Unit 9- Congenital Anomalies-Lower Urinary Tract (Elie)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
In duplication of ureters, what is the prevalence?
Females > Males
Duplication of Ureters can be ______ or _______
Unilateral or bilateral
In a complete duplication of ureters, what is the draining like?
Separate draining of upper and lower poles
How do the ureters enter the bladder in a complete duplication of ureters?
Separately
In a complete duplication of ureters the upper is more ______ than the lower pole ureter
Caudal
In an incomplete duplication of ureters how do the ureters join?
Ureters join together & enter bladder as 1
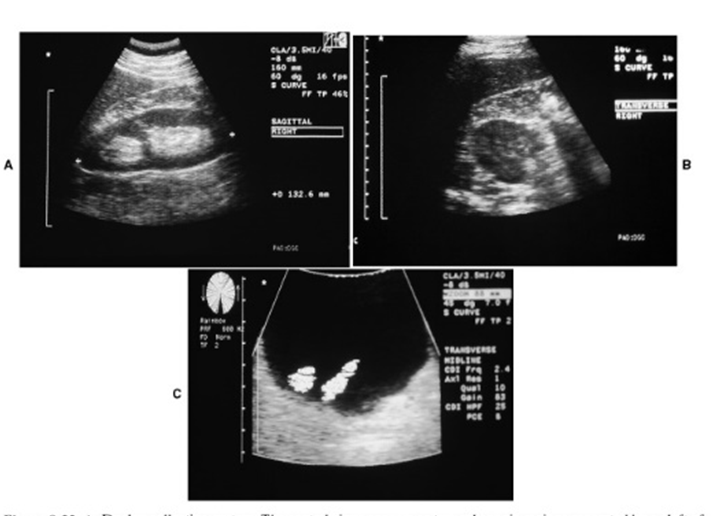
What are these images showing?
Duplication of ureters
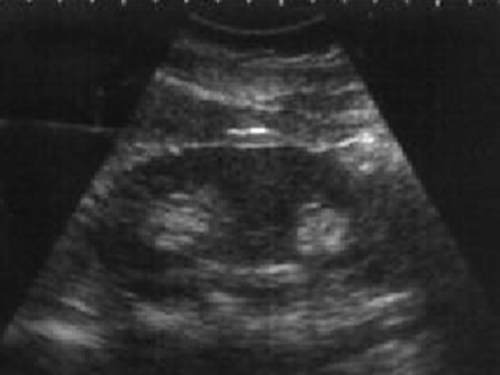
What is this image showing?
Duplication of ureters- 2 ureteral jets confirm complete duplication
A stricture or narrowing of the ureters is caused by what?
Due to internal and external causes
What is a Ureterocele?
Cyst like enlargement of lower end of ureter
Ureteroceles are most common in?
Adults > children
What is a ureterocele caused by?
Congenital or Acquired Stenosis
US appearance of Ureterocele:
Small & Asymptomatic
May cause obstruction & infection of upper urinary tract
May cause bladder outlet obstruction if large
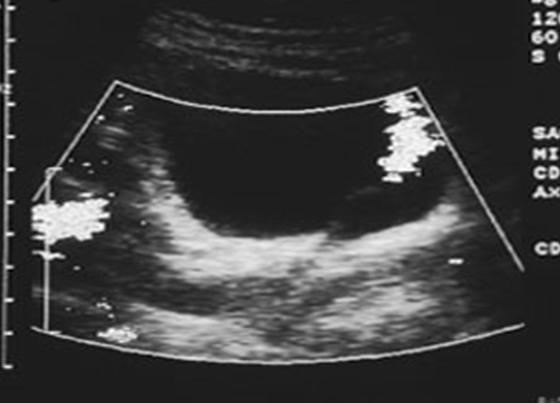
What is this image showing?
Ureterocele
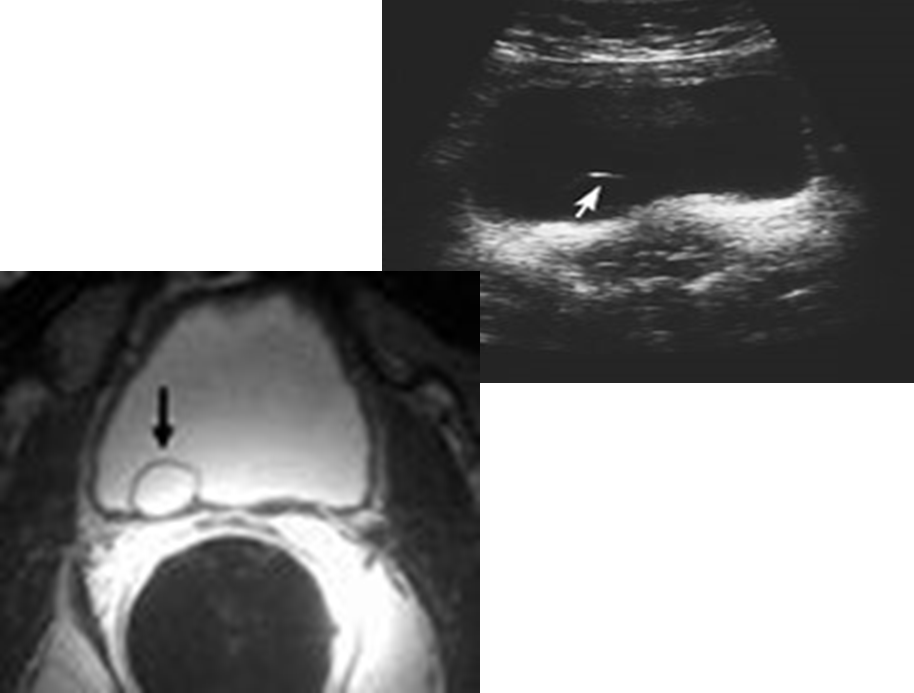
What are these images demonstrating?
Ureterocele
An Ectopic Ureterocele is considered:
Rare
Who is most likely to have an ectopic Ureterocele?
•Female children greatest incidence
What is an Ectopic Ureterocele?
Complete ureteral duplication
Ureters inserts low in bladder near neck
In an ectopic ureterocele, what does a stenotic ureter cause:
Obstruction
Hydroureter
Hydronephrosis
Bladder outlet obstruction or prolapse
“Foley Catheter” appearance
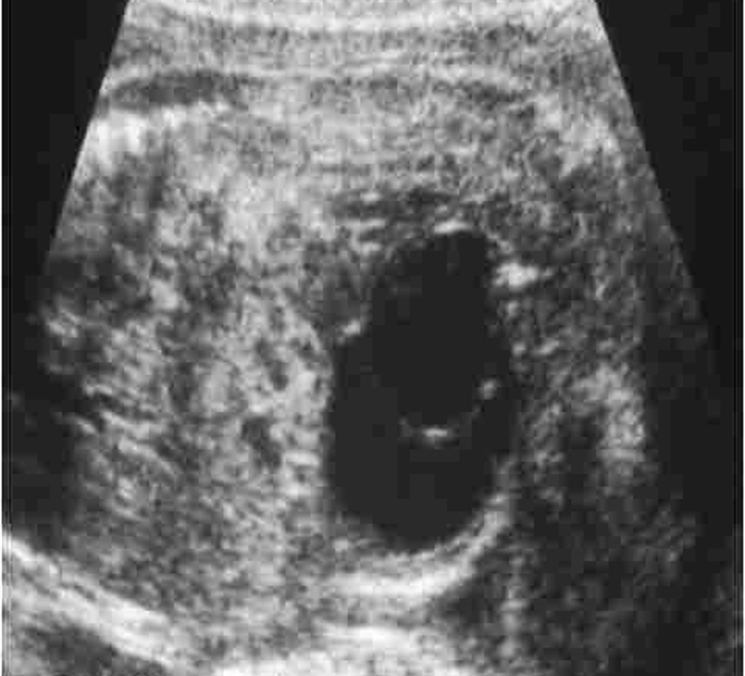
What is this image showing?
Ureterocele in utero
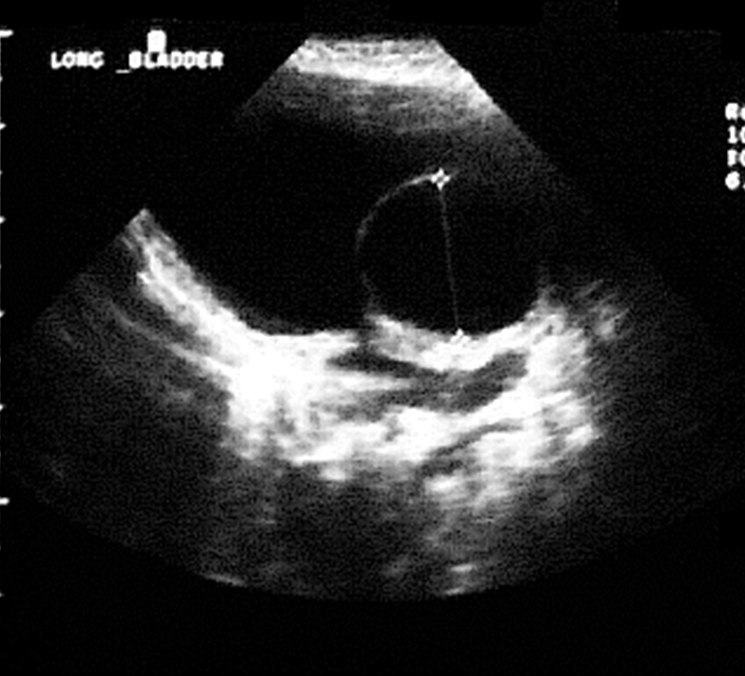
What is this image showing?
“ Foley catheter” appearance
What is used as direct evaluation of bladder?
Cystoscopy
Best to evaluate early CA
Ultrasound visualizes lesions greater than?
5mm
US appearance for a distended bladder:
Smooth walls – not irregular or with asymmetrical indentations
Wall mass or thickening (3-6 mm is normal)
Midline – not deviated or asymmetric indentations
Calculi
Debris
Diverticula
Ureteral Jets
Ureterocele
What is the normal size for a wall mass or thickening in the bladder?
3-6mm
When scanning the bladder movement of the patient is necessary to evaluate what?
Stones
Debris vs mass(attached)
What other organs should the sonographer look for when scanning the bladder?
Look for enlarged prostate, uterus, or pelvic mass which may indent & displace the bladder
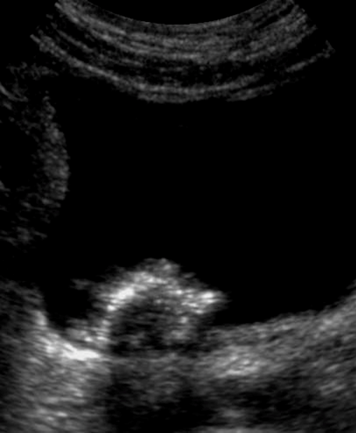
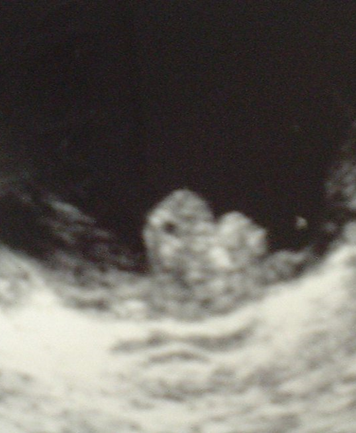
What are these images showing?
Bladder Tumors
Residual Bladder volume is used when?
If there is outflow obstruction
How do you calculate residual bladder volume?
Post void – Long & Trans.
Measure Length, Transverse, & AP at largest dimensions
Calculate volume
L x W x H x 0.625 = cc’s for adults
L x W x H x 0.5233 = cc’s for peds
What is the normal residual measurement for adults?
< 20 cc’s