AP Psych Unit 1.1
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
nervous system
Body's communication system. Receives information form the environment (senses) and generates responses to that information (motor responses).
nerves
are bundled axons that connect the body to the brain
Afferent/Sensory Neurons
Divisions of the Nervous System: Carry messages from the senses inward to the CNS for processing
Efferent/Motor Neurons
Divisions of the Nervous System: Carry instructions from the CNS outward to the body's muscles
Interneurons
Divisions of the Nervous System: Cells in spinal cord /brain responsible for reflex arc. Connect the afferent and efferent neurons. Sensory and motor neurons don't touch.
Peripheral Nervous System
Connects the central system (brain/spinal cord) to the rest of the body
arc
Interneurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons in the spinal cord. It look like a __________.
Reflex
Simple, automatic responses to a sensory stimulus
Reflex arc
Controls knee jerk response fast reflex's
Somatic NS
Is responsible for voluntary muscle movement
Autonomic NS
Is responsible for involuntary muscle movement and internal organs
Sympathetic
Arouses the body to deal with threats/stress. Fight, flight, or freeze. Dilates pupils, inhibits salivation, heart rate increases, stimulates glucose production, and release secretion and adrenaline.
Parasympathetic
Decreasing your heart rate. Takes longer than sympathetic system.
central nervous system
The brain and spinal cord. Body's decision maker. Location of interneurons.
Brain
Is the physical organ. The central processing unit.
spinal cord
Interneurons in this link the sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) neurons.
neural networks
Are interconnected neurons that develop in the brain. They change and grow. They make the electrochemical process faster.
Endocrine system
A set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Interconnected with the nervous system.
Hormones
Chemical messengers produced by the endocrine system that flow through the bloodstream
Adrenaline
A surge of energy, known as the flight, fight, or freeze response.
Leptin
Regulates appetite
Ghrelin
Hunger arousing secreted by empty stomach
Melatonin
regulates sleep
Pituitary gland
controls other glands. Pea-sized structure in the brain near hypothalamus.
cerebral cortex
Location is the outer layer of neural tissue covering the brain. It is folded into the skull. The processing and control center of the body.
glial cells
Nourish the neurons. Important in learning and thinking.
Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
The cerebral cortex is divided into 4 lobes separated by fissures (deep grooves). Name the 4 lobes.
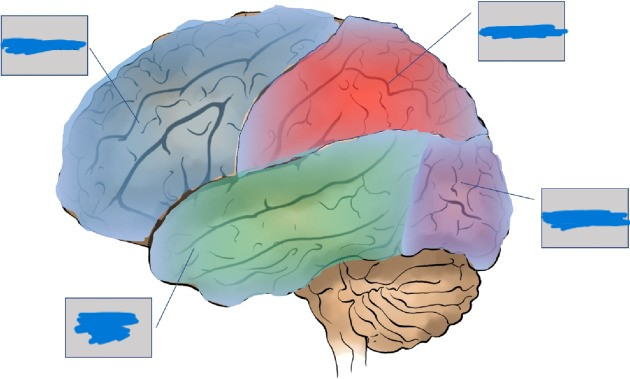
Hemispheres of the Brain: Behind the forehead. Higher order thinking. Executive function.
Frontal lobes
Hemispheres of the Brain: Top of the head. Touch and body position.
parietal lobes
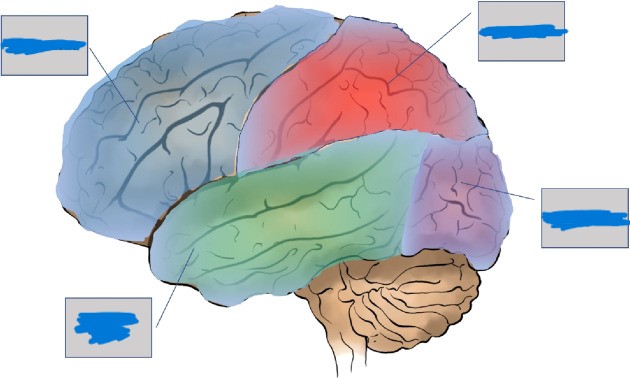
Hemispheres of the Brain: Back of the brain. Visual functions
occipital lobes
Hemispheres of the Brain: Sides of the head/behind the ears. Auditory processing.
Temporal Lobes
Corpus Callosum
Wide band of fibers that divides the right and left hemispheres. Carries messages between the 2 hemispheres.
Functions of the Cortex: Located behind the frontal lobe. Controls voluntary movements.
Motor cortex
Functions of the Cortex: Located in the parietal lobe. Processes touch sensations.
sensory cortex
Functions of the Cortex: The least understood. Control higher order functions (thinking, memory, speaking, planning). This part of the brain is distinctly different to you.
Associations Areas
Functions of the Cortex: Located in occipital lobe. Processes visual information.
Visual Cortex
Functions of the Cortex: Location is the temporal lobe. Processes sound.
Auditory Cortex
sensory; motor
Proportions in the Brain: There are no ____________ neurons in the brain; able to stimulate areas to determine function. Cortex proportions is not proportional to size of the body part. Body parts that have more control have larger ____________ cortex. Same for somatosensory cortex.
Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)
A direct communication link between the brain's electrical activity and an external device (computer or robotic arm). Thinking the words then computer program writes it on the screen.
plasticity
The brain's ability to reorganize neural pathways. Greater in younger brains. Strokes (older people not as successful). The brain does not regenerate.
hemispheric specialization
Different and specific functions performed by the two hemispheres of the brain
creativity, abstract thought, arts and music
Right hemisphere
analytic thought, language, math and science
left hemisphere
When the corpus callosum is cut there are two distinct hemispheres. This surgery is done to treat severe epilepsy. No brain function is lost, but the two hemispheres cannot communicate with one another.
Split brain research
right; left
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization (cross wiring): The left hemisphere controls the _________ side of the body, and the right side controls the __________ side.
corpus callosum
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization (cross wiring): Patients with a severed ________________ look at a dog. This creates left and right visual field.
communication
Aphasia refers to problems in ______________.
Broca's area
Located in the left frontal lobe. Speech articulation. Damage affects person's ability to form words.
Located in the left temporal lobe. Language comprehension. Damage affects ability to understand meaning of words.
Wernicke's area
behavior genetics
the study of how genes and the environment interact to influence behavior
nature
the genes we inherit determine our behavior
the environment which we live (family, culture, friends) determine our behavior
nurture
evolutionary psychology
studies inherited traits over generations and how these traits determine our behavior
natural selection
the genetic mutation of genes that help the survival of a species. Physical change of our body.
adaptation
are traits present today because in the past they helped our ancestor to survive. Ex: fears, tastes for sweets, mate selection, morning sickness in pregnant women.
twin studies
useful to research the impact of nature or nurture
identical (monozygotic)
One egg that splits in two. Genetically ____________. Egg splits in 2 weeks.
Fraternal (dizygotic)
Separate fertilized eggs. Genetically like other siblings. Some women drop 2 eggs. Body releases more than what is average. No different than siblings. Siblings are in the womb as two separate units but they don't have identical DNA.
Read about Thomas Bouchard studies identical twins raised apart.
shows the effects of environment on inherited traits
adoption studies on identical twins
gene environmental interaction
The interactions between genes and environment and how it shapes human development. Environmental influences impact development. Foods we eat, physical activities, educational opportunities etc. shape us.
Explore genetic basis of behavior by studying genetic patterns in families.
Family studies
psychiatric disorders (schizophrenia), intelligence, substance abuse and addiction, Alzheimer's disease
Give examples of genetic patterns in families.
Electrical, magnetic, lesioning
What are the three types of stimulation?
EEG (electroencephalogram)
A recording of the waves of electrical activity across the brain's surface measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. Used to diagnose epilepsy and brain death.
fMRI (functional MRI)
Shows brain activity (functions) and physical structure. Used to understand autism, panic disorder, OCD, and PTSD.
Hindbrain
Oldest part of the brain. Contains brainstem and cerebellum. Basic functions of life.
Brainstem
Hindbrain. Controls automatic survival function (breathing, blinking, heartbeat, sleep, arousal). Contains medulla and reticular activation system. Cross-wiring.
Cross-wiring
Crossover point where nerves from each side of the brain connect with the body's opposite side.
medulla
Hindbrain. Where spinal cord enters the skull. Regulates breathing and heart rate.
reticular formation
Hindbrain. Controls arousal. "Tickle" the RF you instantly wake. Remove the RF you fall into a coma. Reticular activating system control wakefulness.
The Cerebellum
Hindbrain. "Little brain." Enables non-verbal memory (muscle memory). Stores procedural memory. Coordinates voluntary movements. Impacted by alcohol = lack coordination. Ability to walk is stored in this as memory.
hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain
What are the three layers of the brain.
The limbic system
Midbrain. Regulates emotions and drives. Fear, hunger, and sex. Contains thalamus, amygdala, hypothalamus, and hippocampus.
Thalamus
Midbrain. Sensory control center. Located on top of the brain stem. Receives information from the senses except for smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal the the information.
amygdala
Midbrain. 2 almond sized neural clusters. These cluster of neurons (thalamus) is routing everything. Creates emotions such as fear, anger. Stimulate this creates aggression. Linked to the storage of emotional memories.
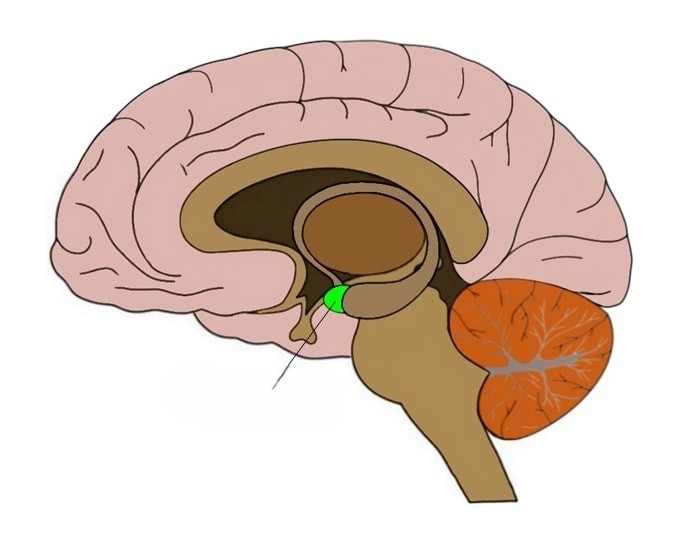
Hypothalamus
Midbrain. Body maintenance (hunger, thirst, body temperature). Reward Center.
Reward Center
Planted electrode in the hypothalamus of a rat that created pleasurable effects. Where we get that positive feeling. Dopamine is produced here.
Hippocampus
Midbrain. Processes conscious memories (explicit memories). Without this, can't form new memories.
biology perspective
Physical basis for behavior. Brain controls behavior. Behavior is inherited/genes.
Eugenics
A set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of human behavior. Mating people with specific desirable hereditary traits. Forcibly sterilize "feebleminded and socially inadequate" people.
neurons and glial cells
What are the two types of cells in neural communication?
neurons
Nerve cells in the nervous system whose function is to receive and transmit signals.
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that nourish the neurons
soma, dendrites, axon
What are the three most important parts of the neuron?
soma
cell body
dendrites
branching treelike fibers, which collects signals from other neurons and sends the down signals down the axon
axon
A long, segmented fiber, which transmits information away from the cell body toward other neurons. It is covered in the myelin sheath.
Electrochemical process
The nervous system operates using this. An electrical charge moves through the neuron then chemicals are released between neurons to transmit information.
myelin sheath
A fatty protein that encases the neurons. It speeds up the impulse of the axon. It continues to develop (age 25), so neural efficiency continues to improve. Deterioration of this can lead to motor impairments.
multiple sclerosis
Problems in Neural Communication: Myelin sheath degenerates. Communication to the muscles slow, with eventual loss of muscle control. Lesions form (brain has been damaged).
Myasthenia Gravis
Problems in Neural Communication: Nerve-muscle autoimmune disease. Body destroys acetylcholine (neurotransmitter). Communication between nerves and muscles breaks down.
Resting Potential
Neural Impulse: When there is no input; it is waiting for a stimulus ( electrical process). The neuron is polarized. Outside of axon is positively charged. Inside of axon is negatively charged.
Action Potential
Neural Impulse: Neuron sends the impulse down the neuron's axon. Occurs when a neuron receives enough stimuli to pass on the electrical signal. One neuron fires the impulse to the next neuron in the link. The neuron is depolarized.
Depolarization
Neural Impulse: Occurs when + ions enter the - charged axon and create a reaction.
Refractory period
Neural Impulse: The neuron must re-set in order to receive another stimuli. It cannot fire during this period. During this period, the neuron pumps to the positively charged sodium back outside the cell. The neuron is repolarizing.
All or none response
The neuron cannot fire until there are enough excitatory stimuli. It does not fire faster with more excitatory signals. Ex: flushing a toilet; it flushes or it doesn't. When the threshold is met an action potential is triggered.
excitatory
These impulses increase the action potential
inhibitory
These impulses slow the action potential.
action
When the excitatory impulses outnumber the inhibitory impulses, the threshold has been reached a _____________ potential occurs.