beam modifiers week 7
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Beam modifiers
Any device placed in the path of the beam
u Four Main Types
u Shielding
u Compensation
u Wedge Filtration
Flattening
What is Shielding?
Goal: Minimize radiation exposure to critical structures and shape the beam.
• Purpose:
• Protects healthy tissues.
• Creates complex radiation field sizes and shapes.

Types of Shielding
Lead Blocks:
• Custom-made blocks to protect critical structures.
• Can be positive or negative shapes.
• MLCs (Multileaf Collimators):
• adjust collimator jaws or asymmetrical fields used to shape and modulate the beam dynamically.
But this stops that from changing isocenter duh
you wanted to block one side more than the other, you’d have to shift the isocenter to keep the target in the beam
• Provides more precise and automated beam shaping.
Shielding positive/negative blocks
Critical structures like heart island
Negative- peripheral surrounding structures are treated
Lead Block Composition
BLT w CHEESE
Bismuth: 50%
• Lead: 26.7%
• Tin: 13.3%
• Cadmium: 10%
What is Tray Transmission Factor?
measures how much radiation passes through the block tray.
• Used when custom blocks are mounted on a plastic tray
Purpose of Tray Transmission Factor
To account for the attenuation (reduction) of the beam by the tray.
• Ensures accurate dose delivery when blocks are used.
What Are Compensators?
Devices used to account for surface irregularities and differences in tissue thickness.
• Ensures a uniform dose across the treatment area

Purpose of Compensators
To modify the radiation beam to maintain an even dose to the target tissue.
• Protect critical structures and reduce hot and cold spots
Types of Compensators
Bolus
• Purpose: Acts as tissue-equivalent material to bring the dose closer to the skin.
• When Used:
• Treating superficial tumors.
• Reducing Dmax (maximum dose depth) for surface treatments
Bolus Reduces Dmax by shifting the maximum dose closer to the skin.
• This ensures better dose coverage for superficial tumors
Wedges
Wedges reduce beam intensity on one side.
They tilt isodose curves.
Reduce dose overlap
Tilt depends on wedge angle (15°, 30°, 45°, 60°).
Made of tungsten, lead, brass, or steel

What kind of wedges
Physical wedge = placed in beam path.
Dynamic wedge = made by moving collimator jaws.
Wedge transmission factor (WTF) = how much radiation passes through.
WTF depends on material and angle (steeper angle = lower WTF).

Flattening filter
Located in the head of the LINAC.
Used in photon beams (not electrons).
Flattens the beam to make dose more even across the field.
Reduces central axis (CAX) dose (beam is more intense in the middle without it).
Dose rate is lower with the filter, especially at the CAX.
What Electron Beams Are Used For:
Treat tumors close to the skin (superficial tumors)
Great when you don’t want the beam to go deep
Dose builds up quickly near the surface
Reaches a peak dose (Dmax)
Then drops off fast — so deeper tissues get very little dose
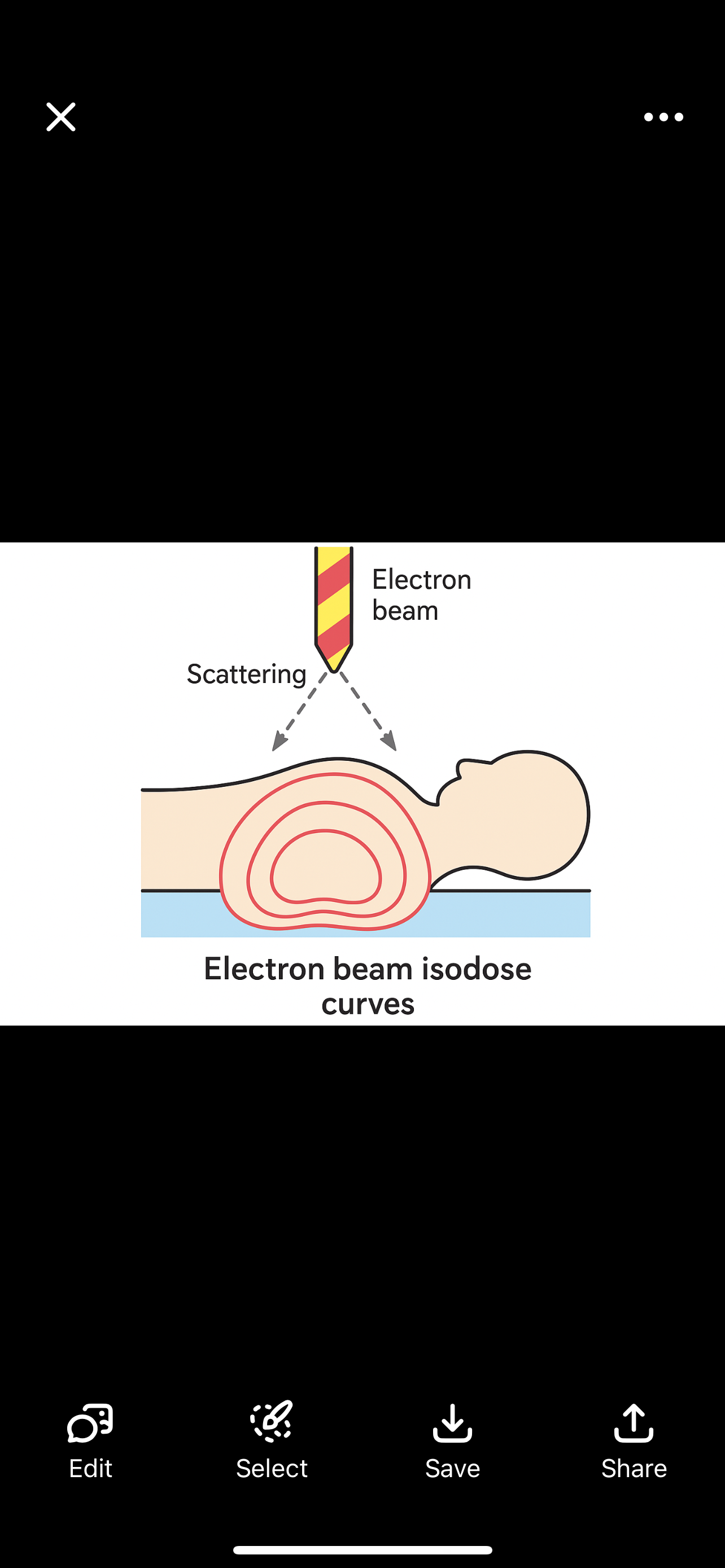
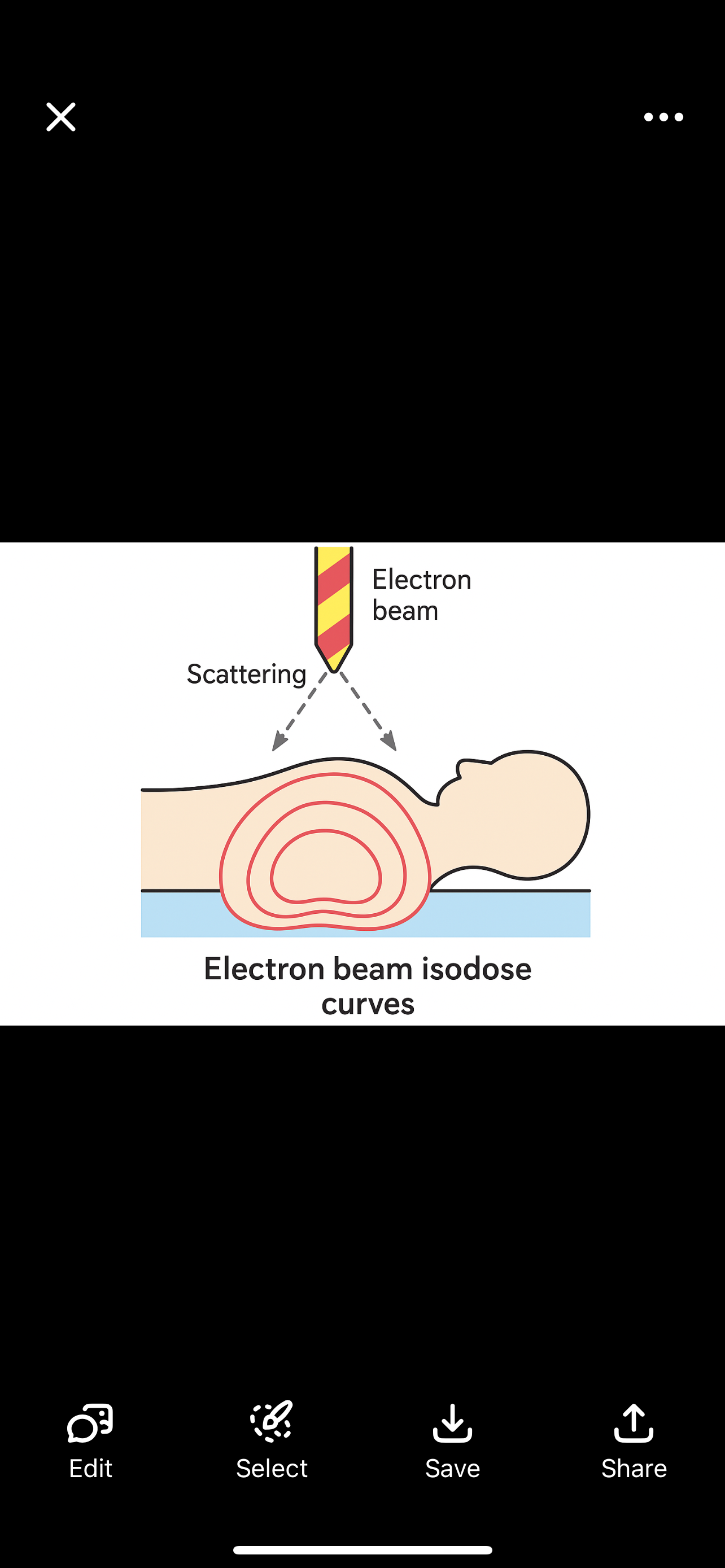
Electron Beam Isodose Curves
The dose lines look like a balloon or bubble shape going into the body.
The sides spread out (lateral scatter), especially near the surface.
With higher energy, the shape is less bubbly and more straight.
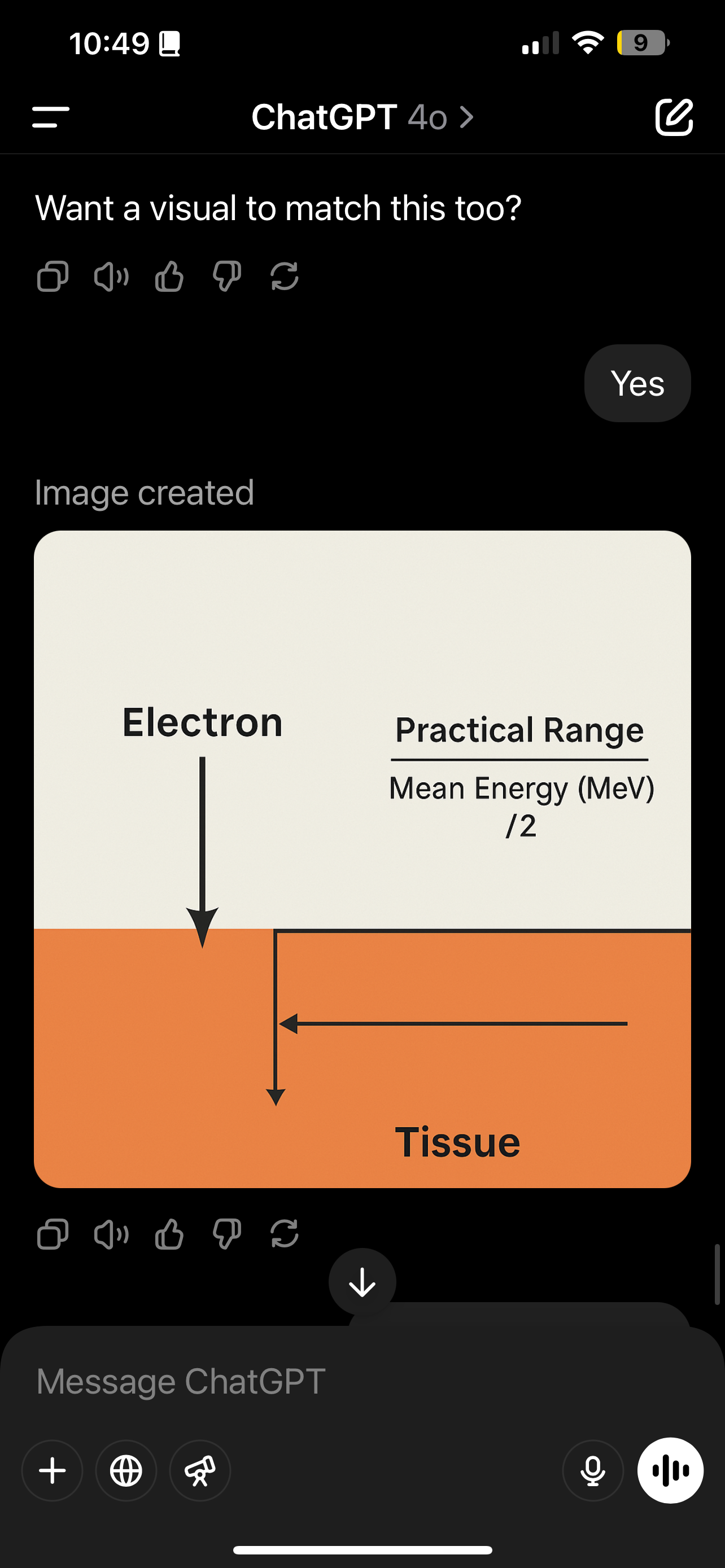
Describe the practical range in centimeters in tissue (mean energy at surface). How is it used?
It tells you how deep the electrons go before the dose basically stops.
It’s the spot where the dose is only a tiny bit left (a few percent).
Used to pick the right energy for how deep the tumor is
80% line
used for most treatments
→ It tells you how deep you can treat safely
→ Formula: Depth = MeV / 3
90% line
used for very shallow tumors
→ It’s closer to the surface
→ Formula: Depth = MeV / 4These help you pick the right energy so the tumor gets the full dose — not too deep, not too shallow.
External Shielding
Lead or Lipowitz cutouts
Placed on skin or cone
Shapes the beam
Internal Shielding:
Lead or tungsten
Placed inside the body near sensitive areas
Bolus
A compensator
Wax or acrylic
Used to shape the dose or even out the skin surface