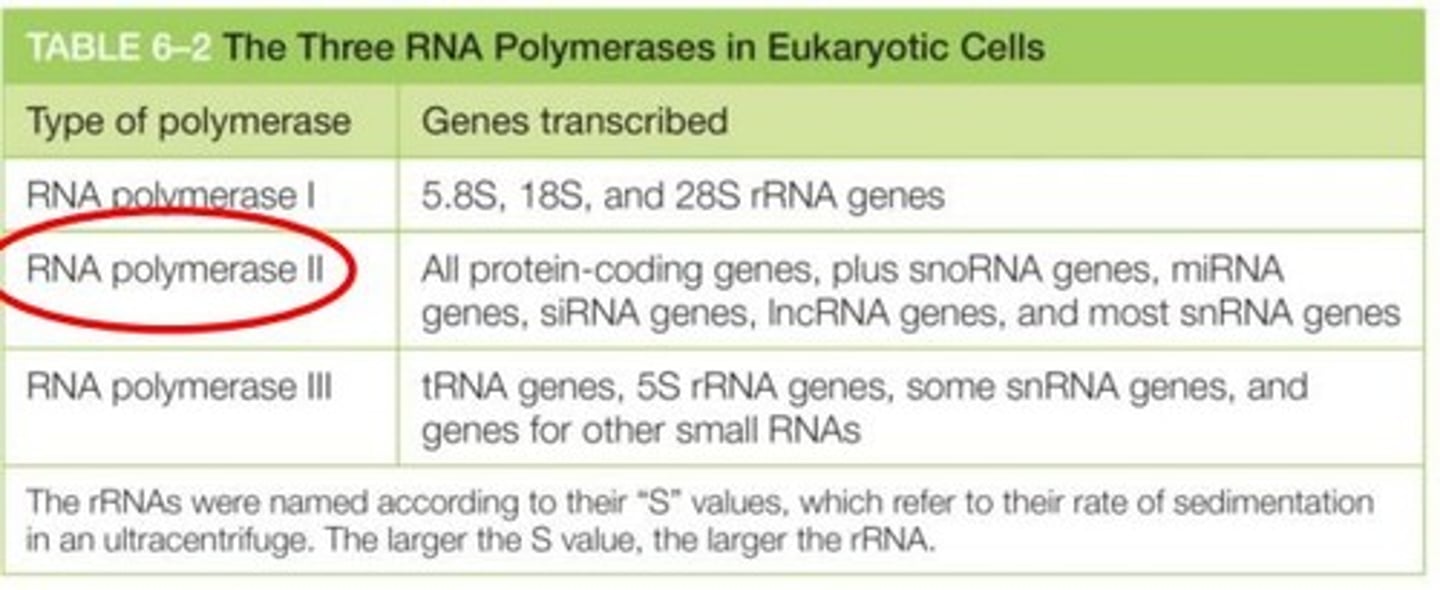
What genes does RNA polymerase I transcribe?
5.8S, 18S, and 28S rRNA genes
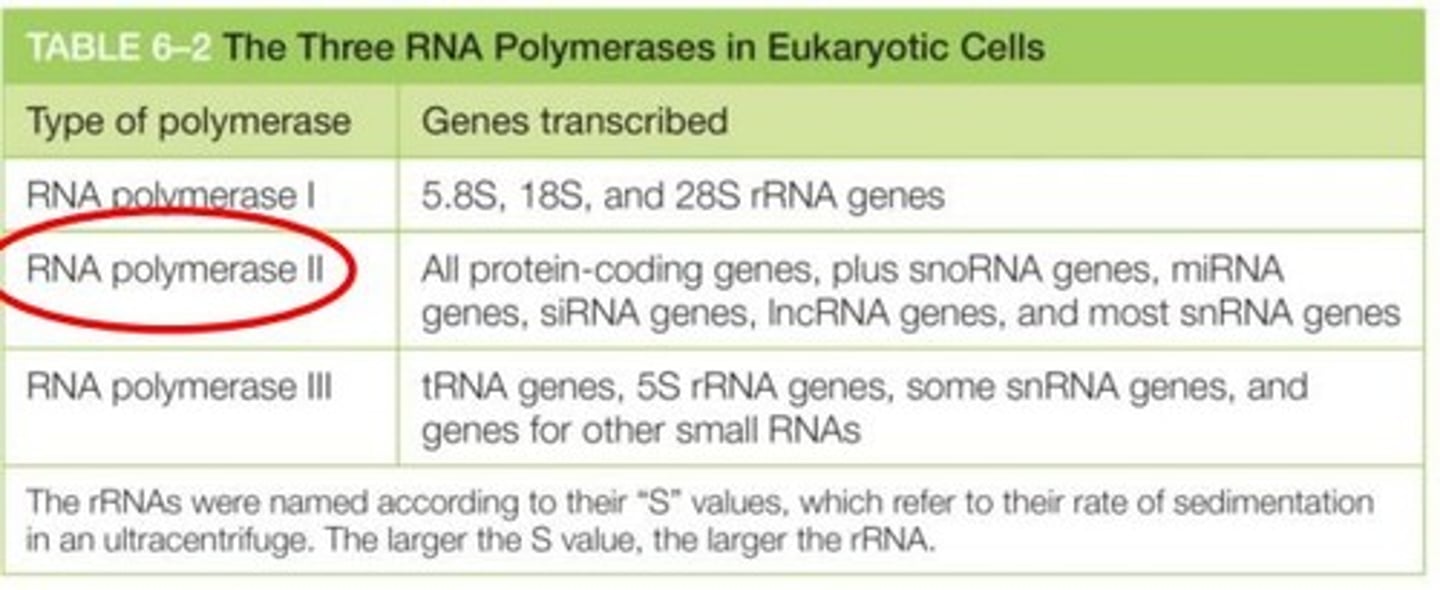
What genes does RNA polymerase III transcribe?
- tRNA genes
- 5S rRNA genes
- Some snRNA genes
- Genes for other small RNAs
Initiation of Transcription in Eukaryotes
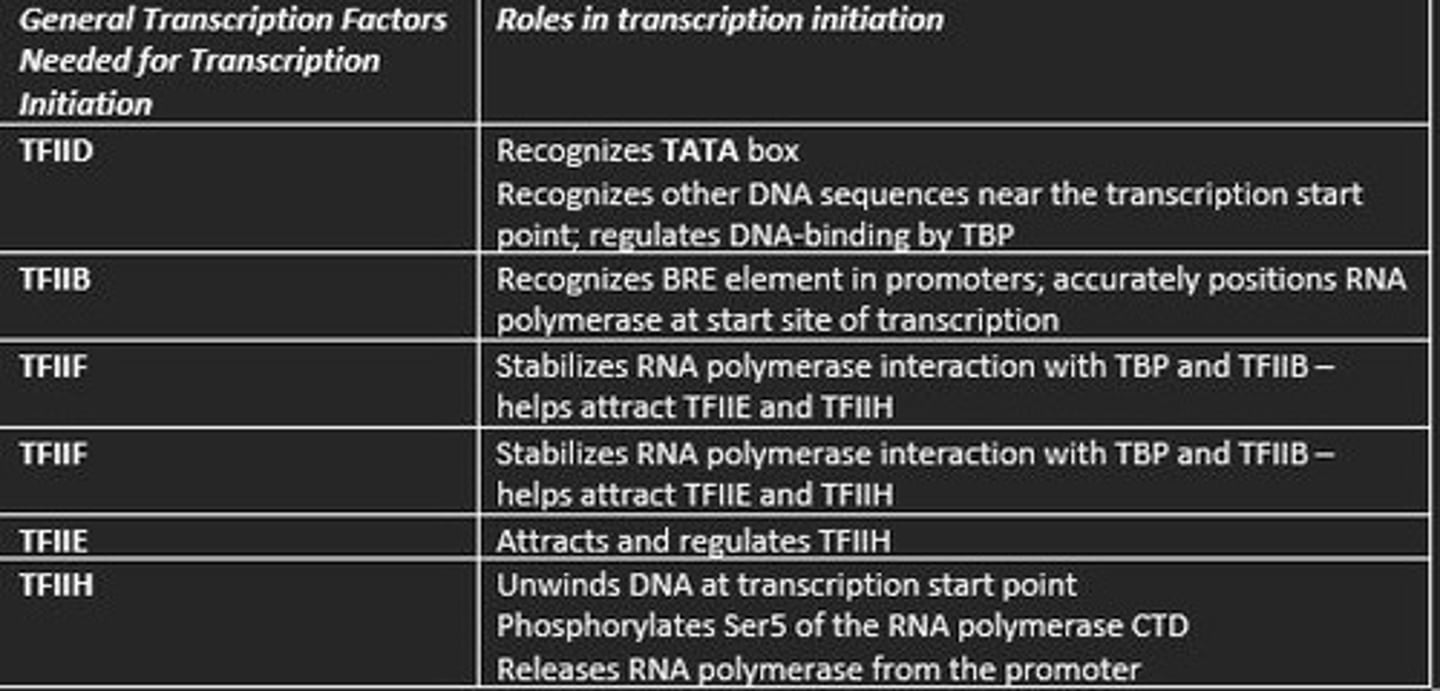
1. Transcription factor TFIID recognize TATA box
2. RNA polymerase II bind to DNA promoter
3. TFIIH contains DNA helicase
4. TFIIH also phosphorylates RNA polymerase II - detaching it from TFs

Different general transcription factors in eukaryotic transcription and their roles in initiation of transcription
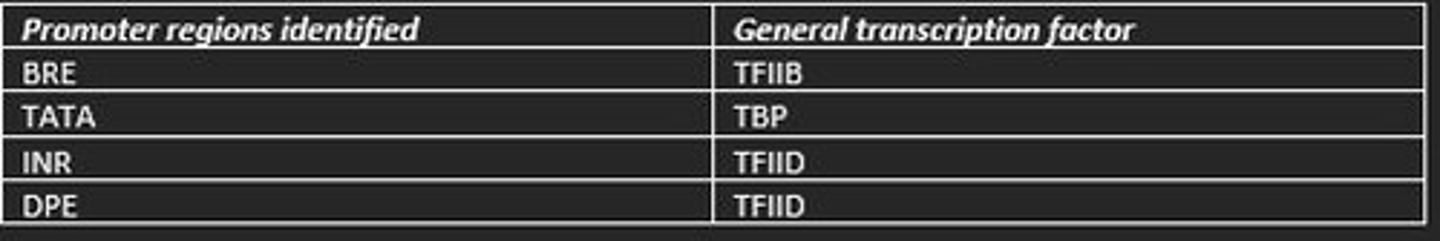
Promoter regions identified in eukaryotic transcription initiation and the general transcription factors which recognise them
Name some other regulatory proteins involved in the initiation of transcription in eukaryotes
- Mediator = coordinates assembly of all these proteins at promoter sites so transcription can start
- Transcription activator proteins = bind enhancer sequences and help attract RNA polymerase II, general TFs and mediator protein complex to the promoter.
RNA polymerase I is devoted to the transcription of...
ribosomal RNA genes
Three main RNA polymerases involved in eukaryotic transcription and what genes they transcribe
Prokaryotes are polycistronic while eukaryotes are ___
monocistronic
Polycistronic
mRNA codes for more than one protein. Found mainly in Prokaryotes.
Monocistronic
This means mRNA only codes for one polypeptide. Eukaryotes
Give example of three post-transcriptional processing of eukaryotic mRNA before translation
1) Capping at the 5' end with 7-methylguanosine (m7G) = protects nascent m-RNA from degradation and assists in ribosome binding for translation
2) Modification of 3' end by addition of poly-A-tail = polyadenylation protects m-RNA from degradation and aids in the export of mature m-RNA to cytoplasm
3) Splicing of the introns at the spliceosome = RNA splicing enables eukaryotes to increase the coding potential of their genomes
mature m-RNA
RNA transcript that has been spliced and processed and is ready for translation in protein synthesis
After transcription of mRNA in the nucleus, mRNA needs to be exported to the cytosol, where translation takes place.
Successfully processed m-RNAs are guided through ___ ___ complexes (NPCs) which are aqueous channels in the nuclear membrane that directly connects the nucleoplasm and cytosol.
Nuclear protein complexes
The abnormal processing of the beta-globin primary RNA transcript in humans leads to ___ ___ (severe anemia due to aberrant hemoglobin synthesis)
Beta-thalassemia
Diseases which are a result of splice-site mutations
- Beta-thalassemia = splice-site mutations
- Phenylketonuria = single base mutation that corresponds to change in splice donor site of intron 12 - making site unrecognisable
Tamoxifen
Reduces risk of breast cancer coming back by 40-50% in postmenopausal women and by 30-50% in premenopausal women
Splicing therapy is used to treat this disease.
This disease is due to mutations in DMD gene that encodes dystrophin, a protein that plays key role in maintenance of skeletal muscle.
The Exondys 51 oligonucleotide blocks splicing to exon 51, restoring the normal reading frame in exon 52 and yielding protein with partial activity
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)