Genetic Chapter 10, 13, 14, 20 (sec 1)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Genetic Material
information contained in genes that gets passed onto new generation
→ source of variability among organism
→ source of variability among organism
2
New cards
Criteria for Genetic Material, molecule must be able to …
(4 things)
(4 things)
1. replicate
2. store information
3. express information
4. allow variation by mutation
3
New cards
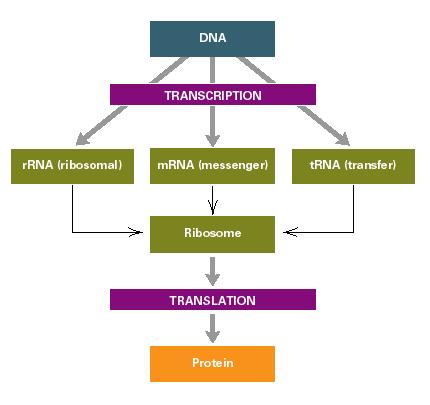
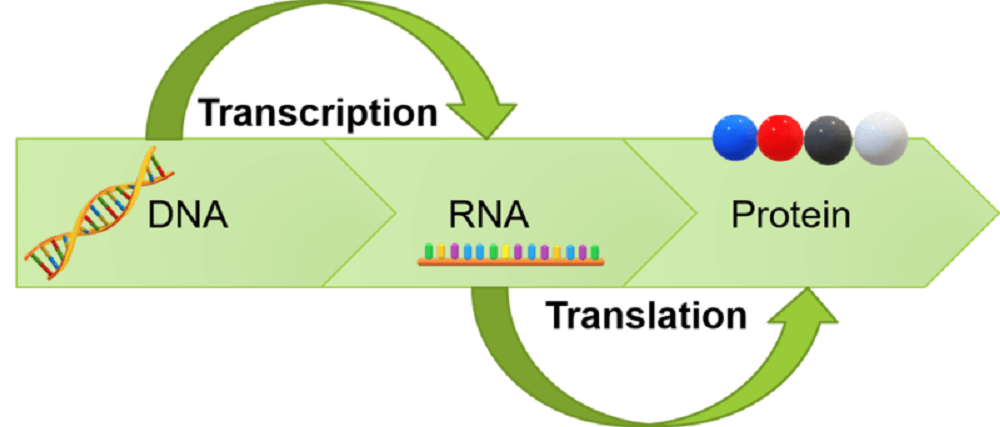
Central Dogma of molecular genetics
DNA → RNA → PROTEIN
DNA makes RNA (transcription), which makes PROTEINS (translation)
DNA → Transcription → Translation
DNA makes RNA (transcription), which makes PROTEINS (translation)
DNA → Transcription → Translation
4
New cards
In 1940s, geneticists favored ____ as genetic material
proteins
5
New cards
Proteins and _____ acids were major candidates for genetic material
nucleic
6
New cards
Proteins were diverse and abundant in ____.
cells
7
New cards
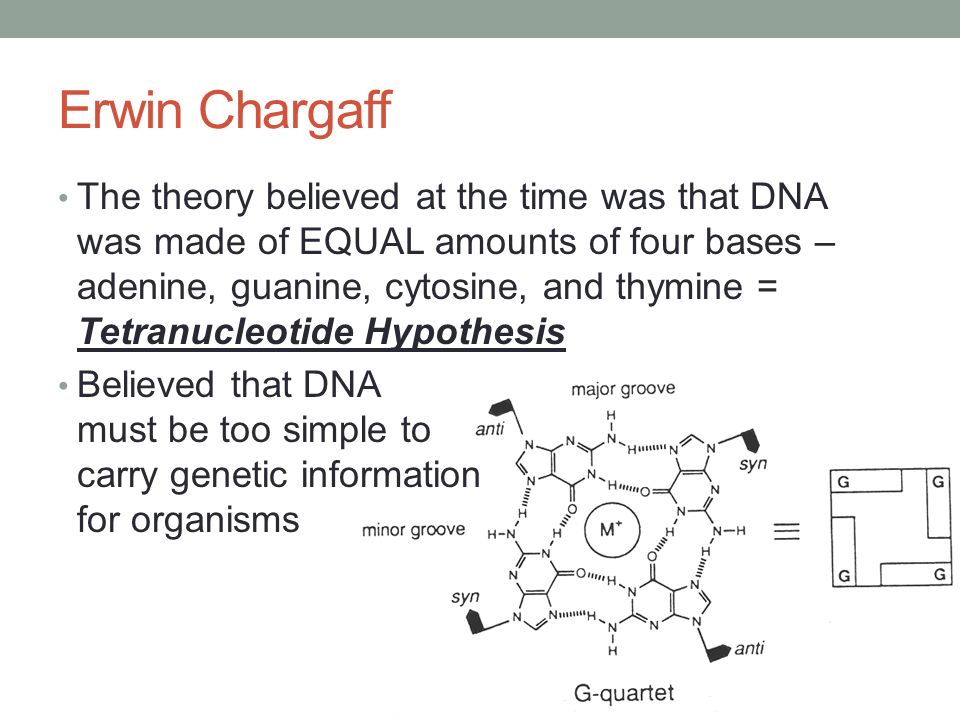
Tetranucleotide hypothesis
* Phoebus Levene
* Phoebus Levene
→ DNA contains = amounts of 4 nucleotides
→ Postulated identical groups and repeats of 4 components was basis for DNA structure
→ Lack of chemical diversity inn DNA = could not store extensive g.i.
→ Proteins favored as g.i.
→ Postulated identical groups and repeats of 4 components was basis for DNA structure
→ Lack of chemical diversity inn DNA = could not store extensive g.i.
→ Proteins favored as g.i.
8
New cards
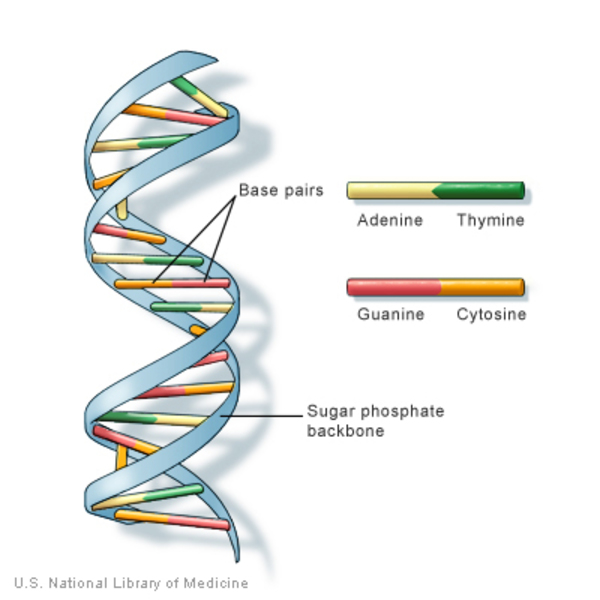
DNA
→ Composed of 2 strand (coiled) helical
→ Each strand is composed of subunits (nucleotides)
→ Each nucleotide consists of :
* 1 PENTOSE SUGAR (deoxyribose molecule)
* 1 PHOSPHATE GROUP
* 1 NITROGENOUS BASE
* adenine
* cytosine
* guanine
* thymine
→ Each strand is composed of subunits (nucleotides)
→ Each nucleotide consists of :
* 1 PENTOSE SUGAR (deoxyribose molecule)
* 1 PHOSPHATE GROUP
* 1 NITROGENOUS BASE
* adenine
* cytosine
* guanine
* thymine
9
New cards
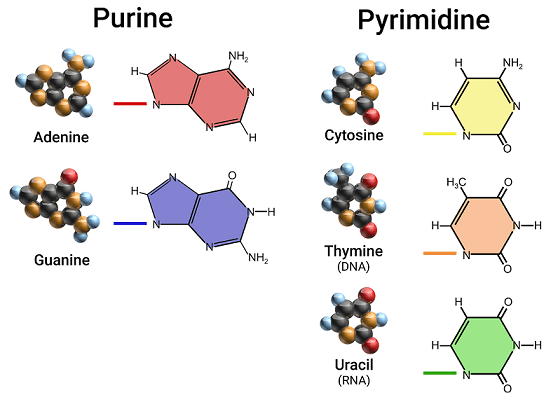
2 Kinds of Nitrogenous Bases
1. Purines (9 member ring)
2. Pyrimidines (6 member ring)
10
New cards
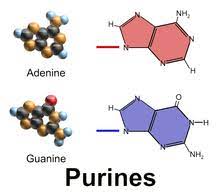
Purines - 9 member ring
→ Adenine ; A
→ Guanine ; G
→ Guanine ; G
11
New cards
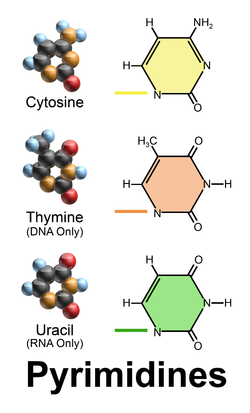
Pyrimidines - 6 member ring
→ Cytosine ; C
→ Thymine ; T
→ Uracil ; U
→ Thymine ; T
→ Uracil ; U
12
New cards
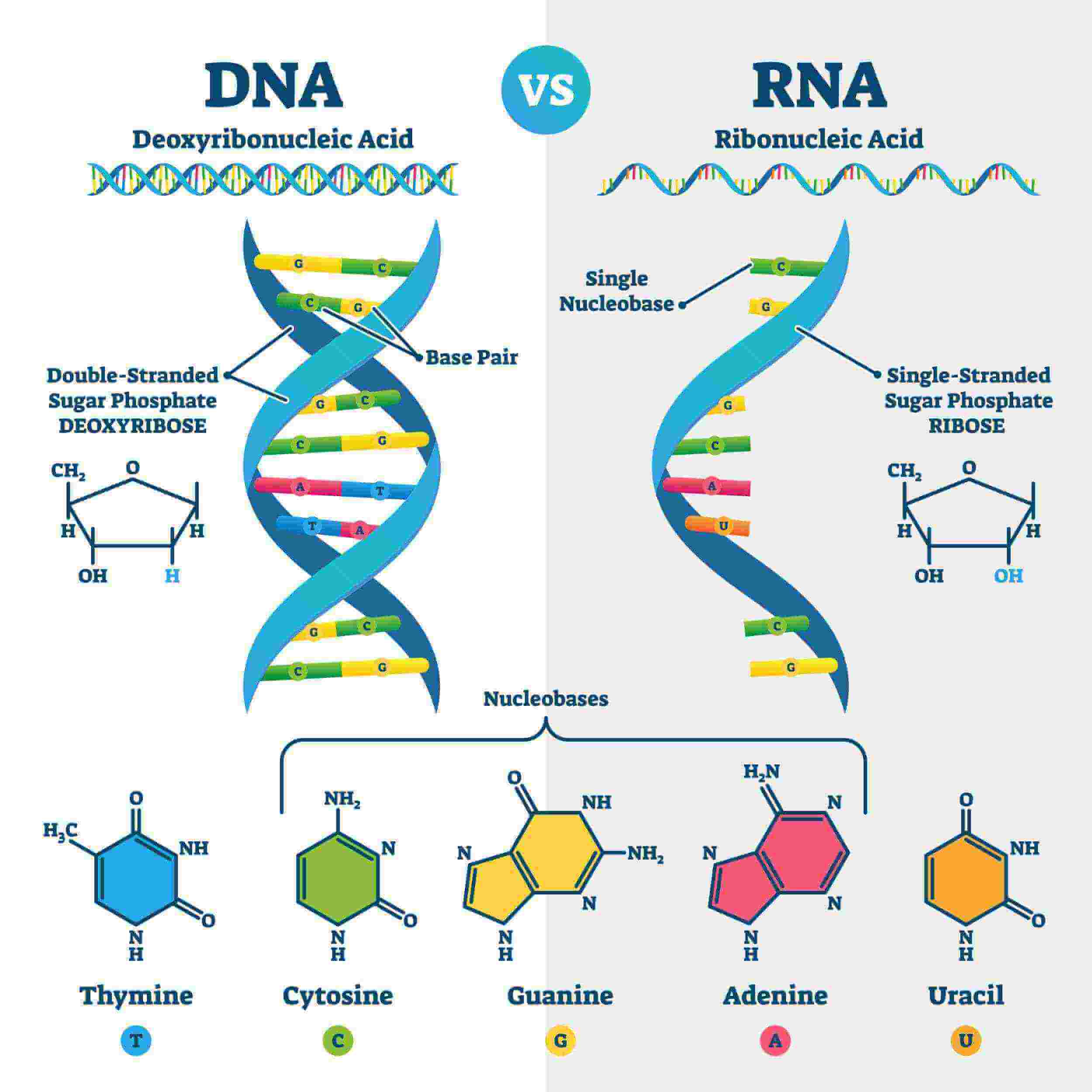
DNA contains ____
deoxyribose
* deoxy - without an oxygen
* deoxy - without an oxygen
13
New cards
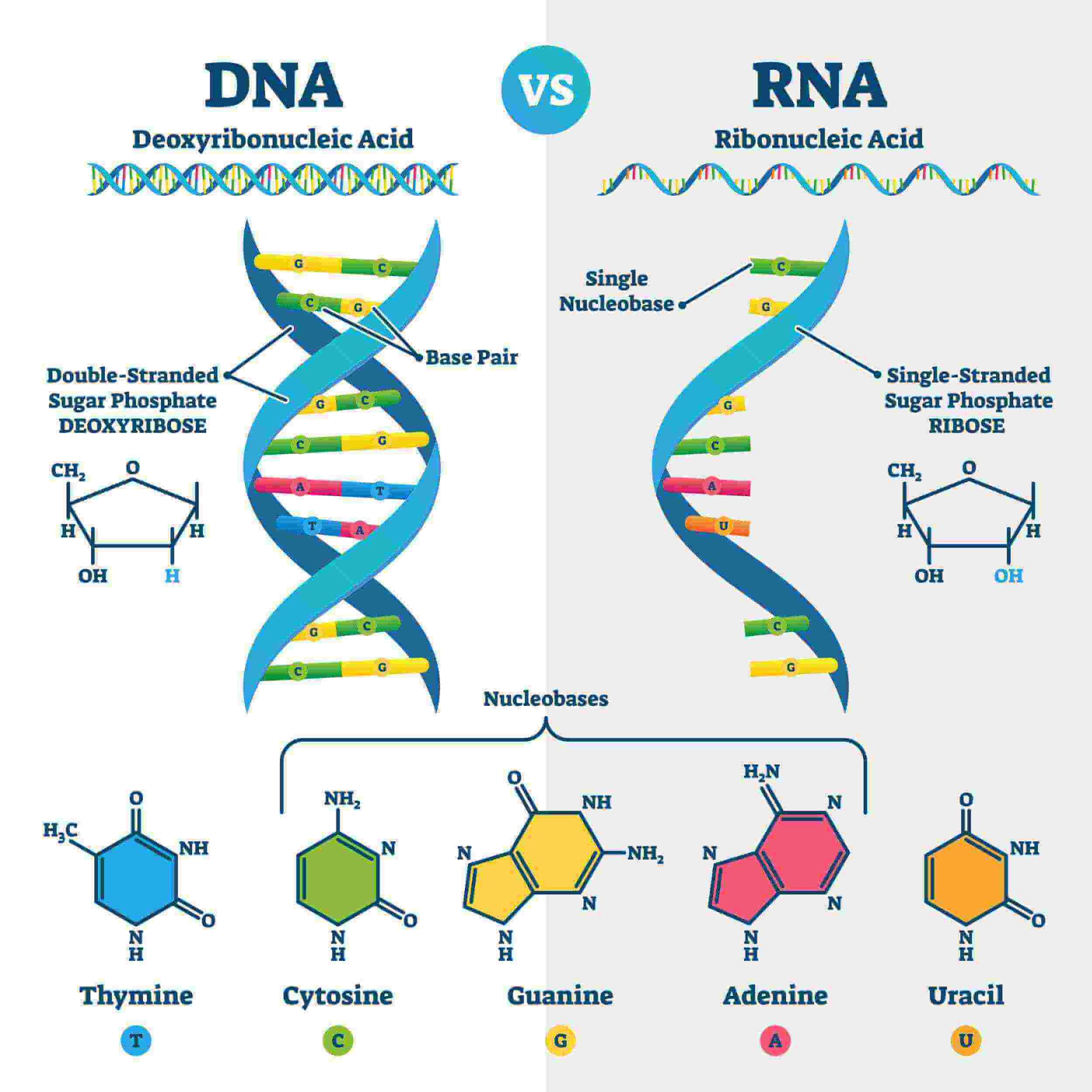
RNA contains _____ sugar
ribose
14
New cards
Bases of DNA and RNA
DNA bases ;
* A, C, T, G
RNA bases ;
* A, C, U, G
\
Only DNA contains T
Only RNA contains U
* A, C, T, G
RNA bases ;
* A, C, U, G
\
Only DNA contains T
Only RNA contains U
15
New cards
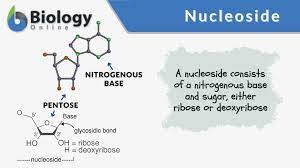
Nucleoside
→ Contains nitrogenous base & pentose sugar
→ molecule is composed of purine or pyrimidine base and ribose or deoxyribose sugar
→ molecule is composed of purine or pyrimidine base and ribose or deoxyribose sugar
16
New cards
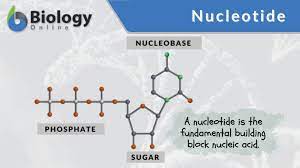
Nucleotide
→ Nucleoside with phosphate group added
17
New cards
Phosphodiester Bonds
→ Nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds between phosphate group at C - 5’ position and O H group on C - 3’ position
18
New cards
Nucleoside Monophosphates ; NMP
a nucleotide
19
New cards
Nucleoside Diphosphate ; NDP
Nucleotide with addition of 2 phosphate groups
20
New cards
Nucleoside Triphosphate ; NTP
Nucleotide with addition of 3 phosphate groups
21
New cards
Triphosphate
→ Serve as precursor molecule during nucleic acid synthesis
22
New cards
ATP and GTP
→ Adenosine triphosphate and guanosine triphosphate
→ large amount of energy involved in adding/removing terminal phosphate group
→ large amount of energy involved in adding/removing terminal phosphate group
23
New cards
Watson and Crick 1953
Proposed the structure of DNA as a double helix
24
New cards
Chargaff 1949-1953
→ Proposed base composition
→ Amount of A is proportional to T
→ Amount of C is proportional to G
→ Percentage of C + G does not equal percentage of A + T
→ Amount of A is proportional to T
→ Amount of C is proportional to G
→ Percentage of C + G does not equal percentage of A + T
25
New cards
Base composition analysis (Chargaff) and X-ray diffraction provided crucial data to _____ and Crick
Watson
26
New cards
X-ray Diffraction
→ studies by Rosalind Franklin 50-53 showed DNA had a 3.4 angstrom periodicity, characteristic of helical structure
27
New cards
Watson and Crick Model of DNA :
→ Double helix
→ 2 anti-parallel strands connected by base pairing
→ Stacked nitrogenous bases
→ 2 anti-parallel strands connected by base pairing
→ Stacked nitrogenous bases
28
New cards
Base Pairing --- Hydrogen Bonds
→ Chemical affinity produces hydrogen bonds in pair of bases
* A-T and G-C base provides complementarity of 2 strands and chemical stability to the helix
* A-T ; Double bond
* G-C ; Triple bond
* A-T and G-C base provides complementarity of 2 strands and chemical stability to the helix
* A-T ; Double bond
* G-C ; Triple bond
29
New cards
Watson and Crick : Semiconservative Model
→ Storage of genetic information in sequence of bases
→ Mutations or genetic changes that could result in alteration of bases
→ Mutations or genetic changes that could result in alteration of bases
30
New cards
Nucleotide Bonding
→ @@Each nucleotide is bound to a nucleotide on the other chain by weak hydrogen bonds between specific pairs of bases@@
→ A pairs w/ T
→ G pairs w/ C
→ 2 chains are complementary w/ opposite polarities
→ A pairs w/ T
→ G pairs w/ C
→ 2 chains are complementary w/ opposite polarities
31
New cards
Genetic Code : Translation
→ involves the synthesis of proteins consisting of a chain of amino acids whose sequence id specified by the coding information in mRNA
* mRNA carries the “genetic code” = chemical info. originating in DNA which specifics the primary structure of proteins
* mRNA carries the “genetic code” = chemical info. originating in DNA which specifics the primary structure of proteins
32
New cards
Translation of mRNA
→ Biological polymerization of amino acids into polypeptide chains
33
New cards
Translation requires : (4)
1. Amino acids
2. mRNA
3. tRNA
4. Ribosomes
34
New cards
tRNAs
→ adapt genetic information present as specific triplet codons in mRNA to corresponding amino acid
→ tRNA anticodons complement mRNAs
→ tRNAs carry corresponding amino acids
→ tRNA anticodons complement mRNAs
→ tRNAs carry corresponding amino acids
35
New cards
Ribosomes
→ Essential role in expression of genetic information
→ Consist of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNAs
→ Consists of large and small subunits
\
* Prokaryote ribosomes are 70s
* Eukaryote ribosome are 80s
→ Consist of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNAs
→ Consists of large and small subunits
\
* Prokaryote ribosomes are 70s
* Eukaryote ribosome are 80s
36
New cards
tRNAs characteristics
→ small in size and very stable
→ 75-90n nucleotides
→ transcribed from DNA
→ Contain posttranscriptional modified bases
* important for hydrogen bonding
* confer structural stability
→ tRNAs have a cloverleaf structure
→ 75-90n nucleotides
→ transcribed from DNA
→ Contain posttranscriptional modified bases
* important for hydrogen bonding
* confer structural stability
→ tRNAs have a cloverleaf structure
37
New cards
Anticodon
→ tRNA has anticodon that complementarily base-pairs w/ codon in mRNA
→ Corresponding amino acid is covalently linked to CCA sequence at 3’ end of all tRNAs
→ Corresponding amino acid is covalently linked to CCA sequence at 3’ end of all tRNAs
38
New cards
Translation
→ tRNAs are covalently attached to specific amino acids and contain anti-codon complementary to the mRNA codon
→ Base pairing between the tRNA anti-codon and the mRNA codon on the ribosome places amino acids in the correct linear sequence in translation
→ Base pairing between the tRNA anti-codon and the mRNA codon on the ribosome places amino acids in the correct linear sequence in translation
39
New cards
Translation of mRNA divides into 3 steps :
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
40
New cards
Initiation of Translation requires :
1. Small and large ribosomal subunits
2. mRNA molecule
3. GTP
4. Charged initiator tRNA
5. Mg^2+
6. Initiation factors
41
New cards
Elongation
→ Both ribosomal subunits assembled w/ mRNA
→ Forms P site and A site
→ Forms P site and A site
42
New cards
Termination
→ signaled by stop codons (UAG, UAA, UGA) in A site
→ Codons do not specify any amino acid
→ Codons do not specify any amino acid
43
New cards
GTP-dependent release factors
→ Stimulates hydrolysis of polypeptide from peptidyl tRNA - released from translation complex
44
New cards
Charging tRNA
→ Aminoacylation : tRNA charging
* before translation can proceed, tRNA molecules must be chemically linked to respective amino acids
* Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
* enzyme that catalyzes aminoacylation
→ 20 different synthetases, 1 for each amino acid
→ Highly specific; recognize only 1 amino acid
* before translation can proceed, tRNA molecules must be chemically linked to respective amino acids
* Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
* enzyme that catalyzes aminoacylation
→ 20 different synthetases, 1 for each amino acid
→ Highly specific; recognize only 1 amino acid
45
New cards
Gene Expression Principles
→ Gene expression involves processes of transcription and translation which result in the production of proteins whose structure is determined by genes