Overview of the Male and Female Reproductive Systems
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Gonads
Primary sex organs: testes and ovaries.
Gametes
Sex cells produced by gonads.
Sperm
Male gametes produced by testes.
Ova
Female gametes produced by ovaries.
Steroid sex hormones
Hormones secreted by gonads.
Androgens
Male steroid hormones, primarily testosterone.
Estrogens
Female steroid hormones, regulate reproductive functions.
Progesterone
Hormone involved in menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Accessory reproductive organs
Ducts, glands, and external genitalia.
Sex hormones functions
Influence reproductive organs, behavior, and growth.
Testes
Male gonads located in the scrotum.
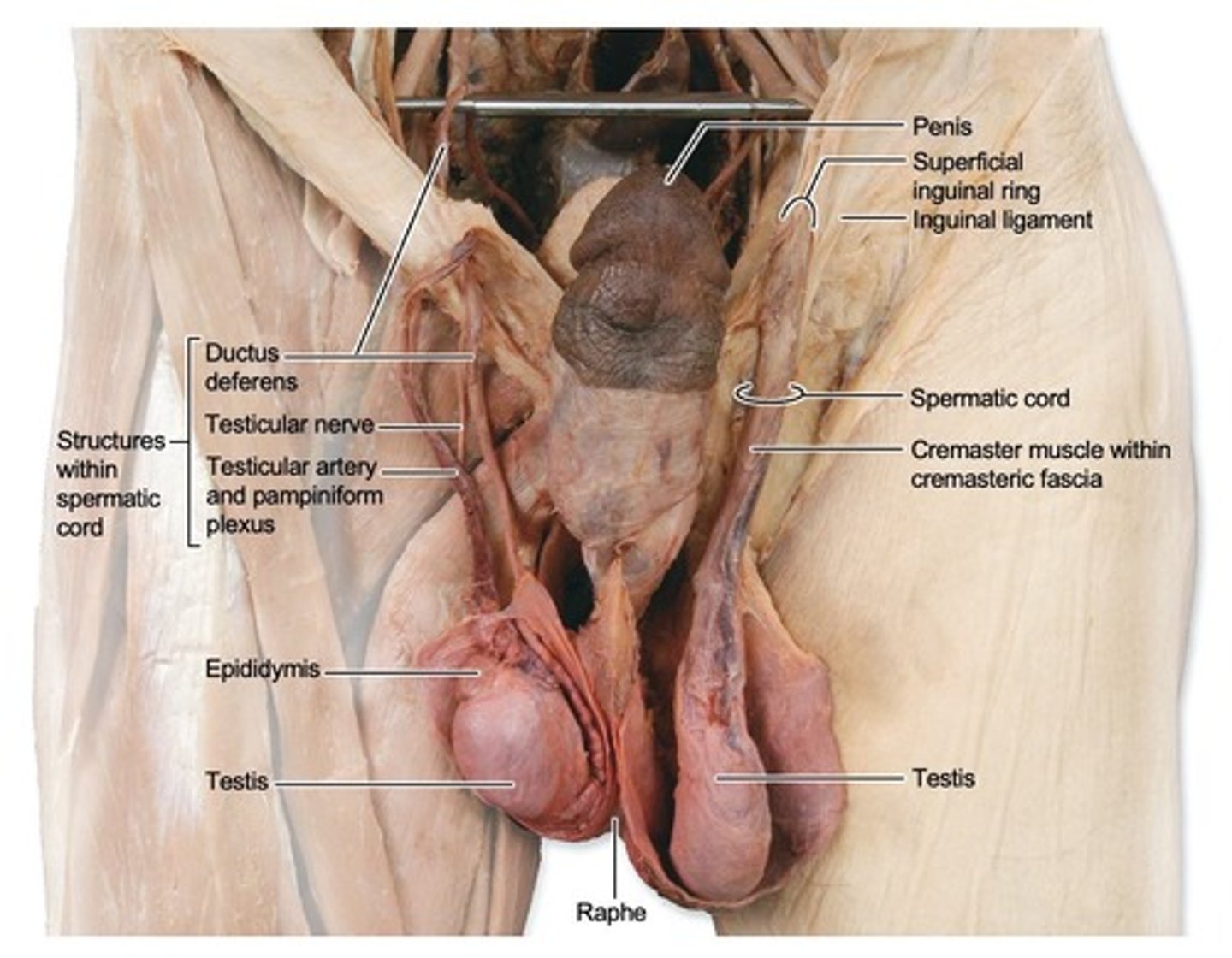
Epididymis
Duct where sperm mature and gain motility.
Ductus deferens
Tube transporting sperm from epididymis.
Ejaculatory duct
Duct merging sperm and seminal fluid.
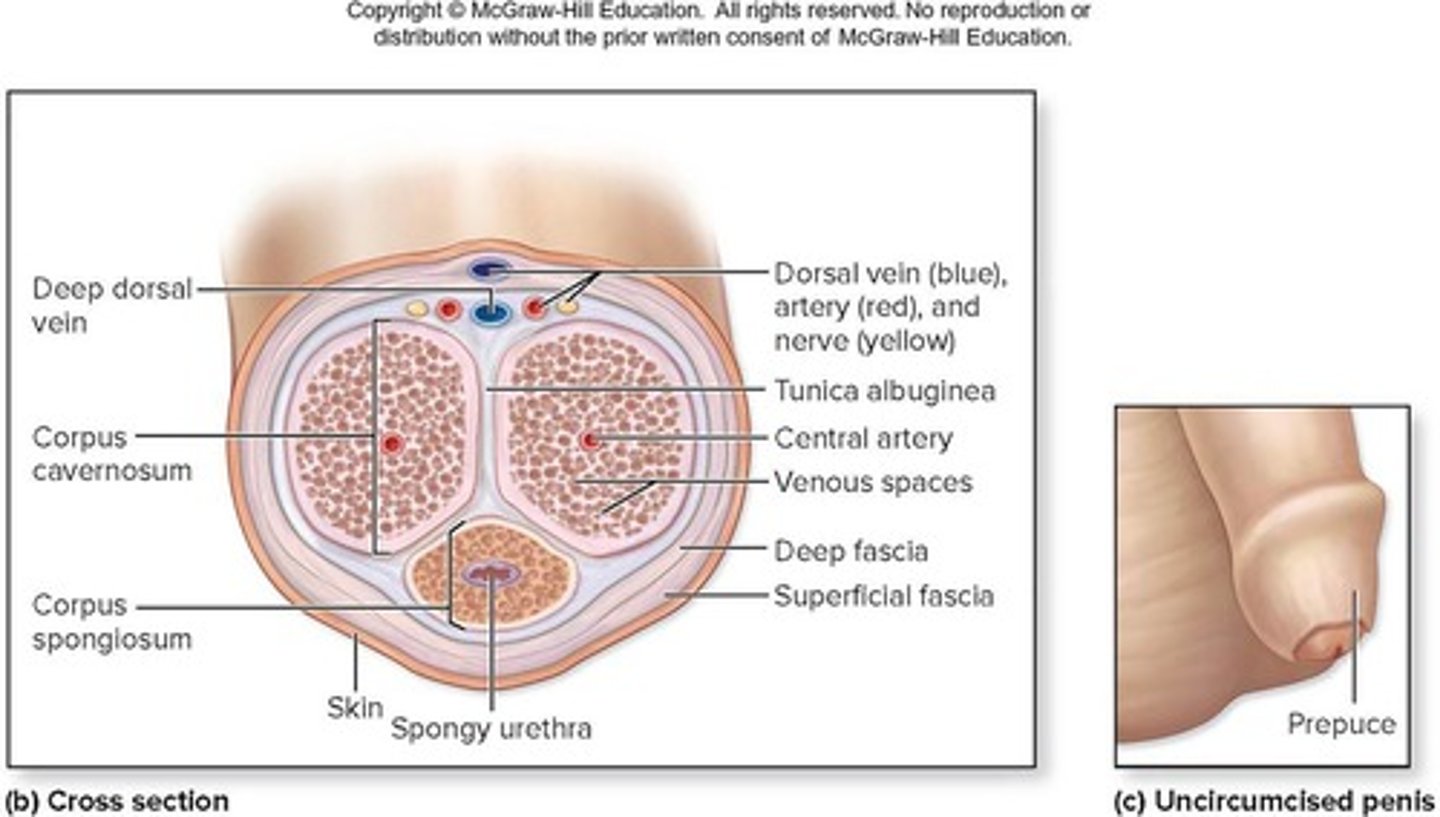
Urethra
Conveys urine and semen externally.
Scrotum
Skin sac housing the testes.
Dartos muscle
Smooth muscle that wrinkles scrotal skin.
Cremaster muscles
Skeletal muscles elevating the testes.
Tunica vaginalis
Outer tunic of the testes, derived from peritoneum.
Tunica albuginea
Fibrous capsule surrounding each testis.
Interstitial cells
Leydig cells producing androgens outside seminiferous tubules.
Corpus spongiosum
Erectile tissue surrounding the urethra.
Corpora cavernosa
Paired erectile tissues forming the penis.
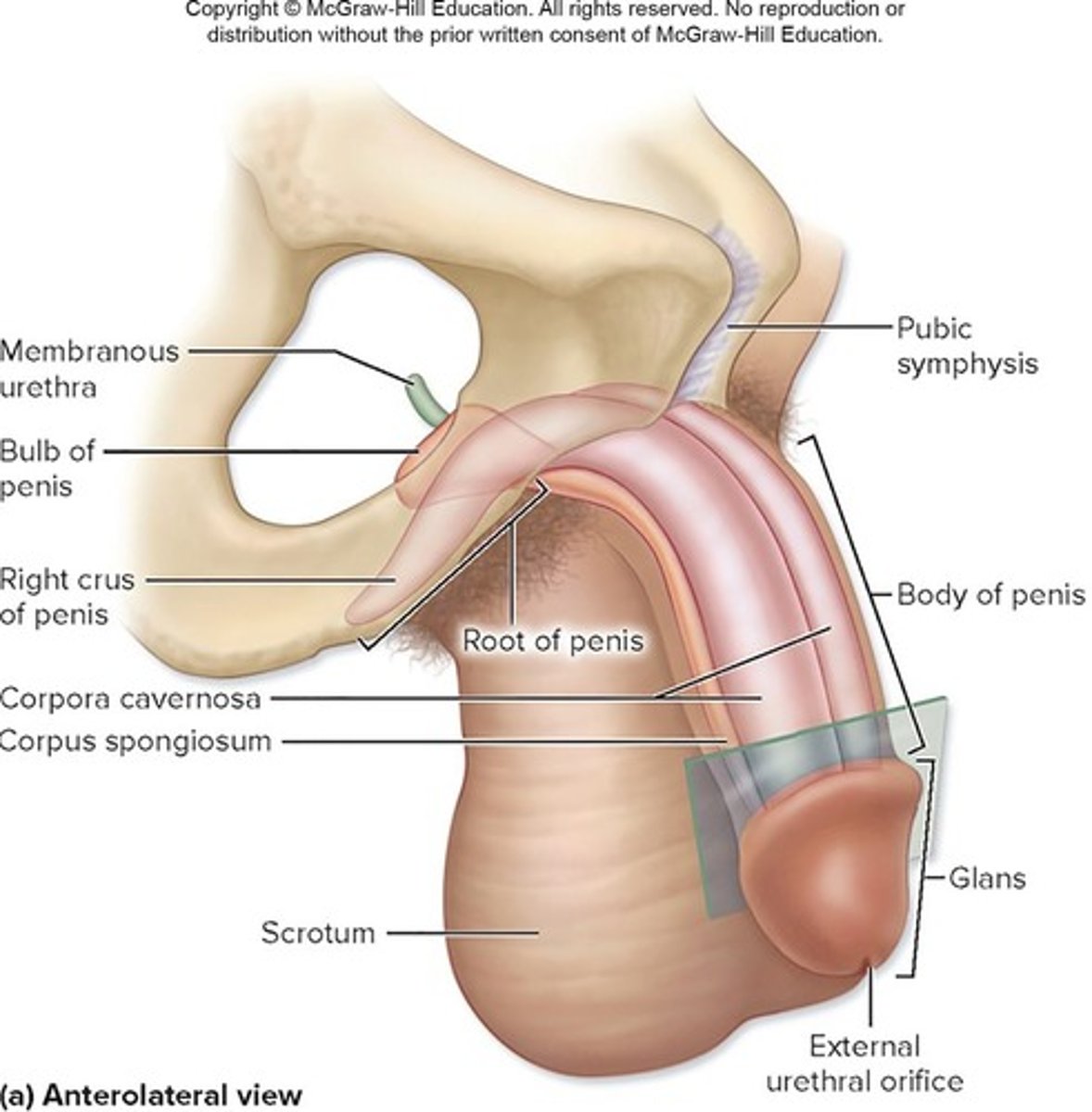
Erection
Blood fills erectile tissue, enlarging the penis.
Seminal vesicles
Glands secreting alkaline seminal fluid.
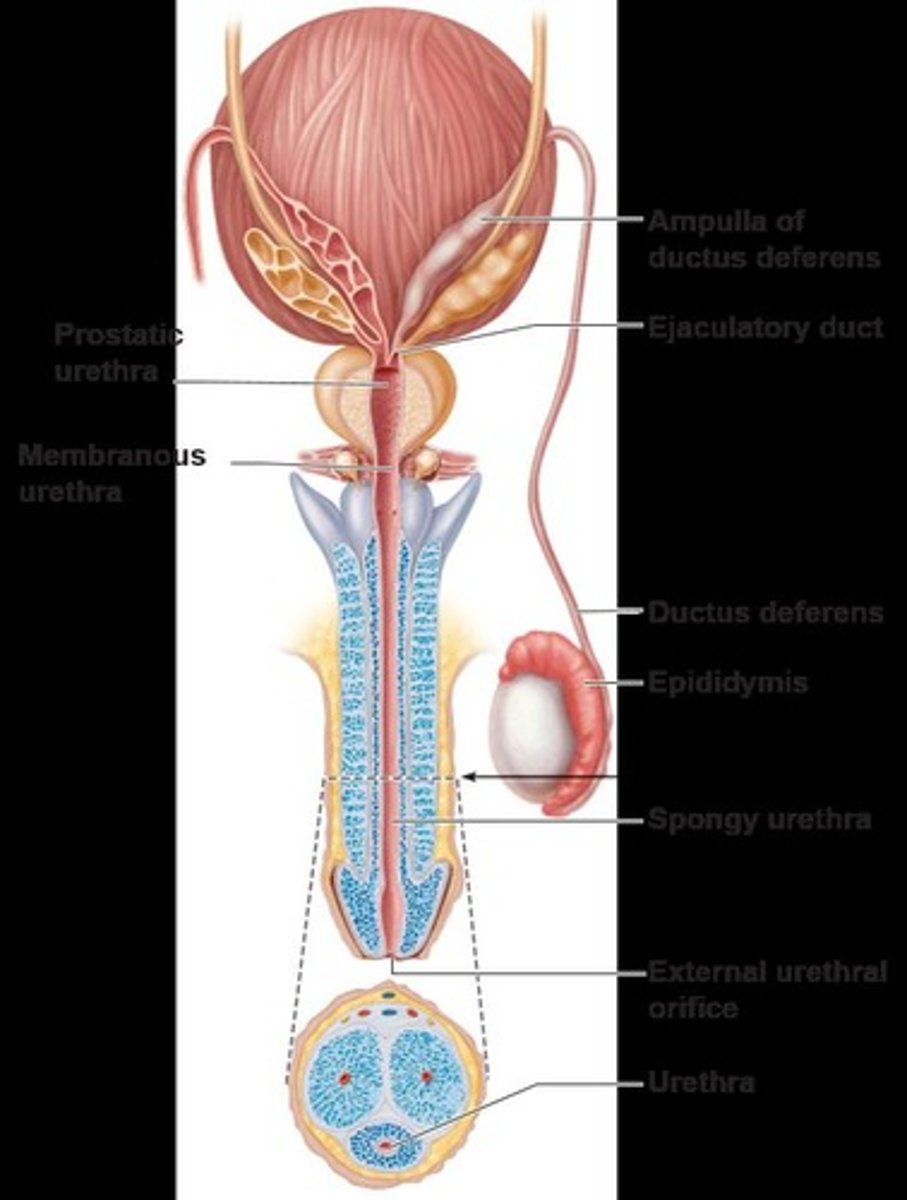
Prostate
Gland secreting milky fluid activating sperm.
Bulbourethral glands
Secrete mucus to lubricate and neutralize urine.
Semen
Mixture of sperm and gland secretions.
Prostaglandins
Compounds in semen reducing cervical mucus viscosity.
Reverse peristalsis
Stimulates uterine contractions to aid sperm movement.
Alkalinity
Neutralizes acidity in male urethra and female vagina.
Antibiotic chemicals
Destroy specific bacteria in reproductive fluids.
Clotting factors
Coagulate semen post-ejaculation for retention.
Fibrinolysin
Liquefies coagulated semen after ejaculation.
Semen volume
2-5 ml per ejaculation; 20-150 million sperm/ml.
Spermatogenesis
Process producing sperm in seminiferous tubules.
Diploid cells
Contain 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes (2n).
Haploid gametes
Contain 23 chromosomes (n) for reproduction.
Spermatogonia
Stem cells that undergo mitosis to form spermatocytes.
Spermatocytes
Undergo meiosis to form spermatids.
Spermatids
Transform into spermatozoa during spermiogenesis.
Spermatozoa
Mature sperm cells with distinct structures.
Sperm head
Contains nucleus and acrosome for egg penetration.
Sperm midpiece
Houses mitochondria for energy production.
Sperm tail
Flagellum providing locomotion for sperm.
Sustentacular cells
Support and nourish developing sperm cells.
Blood-testis barrier
Prevents immune response against sperm antigens.
HPG axis
Regulates male reproductive hormone secretion.
GnRH
Hypothalamic hormone stimulating FSH and LH release.
FSH
Stimulates sustentacular cells to produce ABP.
LH
Stimulates testosterone release from interstitial cells.
Testosterone
Key hormone triggering spermatogenesis and secondary sex traits.
DHT
Active form of testosterone in prostate tissue.
Male secondary sex characteristics
Features like hair growth and voice deepening.
Erection
Blood engorgement of erectile tissue, initiated by stimuli.
Ejaculation
Release of semen via sympathetic spinal reflex.
Estrogen
Primary female sex hormone regulating reproductive functions.
Uterine tubes
Ducts transporting ova from ovaries to uterus.
Uterus
Muscular organ where fetal development occurs.
Vagina
Birth canal and organ of copulation.
Vulva
External female genitalia including labia and clitoris.
Ovaries
Almond-shaped organs producing ova and hormones.
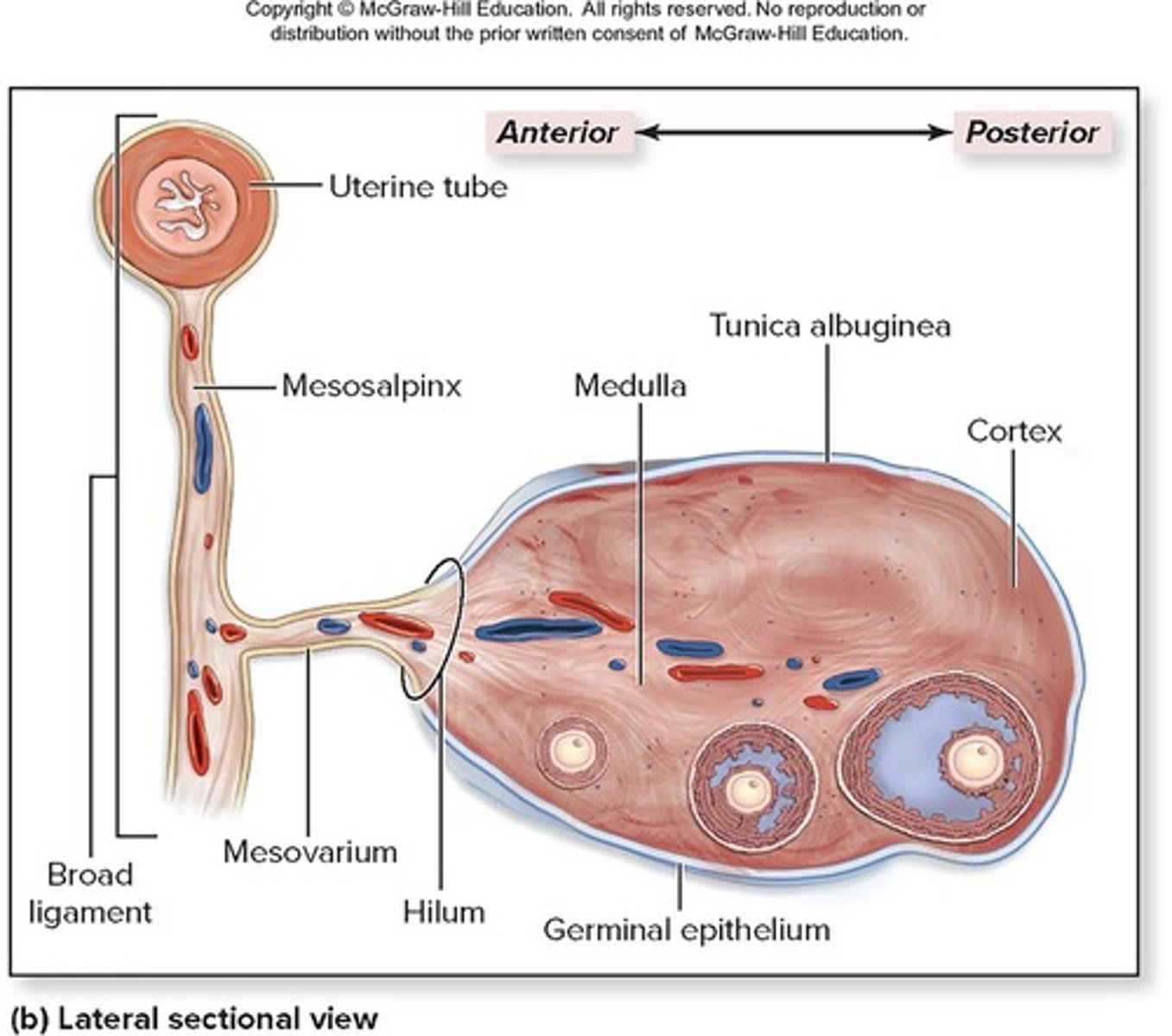
Ovarian ligament
Anchors ovary medially to uterus.
Suspensory ligament
Anchors ovary laterally to pelvic wall.
Mesovarium
Suspends ovary within the broad ligament.
Ovarian arteries
Blood vessels supplying the ovaries.
Tunica albuginea
Fibrous covering surrounding each ovary.
Cortex
Outer region of ovary containing ovarian follicles.
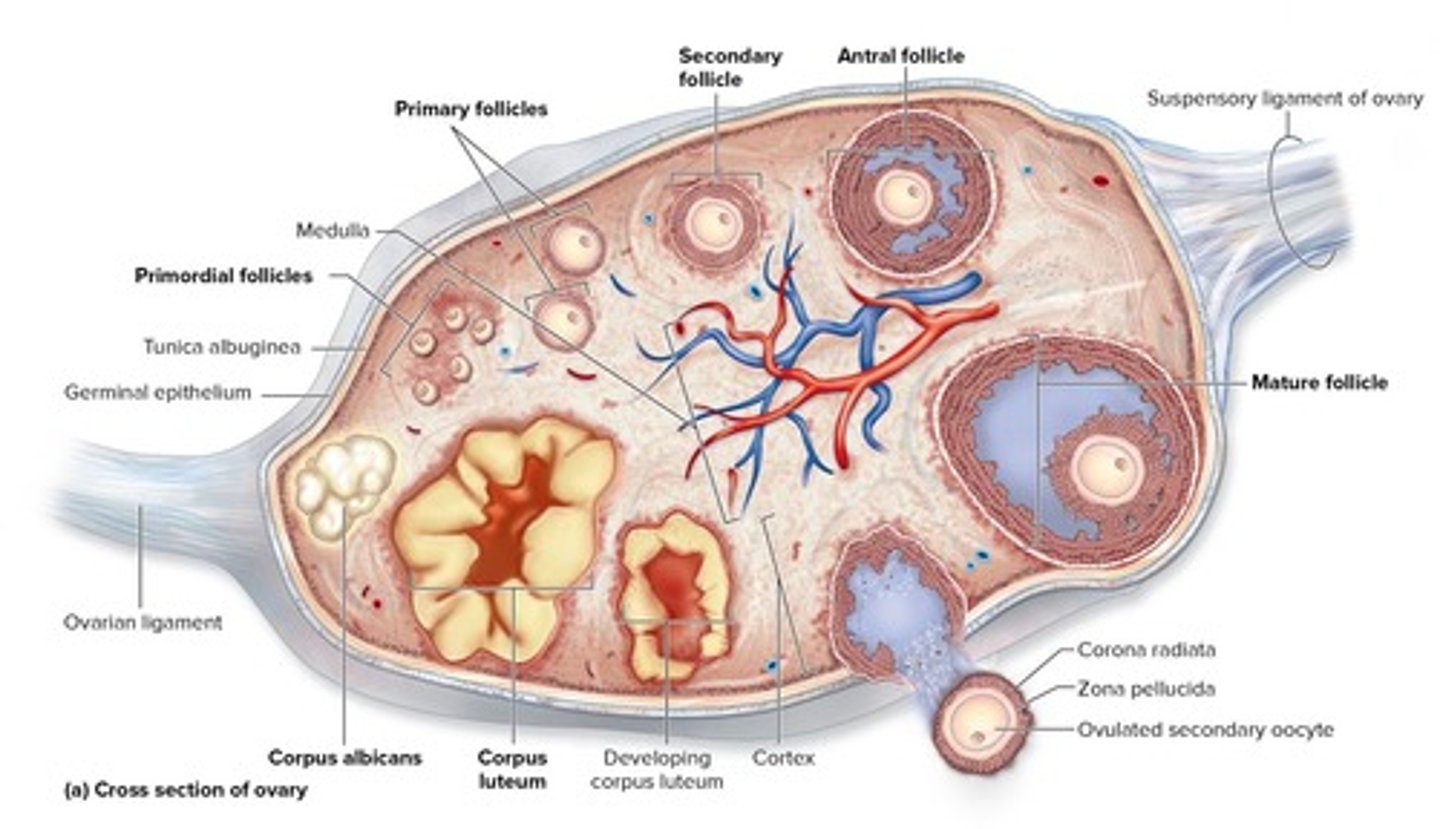
Medulla
Inner region of ovary with blood vessels and nerves.
Primordial follicle
Immature oocyte with squamous follicle cells.
Primary follicle
Oocyte surrounded by cuboidal or columnar cells.
Secondary follicle
Oocyte with multiple layers of granulosa cells.
Vesicular follicle
Mature follicle with fluid-filled antrum.
Ovulation
Ejection of oocyte from the ripening follicle.
Corpus luteum
Structure formed from ruptured follicle post-ovulation.
Cervical canal
Passage connecting uterus to vagina.
Endometrium
Mucosal lining of the uterus, shed during menstruation.
Smooth muscle muscularis
Layer of smooth muscle in vaginal wall.
Stratified squamous mucosa
Multi-layered epithelial tissue in vagina.
Hymen
Incomplete partition near vaginal orifice.
Vaginal fornix
Upper vagina surrounding the cervix.
External Genitalia
Collective term for vulva or pudendum.
Mons pubis
Fatty area over pubic symphysis.
Labia majora
Hair-covered fatty skin folds of vulva.
Labia minora
Skin folds located within labia majora.
Vestibule
Recess between labia minora.
Greater vestibular glands
Mucus-secreting glands for lubrication.
Clitoris
Erectile tissue with a protective prepuce.
Glans clitoris
Exposed portion of the clitoris.
Perineum
Diamond-shaped region between pubic arch and coccyx.
Suspensory ligaments
Connect breast to underlying muscle.
Lobules
Glandular structures within breast lobes.
Oogenesis
Process of egg development in females.
Primary oocytes
Oogonia that stall in prophase I.
Ovulation
Release of secondary oocyte from follicle.
Follicular phase
First half of ovarian cycle, follicle growth.
Luteal phase
Second half of ovarian cycle, corpus luteum activity.
Corpus luteum
Structure formed from ruptured follicle.
Corpus albicans
Degenerated corpus luteum if no pregnancy.
GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone; stimulates FSH and LH release.