Criminalistics exam 2
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ballistics, Firearm and toolmark PSP, Blood, Blood stain, Biological evidence, shoe & tire
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Rifiling
the spiral cut on the internal surface of the barrel of a rifle or pistol and some shotgun barrels
Rate of twist
the distance the projectile needs to travel down the barrel to complete one full revolution
Lands
the projecting component of rifling
Semi-automatic
fires and reloads itself before firing another shot
Wad
part of a shell that separates shot and propellant
Soot
burnt propellant consisting mainly of carbon
Pitch
refers to the angle that rifling is cut into the barrel
Gauge
smooth barrel firearms or shotguns. number of round lead balls of the diameter of the interior of the barrel required to weigh one pound
Chain of custody
documentation of all evidence
Locards’s exchange principle AKA…?
Theory of exchange
Stippling
deposition of fragments of powder. abrasions caused by the impact of unburnt particles of powder impacting the skin
Spatter
The description of a stain that results from blood hitting a target
Serum
The liquid that separates from blood when a clot is formed
angle of impact
also known as angle of incidence; the acute angle created by the intercept of the target with the droplet’s vector
Blunt force
typically causes medium velocity spatter and impact spatter
Sharp force
will typically cause low velocity spatter as well as impact spatter
Projectile
the component of the cartridge that is fired from the barrel and eventually hits a target
Tool
an object used to act on and leave marks on another object
Projected
a bloodstain pattern resulting from the ejection of a volume of blood under pressure
cause cast off, arterial, and expirated patterning
Cast-off
a bloodstain pattern resulting from blood drops released from an object due to its motion
Expirated
a bloodstain pattern resulting from blood forced by airflow out of the nose, mouth, or a wound
Aerial
a bloodstain pattern resulting from the ejection of a volume of blood from a breached artery
Secondary
type of spatter pattern
Satellite spatter
a smaller bloodstain that originated during the formation of the parent stain as a result of blood impacting a surface/blood dripping into blood
Swipe
a bloodstain pattern resulting from the transfer of blood from a blood-bearing surface onto another surface, with characteristics that indicate relative motion between the two surfaces
Wipe
an altered bloodstain pattern resulting from an object moving through a pre-existing wet bloodstain
Drip
a bloodstain resulting from a falling drop that formed due to gravity
Saturated Stain
a bloodstain resulting from the accumulation of liquid blood in an absorbent material
Pool
A bloodstain resulting from an accumulation of liquid blood on a surface
Flow
a bloodstain pattern resulting from the movement of a volume of blood on a surface due to gravity or movement of the target
Impact spatter
A bloodstain pattern resulting from an object striking blood
Clot
gelatinous mass formed by fibrinogen, platelets and other clotting factors
Expiratory stain
A bloodstain pattern resulting from blood forced by airflow out of the nose, mouth, or a wound.
May have bubble rings or mucus or appear diluted
Can be tested for amylase to detect saliva
Void
an absense of blood in an otherwise continuous bloodstain or bloodstain pattern
Fly spots
bloodstains resulting from fly activity that may mimic other bloodstain patterns
Splash
a bloodstain pattern caused by a low velocity impact on a surface
Spine
pointed edge characteristics that radiate away from the center of a bloodstain; formation depends on velocity and surface texture
Parent stain
original stain that satellite spatter forms from
Arterial gush
blood exiting the body under pressure from a breached artery
Patent prints
prints that are visible to the naked eye
What are the categories of blood stains?
Passive stains, Spatter, Altered stains
Do blood stains ever change color?
Yes, relatively fresh blood is reddish brown, Thin layers may appear grayish green, or may assume other colors from black to blue to greyish-white
High velocity blood spatter would most likely be caused by what type of trauma?
Gunshot
What is a blood stain? (full def)
Transfer resulting when liquid blood comes into contact with a surface or a moist or wet surface comes into contact with dried blood
What are the 4 current blood types?
A, B, AB, O
What are the original blood typing names? who created them?
A, B, C created by Dr. Karl Landsteiner in 1900
List examples of passive staining
transfer, flow, swipes, drops, large volume
What is the difference between forward and backward spatter?
Forward spatter is a bloodstain pattern resulting from the blood drops that travelled in the same direction as the impact force
Backward spatter is a bloodstain pattern resulting from the blood drops that traveled in the opposite direction of the external force applied
List some common substances that are easily mistaken as blood stains
Paint, pigments, rust, tobacco, snuff, urine, feces, coffee
What is a transfer stain
a bloodstain resulting from contact between a blood bearing surface and another surface
What are the three preliminary steps of identifying a suspected bloodstain?
1- Visual
2- Presumptive
3- Confirmatory
Describe presumptive step of identifying a suspected bloodstain
In field tests, Phenolphthalein, Leucomalachite green, ortho-tolidine, tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), luminol, fluorescein
Describe Confirmatory step of identifying a suspected bloodstain
Is it blood? - teichmann test
Is it human blood? - ring precipitin test
Whose blood is it? - A,B,O blood typing, DNA, protein/enzyme markers
Describe Visual step of identifying a suspected bloodstain
Using your human senses and judgement
What is a visible impression? provide examples
occurs when footwear steps into foreign substance and is contaminated by it, then comes into contact with a clean surface and is pressed onto it. ex = bloody footprint
What is a Plastic impression? provide examples
occurs when footwear steps into a soft surface such as deep mud, snow, wet sand or dirt creating a three dimensional impression. ex footprint in snow
What is a latent impression? provide examples
impression that requires processing to see most often found on smooth surfaces.
What are methods for documenting visible impressions?
photography, sketching
What are methods for documenting plastic impressions?
photography, casting
What are methods for documenting latent impressions?
lifting
There are three evidentiary considerations to account for in footwear and tire
impressions what are they?
Changing Characteristics → unlike fingerprints, shoes and tires can change
Time Lapse → avoid delay to protect significance of recovery
Partial Prints and Impressions → in most causes ~70% of a partial heel print contains 10 or more times the identification points of a set of fingerprints left at a crime scene
What are the differences between prints and impressions
prints are 2d impressions are 3d
On what surfaces might you find footwear and tire impressions?
mud, dirt, snow, sand
On what surfaces might you find footwear and tire prints?
hard smooth surfaces, asphalt, concrete, flooring, etc
Define visible footwear evidence
Occurs when footwear steps into a foreign substance
and is contaminated by it, then comes into contact
with a clean surface and is pressed onto it
provide examples for what materials may create visible footwear evidence
mud, blood, sand, dust, snow etc
What types of surfaces are latent footwear impressions usually found on?
hard smooth non porous surfaces
What are the four methods of tire/footwear evidence documentation? name and describe each
photography, taking pictures/videos
sketching, self explanatory
casting, creating a mold of impression
lifting, very similar to taking finger prints
what are some reasons why footwear impressions are easily overlooked? (6)
lack of training, undervalued/not understood, belief that impressions have been walked or driven over, incomplete searches, weather, intentional destruction
What are the class characteristics of footwear evidence?
brand, size, style, possible gender
What are the class characteristics for tire evidence?
brand, radial width, tread design, tread dimension, noise treatment, wear patterns
What are the individual characteristics for footwear evidence?
cuts, scratches, gouges, tears, physical damage
what are the individual characteristics for tire impressions?
cuts, scratches, gouges, tears, physical damage, random identifying characteristics
Will tire evidence mostly consist of prints or impressions?
impressions
What is the discipline of ballistics?
the branch of physics that deals with the flight if projectiles
Difference between single action and double action (IDENTIFY PICTURES)
single = handgun cocked by drawing back hammer
double = pulling trigger both cocks and fires gun
Be able to define, differentiate, and provide examples of individual characteristics of firearms
random imperfections, number of lands/grooves, diameter/width of lands/grooves, depth of grooves, direction of rifling twist, pitch, angle of twist
What creates individual characteristics of firearms?
tool surface and manufacturing
Define caliber
determined by diameter of projectile or bore measured in 1/100th in or mm
What does caliber refer to?
designate ammunition for use in refiled firearms
How is caliber determined/measured?
powder charges and cartridge length, not size of projectile fired
What features of a gun/bullet lead to determination of caliber
diameter
What is armalite?
a rifle company
What is Armalite commonly abbreviated as?
AR
What kinds of analysis do these forensic examiners perform?
functionality examinations, examine discharged cartridges, restoring serial numbers, generate report, testify when requested
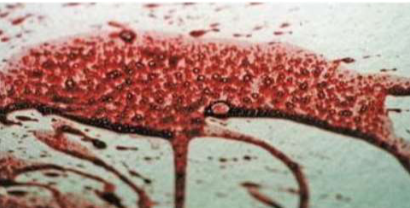
What bloodstain pattern is this?
Expiration pattern (spatter projected)

What bloodstain pattern is this?
Impact spatter

What bloodstain pattern is this?
Forward spatter (spatter impact)

What Bloodstain pattern is this?
Back spatter (spatter impact)
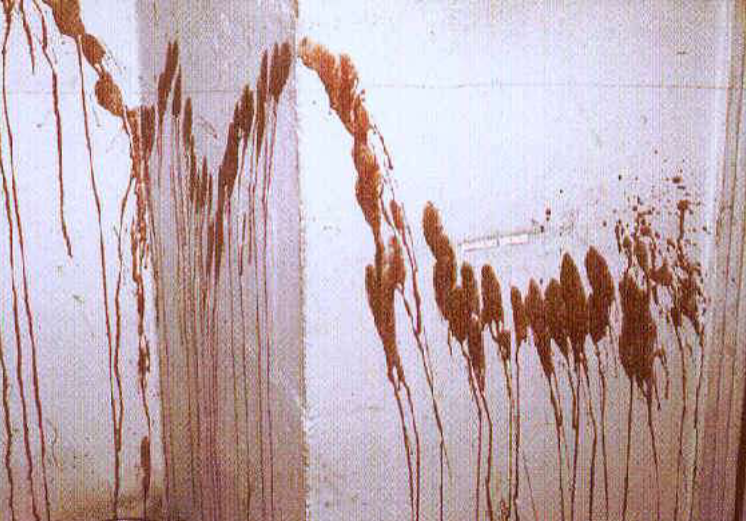

What bloodstain pattern is this?
Arterial pattern (spatter projected)
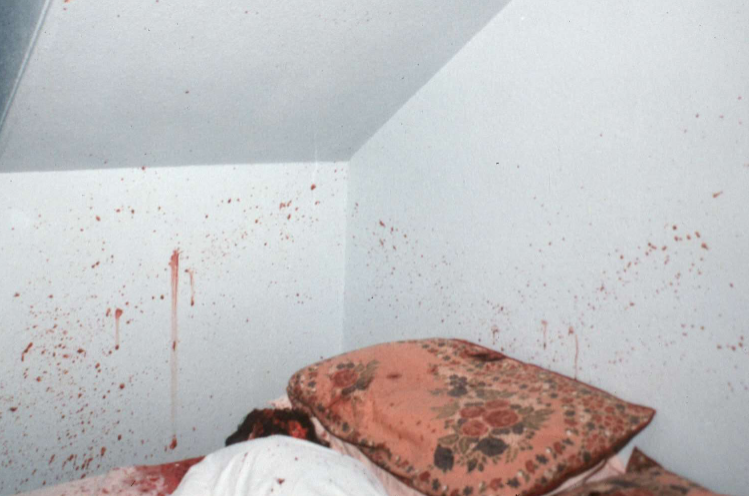

What bloodstain pattern is this?
Cast off (spatter projected)
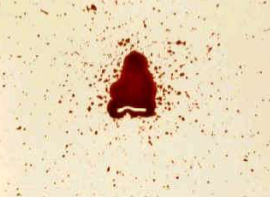
What bloodstain pattern is this?
Drip pattern (passive)

What bloodstain patterns are shown here?
a parent stain and satellite spatter (spatter secondary)
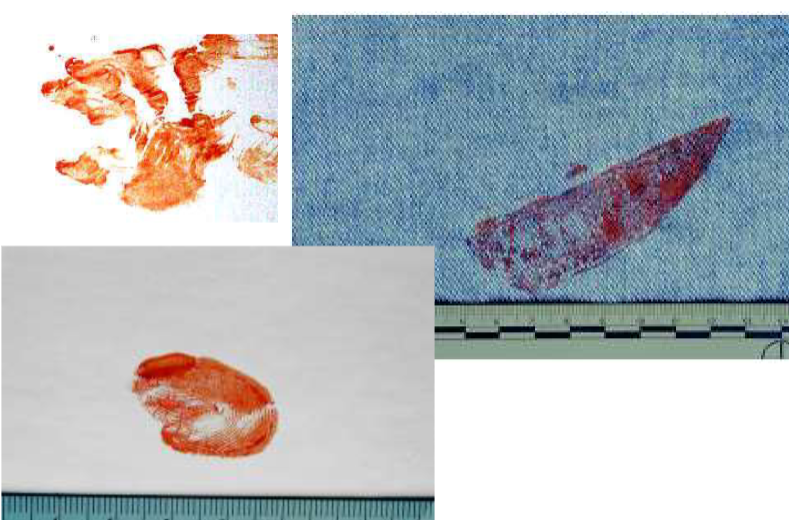
What bloodstain patterns are these?
Transfer pattern (passive)
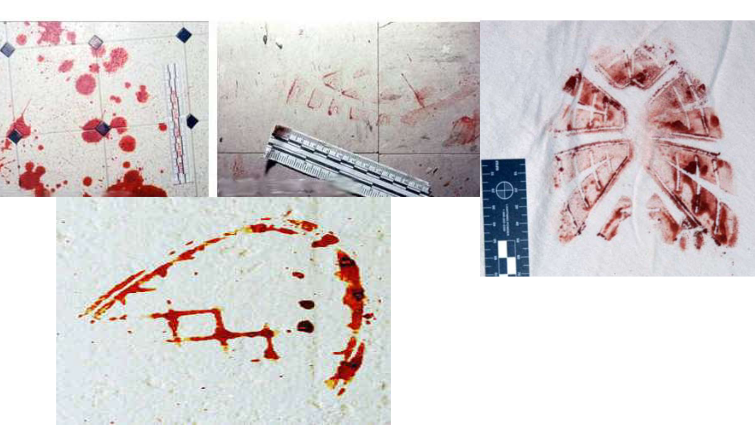
what type of bloodstain patterns are these?
Transfer pattern (passive)
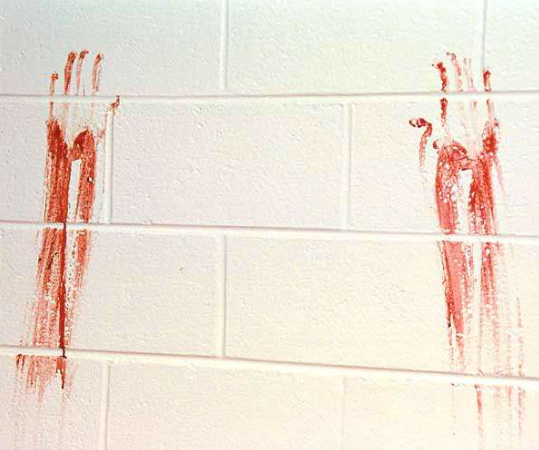

What bloodstain pattern is this?
Swipe pattern (passive)
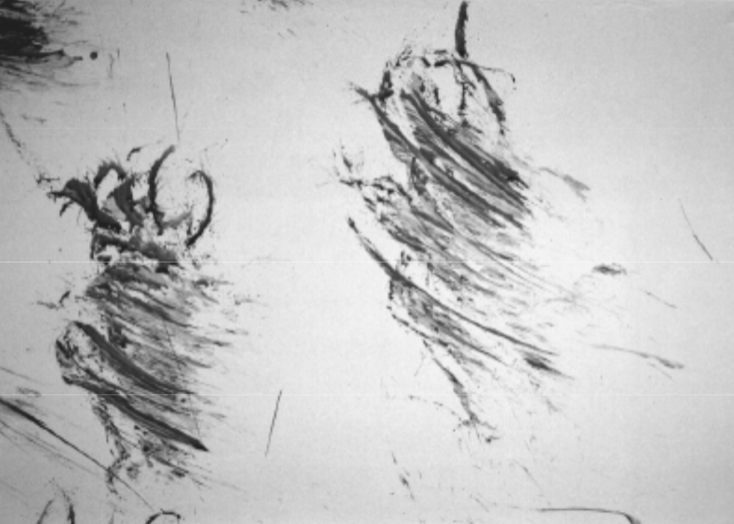
What bloodstain pattern is this?
Swipe pattern (passive)
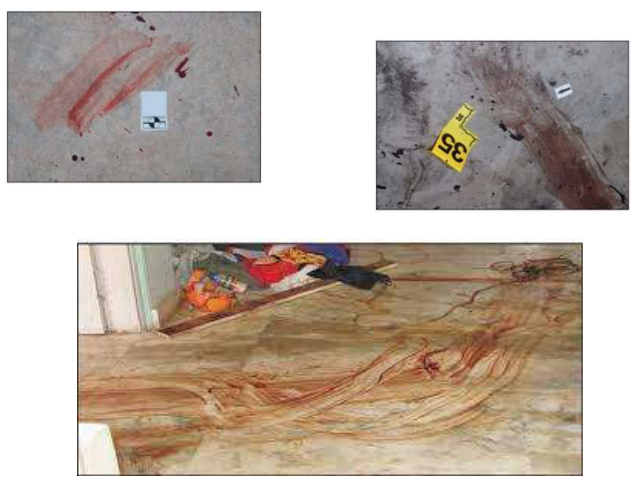

What bloodstain pattern are these?
Swipe pattern (passive)
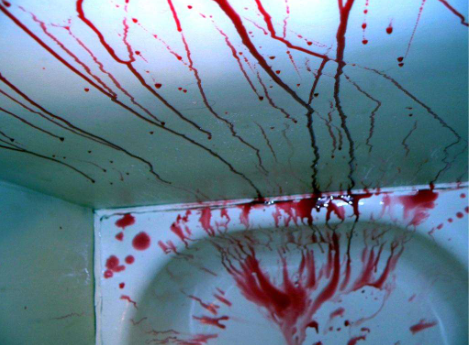
What bloodstain pattern is this?
flow pattern (passive)

what bloodstain pattern is this
flow pattern (passive)