2.2 - profit maximization, PED, PES, YED,
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
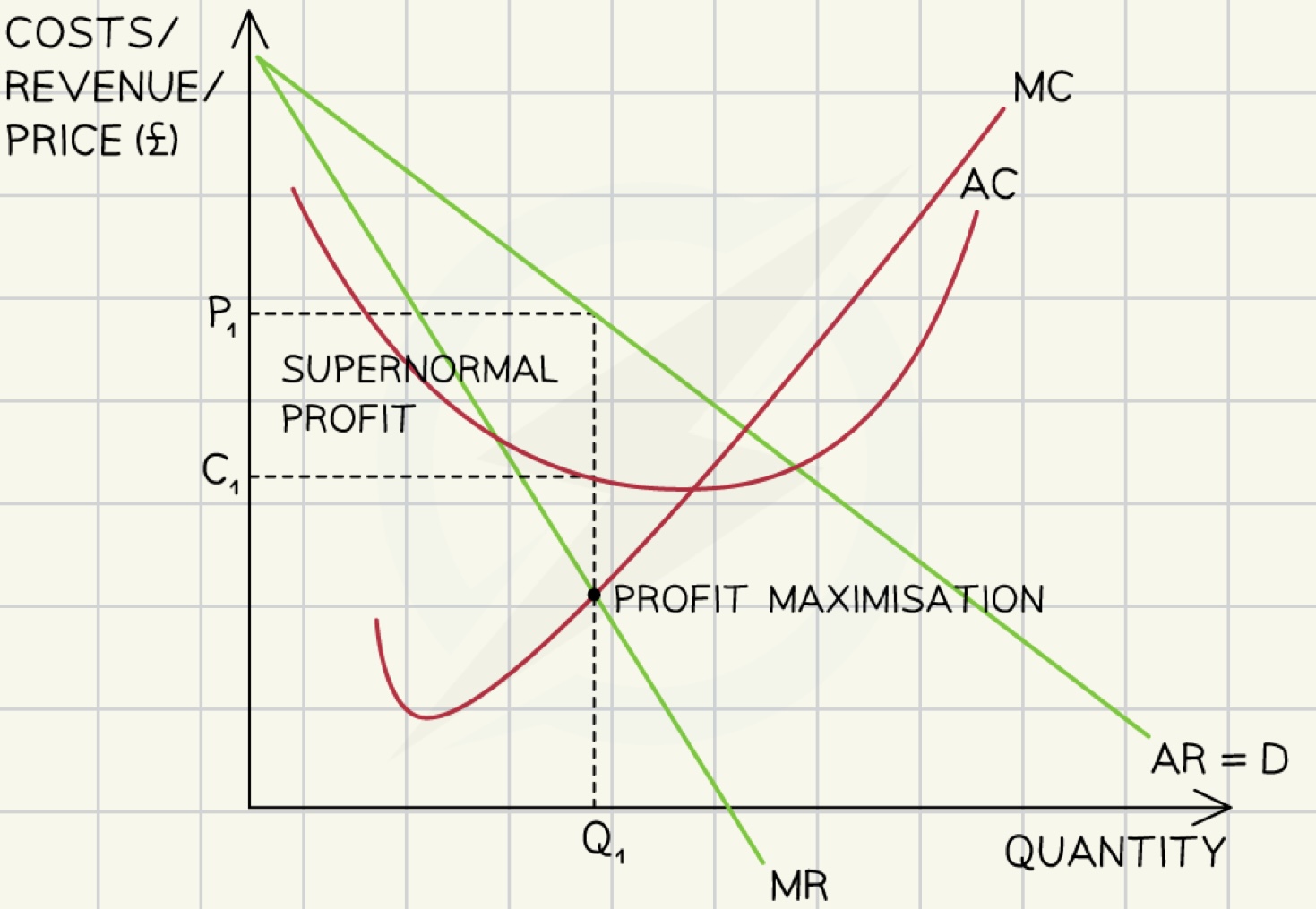
profit maximization
most effective level of production and pricing strategy.
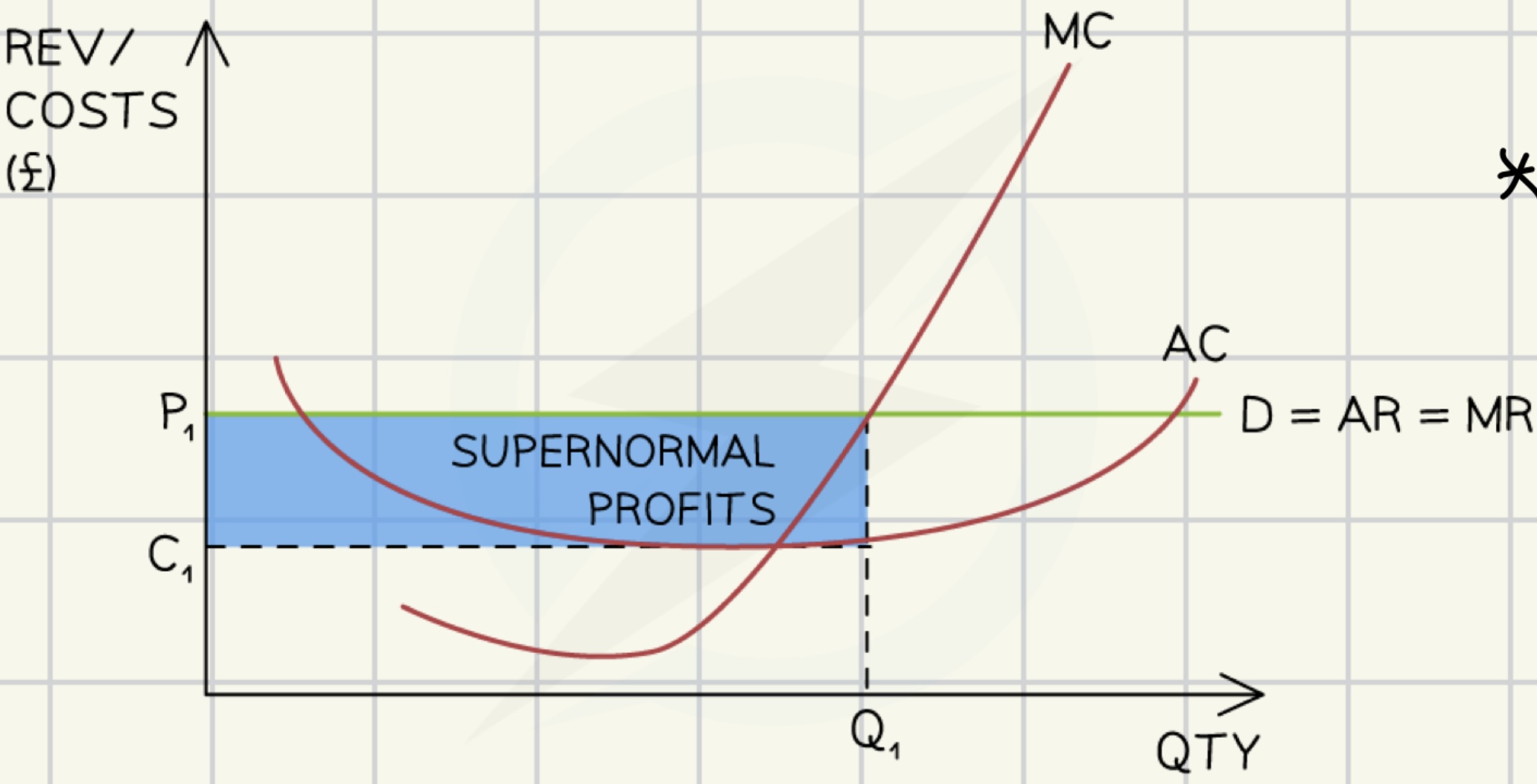
marginal costs = marginal revenue
→ beyond this point with each unit produced marginal loss occurs
p1 = selling price
c1 = average cost
advantages of profit maximization
enables financial stability and growth
enhances shareholder values
efficient allocation of resources
drives innovation and competitiveness
disadvantages of profit maximization
ethical and social concerns
may neglect long-term sustainability and employee welfare.
lack of knowledge about the point of profit maximization
often results in higher prices for consumers
growth
increase in the capacity of an economy to produce goods and services
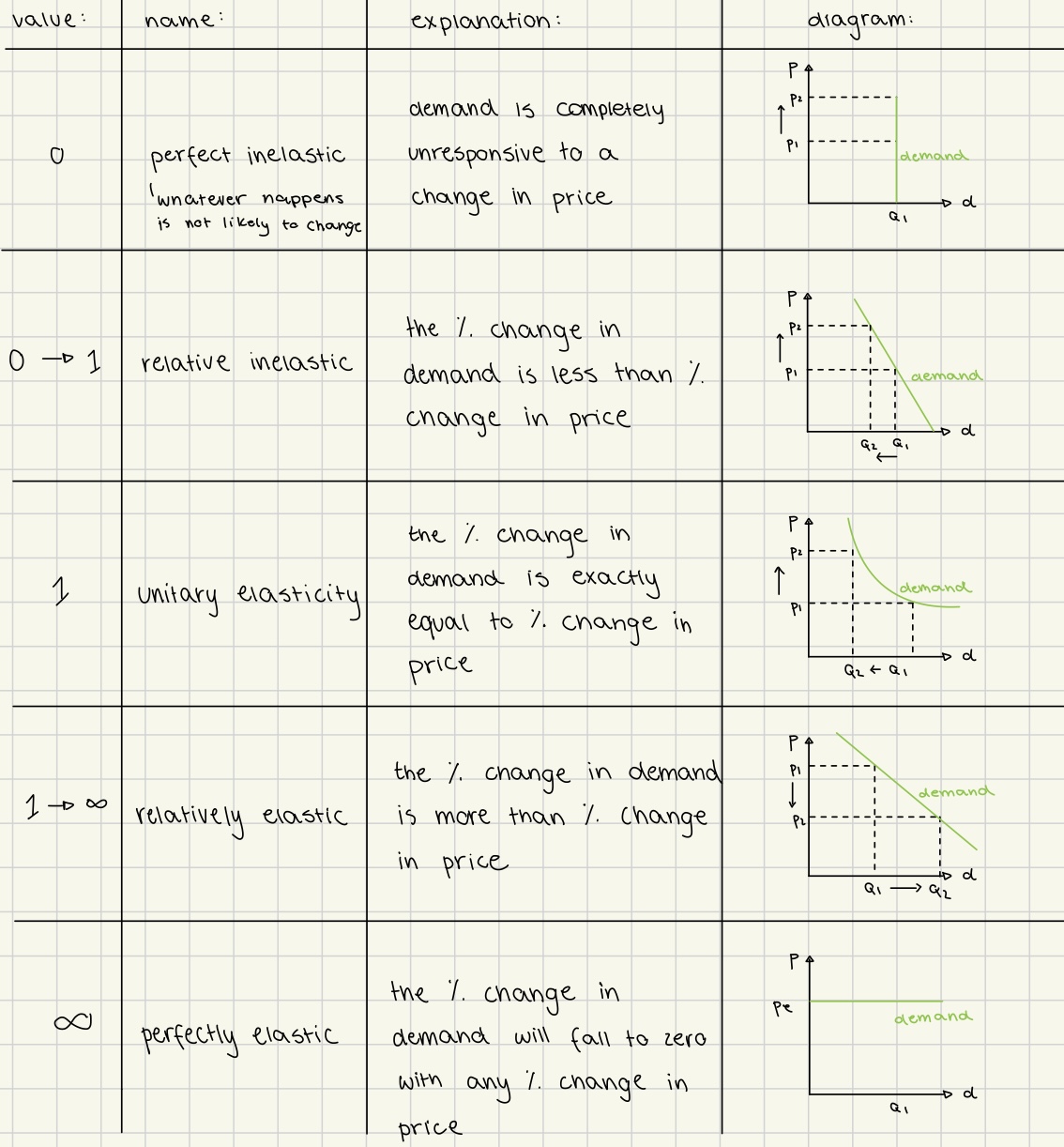
price elasticity of demand
measure of how responsible the quality demanded is to a change in its price
indicates consumers’ sensitivity to price changes
price↑ = demand ↓
price elasticity of demand formula
PED = % change in quantity demanded / % change in price
interpreting PED values
determinants of PED
availability of substitutes ↑ = PED ↑
addictiveness of the product ↑ = PED↓
price of products as proportion of income ↓ = PED ↓
consumers are less responsive to price changes of cheap products
time period
short term = low PED
long term = high PED
total revenue rule
to maximize revenue businesses should
increase the price of products that are inelastic in demand
big increase in price results in small decrease in demand
decrease the price of products that are elastic in demand
small decrease in price results in big increase in demand
income elasticity of demand YED
measures the responsiveness of demand for a product to changes in consumer income
positive YED indicates that a good is a normal good,
negative YED signifies an inferior good.
influenced by factors that affect the wages
minimum wage
taxes
YED formula
YED = % change in quantity demanded / % change in income
YED values
inferior goods
YED<0
income ↑ = demand ↓
normal goods
YED>0
income↑ = demand↑
luxury goods
YED> 1
income↑ = demand↑↑
price elasticity of supply PES
measures the responsiveness of the quantity supplied of a good to changes in its price.
higher PES value indicates that supply is more responsive to price changes.
PES formula
PES = % change in quantity supplied / % change in price
PES values
0 → perfectly inelastic/ unresponsive
0-1 → relatively inelastic
1→ relatively elastic
1-∞→ perfectly elastic/fully responsive
determinants of PES
production time ↑= PES↑
availability of resources↑ = PES ↑
profit maximisation
profit = marginal (total) revenue - marginal (total) costs
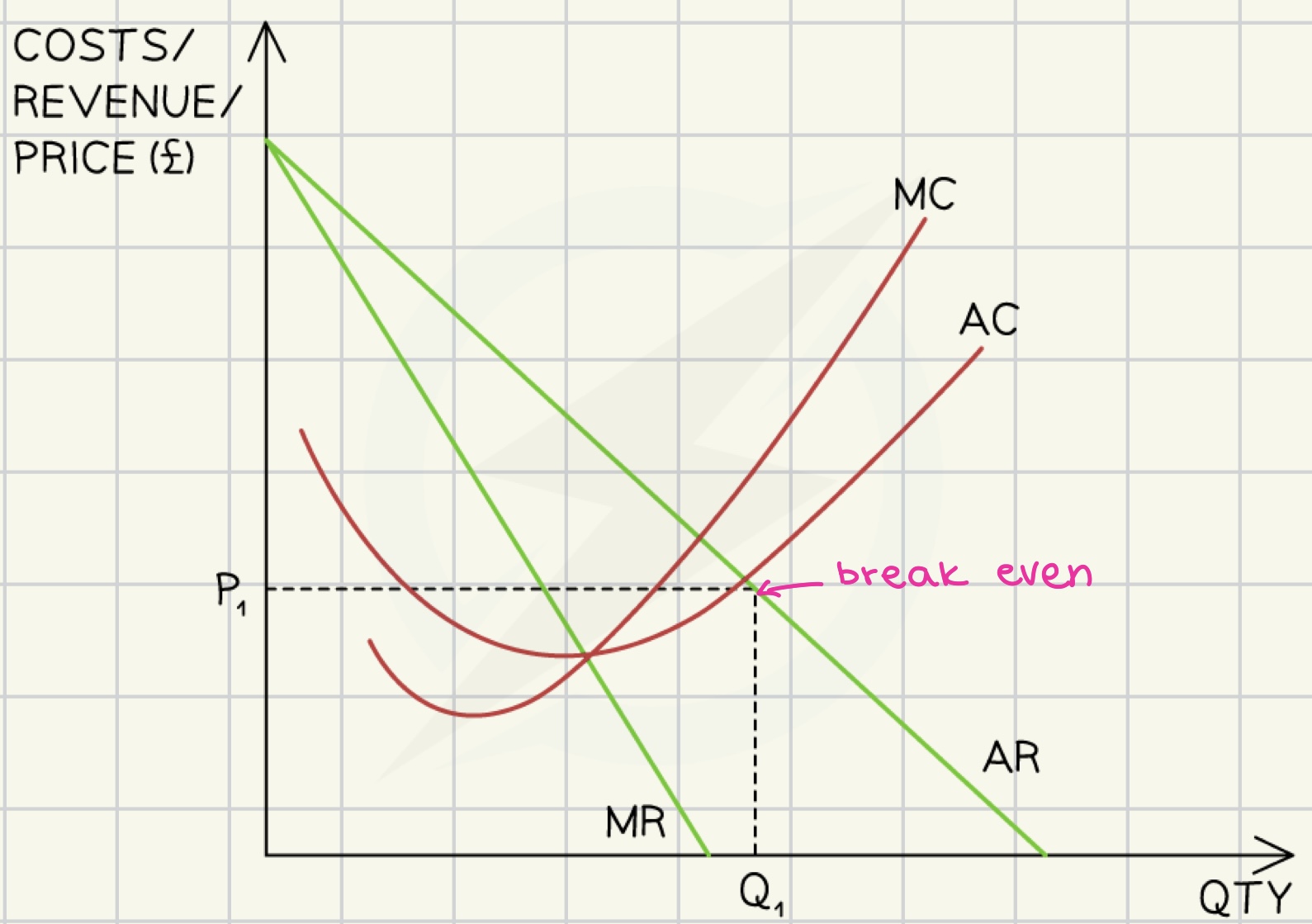
break even/ normal profit
total revenue = total costs
abnormal profit
total revenue > total costs
profit loss
total revenue < total costs
profit maximisation rule
a firm should continue producing additional units until
marginal costs MC = marginal revenue MR