Atomic structure & periodic table
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Define atom
The smallest part of an element
Define compound
2 or more elements chemically bonded together which can only be separated by a chemical reaction
Define mixture
2 or more elements/ compounds not chemically bonded together
Ways to separate mixtures
Filtration
crystallisation
Simple distillation
Fractional distillation
Chromatography
Don't Try Reading Books Chad!
John Dalton
↳ All matter was made of tiny spheres called atoms which couldn't be divided
J J Thomson
↳ Plum pudding model→ discovered electrons
↳ Atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it
Ernest Rutherford
↳ Alpha particle scattering experiment → nuclear model
Niels Bohr
↳ Electrons orbit the nucleus shells
James Chadwick
↳ Dicovered neutrons
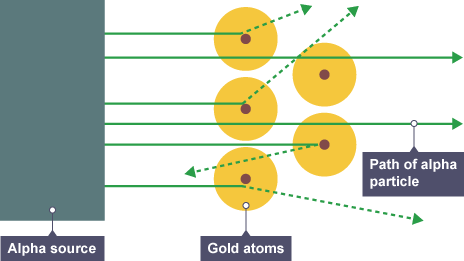
What did the alpha particle scattering experiment prove?
This experiment proved:
The mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus
The nucleus is positively charged ( positively charged particles were fired and like charges repel)
How small is the radius of an atom?
0.1nm (1 × 10-10 m)
the radius of a human hair is around (1 × 10-4 m)
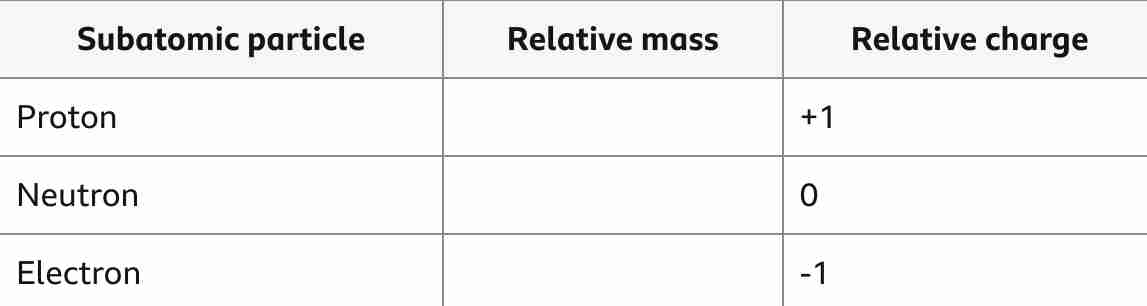
Fill in the blanks
1
1
very small
How do you calculate protons and electrons?
Atomic number
How do you calculate neutrons?
Mass number - atomic number
Define isotope
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
What is the trend in group 1?
Reactivity increases as you go down the group
What is the trend in Group 7
Reactivity Increases as you go up the group
Why? (alkali metals)
✓Atoms get bigger as you go down
✓ Outermost electron is further away from the nucleus
✓ Electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and electron is weaker so the electron can be lost more easily
Why? (halogens)
✓ The size of the atom increases as you go down the group
✓ Outermost electron is further from the nucleus
✓ Weaker electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and electron makes it harder for the atom to gain an electron
What are the physical properties of transition metals?
Conducts electricity
Shiny
What are the chemical properties of transition metals?
Produces ions with different charges
Coloured compounds
Great catalysts
What are the differences between properties in group 1 and transition metals?
Physical
Transition metals have: higher melting points, higher densities, stronger, harder
Chemical
Group 1: react quickly with oxygen, react vigorously with cold water, and halogens
Why did mendeleev leave gaps in his periodic table?
Not all elements had been discovered yet and when they were, they filled the gap
Changed the order based on atomic weight but the knowledge of isotopes explained why it was not always correct to do so
hii