Nervous System Anatomy, Diseases, and Disorders
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:58 AM on 2/14/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Afferent nerves
nerves that carry impulses toward the CNS; also known as sensory nerves
2
New cards
Brain
the prominent organ located within the cranial cavity; it is the center of conscious thought, memory, emotions, and muscle stimulus.
3
New cards
Brain stem
the lowermost part of the brain; it includes the medulla and the pons, which transmit impulses between the spinal cord and other parts of the brain. Controls basic body functions such as breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness, and whether one is awake or sleepy.
4
New cards
Central nervous system
a main division of the nervous system that contains the brain and spinal cord; abbreviated CNS
5
New cards
Efferent nerves
nerves that carry impulses away from the CNS; also called motor nerves
6
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
a main division of the nervous system that contains the peripheral nerves and ganglia
7
New cards
Synapse
a tiny gap between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite or cell body of another neuron, across which information travels by way of neurotransmitters
8
New cards
Parkinson's disease
Chronic degenerative disease of the brain indicated by hand tremors, rigidity, expressionless face, and shuffling gait; also called Parkinsonism and abbreviated PD
9
New cards
Alzheimer's Disease
deterioration of brain function characterized by confusion, short term memory loss, and restlessness; abbreviated AD
10
New cards
dementia
literally "not in the mind,"impairment of mental function that is characterized by memory loss, disorientation, and confusion
11
New cards
Palsy
Paralysis of localized areas; the most common is Bell's palsy, in which facial muscles are paralyzed on one side of the head
12
New cards
Seizure
A sudden attack of spasms or convulsions; seizures are classified as grand mal which involves all muscle groups, petit mal which involves brief losses of consciousness without motor involvement, or partial which involves only limited areas of the brain with local symptoms
13
New cards
Transient ischemic attack
A brief episode of loss of blood flow to the brain that results in a temporary neurologic impairment, and often precedes a CVA; abbreviated TIA
14
New cards
Magnetic resonance imaging
Use of magnets to identify structural details of soft tissues within the body, coupled with computer imaging, to produce 3-dimensional images that are useful in targeting brain tumors, brain trauma, MS and other conditions; abbreviated MRI
15
New cards
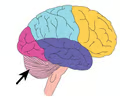
cerebellum
coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance, coordination, and speech, resulting in smooth and balanced muscular activity
16
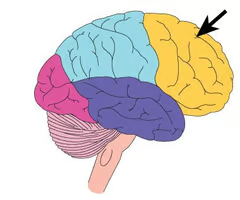
New cards
frontal lobe
Involved in problem solving, spontaneity, memory, language, initiation, judgement, impulse control, and social and sexual behavior.
17
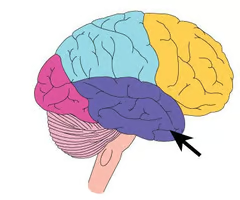
New cards
temporal lobe
Involved in hearing and selective listening. It receives sensory information such as sounds and speech from the ears. It is also key to being able to comprehend, or understand meaningful speech
18
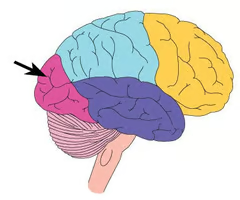
New cards
occiptal lobe
Lobe in the brain which makes sense of visual information so that we are able to understand it.
19
New cards
parietal lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position
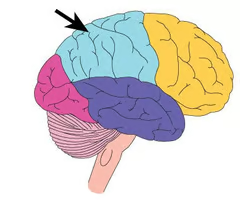
20
New cards
cerebrovascular accident
disruption in the normal blood supply to the brain; stroke
21
New cards
transient ischemic attack
temporary interruption in the blood supply to the brain
22
New cards
cerebral palsy
paralysis caused by damage to the area of the brain responsible for movement
23
New cards
Epilepsy
chronic brain disorder characterized by recurrent seizure activity
24
New cards
Huntington chorea/disease
hereditary disease of the central nervous system characterized by bizarre, involuntary body movements and progressive dementia
25
New cards
multiple sclerosis
myelin sheath destruction. disruptions in nerve impulse conduction
26
New cards
poliomyelitis
inflammation of the gray matter of the spinal cord caused by a virus, commonly resulting in spinal and muscle deformity and paralysis
27
New cards
Amyotropic Lateral Sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's Disease)
A nervous system disease that weakens muscles and impacts physical function. In this disease, nerve cells break down, which reduces functionality in the muscles they supply. The cause is unknown. The main symptom is muscle weakness. Medication and therapy can slow ALS and reduce discomfort, but there's no cure.
28
New cards
carpal tunnel syndrome
A condition caused by compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel and characterized especially by weakness, pain, and disturbances of sensation in the hand and fingers
29
New cards
herpes zoster
viral disease affecting the peripheral nerves, characterized by painful blisters that spread over the skin following the affected nerves, usually unilateral; also known as shingles
30
New cards
myasthenia gravis
a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the neuromuscular junction and produces serious weakness of voluntary muscles
31
New cards
Botulism
a rare but serious illness caused by a toxin that attacks the body's nerves. Symptoms usually start with weakness of the muscles that control the eyes, face, mouth, and throat. This weakness may spread to the neck, arms, torso, and legs.
32
New cards
hydrocephalus
accumulation of fluid in the spaces of the brain
33
New cards
spina bifida
a congenital defect that occurs during early pregnancy when the spinal canal fails to close completely around the spinal cord to protect it
34
New cards
hemmorhagic stroke
Type of CVA that occurs when a weakened blood vessel, such as an aneurysm, ruptures and bleeds into the surrounding tissue of the brain.
35
New cards
ischemic stroke
occurs when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery leading to the brain.
36
New cards
sciatica
pain that follows the pathway of the sciatic nerve, caused by compression or trauma of the nerve or its roots