Exam 3
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ace it again!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Functions of color vision
Classify
Organize
Survival
Isaac Newton proposed:
…white light is mixture of many colors
Prism
Object that separates different colors from white light
Visual Spectrum
Colors that humans can perceive; 400-700 nm
Blue: short wL
Green: medium wL
Yellow: medium/long wL
Red: long wL
Chromatic Colors
Light that reflects different wL’s (e.g., red, green, blue)
Selective Reflection
Some colors reflect more than others
Achromatic Colors
Light reflects equal wL’s
(e.g., white, black, & gray)
Selective transmission
Transparent objects (liquids, plastics, glass) allow wL’s to pass
Reflectance & Transmission Curves
Plot % of light reflected/transmitted to perceive specific wL’s
Describing wL’s based on mixing colors
Mixing paints
Mixing lights
Mixing Paints
Paint absorbs/takes away colors
short, medium, long wL’s mixed together makes black
Subtractive Color Mixture
Paint from 2 mixed wL’s lose their colors
(e.g., blue (short) + yellow (long) = green (med)…blue & yellow no longer present
Mixing Lights
Short, medium, & long wL light shown together
reflecting white light
(e.g., blue (short) + green (med) + red (long) = white)
Additive Color Mixture
Light from 2 different wL’s come together to make new color
(e.g., green (med) + red (long) = yellow (med, long)
Perceptual Dimensions of Color
Hue - color being assessed
Saturation - intensity & pureness of color
Desaturation - fading of a color
Value - brightness of the color
Theories of Color Theory
1. Trichromatic (Helmholtz, Young, Maxwell) -
Color vision based on 3 color receptors (red, green, and blue cones) combine to make colors
Ex: Red and green cones activated together, we perceive yellow
2. Opponent-Process (Hering) -
Color perception relies on opposing pairs of colors (red vs. green, blue vs. yellow). Activation of 1 color suppresses the other
Ex. Staring at a red object, then seeing brief green afterimage (cus of suppression of red cones)
Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision
Idea: Our perception of color is determined by 3 receptor mechanisms
Color Matching Experiment
Prompt: Adjust 3 wL’s in comparison field to match test field of 1 wL
Test & Comparison Field of Color Matching Experiment
Test Field - color of light experimenter wants observer to match
Comparison Field - observer manipulates lighting to match test field color
Results of Color Matching Experiment
Adjusting 3 wL’s - possible to match any colors in field
Adjusting 2 wL’s Only - can’t match all colors
Normal Vision - needs 3 receptors
Cones have which 3 pigments (colors)?
1. Short wL
2. Medium wL
3. Long wL
Visual Pigment Molecule
Where retinal bends from opsin to make light
Opsin
Protein structure differs representing the 3 diff. pigments
Metamerism
Colors of different wL’s create an identical color
process of mixing
Metamers
Different wL’s come together to make similar color
what we see when colors mix
Why are 3 Visual Pigments Necessary?
1 receptor (pigment)
wL’s can’t be identified (shades of gray)
2 receptors = 2 pigments
Can identify 2 wL (not just intensity of light)
3 receptors = 3 pigments
Can identify 3 wL (perception of many colors)
Principle of Univariance
Receptors respond to light intensity (NOT different wL’s)
Opponent-Process Theory
Idea: One member of color pair suppresses other color
Phenomenological Method
An observation; describing what you see
Hering's Color Circle Experiment
People observed color circle & identified hue changes
Color differences seen as primary colors added in small amounts
(e.g., can’t have bluish yellow, but can have bluish red)
Primary Colors
Red, Green, Blue, Yellow
Unique Hues
(Don't mix/opposites)
Red/green
Blue/yellow
Black/white
Opponent Neurons
Location: Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
excitatory on one end of visible spectrum
inhibitory on other end
How do the Trichromatic and Opponent-Process Theories work together?
Each describes physiological mechanisms in visual system
Trichromatic - explains cones in retina
Opponent-process - explains neural response from cones to brain
Color Deficiency
Partial loss of color perception
Color Blindness
Can’t see colors at all (only white, black, & gray; a monochromat)
Color Deficient-Dichromats
Some color can be observed
Types of Color Vision Deficiency
1. Monochromat
2. Dichromat
3. Anomalous trichromat
Monochromat
1 wL to see colors (gray, white, black)
Rare condition of color blindness
No cone functioning, only rods
Poor visual acuity & sensitive to bright light
Dichromat
2 wL’s to see color; some color
Males have it more than females
They lack extra x chromosome (only need 1 x for normal vision)
Types of Dichromats
1. Protanopia
2. Deuteranopia
3. Tritanopia
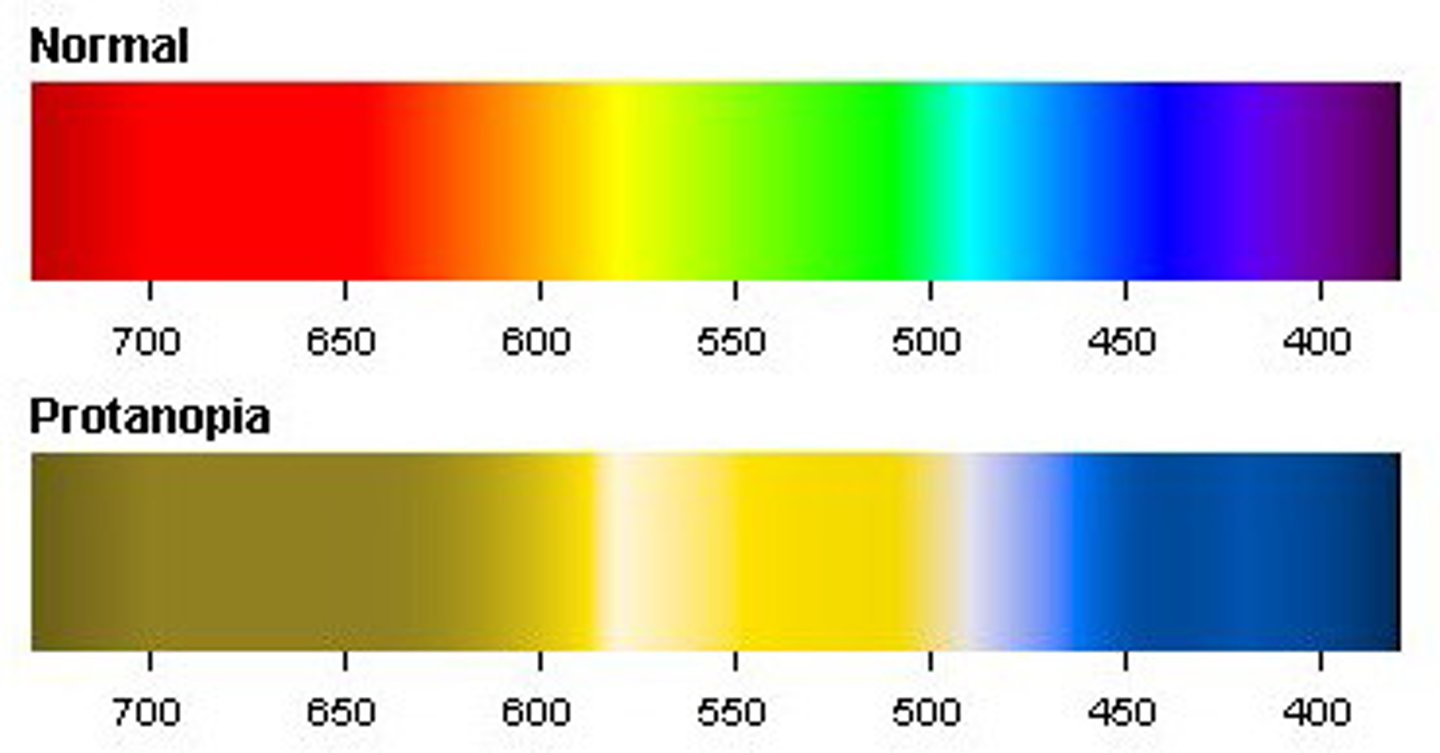
Protanopia
Can't see red properly
May confuse with greens or browns
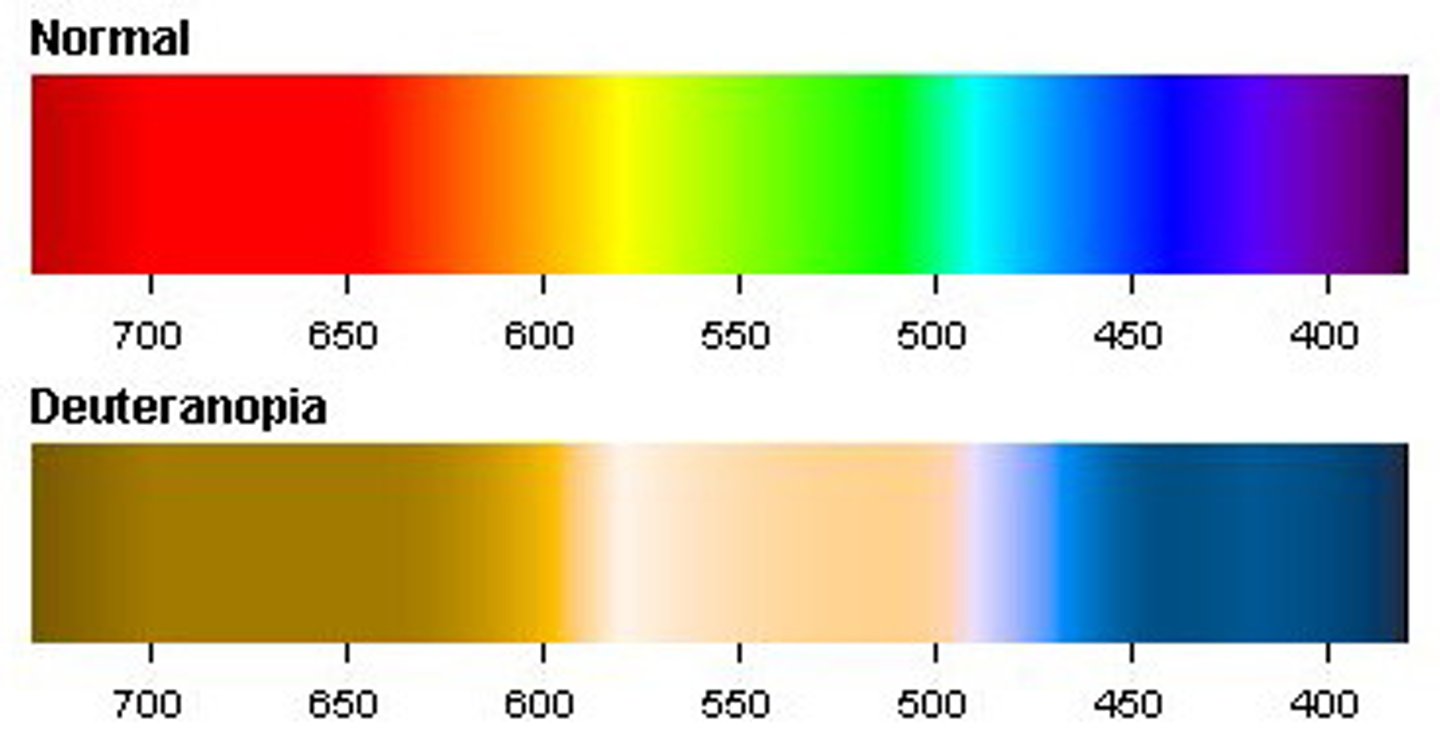
Deuteranopia
Can't see green properly
(difficulty distinguishing reds, greens, and browns)
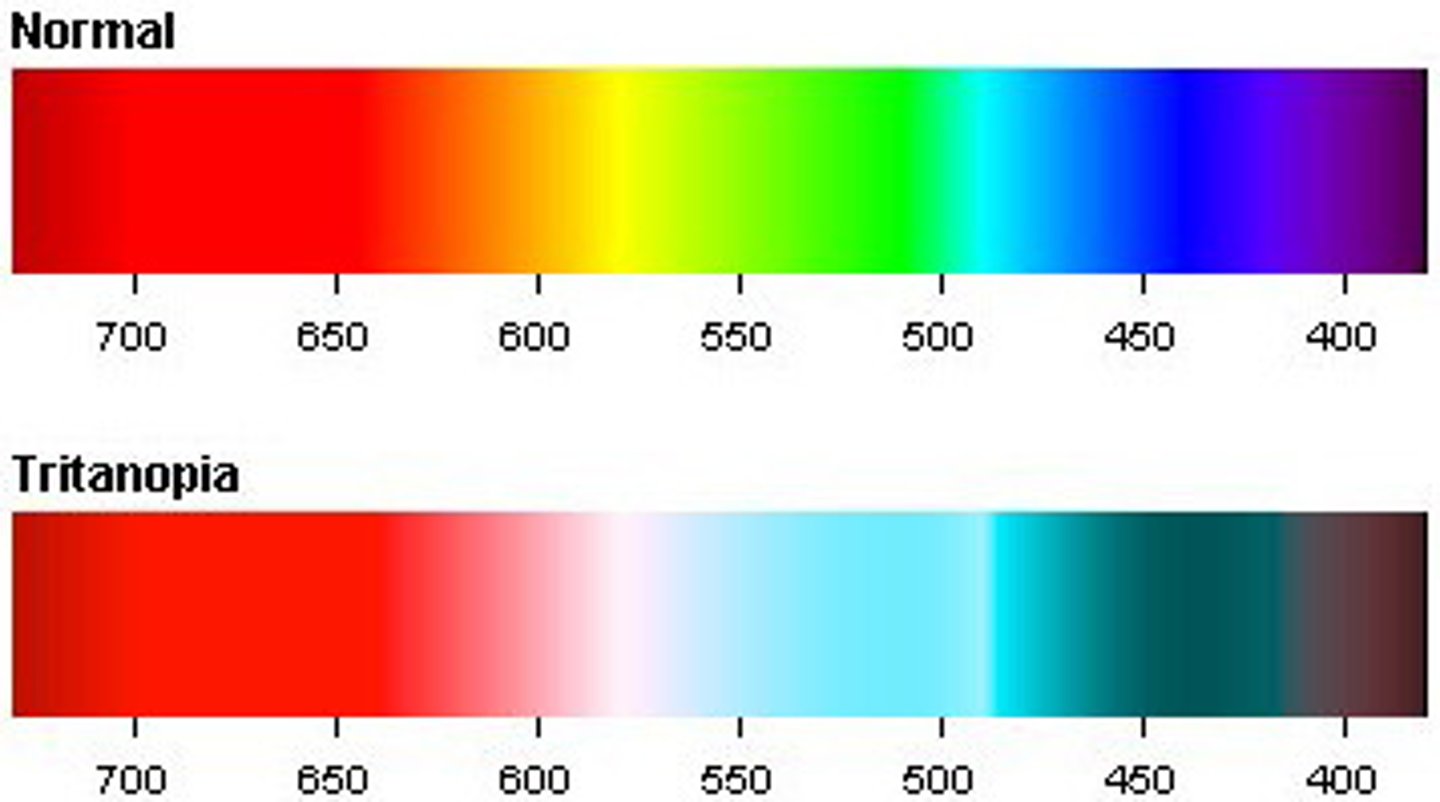
Tritanopia
Can’t see blue properly
(may confuse blue and yellow)

Unilateral Dichromats
People w/ trichromatic vision in 1 eye & dichromatic vision in other
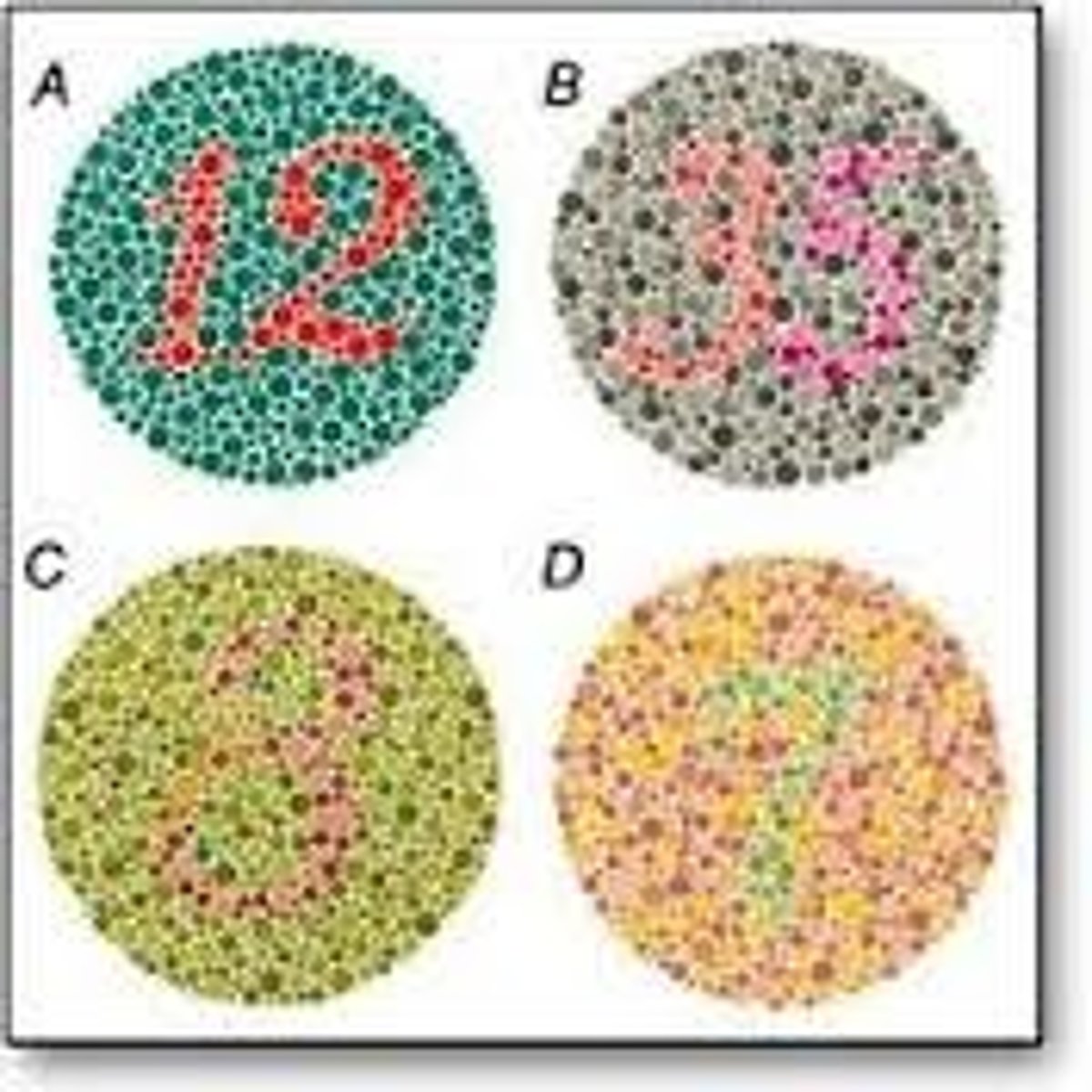
Ishihara Plates
Color vision test to diagnose people w/ color deficiencies
Anomalous Trichromat
3 wL’s, but colors are mixed
colors perceived abnormally
Color Constancy
Perceive colors as constant under diff. lighting
Explanation for Blue/Black or Yellow/White Dress
Influenced by illumination of light/type of light
Lightness Constancy
Perceive achromatic colors (white, gray, black) as constant under diff. lighting
Depth Perception
How far/deep something is (visually)
happens automatically through repeated exposure of cues
Cues to Signal Depth
1. Oculomotor
2. Monocular
3. Binocular
Oculomotor
Cues based on sensing position of eyes via eye muscles tension
Convergence
Inward movement of eyes when focusing on nearby objects
Accommodation
Lens shape changes focusing on objects at different distances
Lenses flatten - far away
Lenses thicken - nearby
Monocular
Cues available in 1 eye:
Pictorial
Movement-based
Pictorial Cues
Depth cues from 2D images from 1 eye (8 total)
Pictorial Cue #1. Occlusion
When one objects hides/partially hides from another object
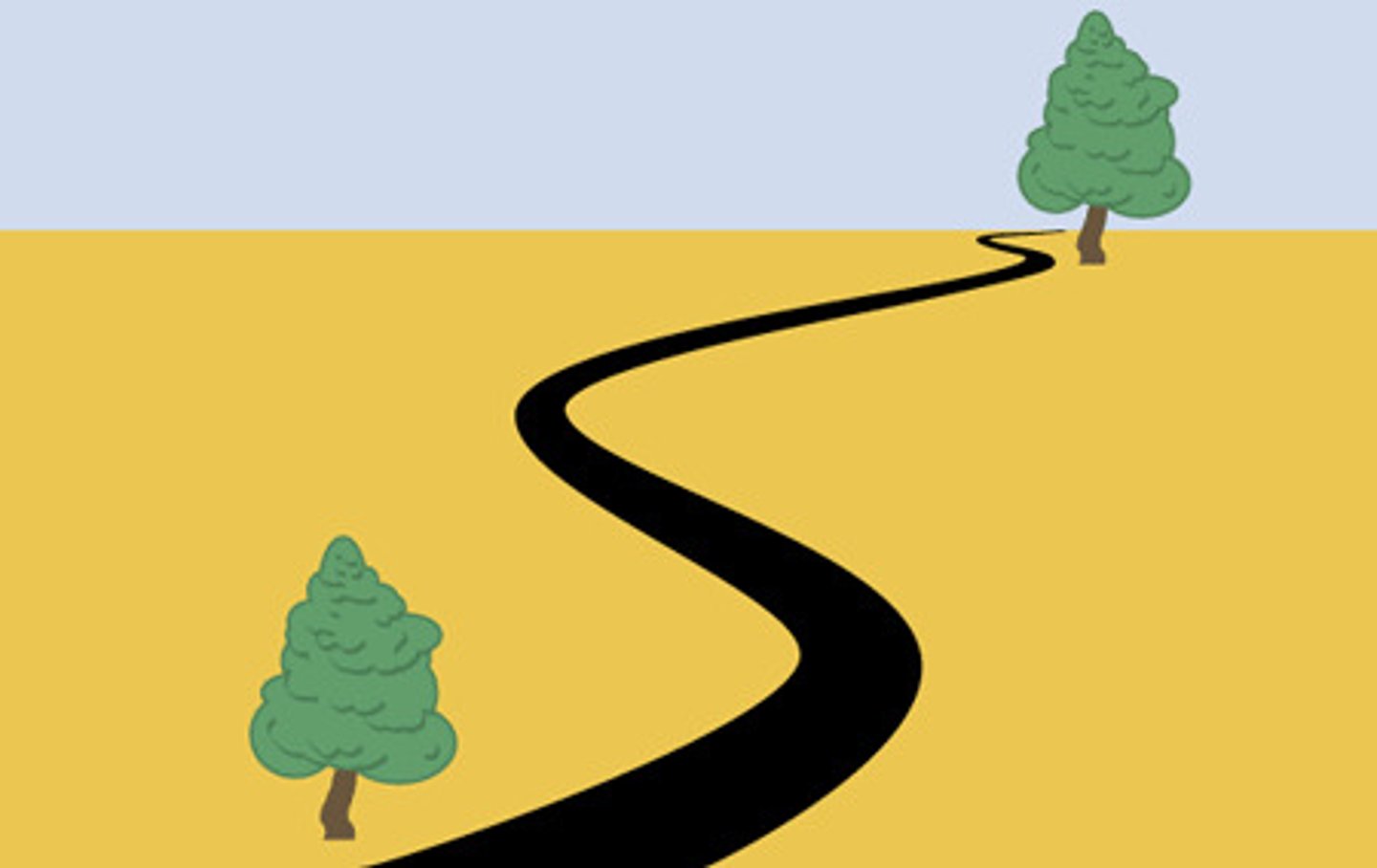
Pictorial Cue #2. Relative Height
Objects closer to base of horizon seem more distant, objects away from base seem closer

Pictorial Cue #3. Relative Size
Equal size objects, closer one looks bigger, far away one looks smaller

Pictorial Cue #4. Familiar Size
Judging distance according to prior knowledge
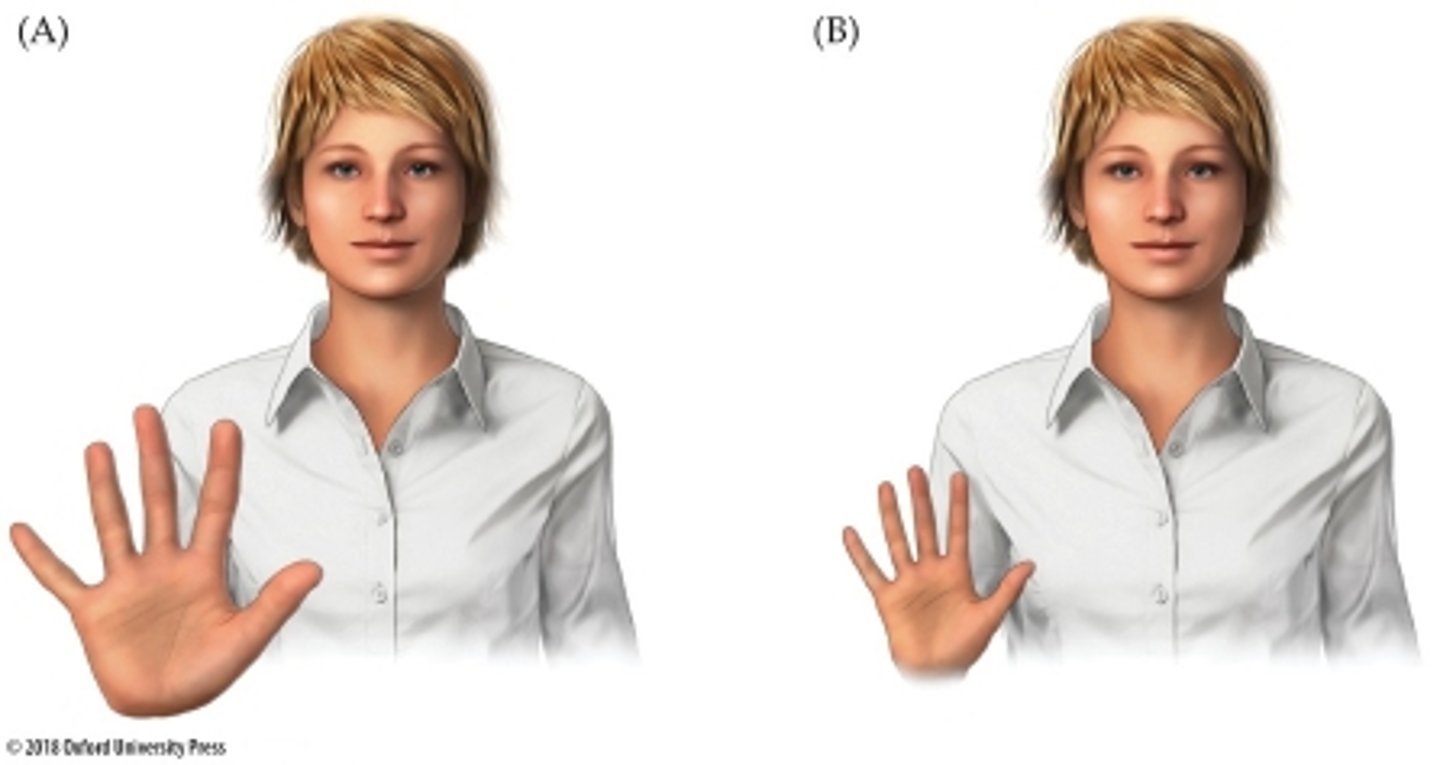
Pictorial Cue #5. Perspective Convergence
Parallel lines appear to come together in the distance

Pictorial Cue #6. Atmospheric Perspective
Distant objects appear less sharp than nearer objects
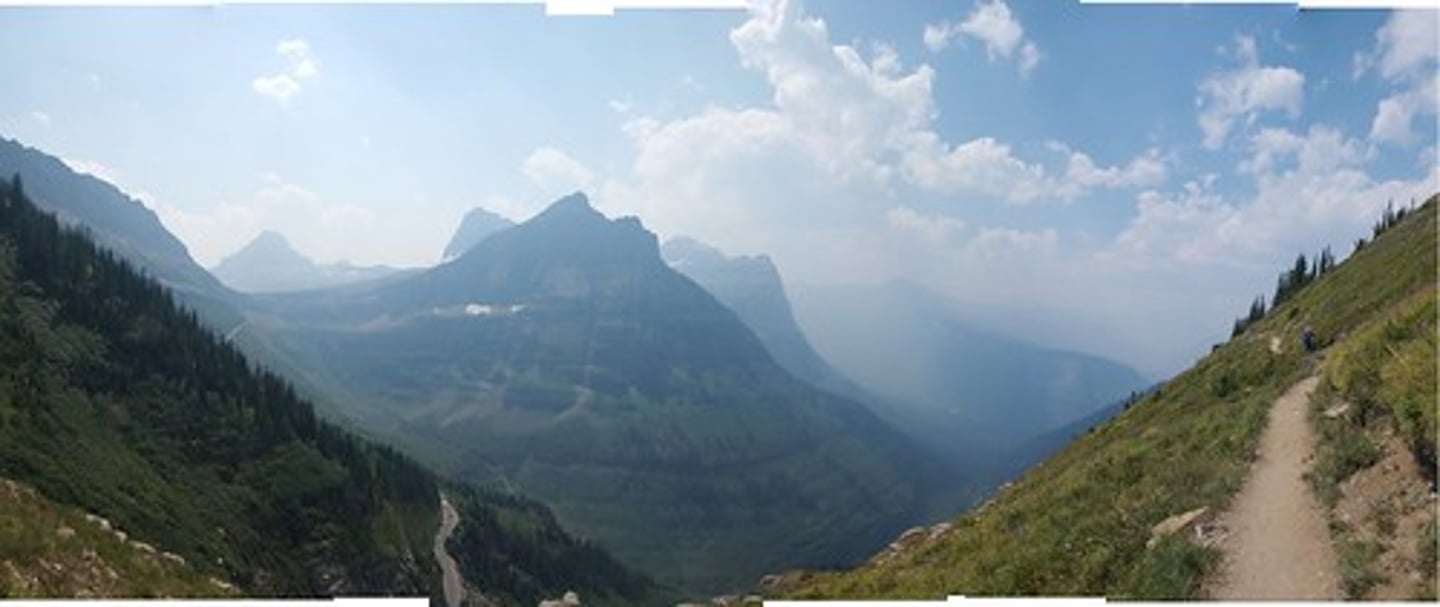

Pictorial Cue #7. Texture gradient
Elements in a scene seem more closely packed when distance increases
Pictorial Cue #8. Shadows
Decrease in light intensity (blockage of light)
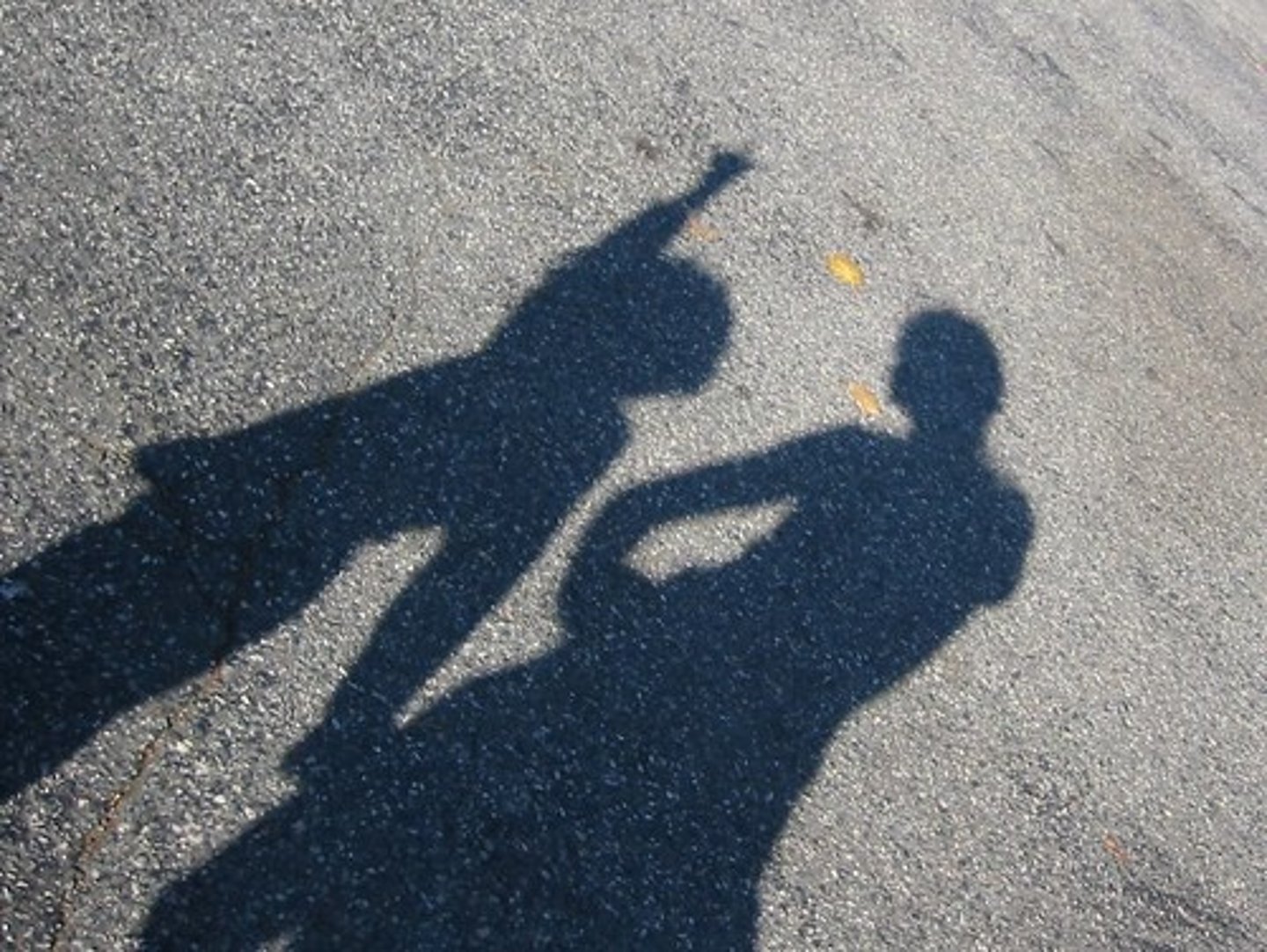

Movement-Based Cues
Sources of depth info from an observer's movement
1. Motion Parallax
2. Deletion & Accretion
Motion Parallax
In direction of movement:
Close objects move fast
Far objects move slow
(e.g., Looking out car window & observing)
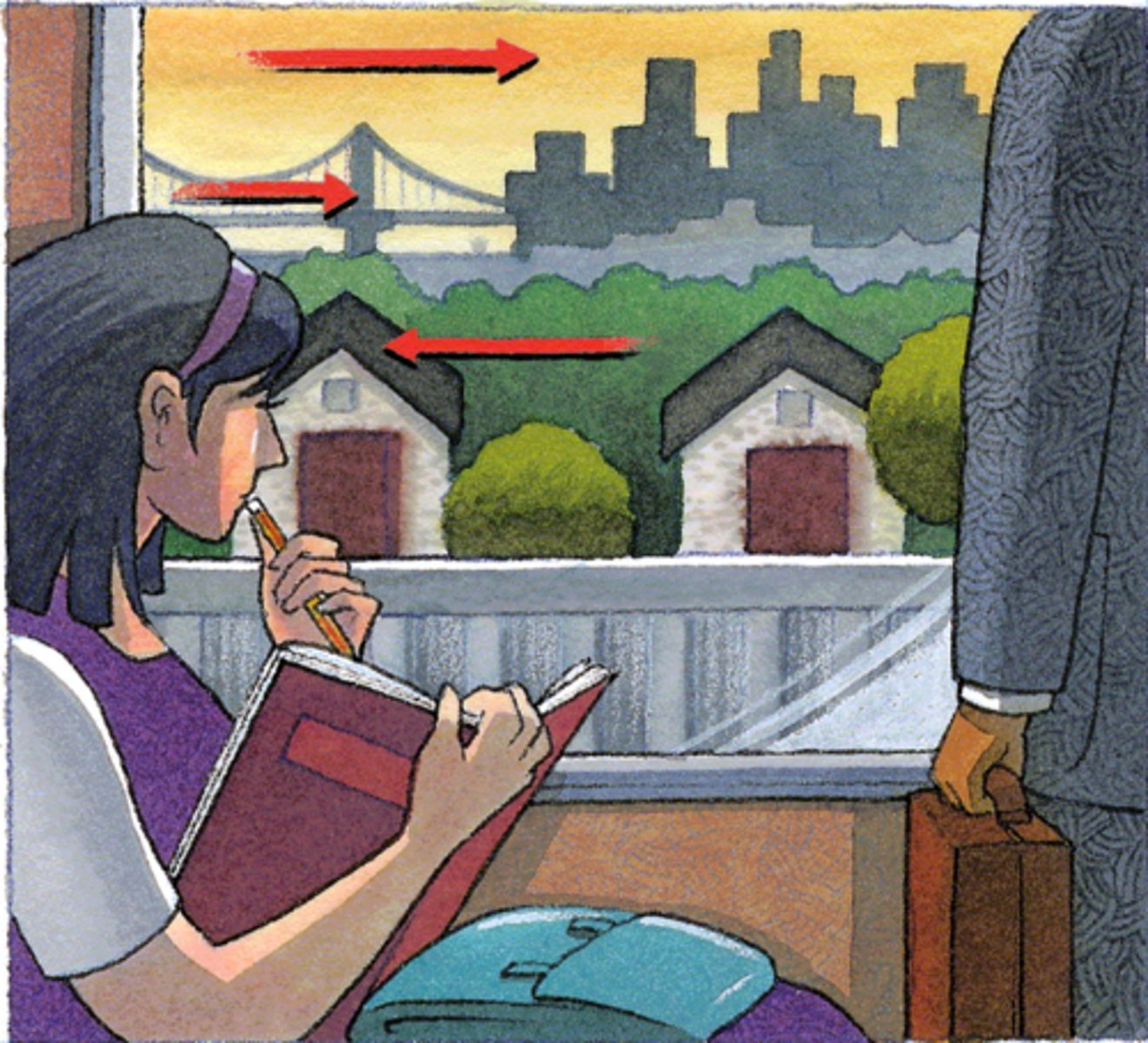

Deletion & Accretion
Object distance perception based on covering/uncovering objects as observer moves
Deletion - covering object
Accretion - uncovering object

Binocular
Cues depending on 2 eyes
Stereoscopic Depth Perception
Awareness of depth through input from both eyes
Difference Between 2D & 3D Image
2D - Both eyes receive same info
flat images
relying on monocular cues (pictorial) for both eyes
3D - Both eyes receive different info
images positioned in diff. viewpoints for 3D experience
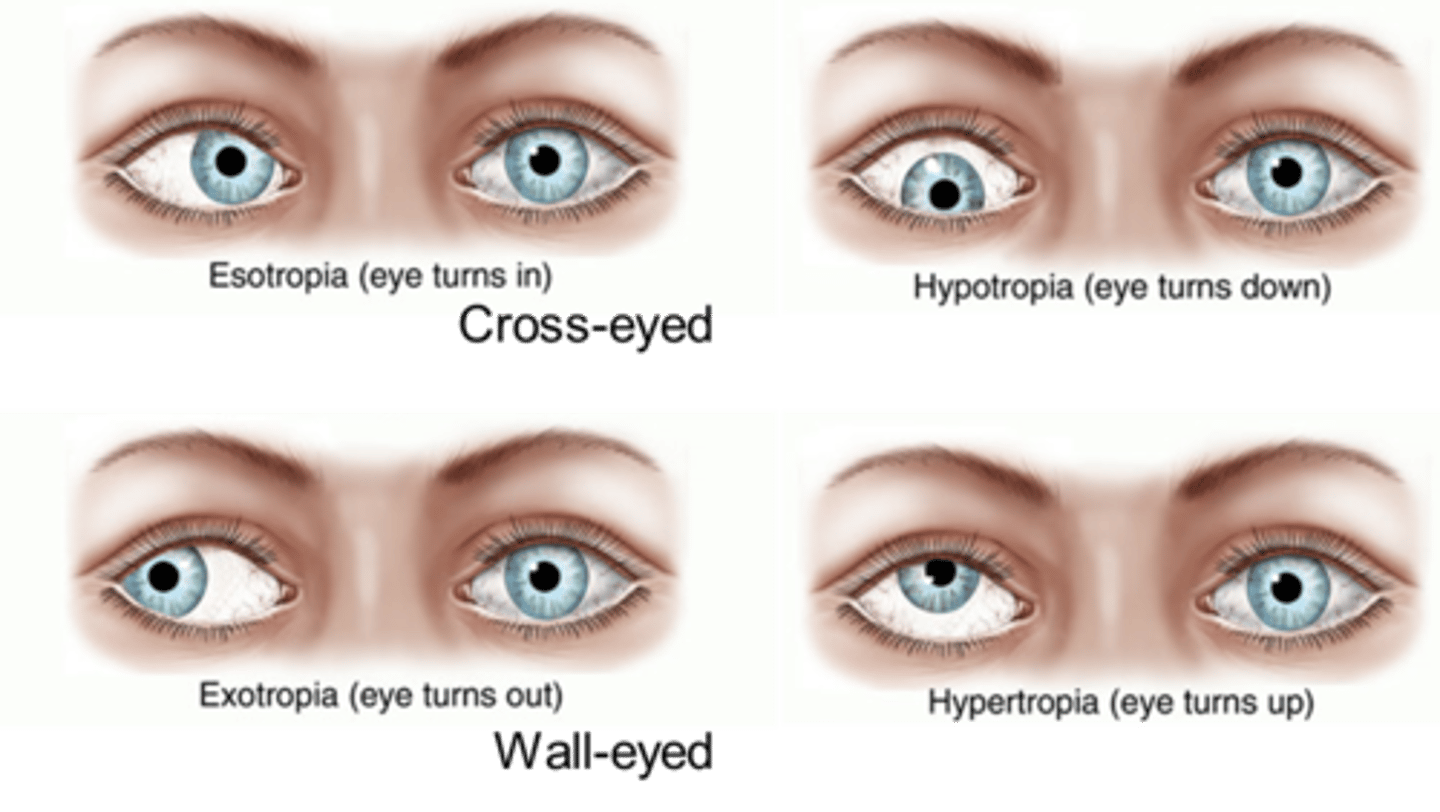
Strabismus
Eye misalignment; 1 eye is suppressed causing an individual to use one eye to avoid double vision
• People rely on monocular instead of binocular cues
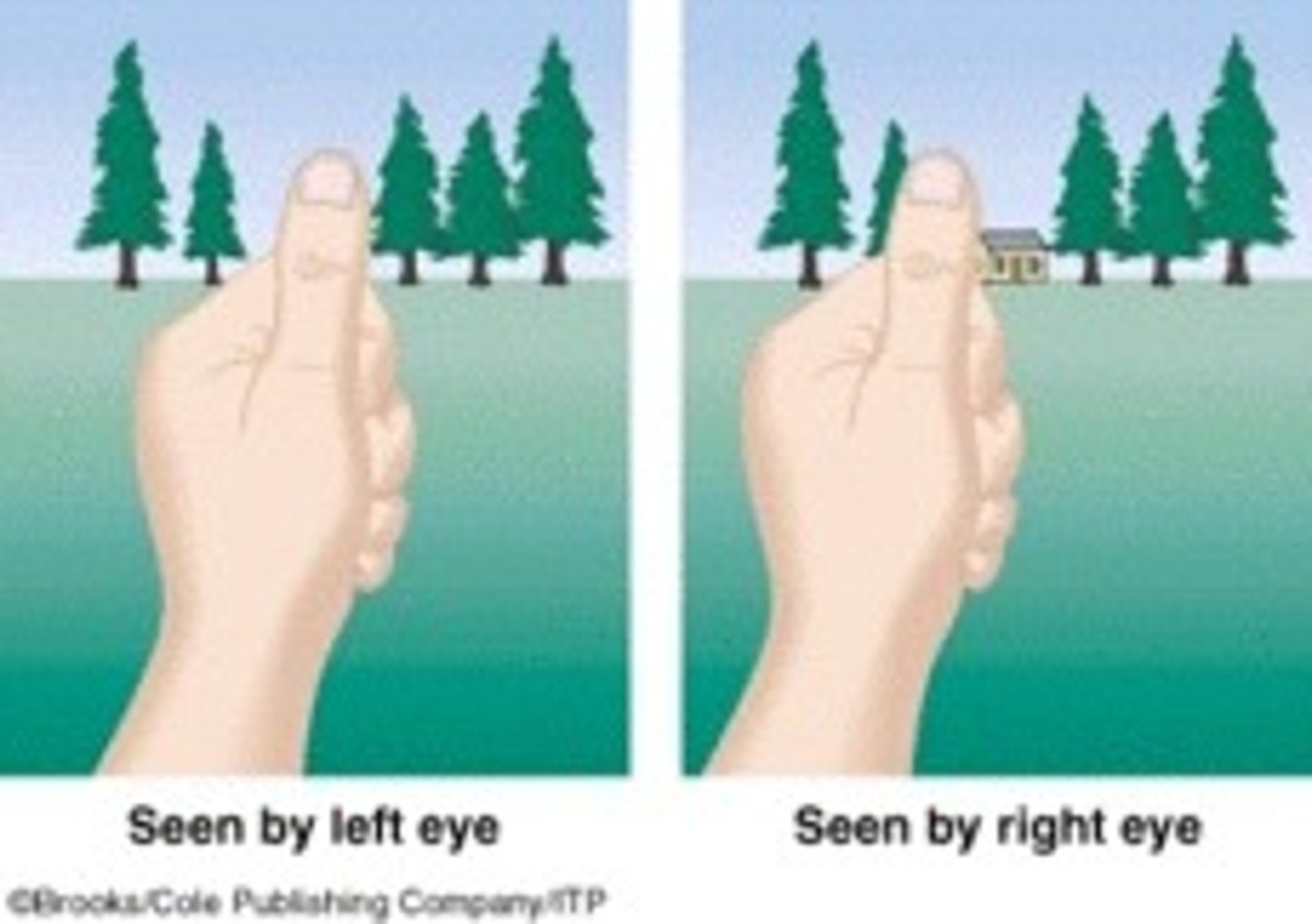
Binocular Disparity
Difference in images from left & right eyes
Corresponding Retinal Points
Points on retina where image overlap (same)
Horopter
Imaginary sphere that passes through point of focus
Noncorresponding Retinal Points
Objects that don’t fall on horopter
makes diff. images in both eyes
Absolute Disparity
Objects deviate from falling on corresponding retinal points
Angle of Disparity
Amount of absolute disparity indicates how far an object is from horopter; POV
Relative Disparity
Diff. between absolute disparity of 2 objects, switching both angles
Crossed Disparity
When you focus your horopter far away
close object in front of you creates crossed disparity
close object is doubled
Uncrossed Disparity
When you focus your horopter close up
far object creates uncrossed disparity
far object is doubled
Stereopsis
Ability to perceive depth through binocular disparity (diff. in viewpoint for both eyes)
• 3D movies: slightly different positions of an image in left-eye and right-eye are superimposed (placed over each other) on a screen
Correspondence Problem
How does visual system match images from both eyes when both are shown diff. viewpoints in 3D?
• Our visual system can detect specific features/parts of an object from both eyes together to form a single 3D object
Binocular Depth Cells/Disparity-Selective Cells
Specialized neurons that respond to binocular disparity; located in primary visual cortex
• Respond to absolute disparity (when your left and right eyes create different images and not a single image)
Perceiving Size
Depth & size perception are interrelated
Holway and Boring Experiment
Observers presented 2 light circles at intersection of 2 hallways
Right hallway - luminous test circle placed 10-120 ft away
Left hallway - luminous comparison circle 10 ft away
Visual Angle
Angle of an object relative to observer's eye
depends on size & distance from observer
Results of Holway and Boring Experiment
Part 1 - Depth cues (binocular disparity, motion parallax, shading) were given to observer
Result - Judgments of circle size were based on physical size cus they had cues of distance
Part 2 - No depth cues were given instead were eliminated
Result - Judgments of circle size were similar based on size of retinal images w/o cuing of distance
Size Constancy
Perception of an object's size remains relatively the same even when we view object at different distances
Visual Illusions
Our size perception can be tricked by different visual illusions
Müller-Lyer Illusion
Misperceiving 2 lines w/ equal lengths as different due to fins connected to the lines
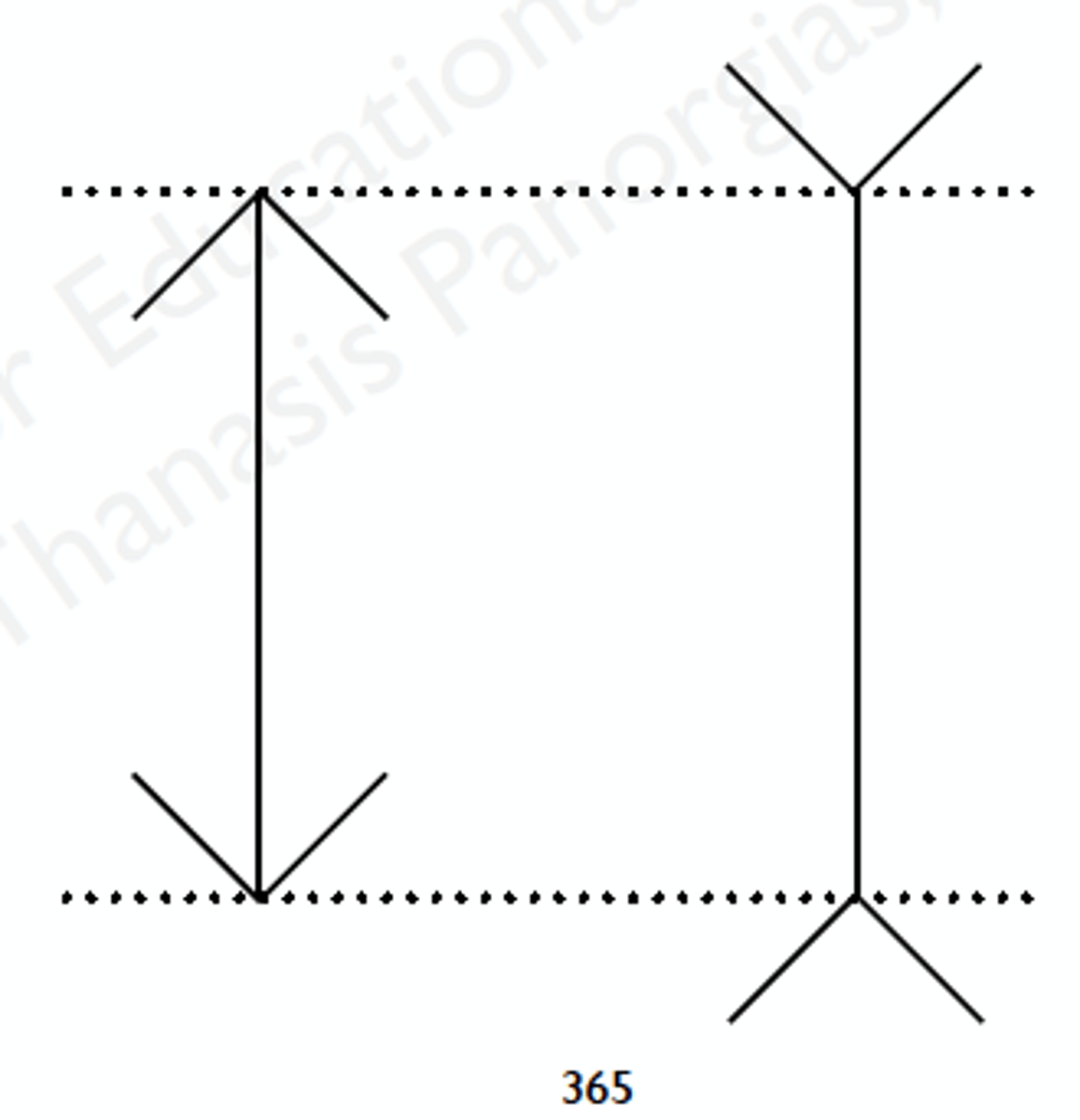
Explanations for Müller-Lyer Illusion
Misapplied Size Constancy Scaling - We view 2D as though it’s 3D
Conflicting Cues Theory - Our misperception of line length is caused by conflicting info: actual length of lines & overall length of figure
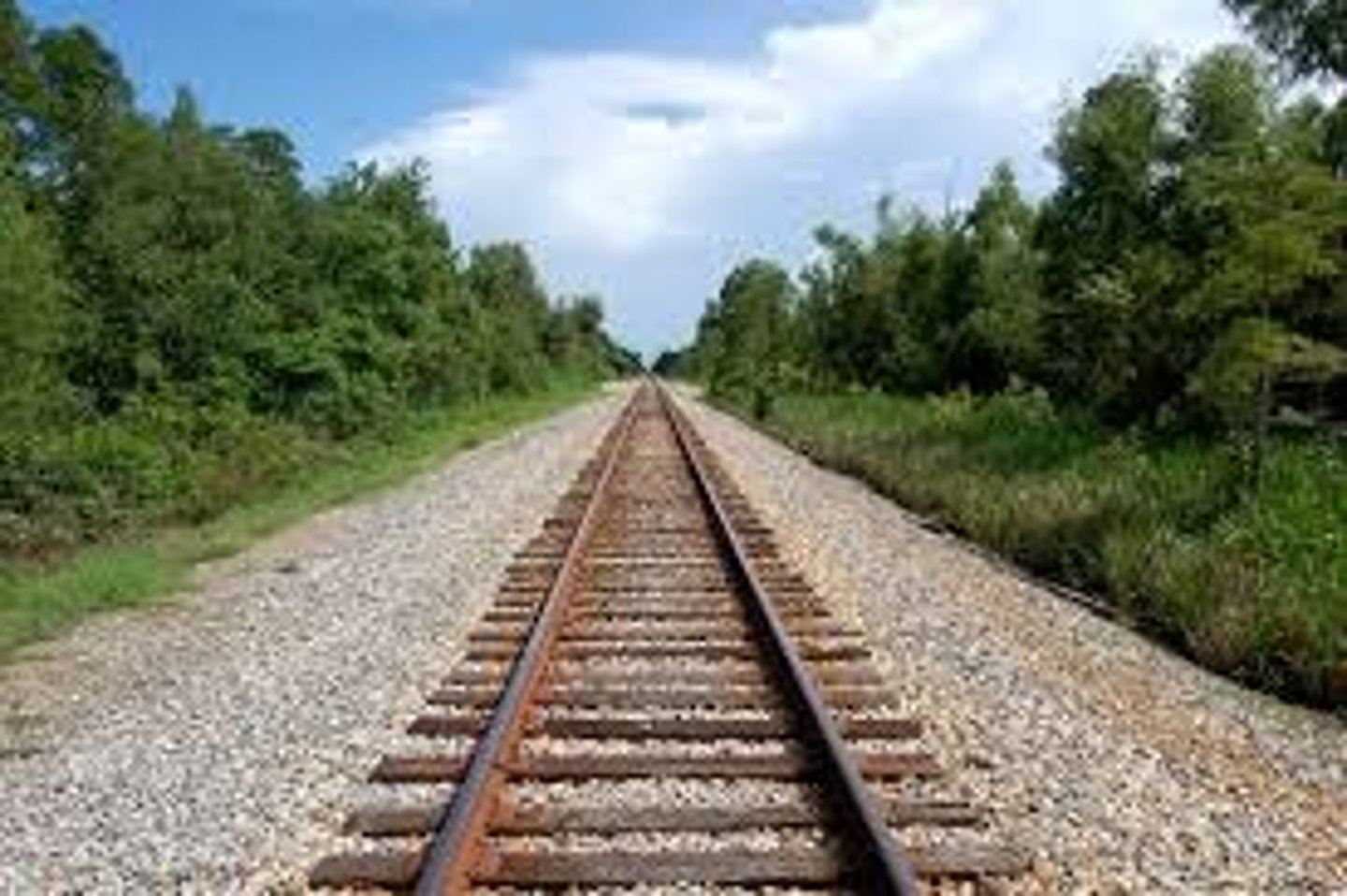
Ponzo Illusion
2 same sized objects placed over different areas of railroad track in picture
Far object appears larger than closer object although both are same size
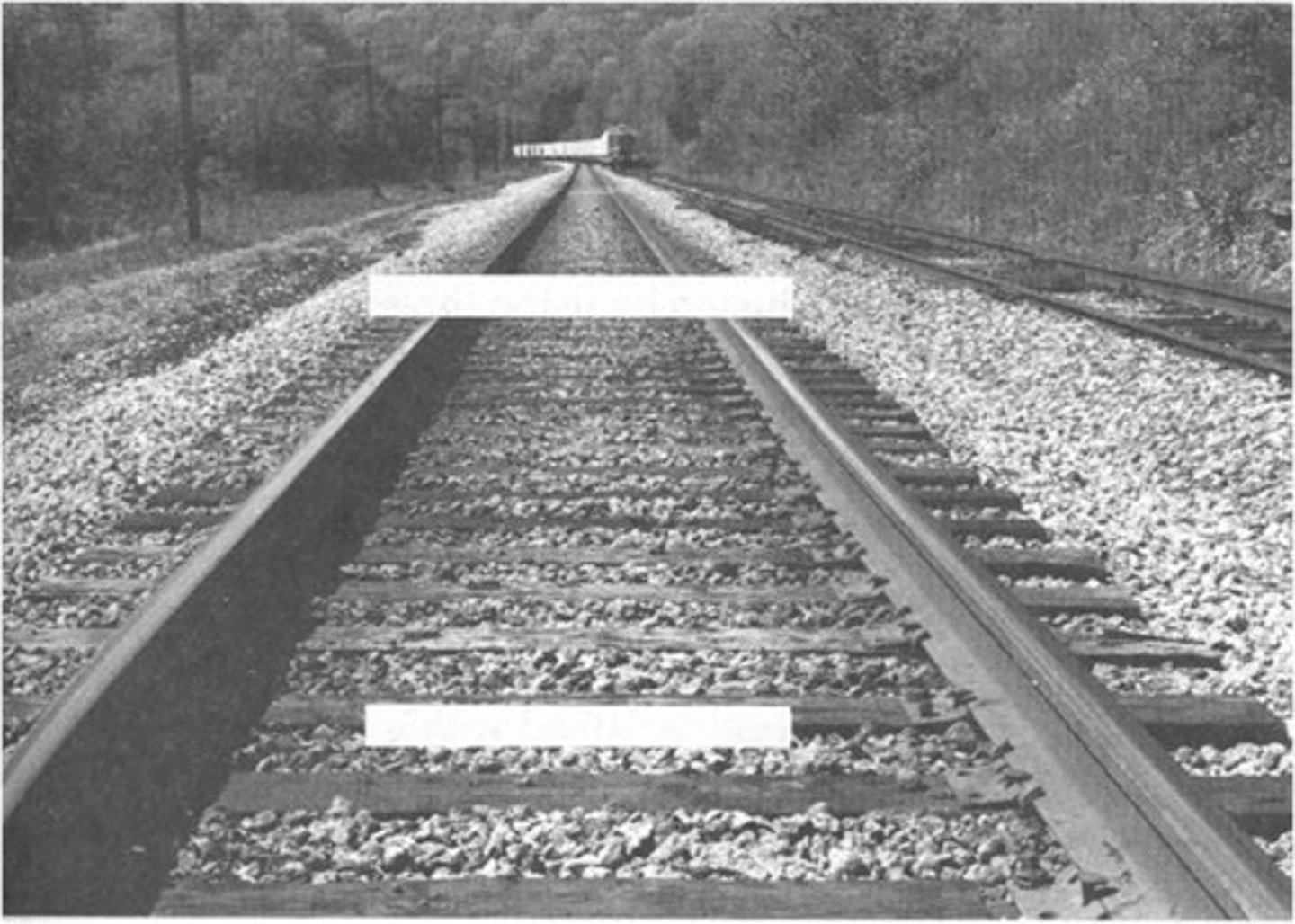
Explanation for Ponzo Illusion
Misapplied size-constancy scaling
Ames Room
2 people of equal size appear very different in size in a room
One appears like a giant over the other
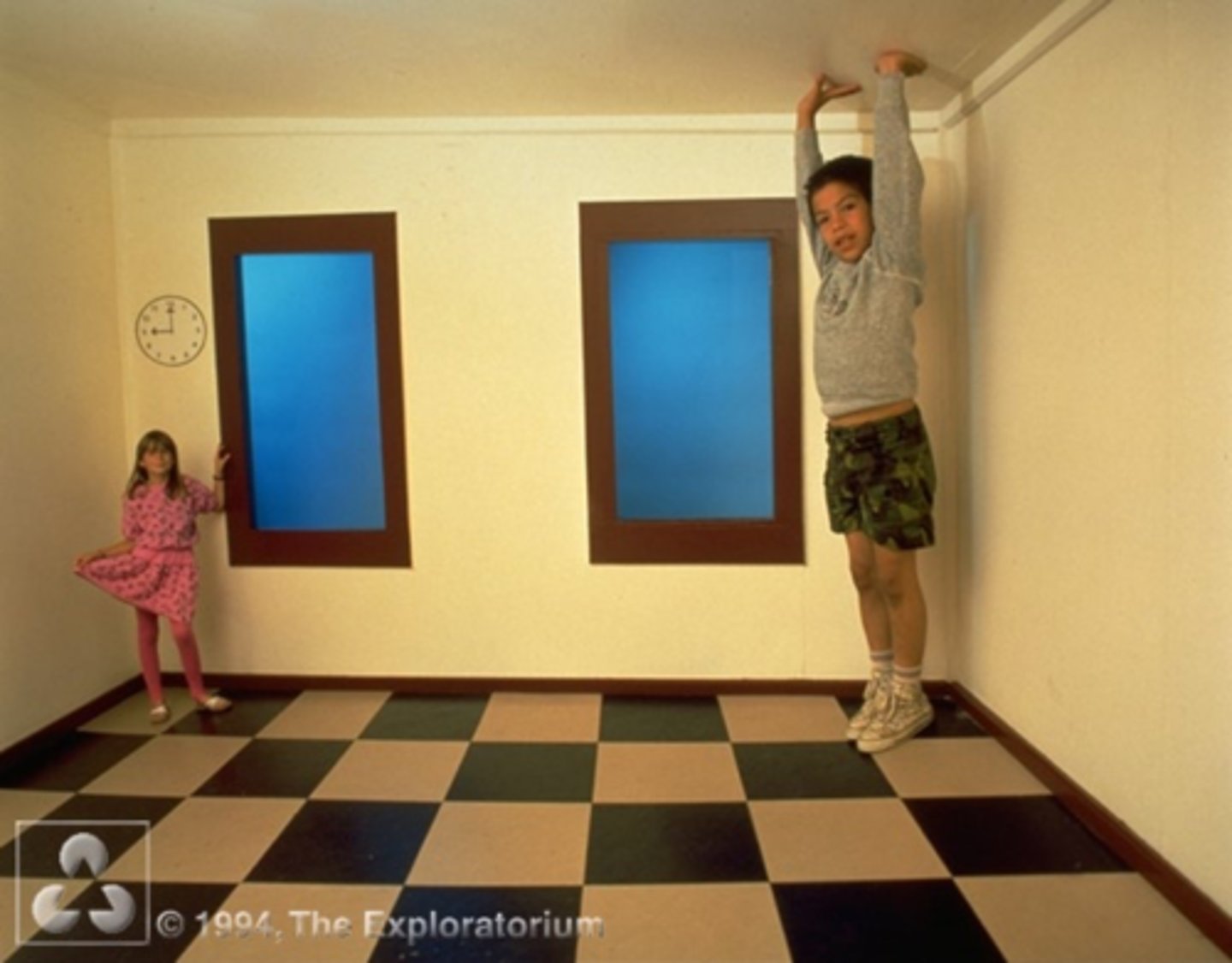

Explanations for Ames Room
Size-distance scaling - Distance is the same for both people but not the size
Relative size - One person is taking up more space than the other in same distance
Moon Illusion
Moon appears larger on horizon than when it is higher in the sky
Explanations for Moon Illusion
Apparent-distance theory - Horizon moon is surrounded by depth cues while moon higher in the sky has none
Angular size-contrast theory - The moon appears smaller when surrounded by larger objects
Sound is Defined in 2 Ways
1. Physical
2. Perceptual
Physical Sound
What a person senses during hearing through pressure changes occurring in ears