Ancient Egypt: Old and Middle Kingdom
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
River Nile
Crucial for agriculture and transportation in Egypt.
Polytheistic Society
Belief in multiple gods influencing daily life.
Absolute God-King
Pharaoh held ultimate power and divine status.
Old Kingdom
Period from 2686 to 2125 BCE in Egypt.
Middle Kingdom
Era of prosperity from 2040 to 1640 BCE.
New Kingdom
Period from 1550 to 1070 BCE, marked by expansion.
Baked Mud Brick
Common construction material for homes and walls.
Monumental Stone Construction
Durable building material for temples and pyramids.
Mastaba Tombs
Early tombs with flat roofs and mud brick.
Interior Decorations
Colored carvings depicting daily life for deceased.
Deep Shaft
Added to tombs to deter grave robbers.
Pyramids
Tombs symbolizing rebirth and divine power.
Mortuary Temple
Site for rituals associated with the deceased.
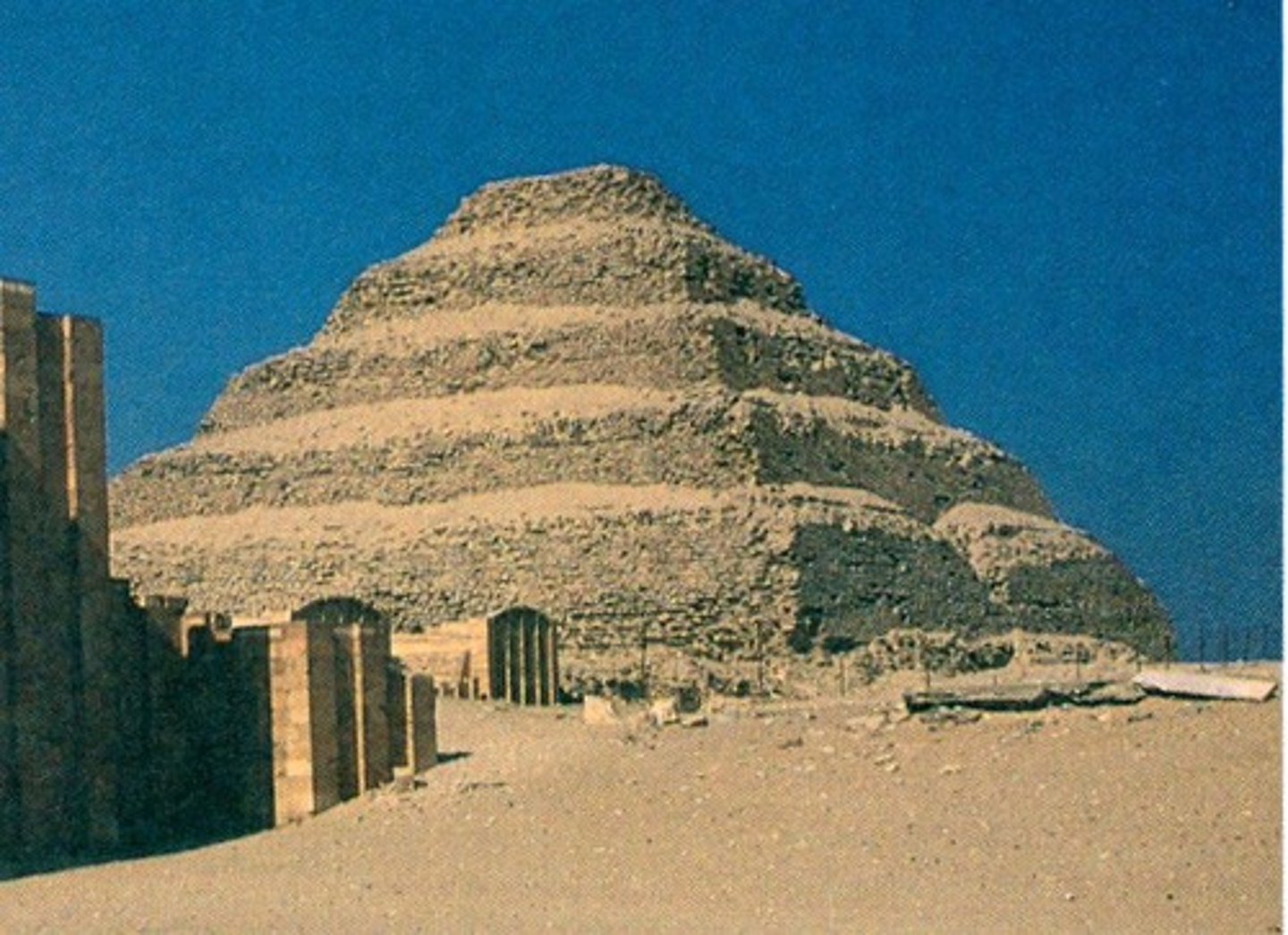
Stepped Pyramid of Djoser
First monumental stone structure, designed by Imhotep.

Angle of Repose
Critical for pyramid stability in construction.
Bent Pyramid
Pyramid with an unusual angle, built by Snefru.
Great Pyramid of Khufu
Largest pyramid, built with 2.3 million limestone blocks.
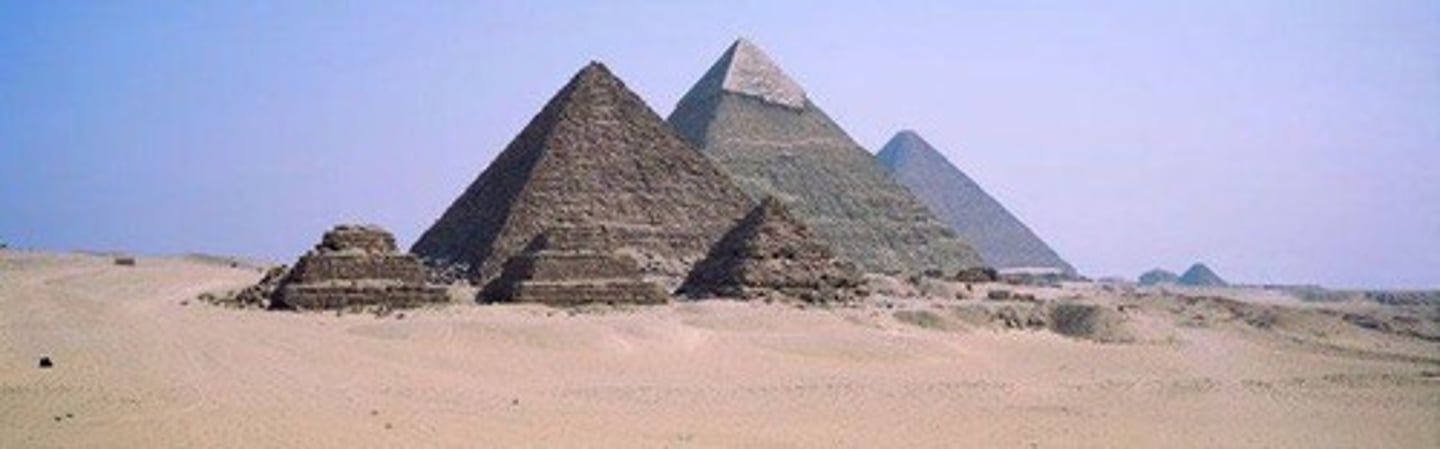

Khafre Pyramid
Notable for surviving smooth limestone apex.
Menkaure Pyramid
Incomplete pyramid due to the pharaoh's early death.
Hypostyle Halls
Large halls supported by columns, enhancing ritual atmosphere.
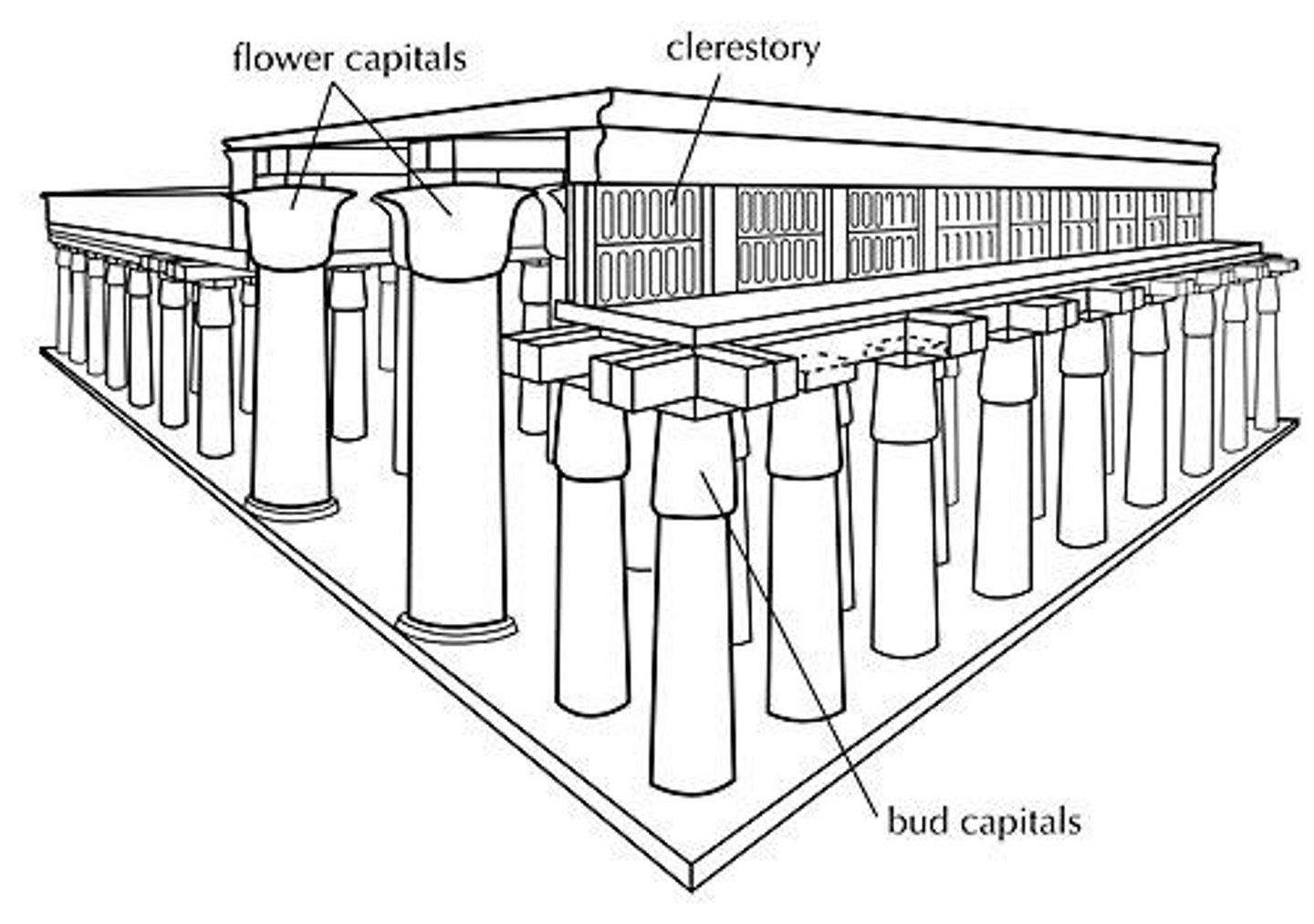
Post and Lintel System
Construction method using vertical posts and horizontal beams.
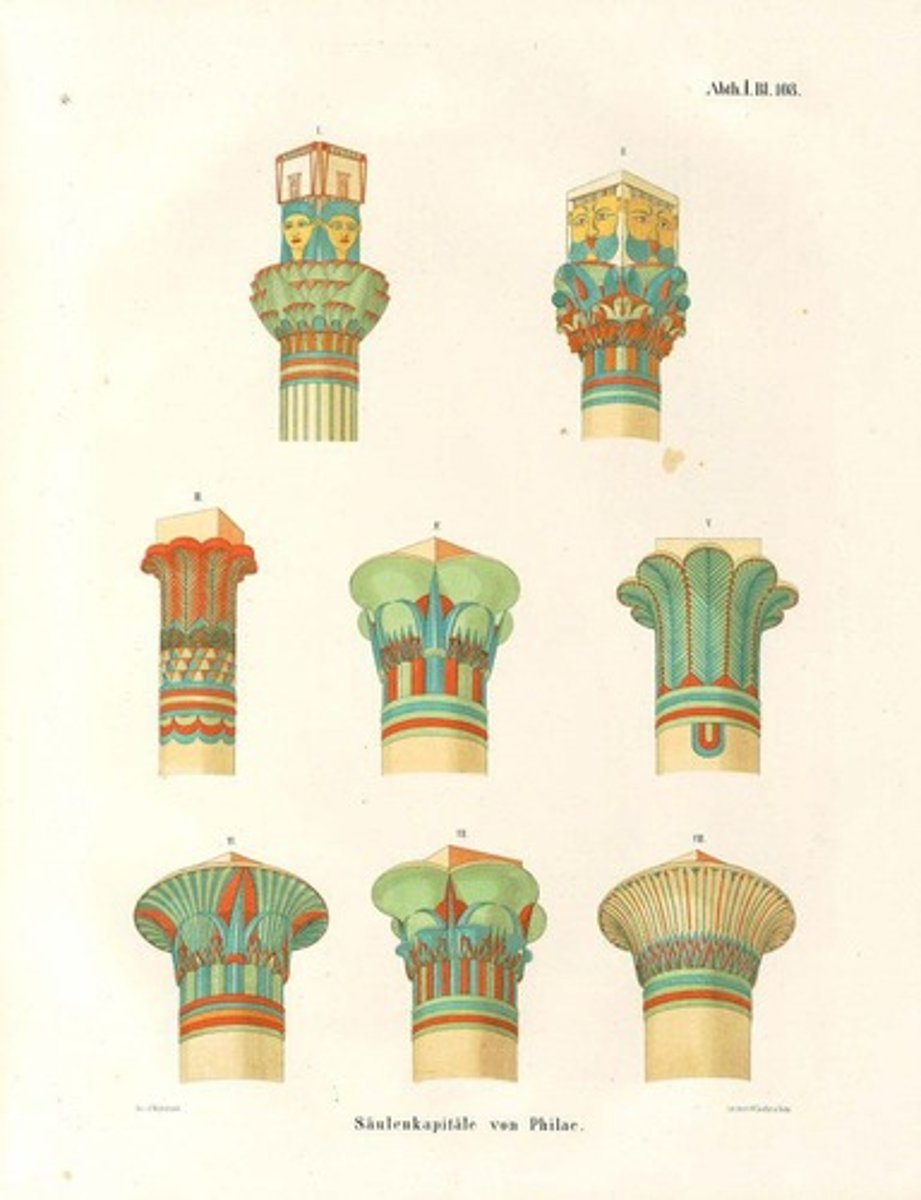
Flower/Bud Capitals
Column tops designed to resemble papyrus plants.

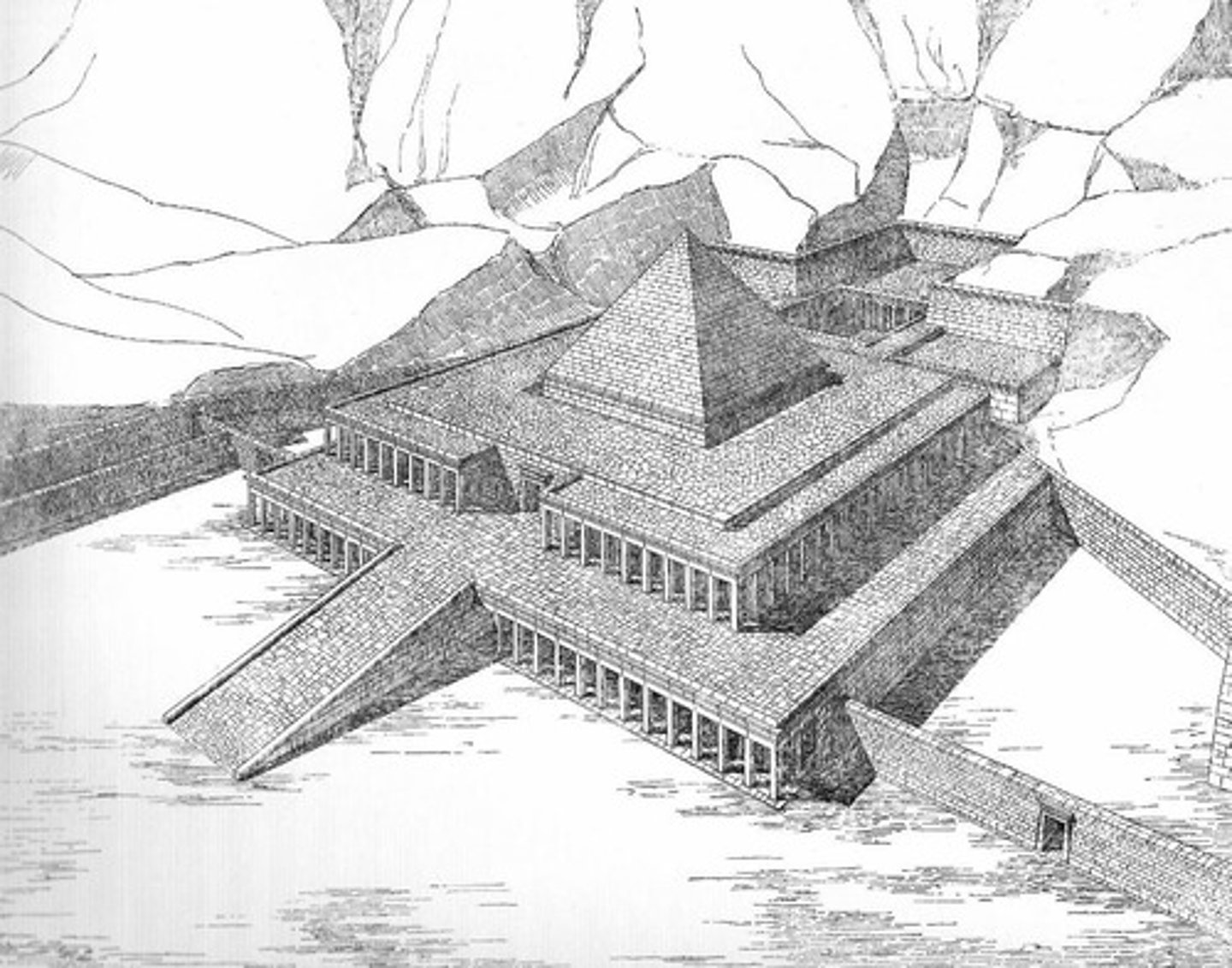
Tomb of Mentuhotep
Notable for its conjectural pyramid and column spacing.