hydrology and fluvial geomorphology
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What is a drainage basin?
The area of land drained by a major river and its tributaries.
What is the boundary of a drainage basin called?
The watershed.
What is evaporation in the context of a drainage basin?
The process where water is heated by solar energy and evaporates into the atmosphere, making it an output from the basin.
Define evapotranspiration.
The combined process of evaporation and transpiration, where water evaporates from leaves due to heat.
What is river discharge?
The volume of water passing through a cross-sectional point of the river at any one point in time.
What is interception in hydrology?
A short-term store where water is intercepted by vegetation before hitting the ground.
What are the different types of water stores in a drainage basin?
Soil water, surface water, groundwater, and channel storage.
What is soil water?
Water stored in upper levels of the soil, utilized by plants.
What constitutes surface water?
Puddles, lakes, and ponds.
What is groundwater?
Water stored in the pores of rock or lower soil.
What is throughfall?
Water that flows from leaves or foliage onto the ground.
Define stemflow.
Intercepted water that flows down the stem of a plant.
What is surface runoff?
Water that cannot be infiltrated and flows off a surface, seen as sheet flow or in rills.
What is channel flow?
Water that flows through established channels.
What is infiltration?
The process when water above ground flows into the ground.
Define percolation.
Water that flows from the ground into porous or fractured rock.
What is base flow?
The level of channel flow when there is no overland flow.
What is the water table?
The upper surface of the zone where groundwater fills the pores and fractures in soil or rock.
What is groundwater recharge?
The process of replenishing groundwater levels through precipitation or bodies of water seeping into the ground.
What are springs in hydrology?
Natural outlets of groundwater that can form when permeable rock meets impermeable rock or when the water table meets the surface.
What is a hydrograph?
A graph that shows how river discharge changes over time, combining river velocity with cross-sectional area.
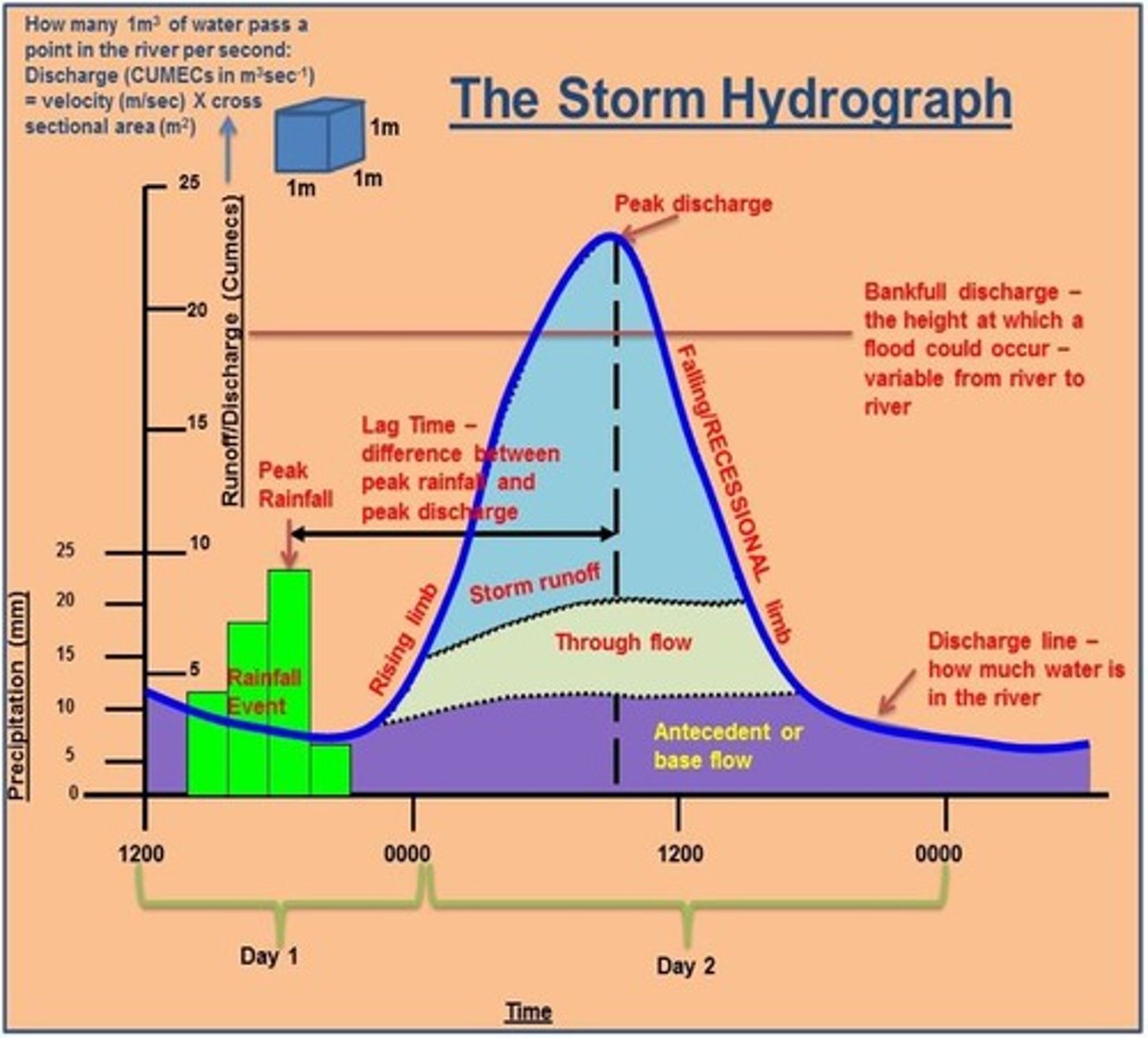
What distinguishes a storm hydrograph from an annual hydrograph?
A storm hydrograph shows changes in river discharge due to storm events, while an annual hydrograph shows discharge trends over a year.
What factors affect hydrographs?
Climate and precipitation, as more precipitation leads to a flashier hydrograph and increased discharge.
What happens to rainfall when there is antecedent moisture?
The rainfall cannot infiltrate, leading to an increase in discharge.
How does temperature affect evaporation?
Higher temperatures lead to more evaporation.
What is the impact of warmer climates on water infiltration?
Warmer climates can infiltrate more water due to previous evaporation.
How does vegetation affect lag time during spring and summer?
More vegetation leads to more interception, resulting in a longer lag time.
What happens to soil during autumn and winter?
There is less vegetation growth, leading to soil saturation and frozen ground, which makes it more impermeable.
What is the relationship between drainage basin size and peak discharge?
Larger basins have higher peak discharge.
How does the shape of a drainage basin affect lag time?
In circular basins, overland flow reaches the river at similar times, shortening lag time; in oval basins, flow arrives at different times, lengthening lag time.
What is drainage density and how does it affect peak discharge?
Drainage density is the total length of rivers and streams divided by the basin area; high drainage density leads to high peak discharge and short lag time.
How does soil porosity affect infiltration?
Larger pores allow for easier infiltration.
What is the effect of topography on water velocity?
Rough, jagged rocks reduce velocity, while steeper slopes allow water to run faster.
How does vegetation influence soil moisture?
More vegetation leads to increased interception and soil moisture.
What are the effects of deforestation on hydrographs?
Deforestation decreases interception and soil water storage, leading to a flashier hydrograph.
How does agriculture impact soil infiltration?
Livestock trampling reduces infiltration, while ploughing can either increase or decrease it.
What is the impact of urbanization on river channels?
Urbanization creates less permeable surfaces but increases drainage directly into river channels.
What is corrasion/abrasion in river processes?
It is the scraping and grinding of rocks along a river channel.
What is hydraulic action?
The sheer force of water can fragment rocks off the riverbed.
What is cavitation in river processes?
Cavitation occurs when water forces its way into cracks, pressurizing air inside and widening the cracks.
What are the four methods of sediment transportation in rivers?
Traction (rolling), saltation (bouncing), suspension (carried within water), and solution (soluble materials carried in water).
What does the Hjulström curve illustrate?
It shows the relationship between sediment size and the velocity required to erode, transport, and deposit it.
What happens to larger particles in terms of velocity and deposition?
Larger particles require more velocity to be lifted and are deposited at higher velocities.
What are the characteristics of laminar flow in rivers?
Laminar flow is the flow of water in parallel lines, moving in one orderly direction.
What defines turbulent flow in rivers?
Turbulent flow is characterized by disorderly movement, changes in velocity, and can be caused by friction and irregular channels.
What is helicoidal flow and where does it occur?
Helicoidal flow is a corkscrew movement of water that occurs in bends of the river channel (meanders), responsible for erosion and deposition in those areas.
What is the thalweg in a river?
The thalweg is the line of fastest flow and the deepest point within the river channel, where erosion is greatest.
What are the three types of river channels?
The three types of river channels are straight, meandering, and braided.
Describe the characteristics of straight river channels.
Straight channels are mainly found in the upper course, where vertical erosion is prevalent and the thalweg moves from side to side.
What is a meandering river channel?
Meandering channels are found in the middle and lower course, characterized by deposition on the inside of bends and erosion on the outside.
What defines a braided river channel?
Braided channels have large deposits of sediment that create multiple channels and eyots, occurring when discharge fluctuates and deposits sediment as the river loses energy.
How is a waterfall formed?
A waterfall forms where a river flows over hard and soft rock, with the soft rock eroding quicker to create a step, leading to undercutting of the hard rock and the formation of a plunge pool.
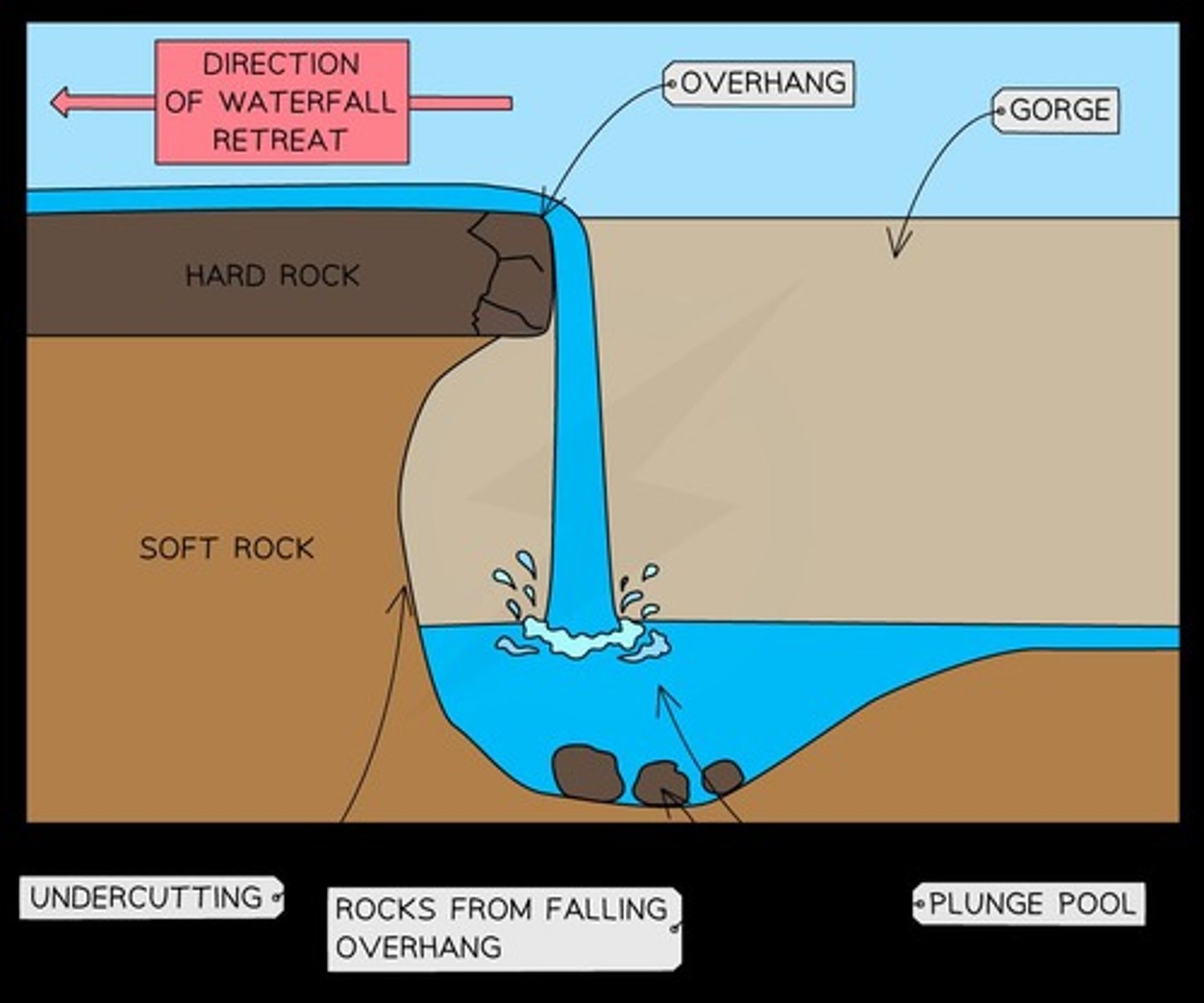
What happens to the overhang of a waterfall over time?
The overhang collapses due to gravity, and the unconsolidated rock created contributes to further erosion, causing the waterfall to retreat upstream.
What is headward erosion?
Headward erosion is the process by which a river erodes its channel upstream, contributing to the formation of features like gorges.
What is the process of meander formation?
Meanders form through erosion on the outside bend, where water moves faster, and deposition on the inside bend, where water moves slower.
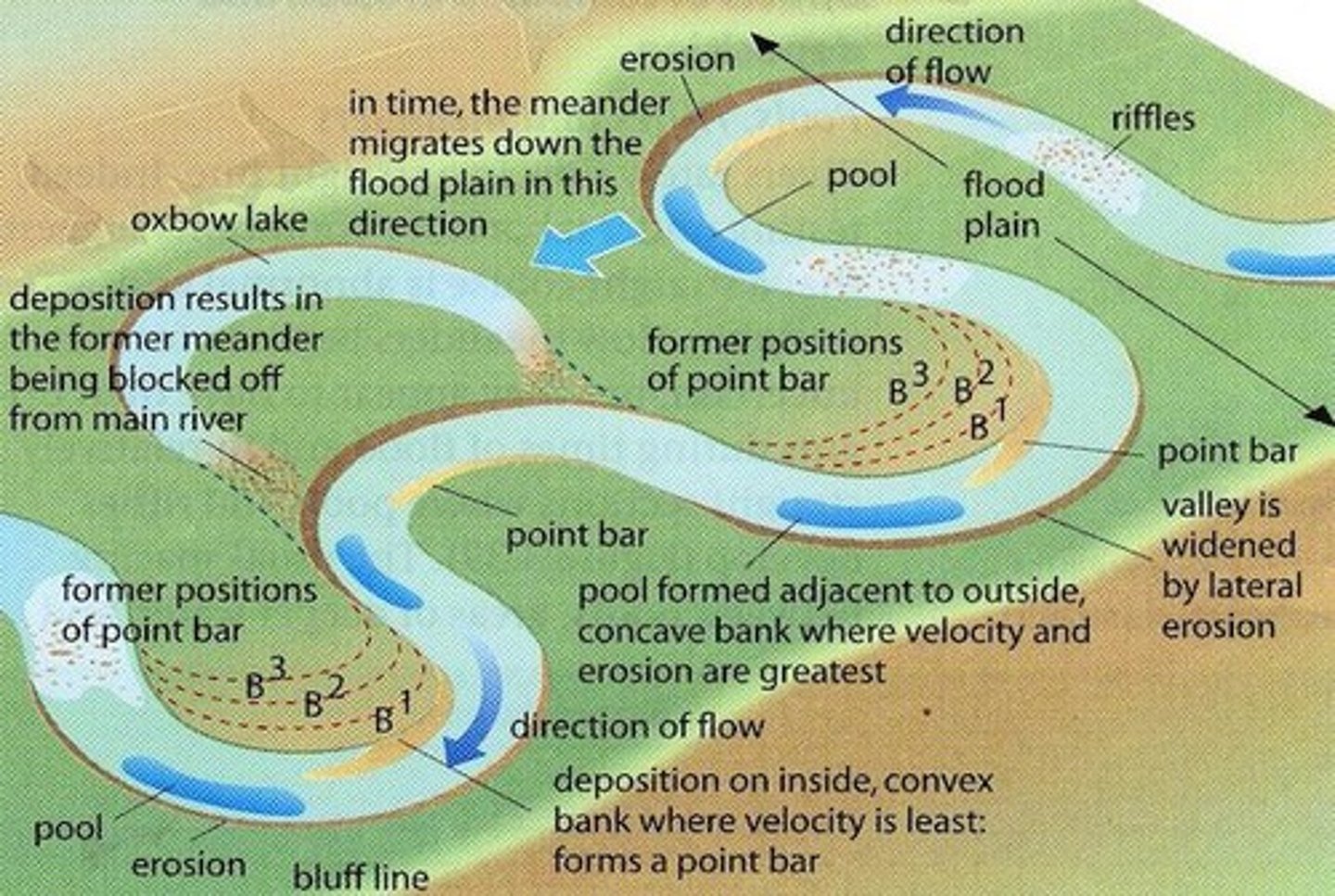
How is an oxbow lake formed?
An oxbow lake is formed when a river cuts through the neck of a meander, creating a straighter path and leaving the abandoned meander loop to fill with sediment.
What are bluffs in relation to river meanders?
Bluffs are large, rounded cliffs formed on the outside bend of a meander due to high erosion, where the lower section of the riverbank is eroded.
What is the significance of Loess Bluffs along the Mississippi River?
Loess Bluffs mark the transition from the floodplain to the upland plateau and show the past extent of the river valley, formed by erosion and river incision.
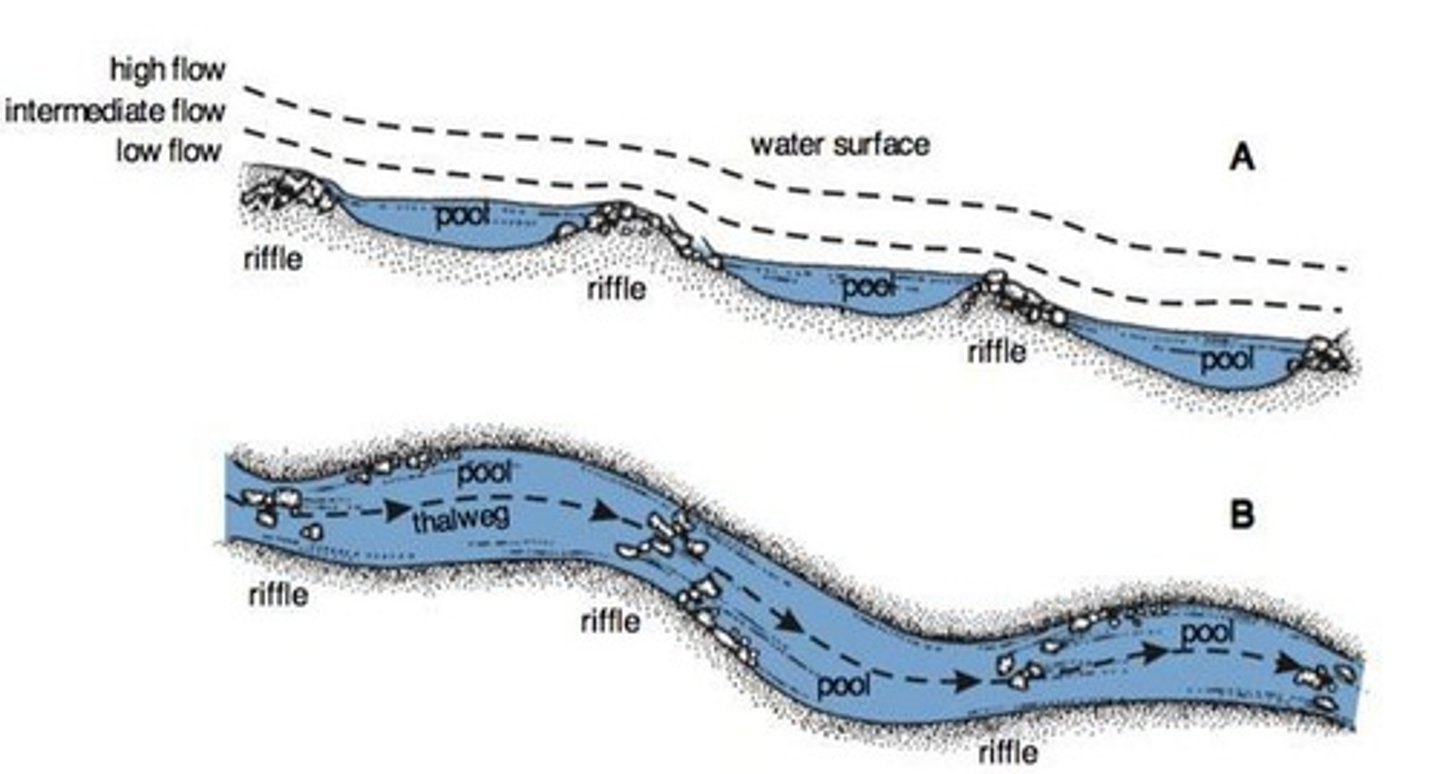
What are riffle and pool sequences in a river?
Riffle and pool sequences are alternating patterns of shallow (riffle) and deeper (pool) water in a river channel, formed as the river adjusts its course to efficiently transport its load.
What occurs on a floodplain during a river flood?
During a flood, sediment leaves the channel and spreads onto the riverbank, where the water loses energy and deposits sediment, creating a fertile floodplain.
What is an example of a significant floodplain?
The Ganges River Floodplain is one of the largest in the world, formed by seasonal flooding depositing layers of fine silt and clay.
What are levees and how do they form?
Levees are natural embankments along a river that build up due to repeated flooding.
What happens to sediment as it moves further away from the river?
The further away, the less energy and finer the sediment, leading to sorting.
How do natural levees form?
Natural levees form over centuries as repeated flooding causes heavier materials like sand and silt to deposit closest to the riverbanks.
What is the purpose of artificial levees in the Mississippi Basin?
Artificial levees are constructed to manage frequent and severe flooding, containing floodwaters and protecting farmland, towns, and cities.
What is a delta and where does it occur?
A delta occurs at the mouth of a river where it carries a lot of sediment, leading to mass deposition when it meets a body of water.
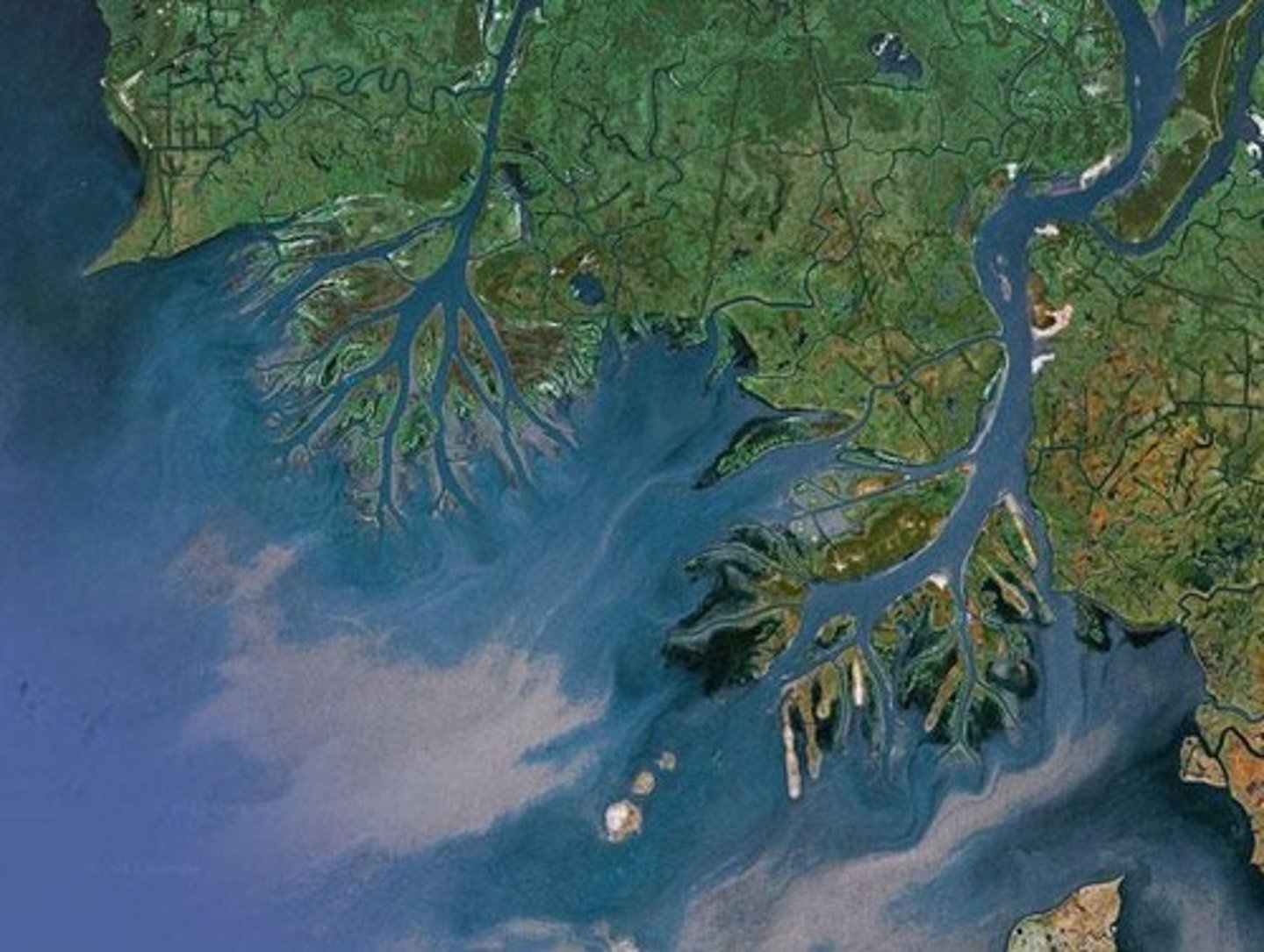
What are the two types of delta shapes?
Deltas can be digitate (extended out into the sea) or arcuate (fan-shaped and does not extend out into the sea).
How does flocculation affect sediment deposition?
Flocculation, caused by a negative charge, leads to sediment deposition.
What is the hydraulic radius and how is it calculated?
The hydraulic radius measures river efficiency; it is calculated as R = A/P, where R is the hydraulic radius, A is the cross-sectional area, and P is the wetted perimeter.
What human activities impact river dynamics?
Human activities such as land use changes, deforestation, urbanization, and water abstraction significantly impact river dynamics.

How does deforestation affect infiltration rates?
Deforestation decreases infiltration rates because roots that help with infiltration are removed.
What is the effect of urbanization on river channels?
Urbanization causes larger flows into river channels due to drains and impermeable surfaces, increasing overland flow.
What is water abstraction?
Water abstraction is the removal of water from a body of water to meet demands, which can deplete surface and groundwater levels.
What role do aquifers play in water storage?
Aquifers are underground water storage systems that store water and can affect surface water levels.
How do dams and reservoirs affect river flow?
Dams can stop and control channel flow, while reservoirs can raise the water table and affect soil saturation.
What are some causes of river flooding?
Causes of flooding include heavy rainfall over a short period, prolonged rainfall, impermeable surfaces, and melting snow or glaciers.
What are the impacts of flooding?
Flooding can block drains, waterlog plants, deposit materials into clean water supplies, damage buildings, and cause economic loss.
What is a flood recurrence interval?
A flood recurrence interval is the probability of a flood of a certain size occurring based on past flooding records.
What does a 100-year flood mean?
A 100-year flood means there is a 1% chance of a flood of that size occurring in any given year.
How can floods be predicted?
Floods can be predicted using software to model how different factors like slope, topography, precipitation rates, and soil moisture content would affect flooding.
What is the significance of the Hjulstrom curve?
The Hjulstrom curve illustrates the relationship between sediment size and the velocity required for erosion, transport, and deposition.
What is the effect of flooding on wildlife?
Flooding can waterlog plants, disrupt habitats, and negatively affect wildlife.
How can flooding affect the economy?
Flooding can lead to costly repairs, loss of infrastructure, and increased spending on future flood defenses.
What are the key components in assessing the risk of flooding in an area?
Prevention and amelioration, forecasts and warnings, precipitation forecasts, and streamflow data.
How can forecasts and warnings help in flood situations?
They allow people to prepare or evacuate depending on the severity of the flood.
What is hard engineering in flood management?
It includes physical structures like dams, channel straightening, levees, and diversion spillways that obstruct or alter a river's natural course.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using dams for flood prevention?
Dams can effectively obstruct a river's flow but are expensive, can displace settlements, disrupt wildlife, and may fail if not maintained.
What is channel straightening and what are its consequences?
Channel straightening removes bends and irregularities to allow faster water flow, reducing overflow risk, but can cause flooding downstream.
What is the purpose of levees in flood management?
Levees provide a raised embankment to allow water to rise further before overflowing.
What is a diversion spillway?
A constructed channel that allows excess water to flow into it, directing water downstream or into a different river, usually controlled by floodgates.
What are some examples of soft engineering techniques for flood management?
Dredging, riparian restoration, and afforestation.
What is the impact of agricultural land use on flood plains?
It is seen as damaging due to livestock trampling and the use of heavy machinery.
What is floodplain mapping?
Using river flooding records to identify areas at risk of flooding, allowing for better management and lower restoration costs.
What were the physical causes of the Cockermouth 2009 flood?
Heavy rainfall (316mm), prolonged rainfall, and impermeable surfaces like Skiddaw slate.
What human factors contributed to the Cockermouth 2009 flood?
Lack of dredging in the river and clogged drains due to autumn leaves.
What were the social impacts of the Cockermouth 2009 flood?
One police officer died, 1300 homes were flooded, and there was a lack of food and water for 24 hours.
What environmental impacts were observed during the Cockermouth 2009 flood?
Crops were ruined, afforestation trees fell, and water levels rose by 2.5 meters.
What were the economic impacts of the Cockermouth 2009 flood?
Damage costs of £277 million, loss of tourist income, loss of small businesses, and expenses on flood defenses.
What types of flood defenses were implemented post-Cockermouth flood?
Soft defenses like land use zoning and afforestation, and hard defenses like flood walls and flood defense windows.
How much was spent on flood defenses after the Cockermouth flood?
£4.4 million.