Biology: CQA 2nd quarter
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment, CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS
pH scale
scale with values from 0 to 14, a pH of 0 to 7 is acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH 7 to 14 is basic/alkaline (pure water = pH 7)

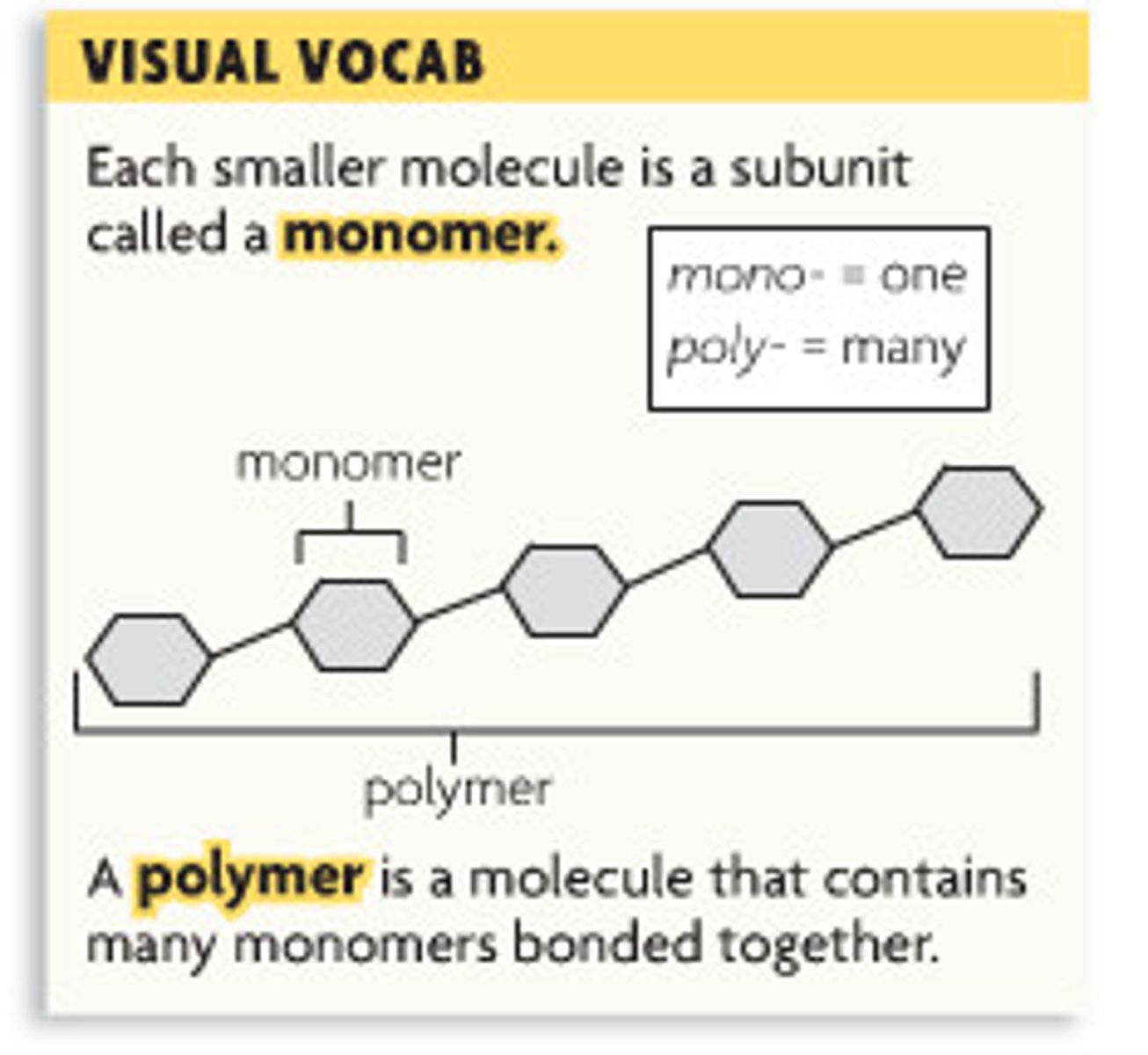
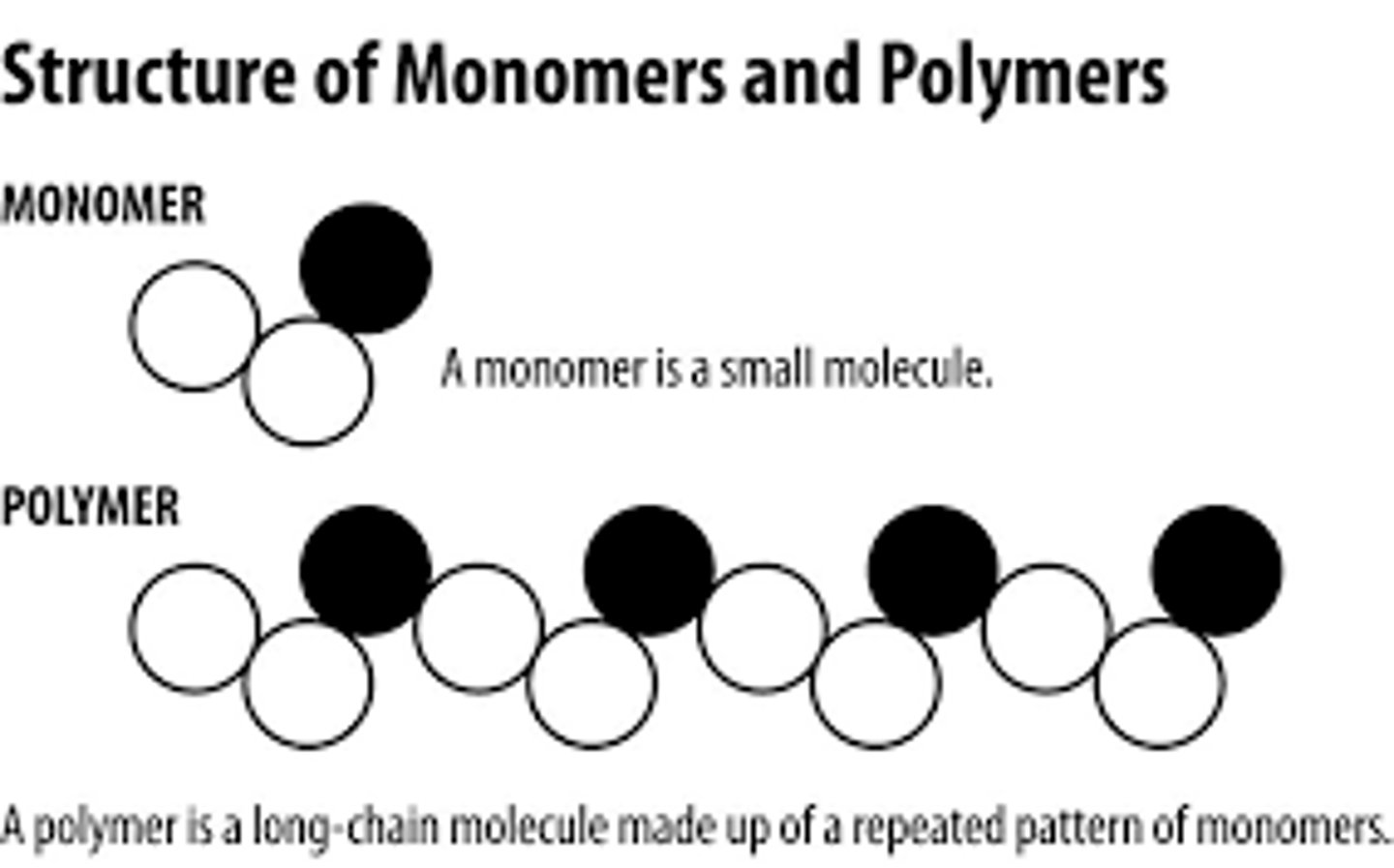
polymer
molecules composed of many monomers; makes up macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids and proteins can be polymers)
carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods, polysaccharides are polymers made of sugars such as glucose, have an -ose suffix
lipids
Compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes. Function as long term energy storage & thermal insulation for the body (made of glycerol & fatty acids)
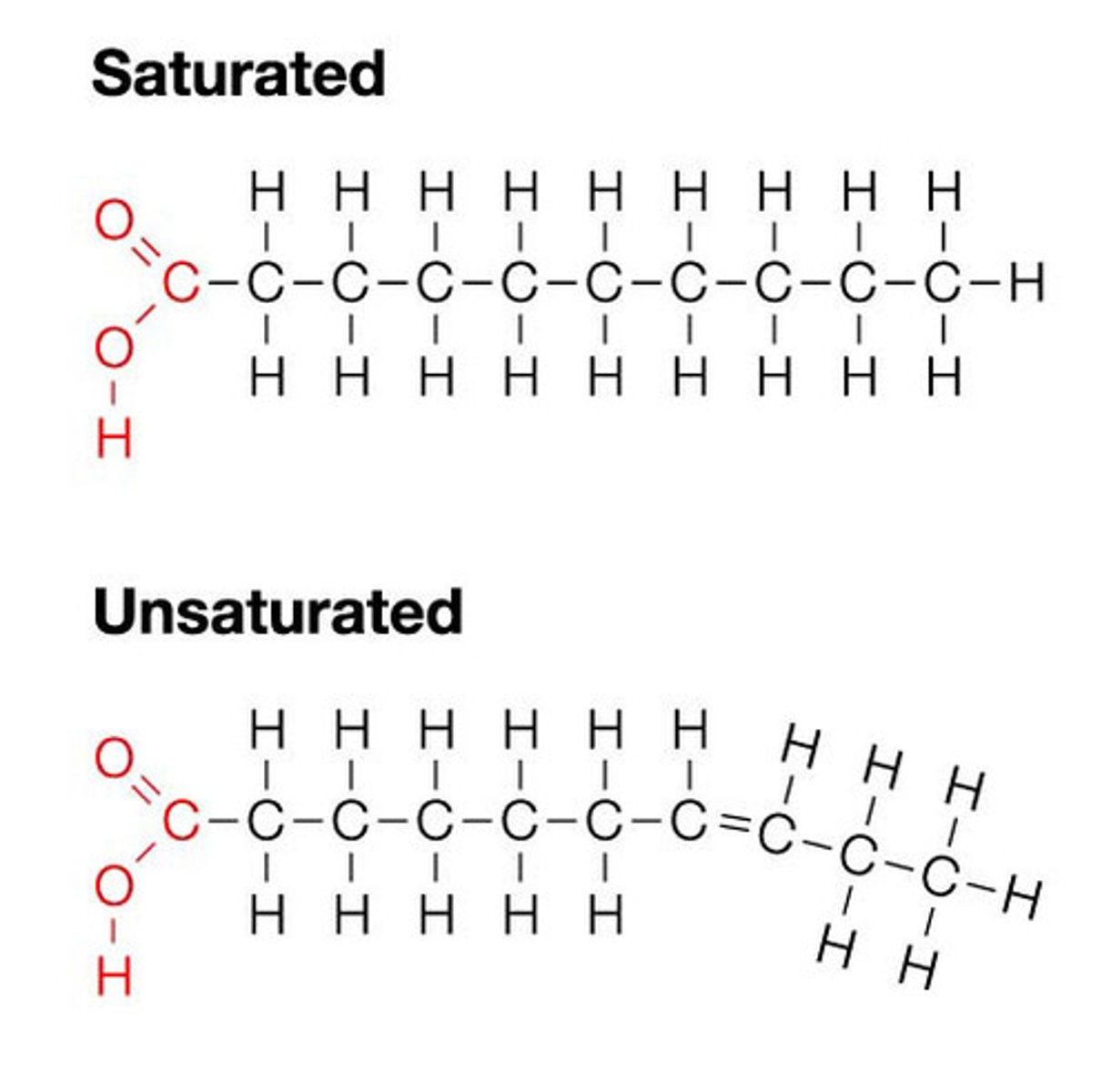
protein
organic compound made of amino acids and that is a building block of all cells (polymer made of amino acids)
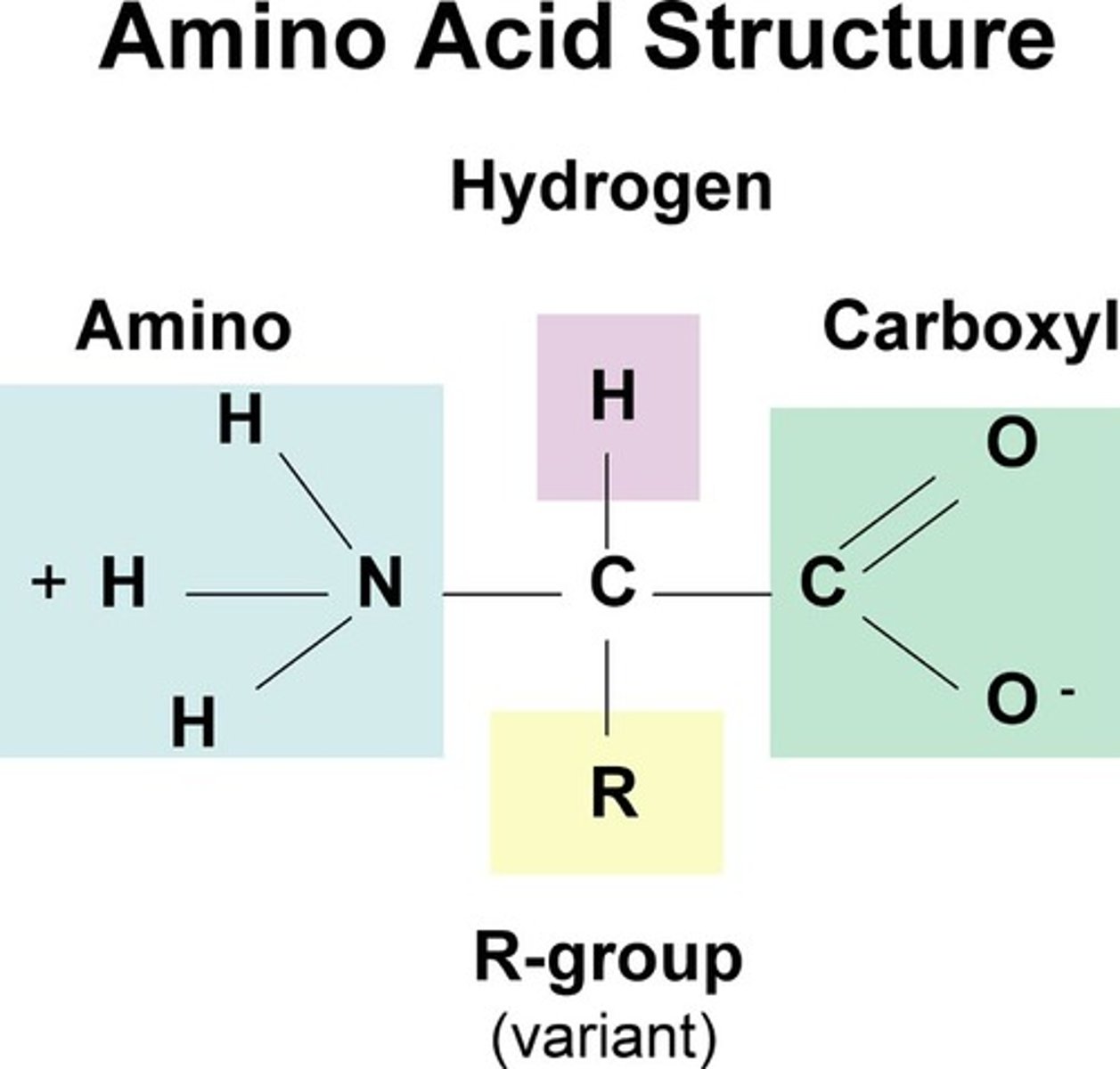
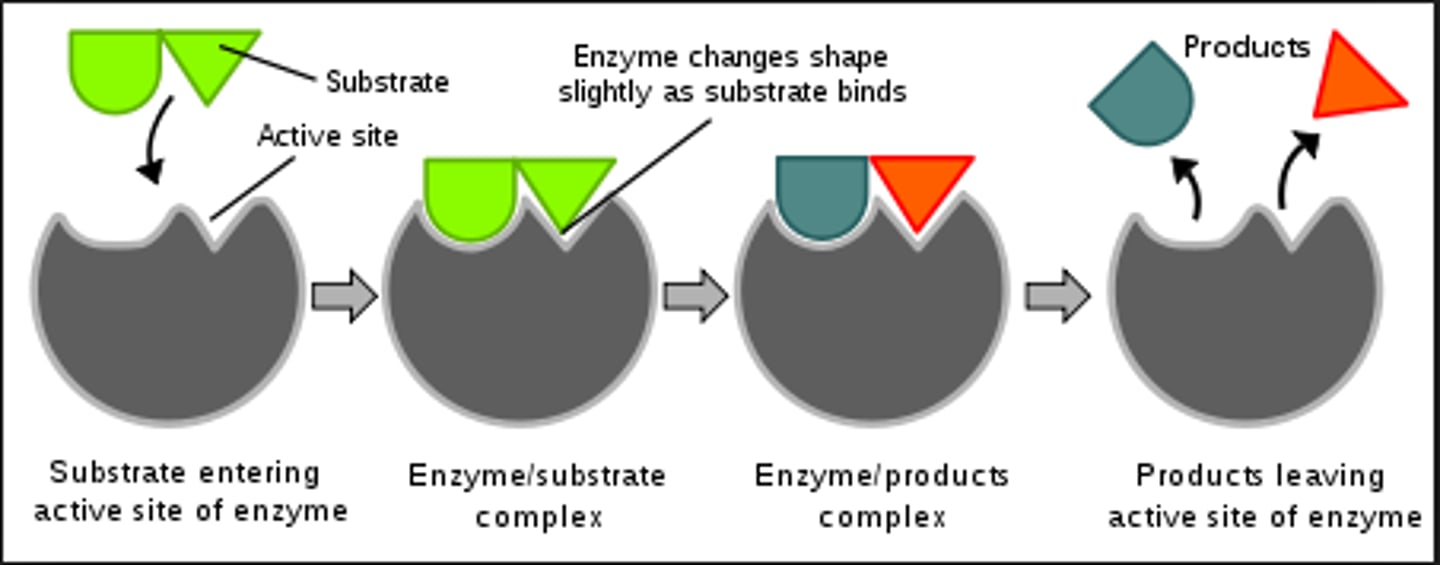
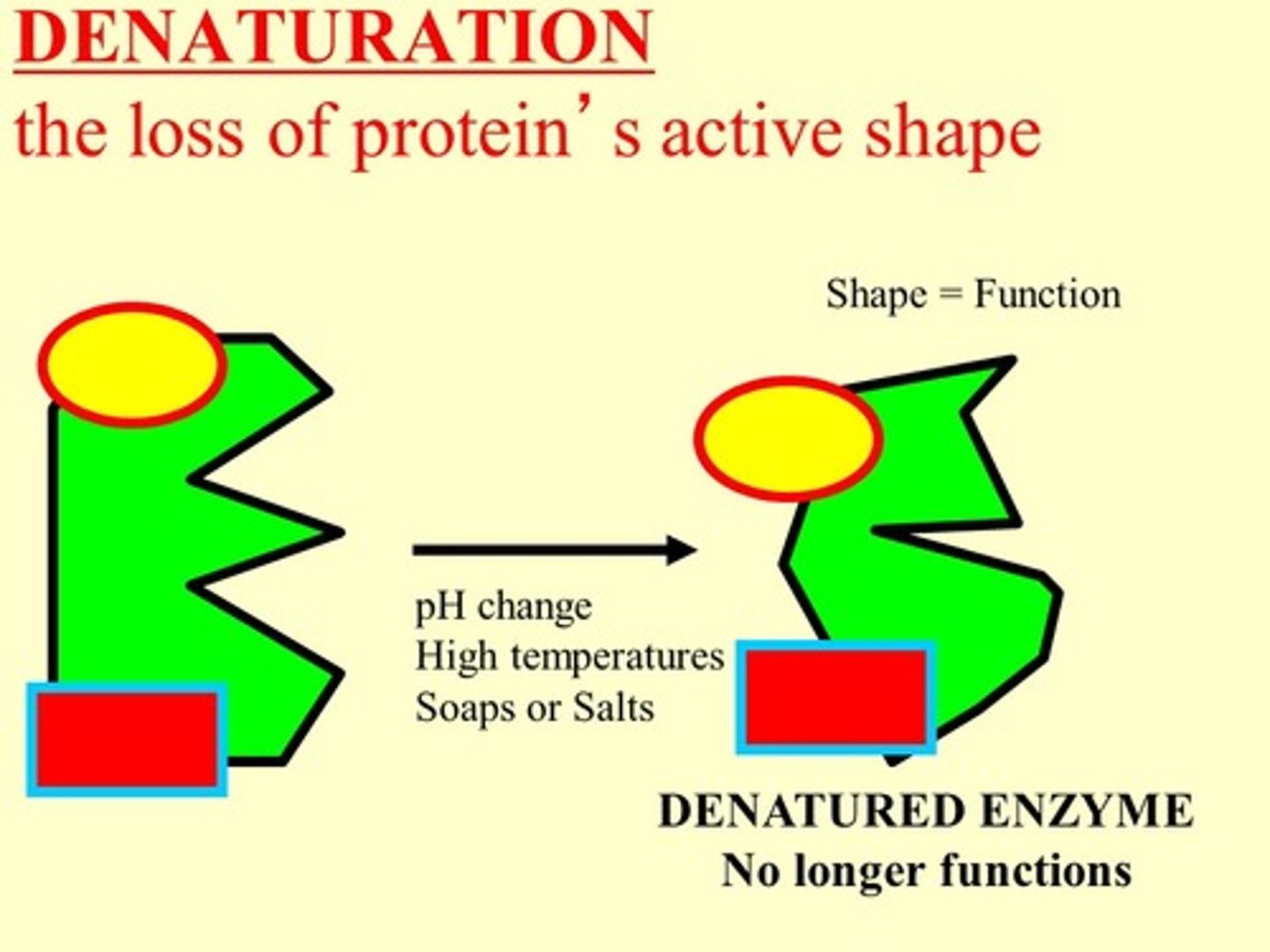
enzymes
A type of special protein that speeds up a chemical reactions in a living things, can be denatured by extreme pH or temperatures
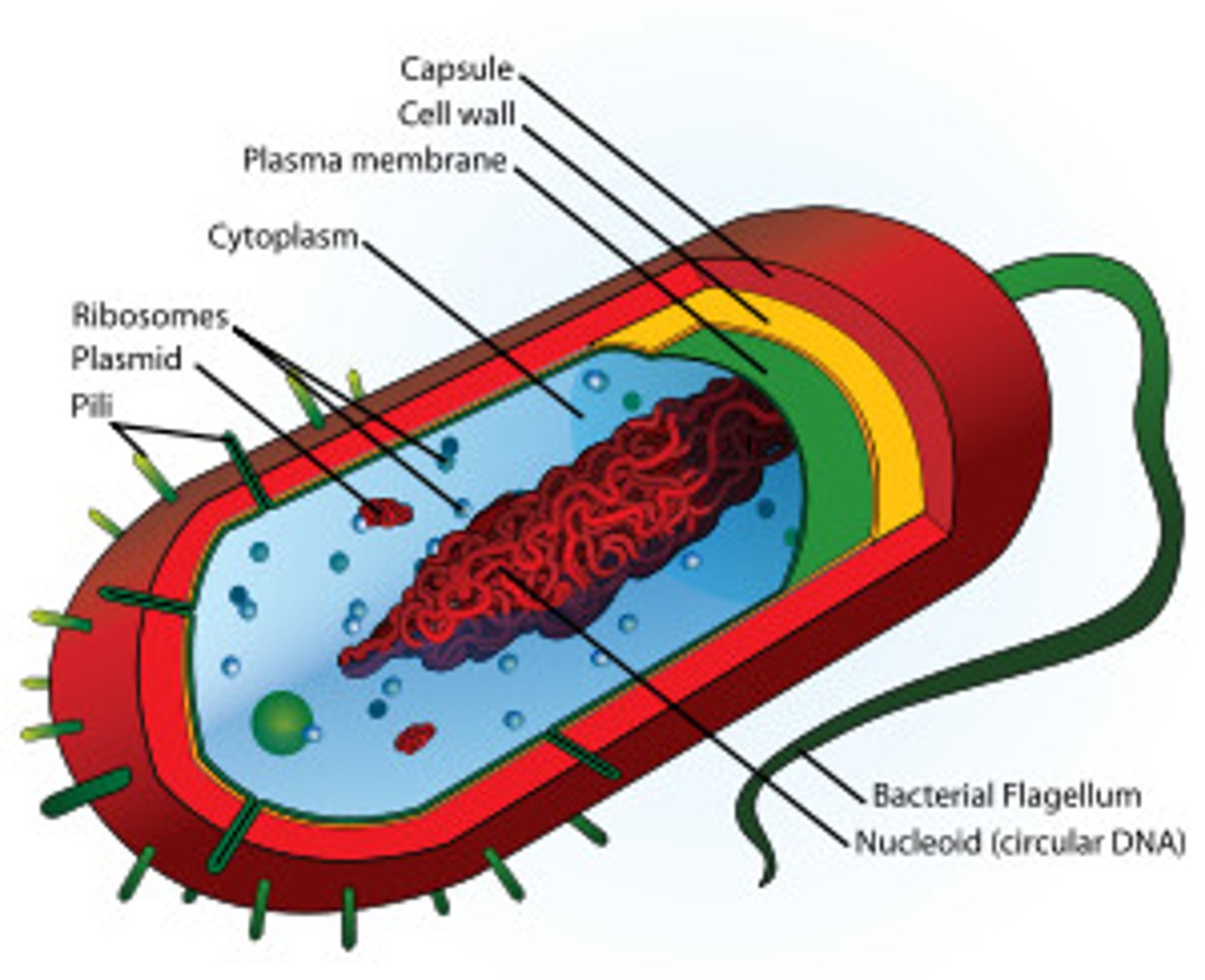
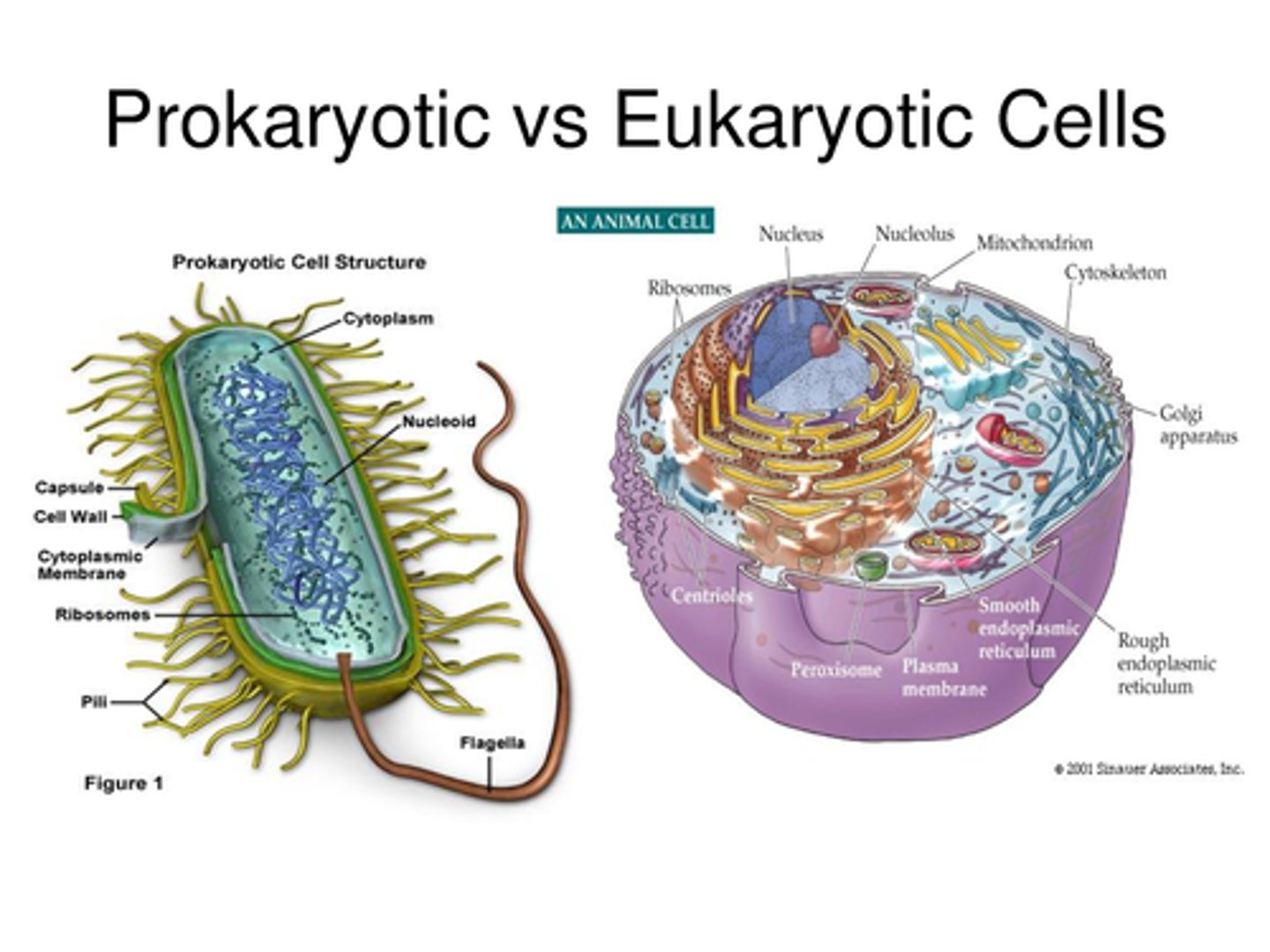
prokaryotic cell (bacteria cell)
cell that does NOT have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles (includes Kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria)
eukaryotic cells
Larger, complex, with nucleus enclosing DNA, membrane bound organelles ( Kingdoms: Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protista)
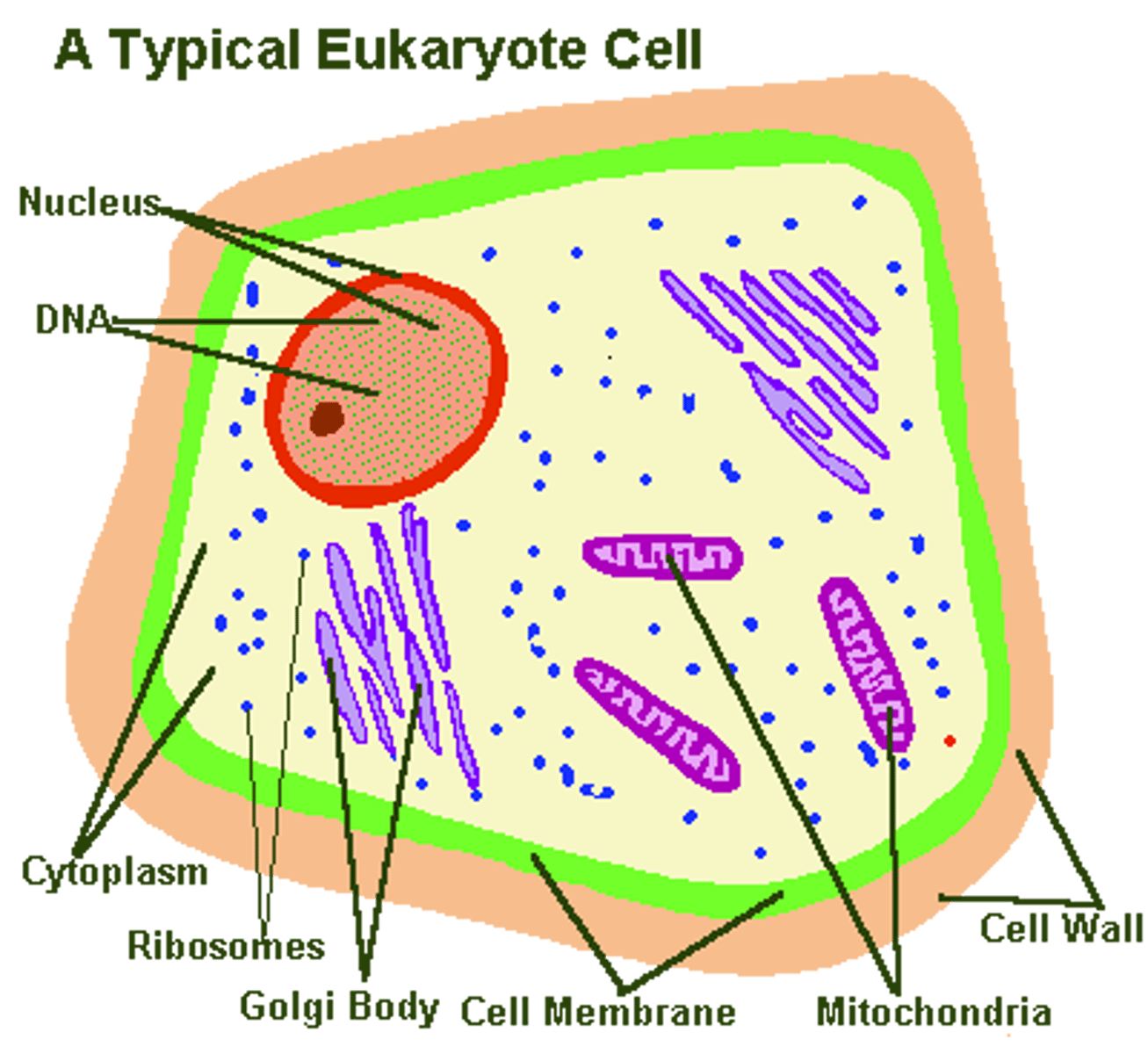
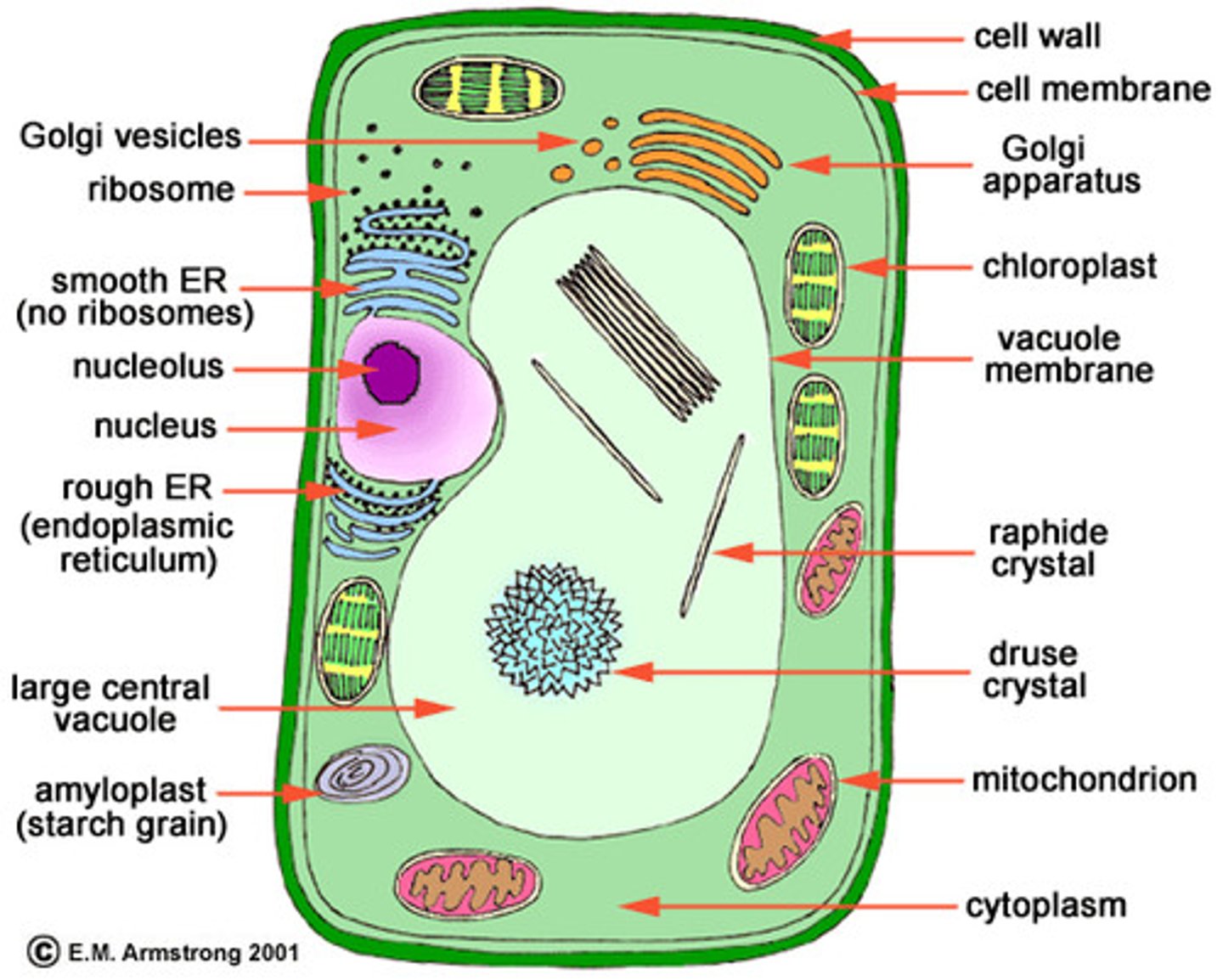
unique to PLANT cells
contains a cell wall, chloroplasts, and large central vacuole for water storage, animals do not have these features
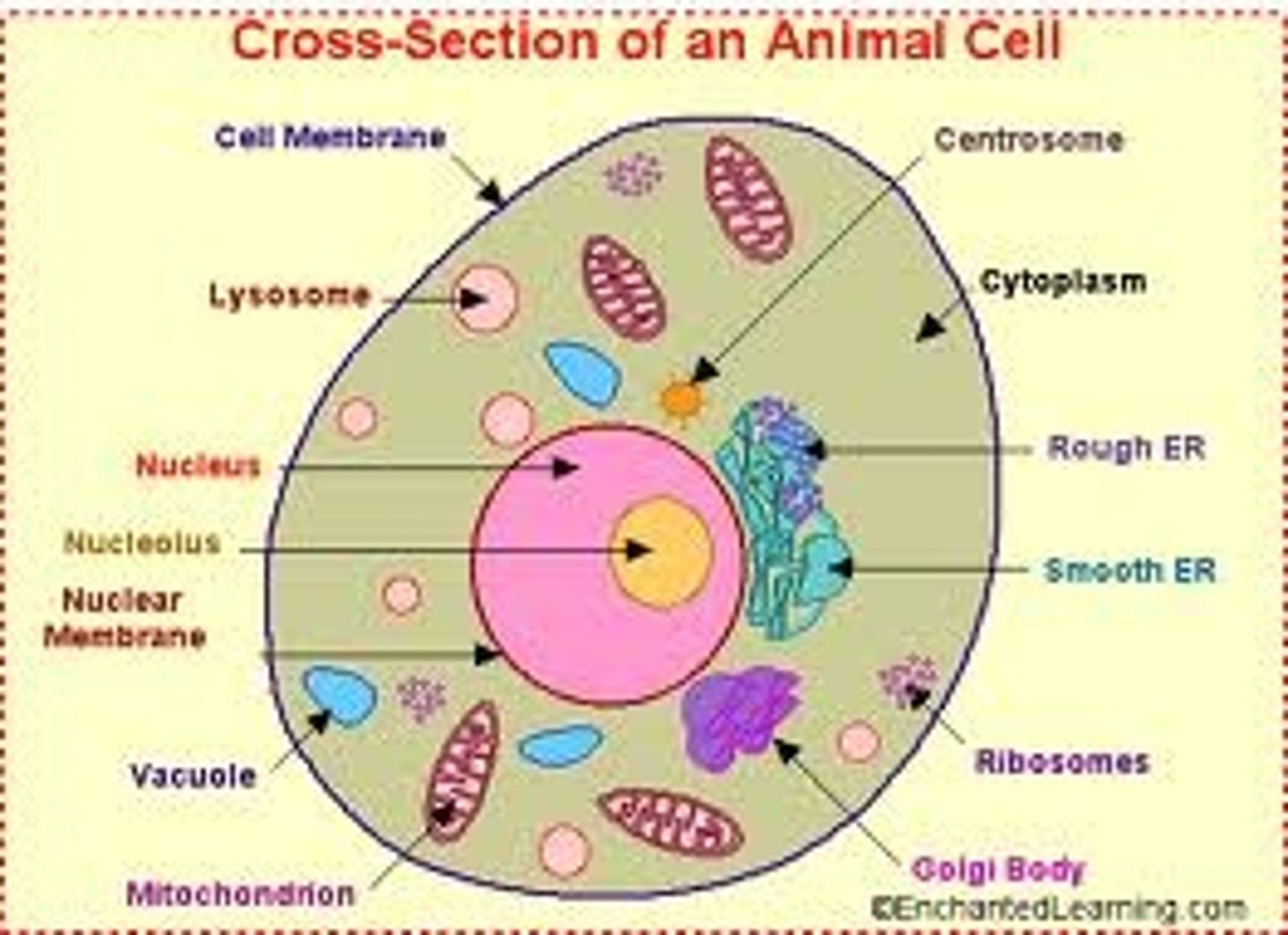
unique to ANIMAL cells
lysosomes and centrioles, plants do not
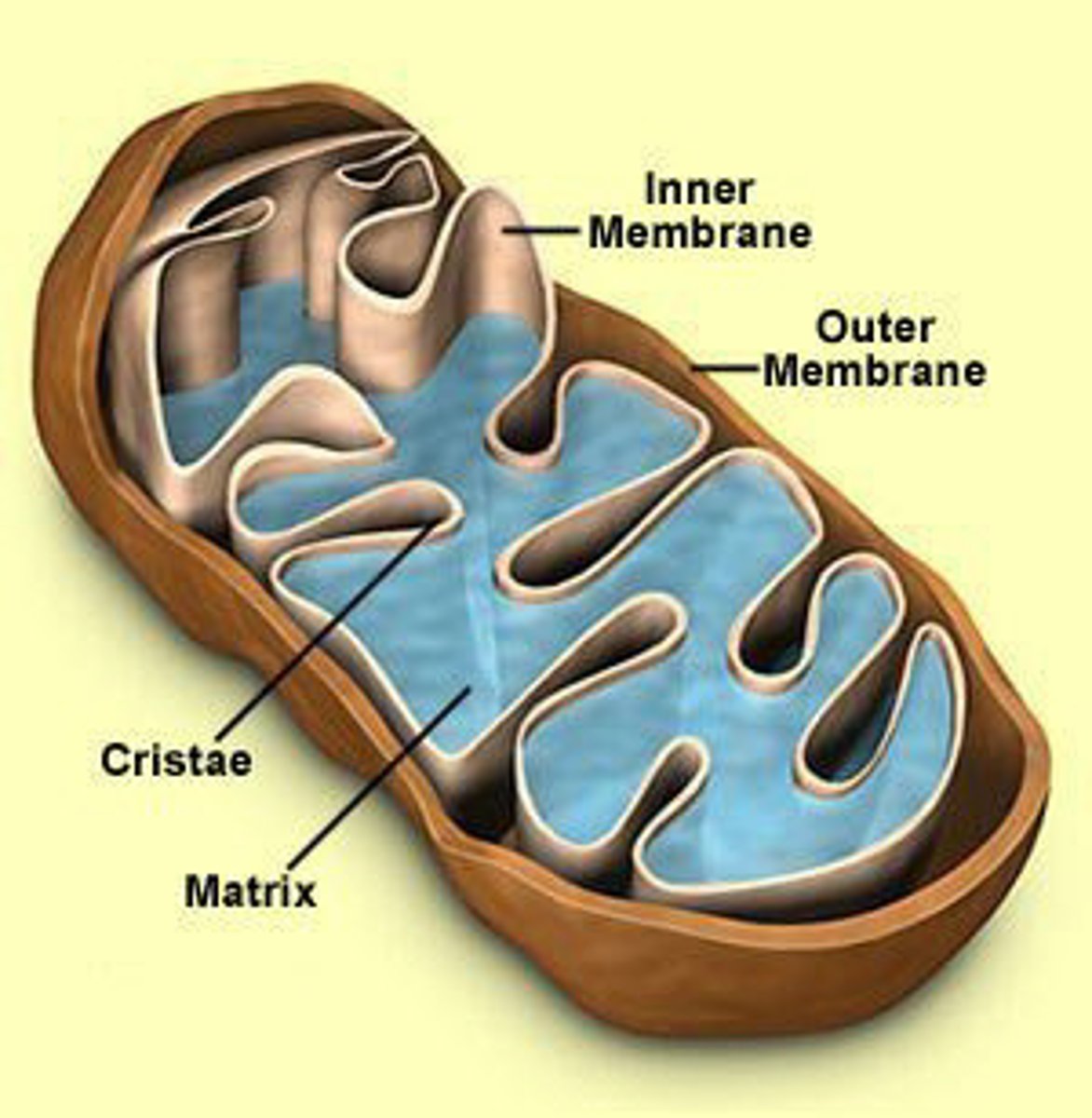
mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP energy production by respiration, uses glucose for fuel
nucleus
control center of cell, contains DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction, found in all eukaryote cells
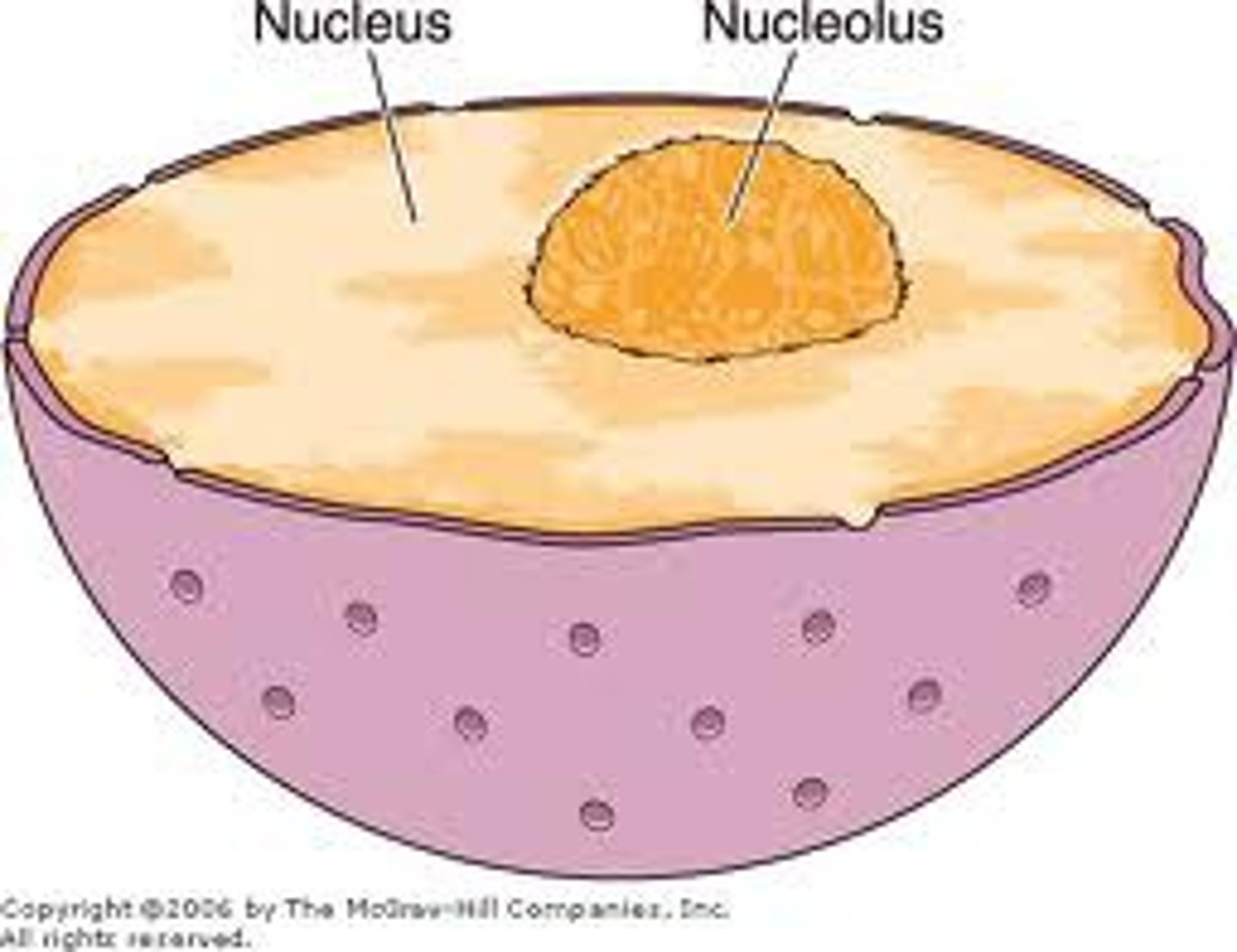
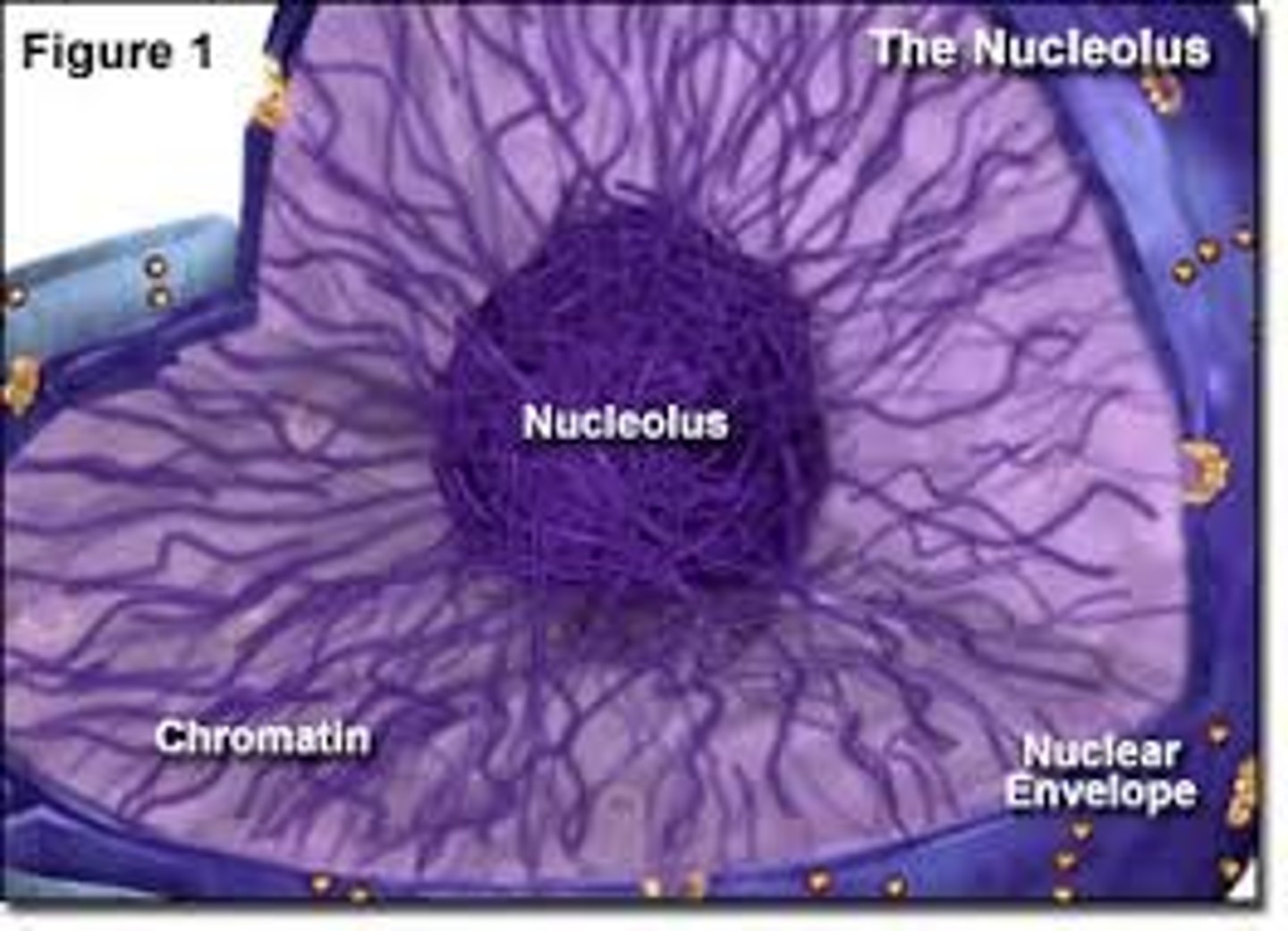
nucleolus
region inside the nucleus that produces ribosomes
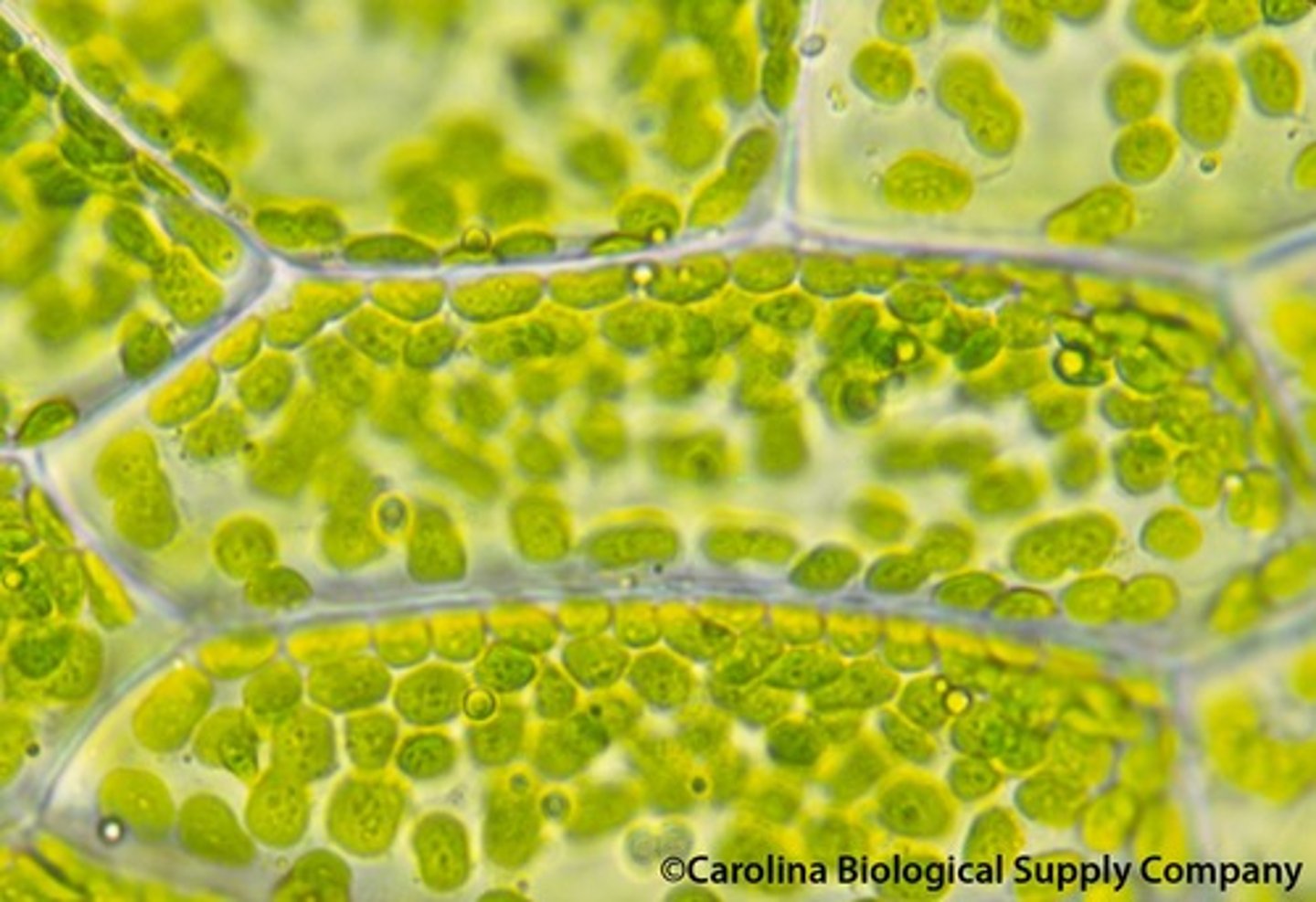
chloroplast
organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs, contains chlorophyll
smooth ER
part of the endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes, makes and transports lipids
rough ER
part of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes, makes and transports proteins

ribosome
makes proteins, found in ALL cells & cell types
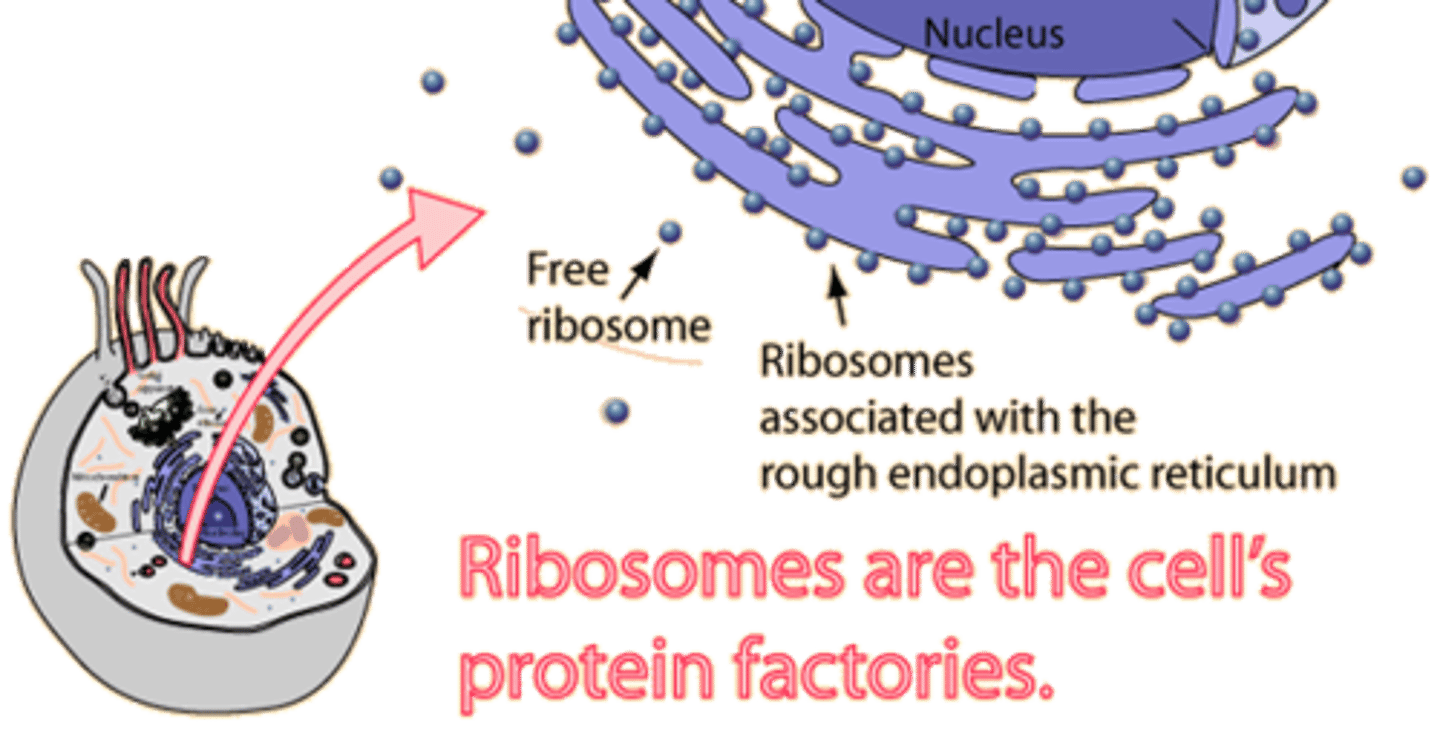
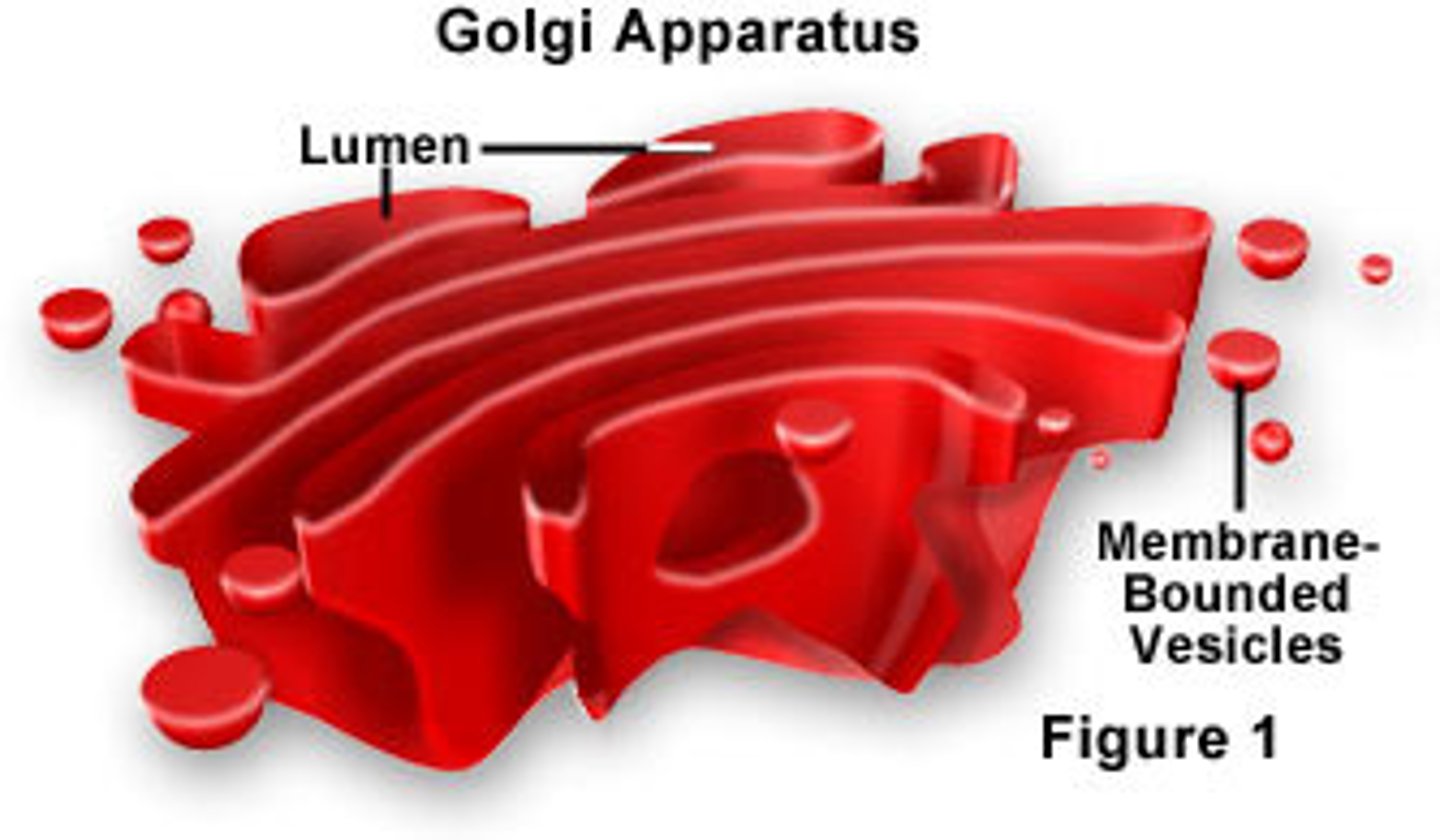
golgi apparatus
system of membranes that modifies and packages substances for export by the cell
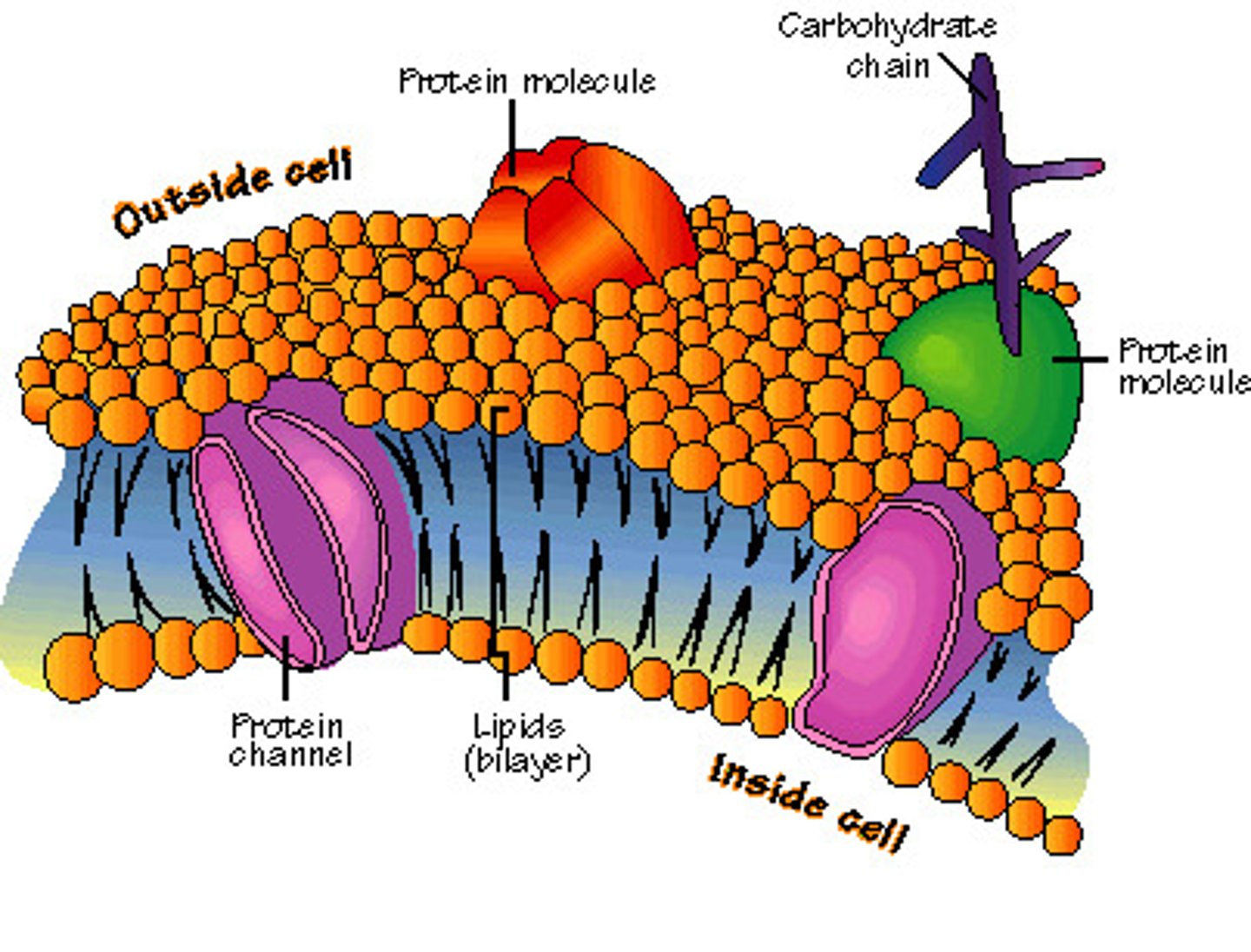
plasma membrane (cell membrane)
controls what enters and leaves the cell and separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment, MAINTAINS HOMEOSTASIS
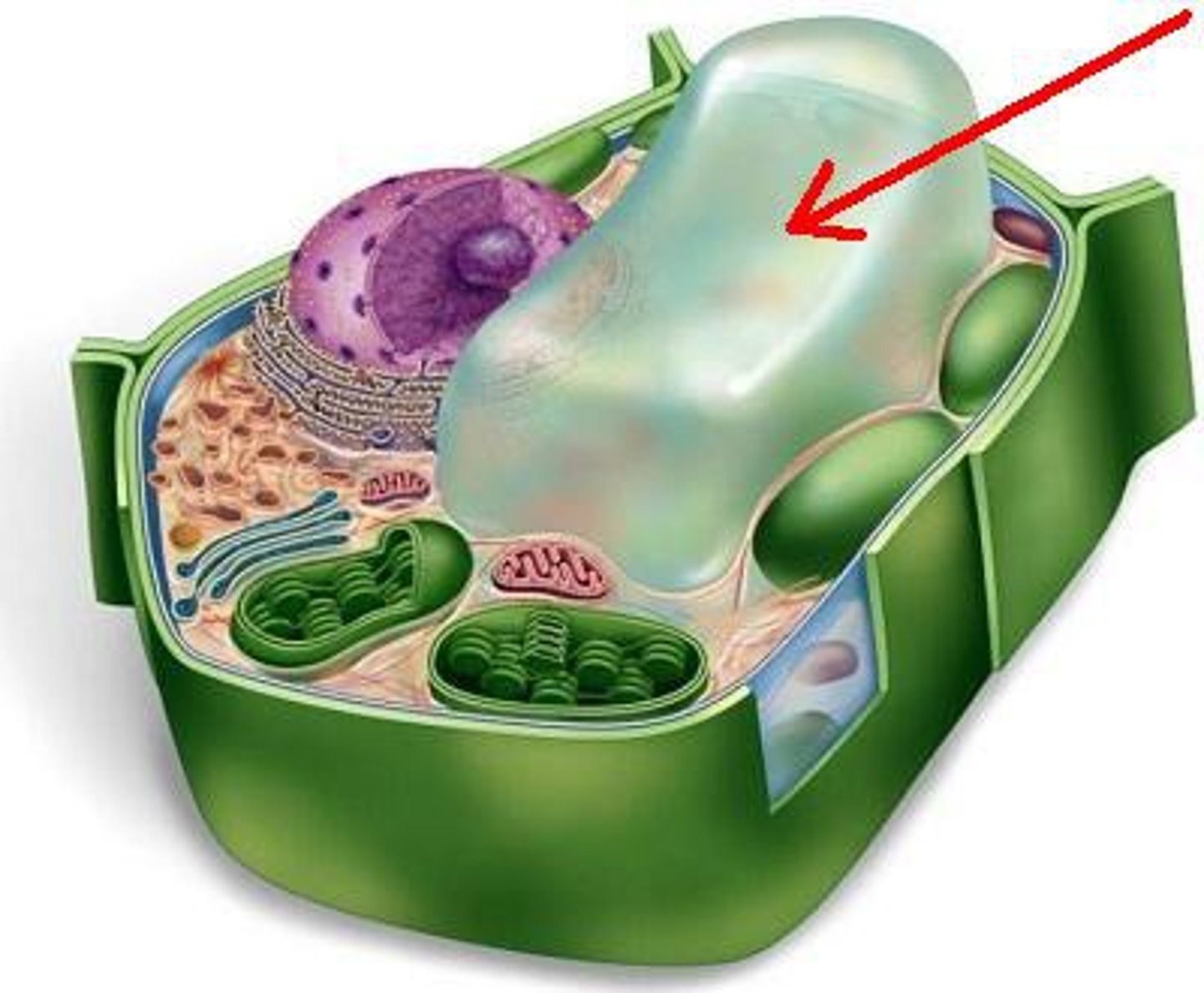
vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area, larger in plants
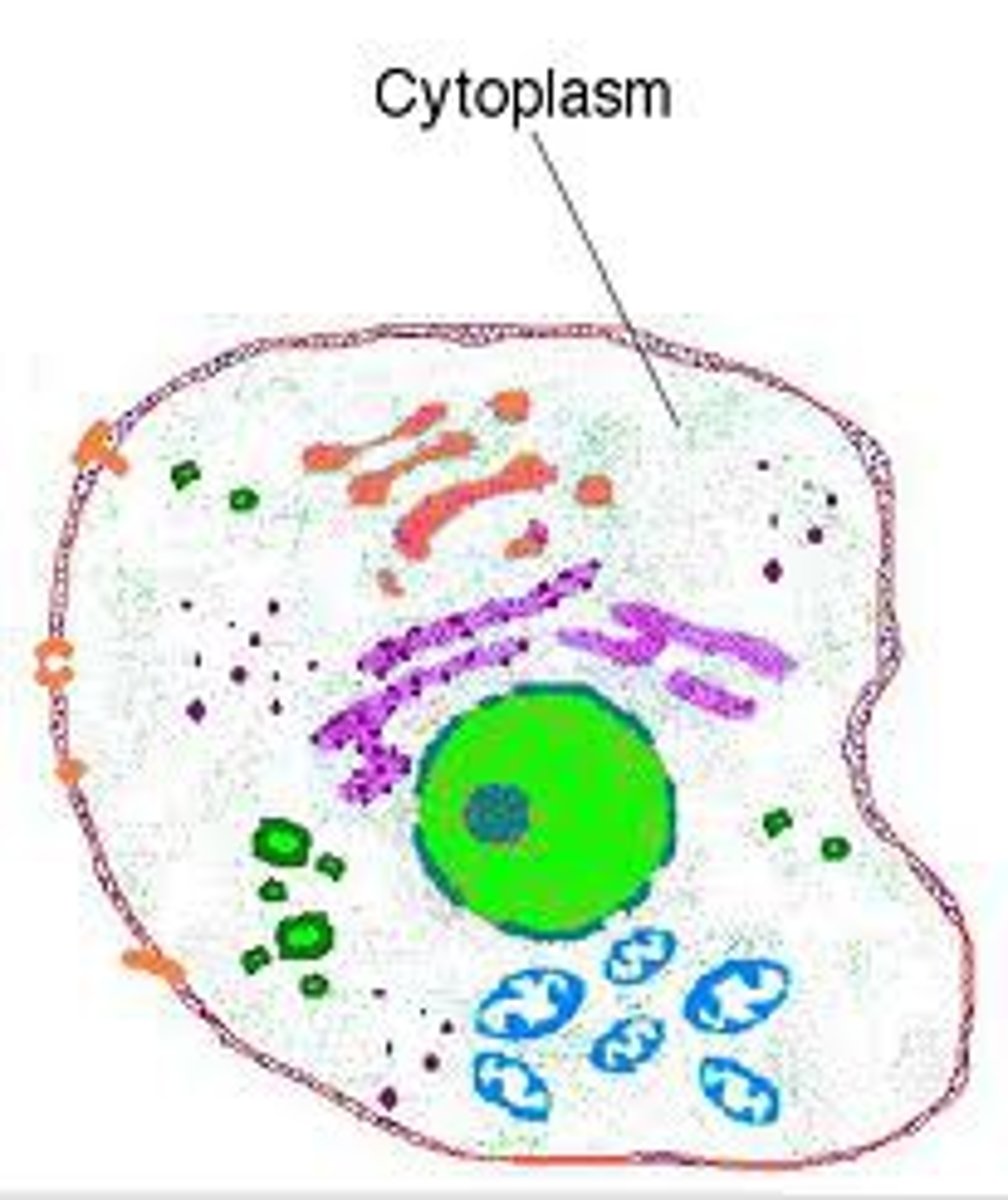
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
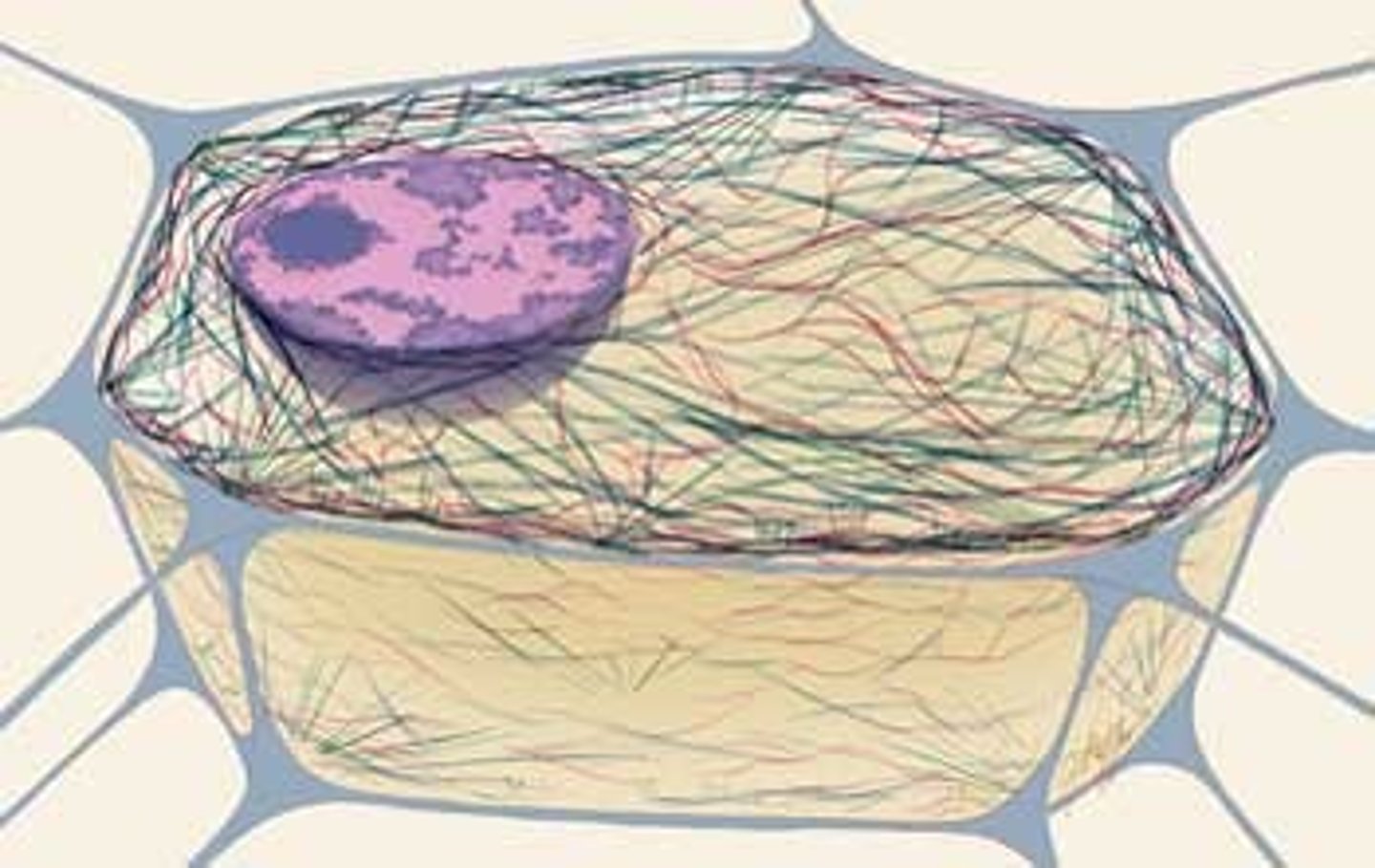
cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in many forms of cell movement
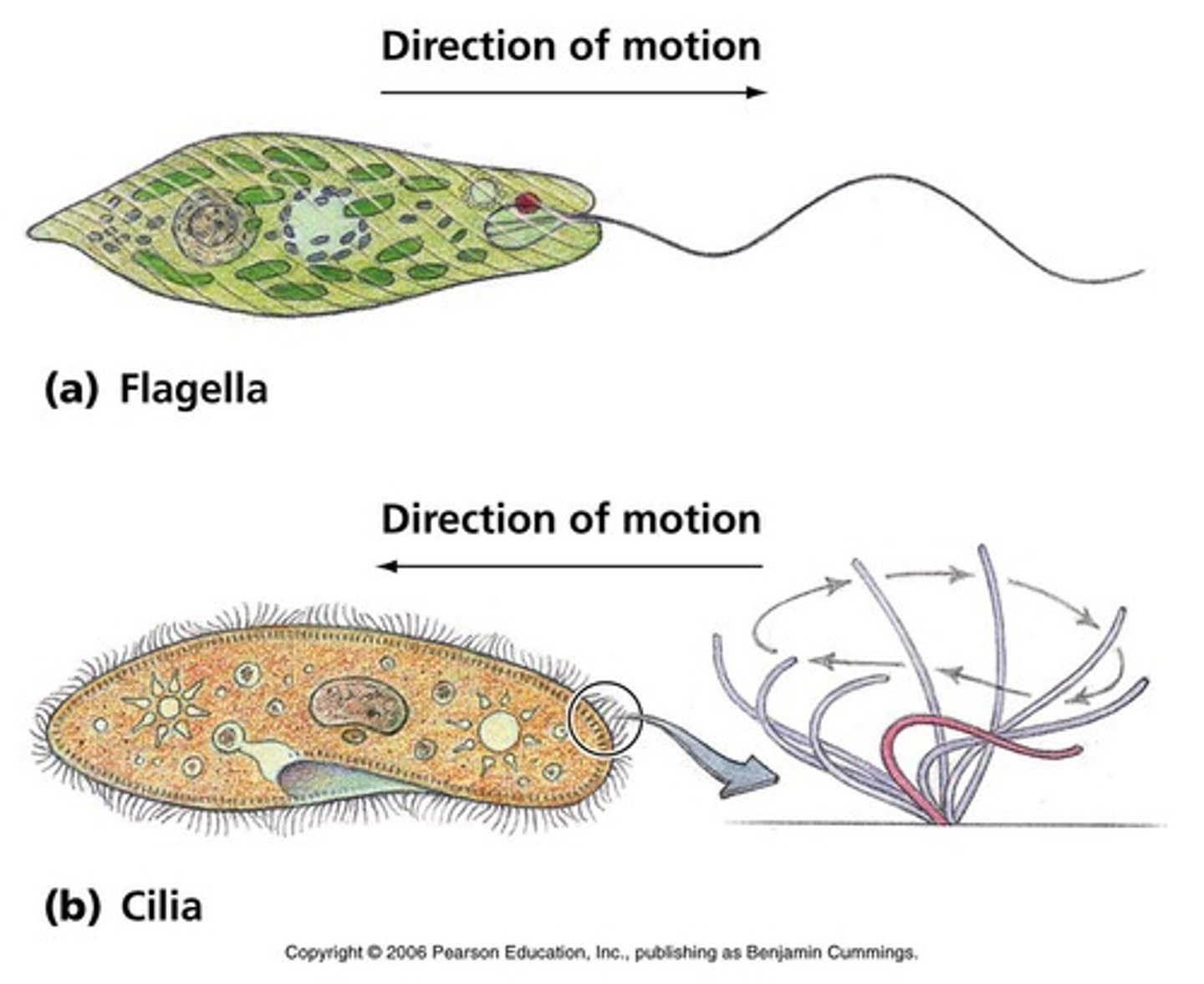
cilia and flagella
hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement
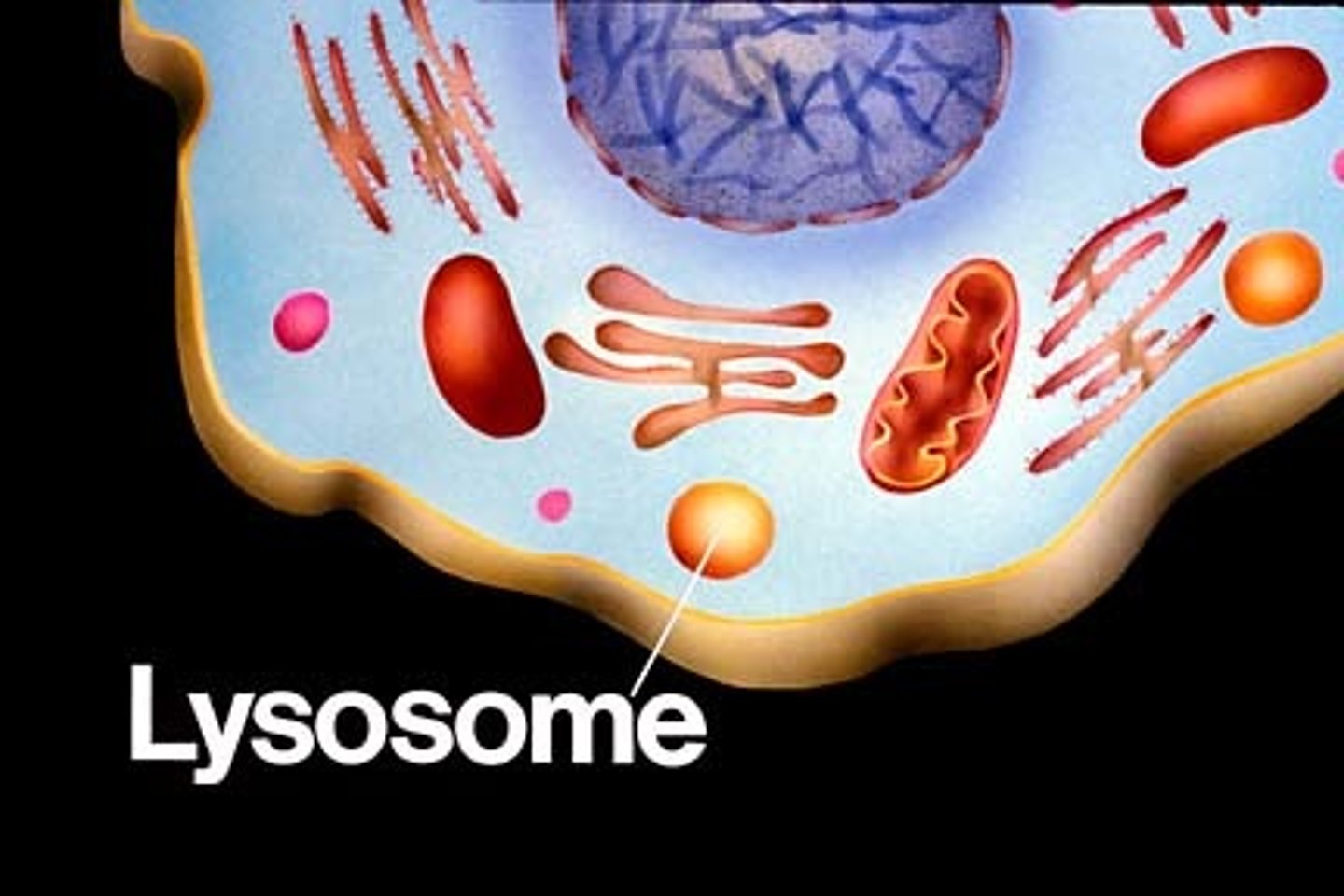
lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
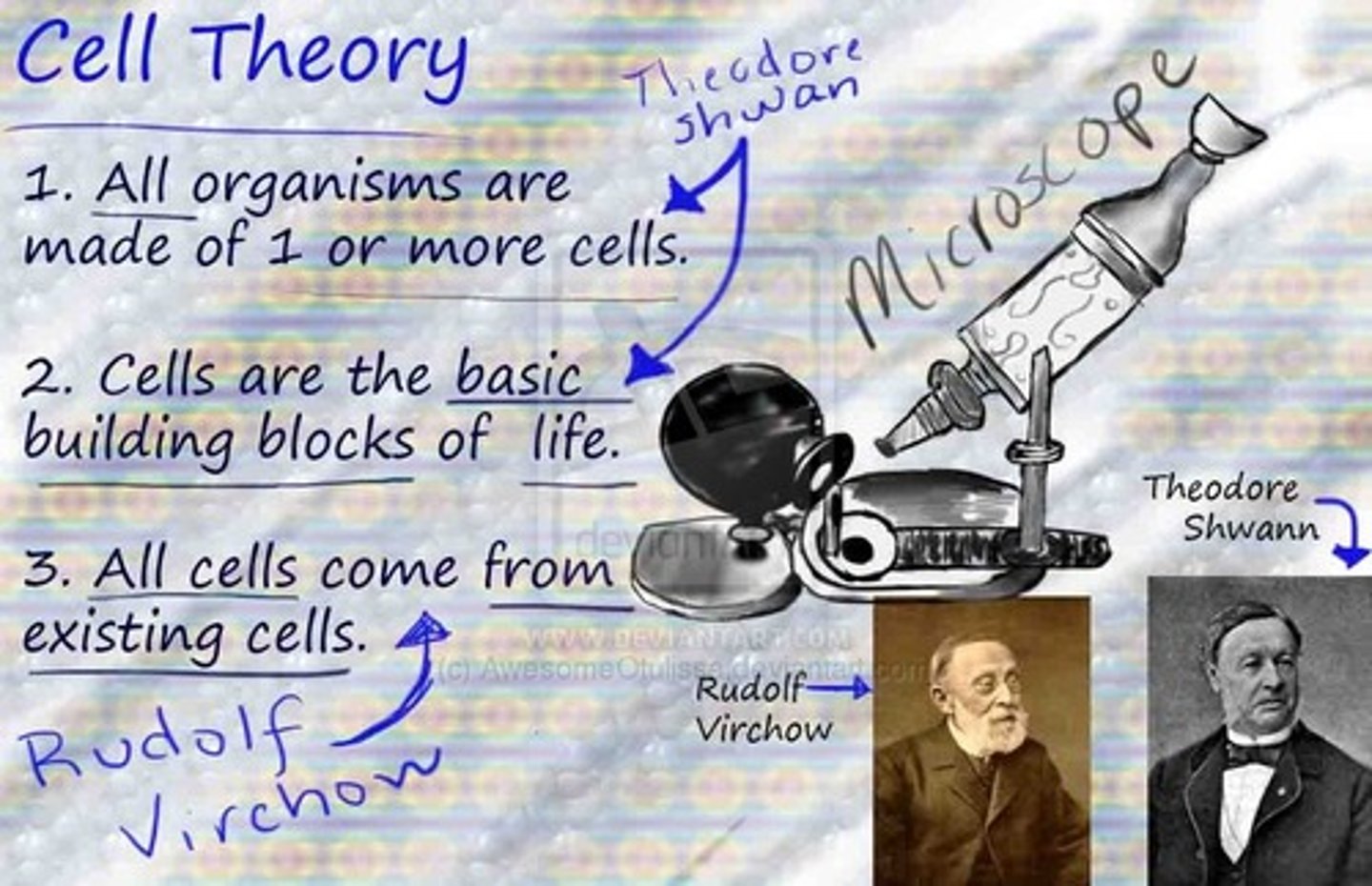
cell theory
1. all living things are composed of cells, 2. cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and 3. new cells are produced from existing cells
monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
osmosis
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
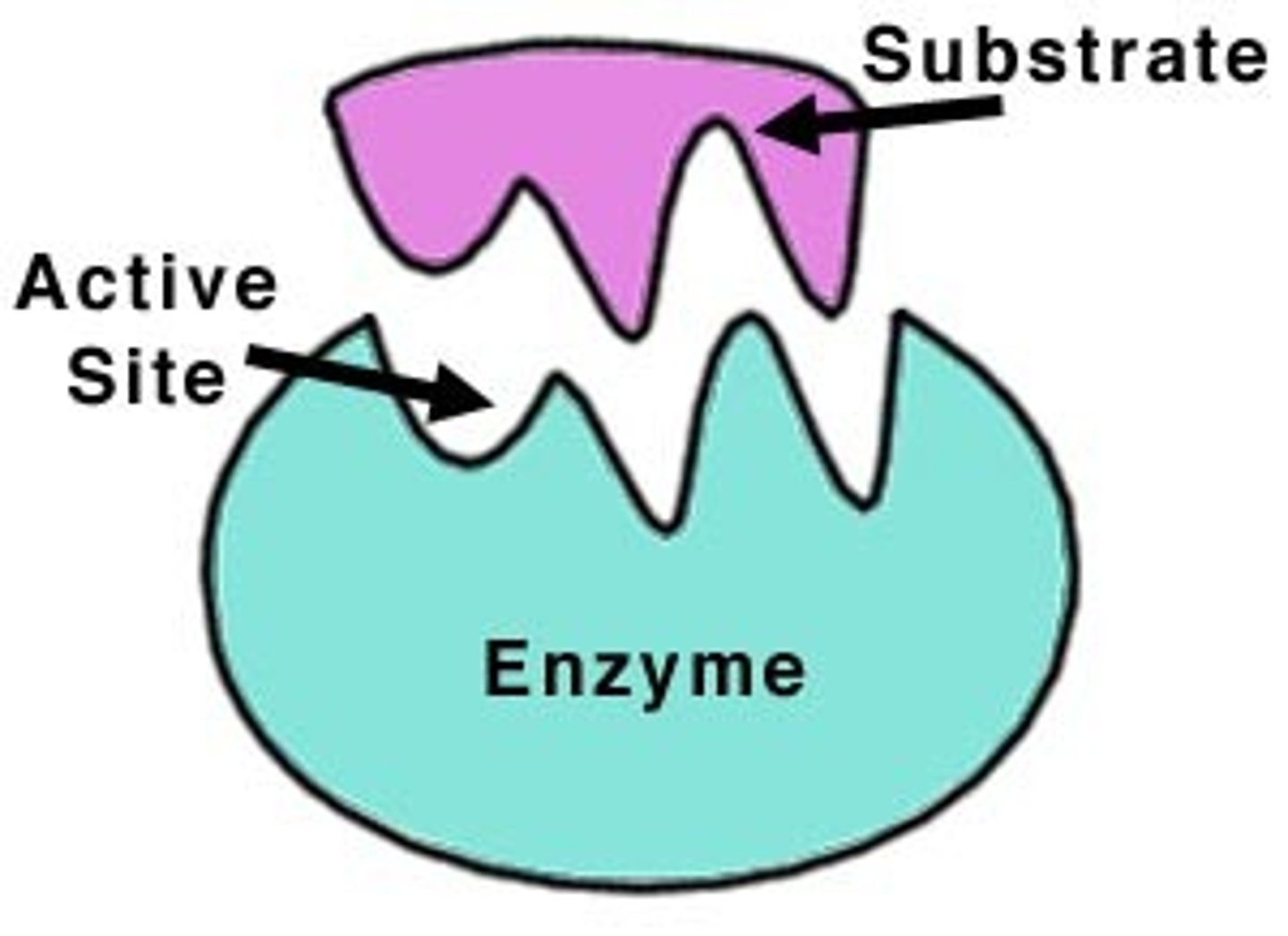
active site
a region on an enzyme that binds to the substrate during a reaction.
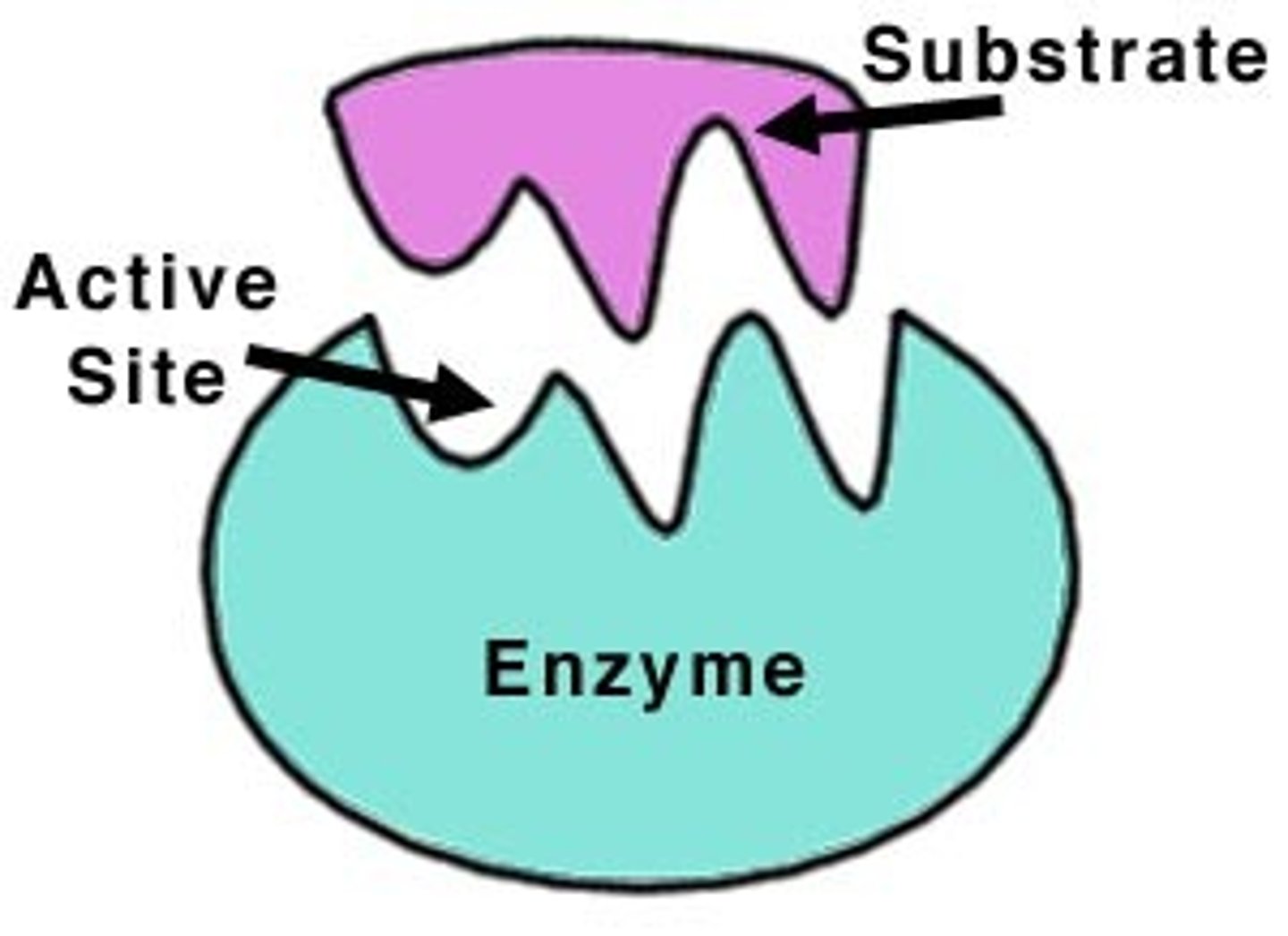
substrate(s) & products of enzymes
substrate(s) are either put together or broken down by enzymes into a new product(s)
denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH, enzyme no longer functions
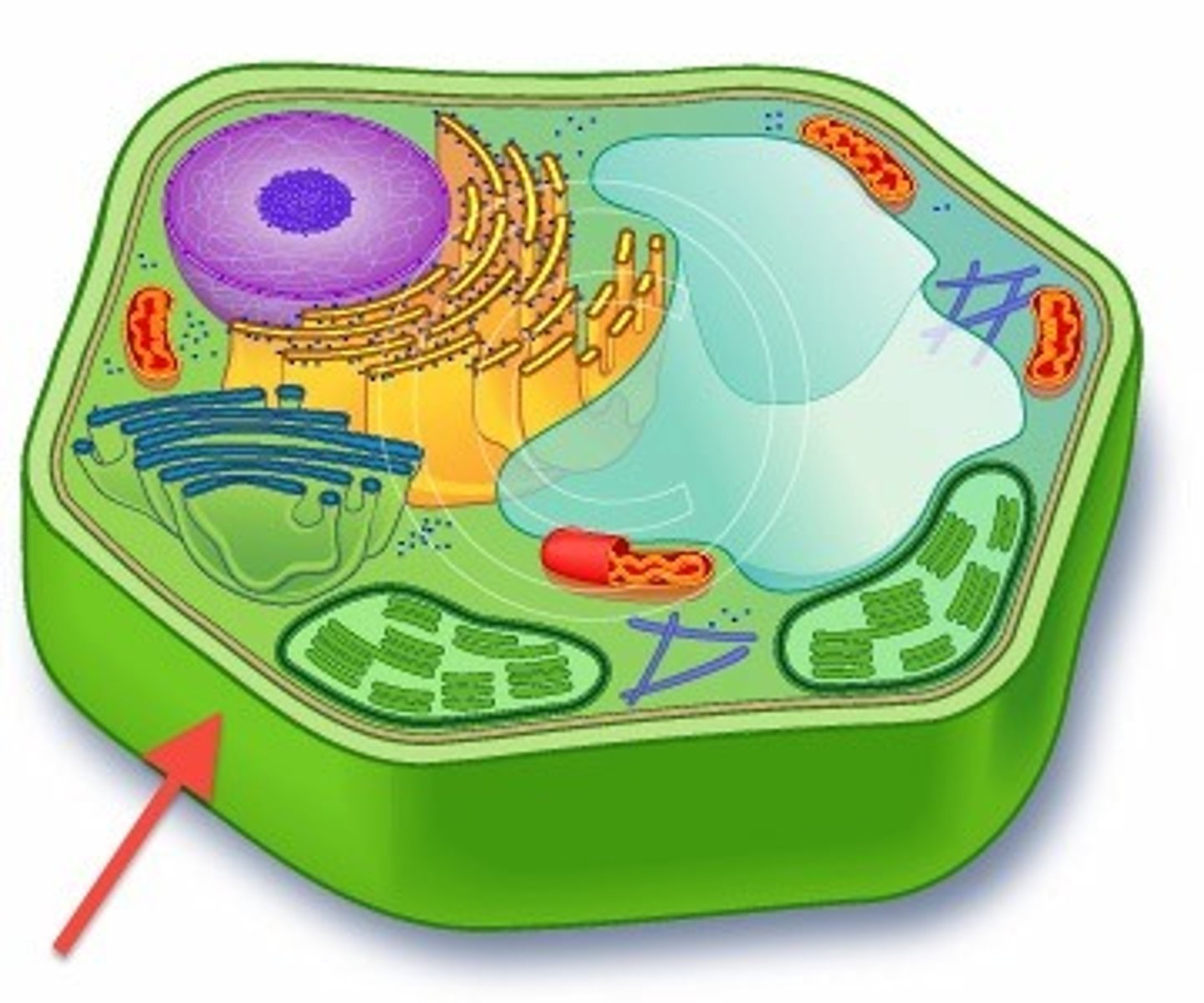
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants, provides support & protection
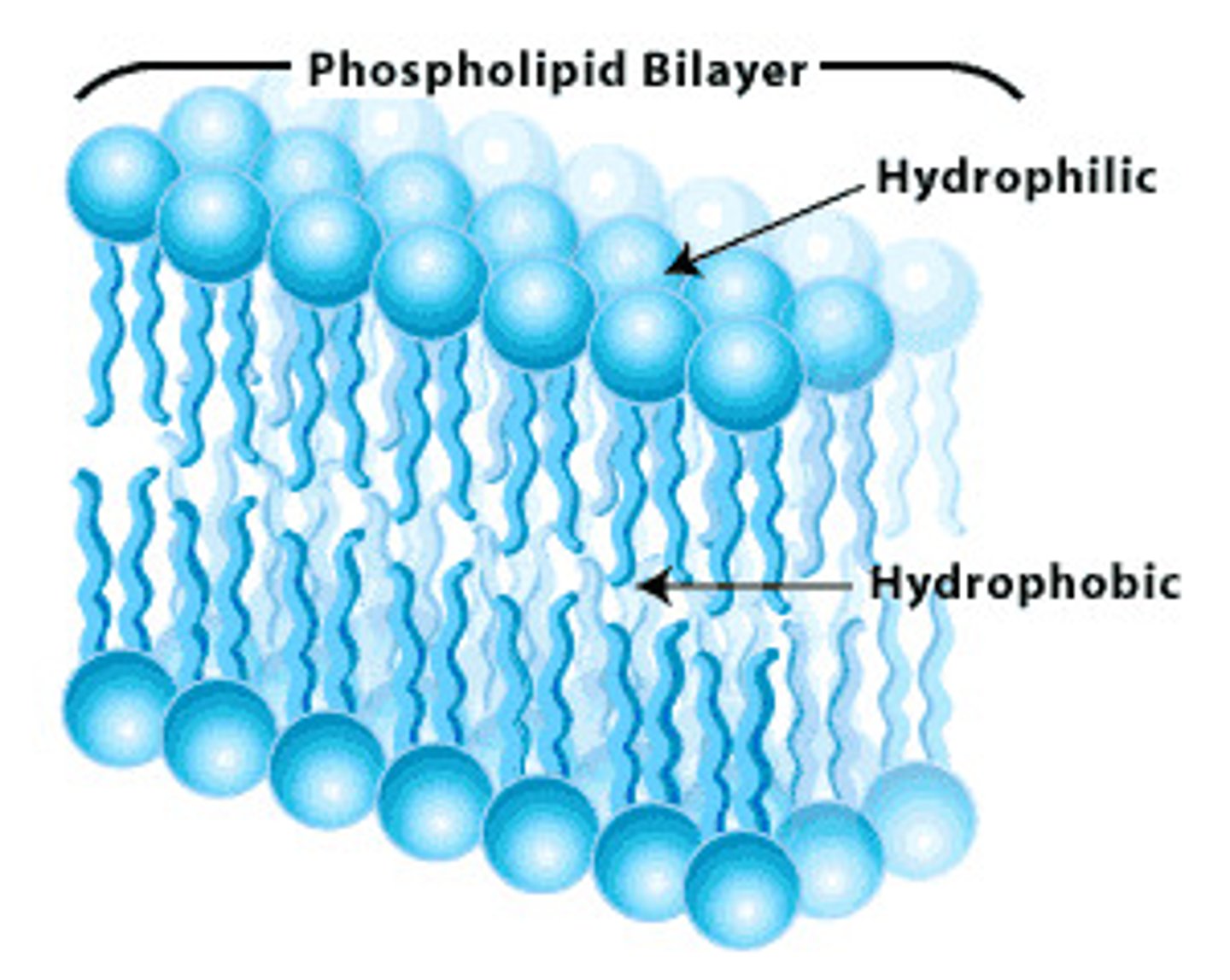
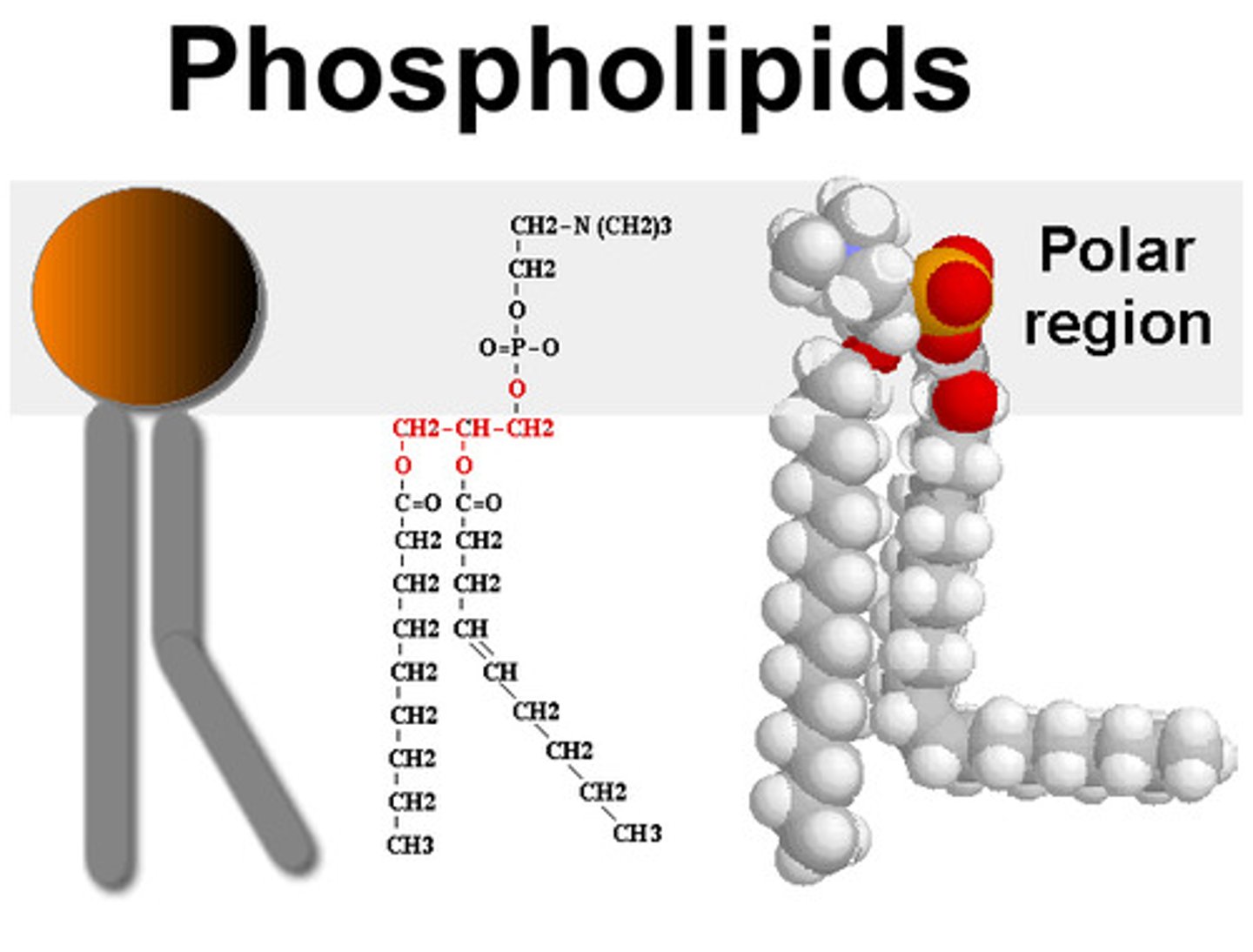
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up the cell membrane
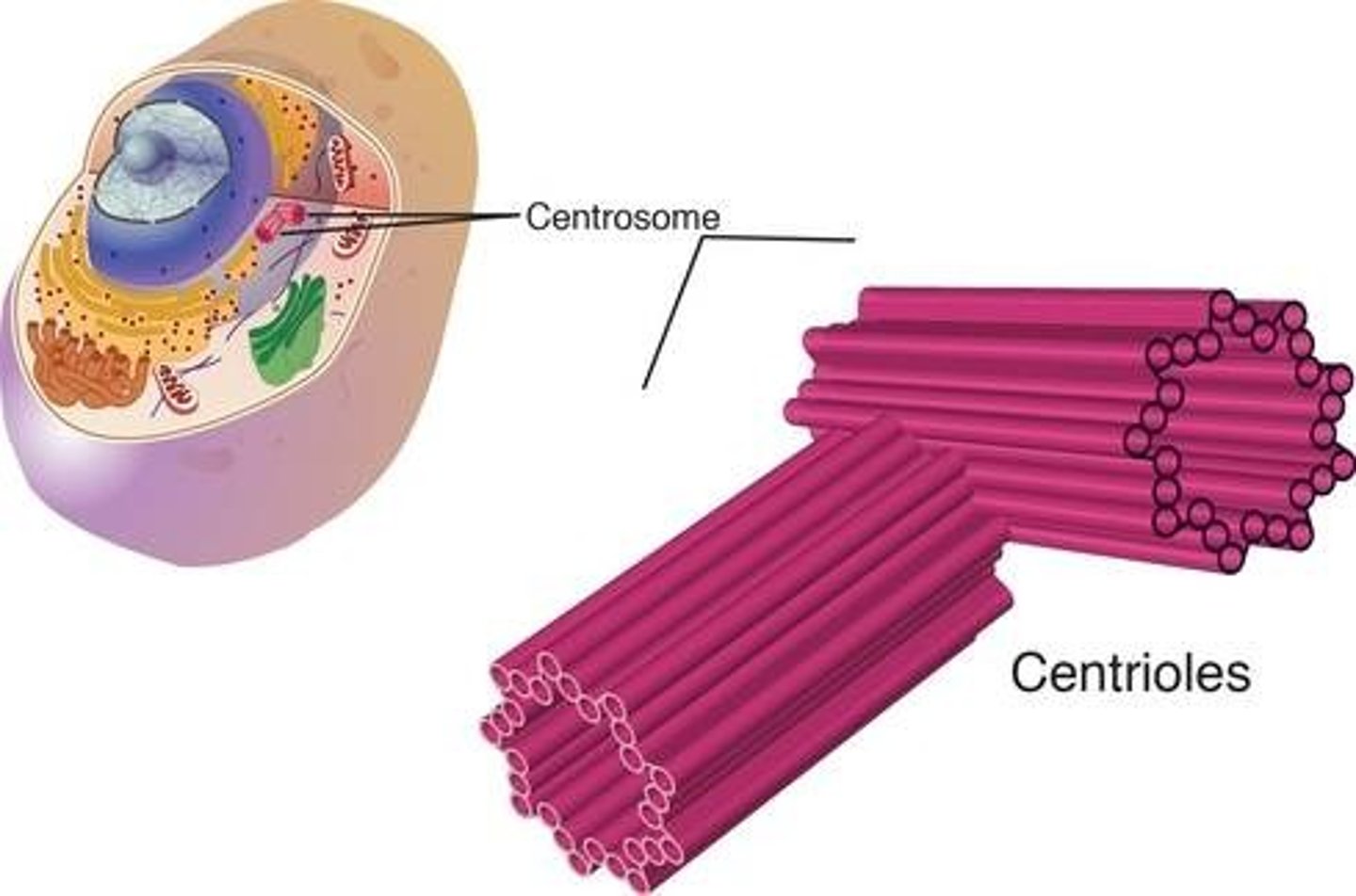
centrioles
organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, involved in the formation of spindle fibers in cell division.
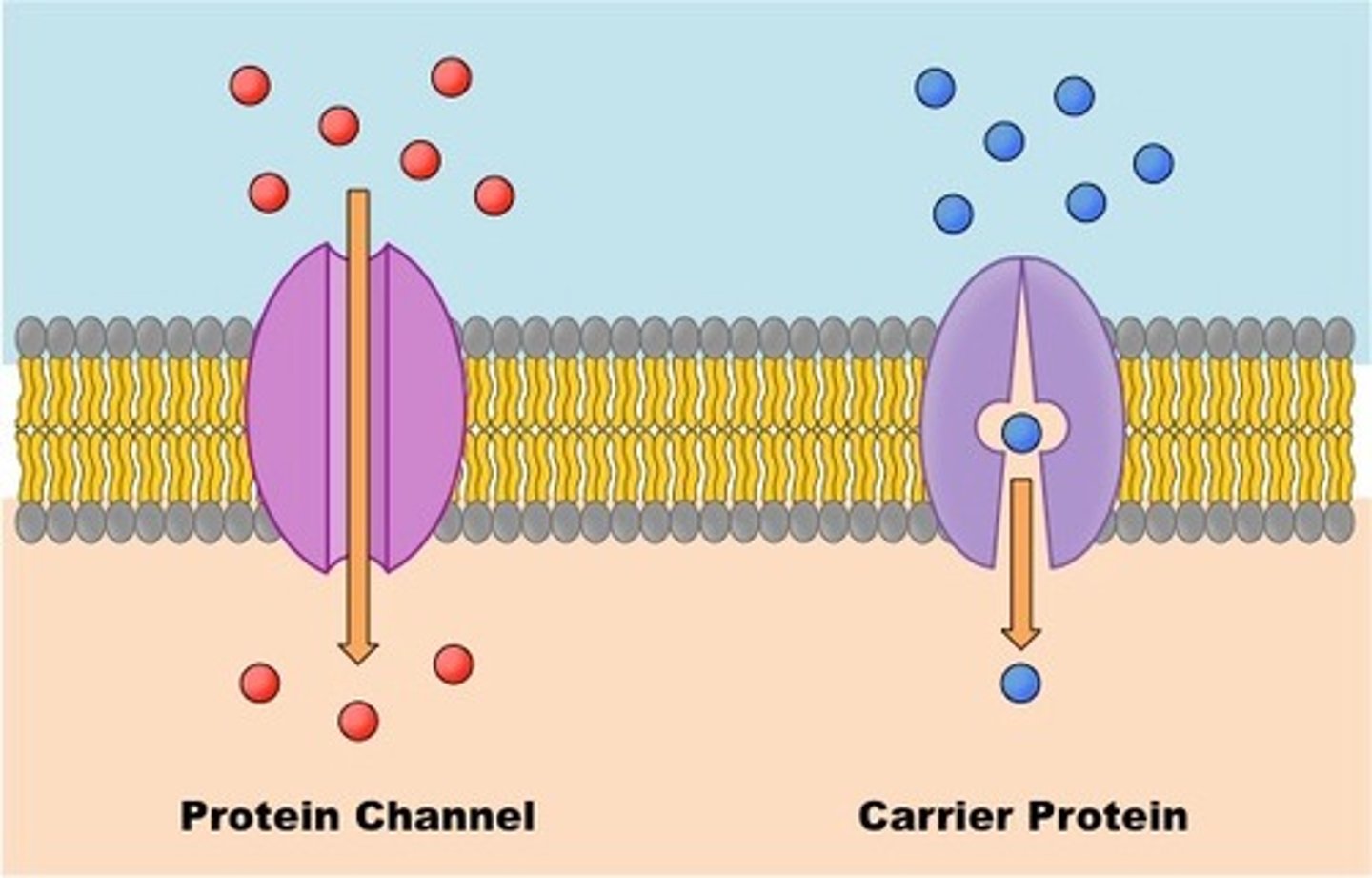
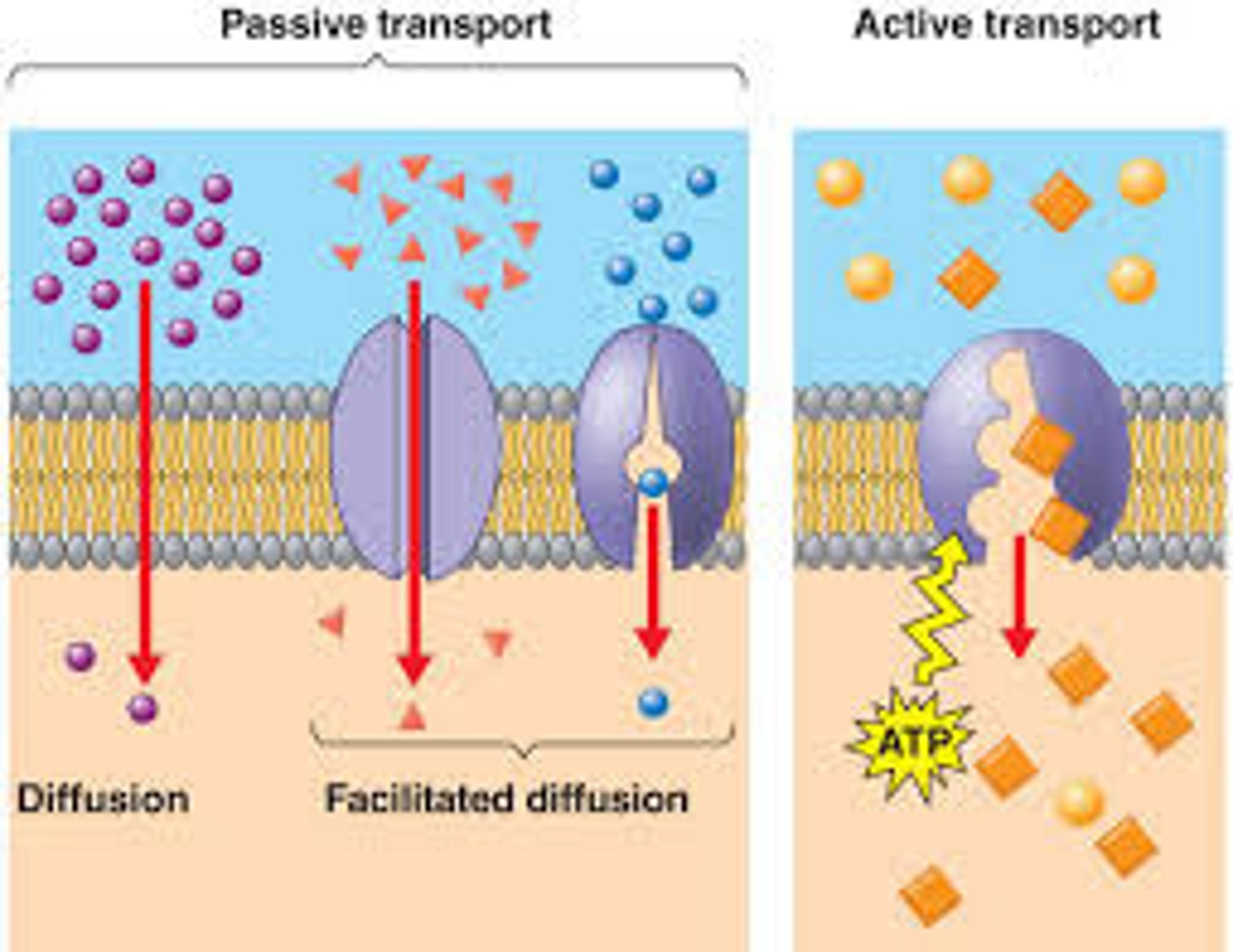
channel proteins & carrier proteins
two types of transport proteins in facilitated diffusion (passive transport)
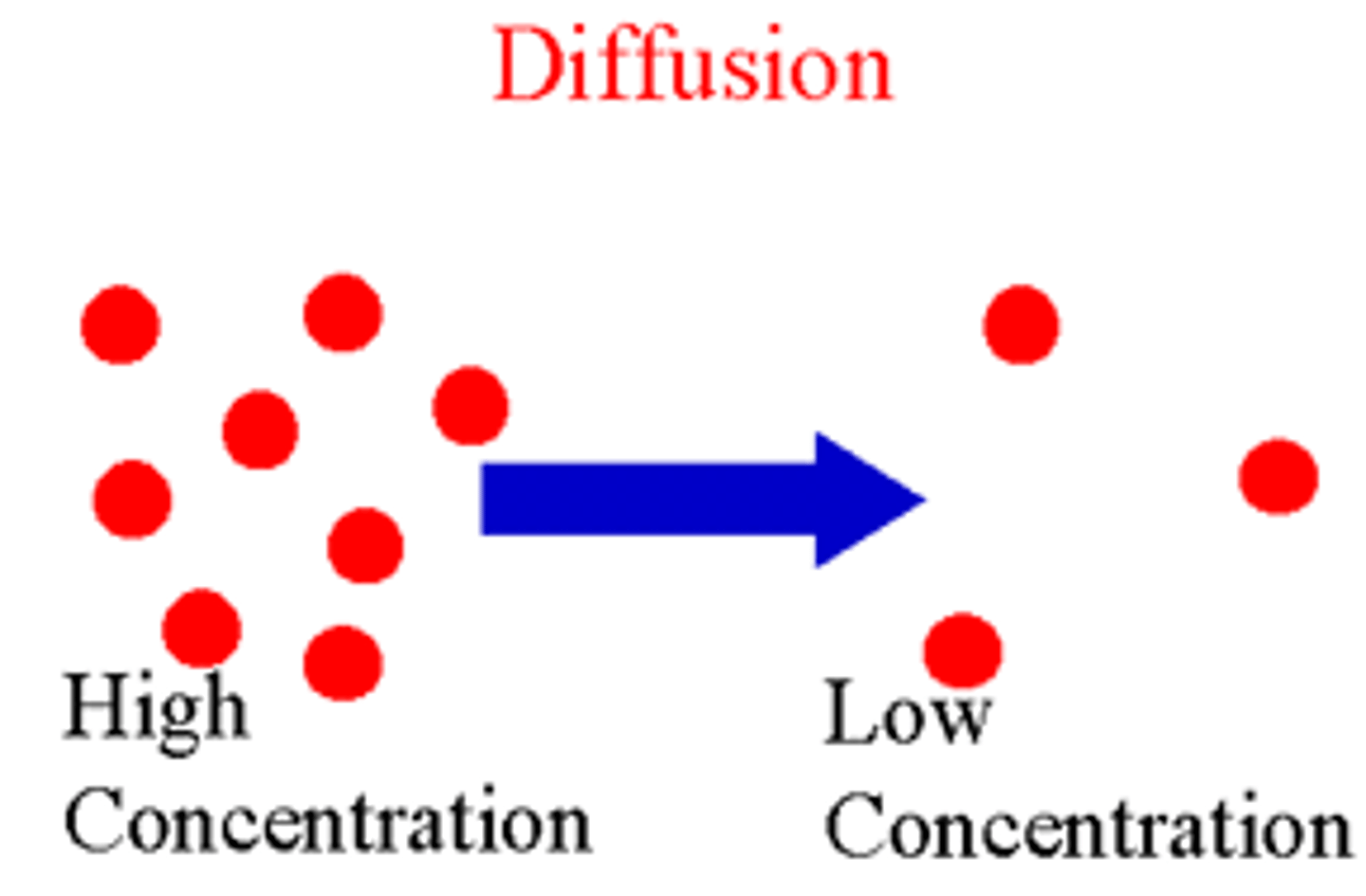
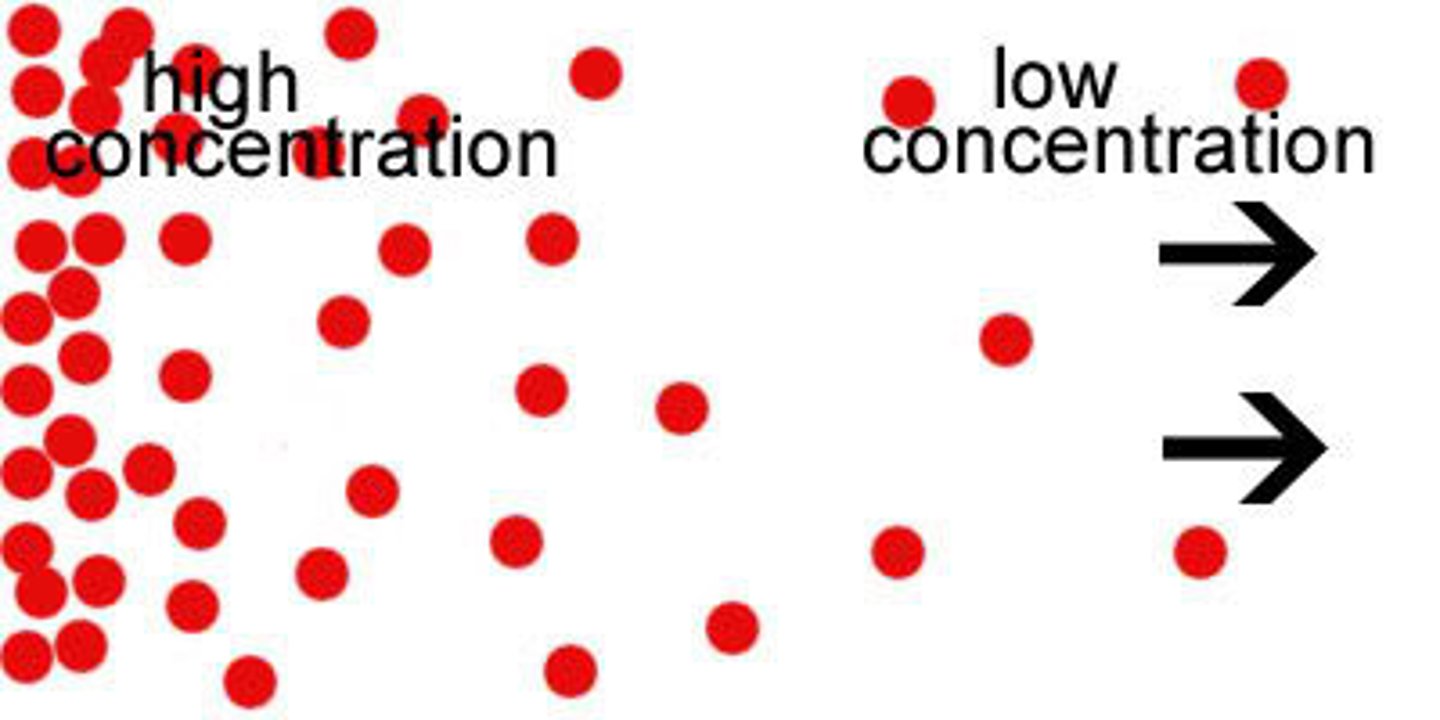
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, happens naturally
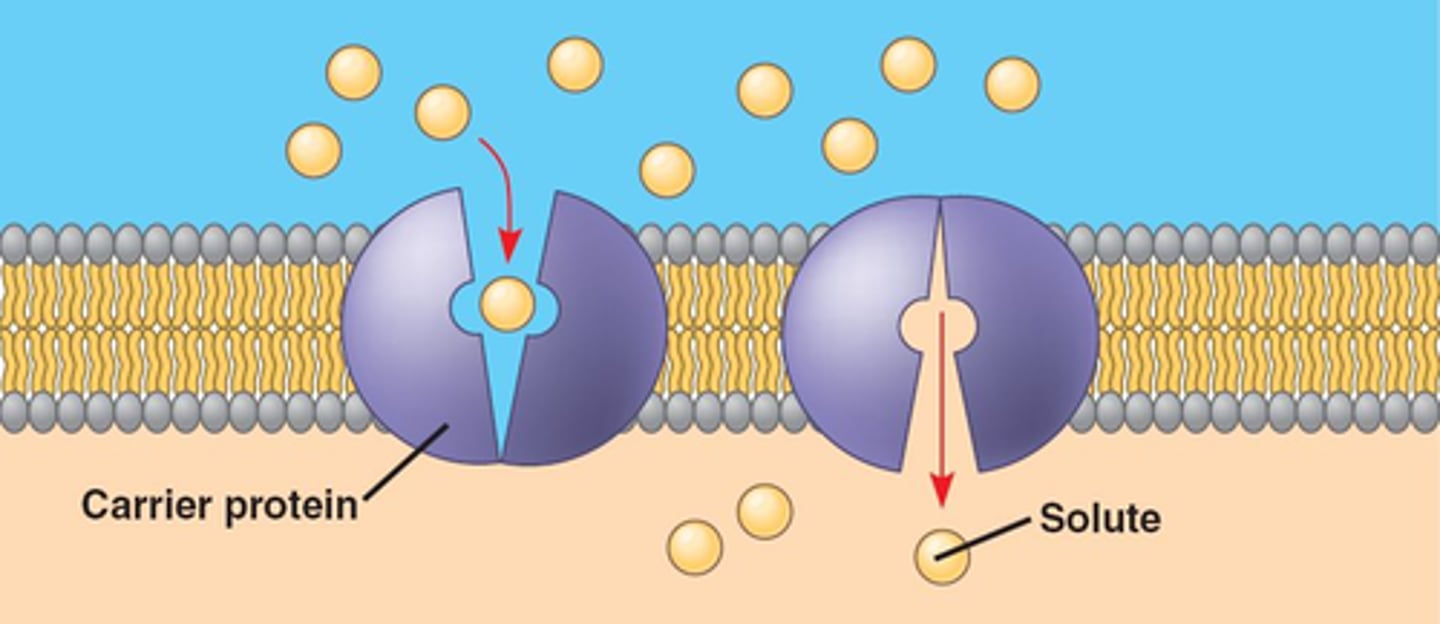
facilitated diffusion
process of diffusion in which molecules pass across the membrane through proteins in cell membrane, NO ATP (energy) required
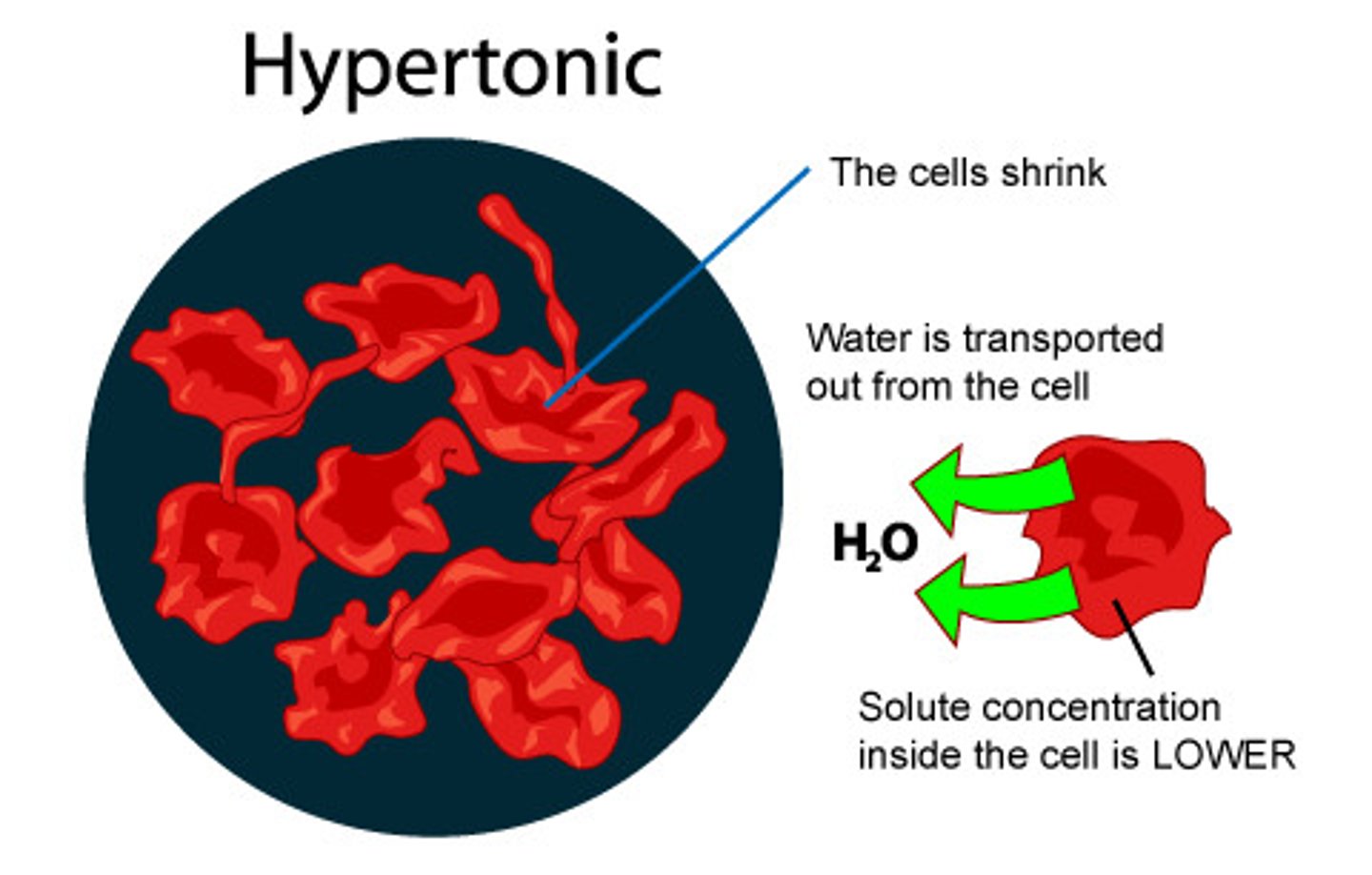
hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes/salts (cells shrink in these solutions)
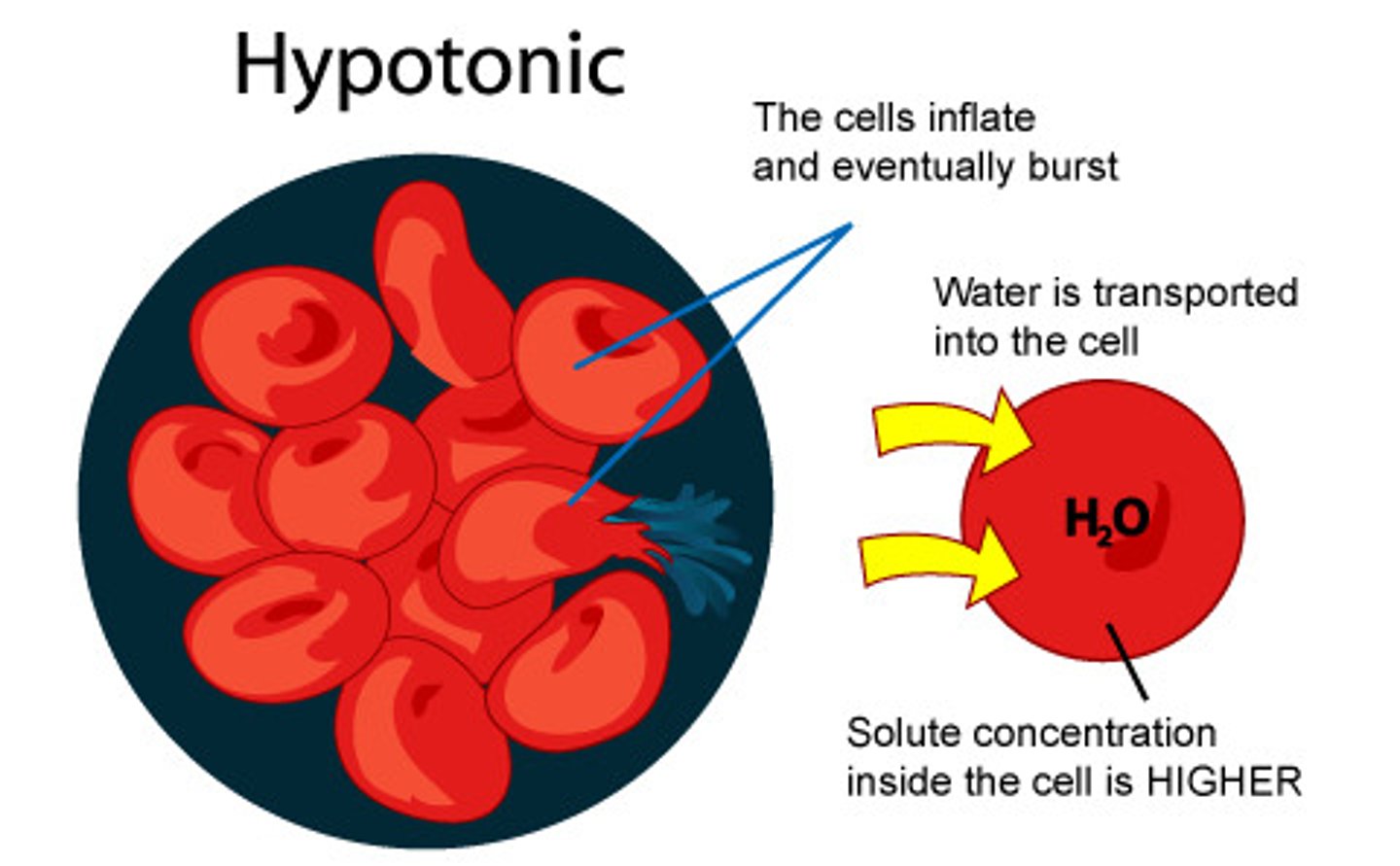
hypotonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the lesser concentration of solutes/salts (cells swell in these solutions)
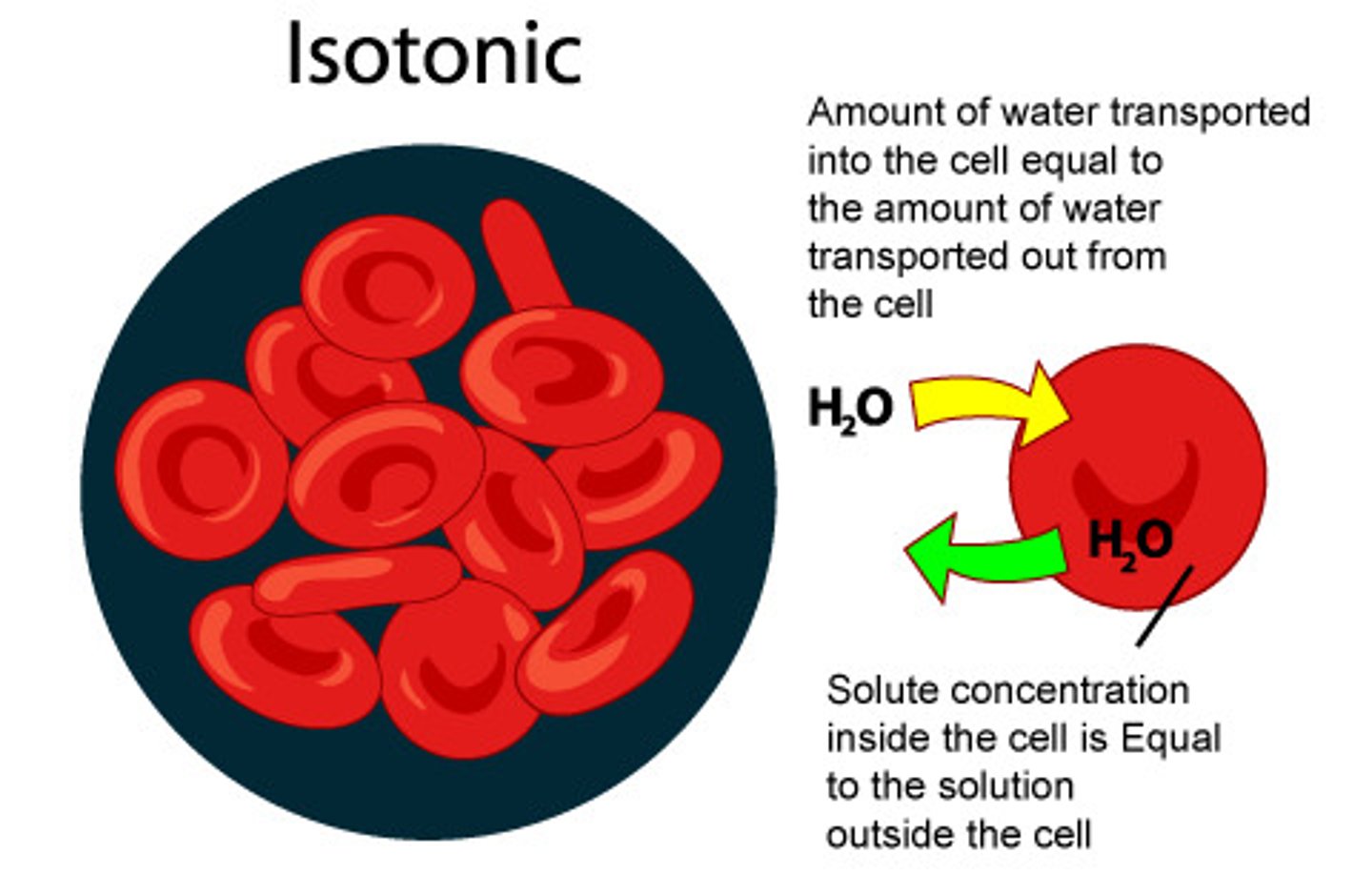
isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same on both sides of the cell membrane (in equilibrium)
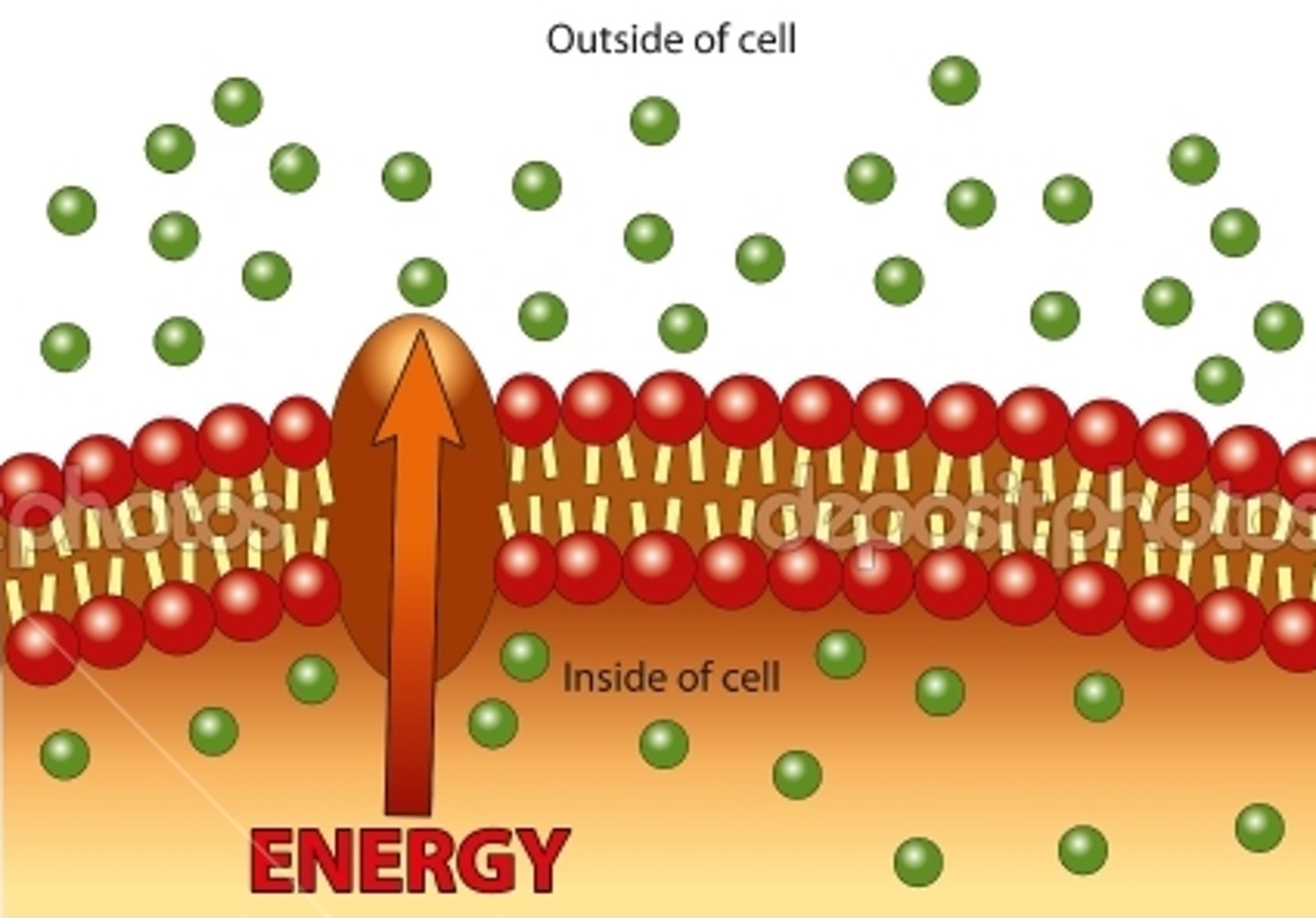
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference, ATP ENERGY IS REQUIRED, often uses a protein pump
passive transport
NO ATP energy required, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient (includes: osmosis, diffusion & facilitated diffusion)
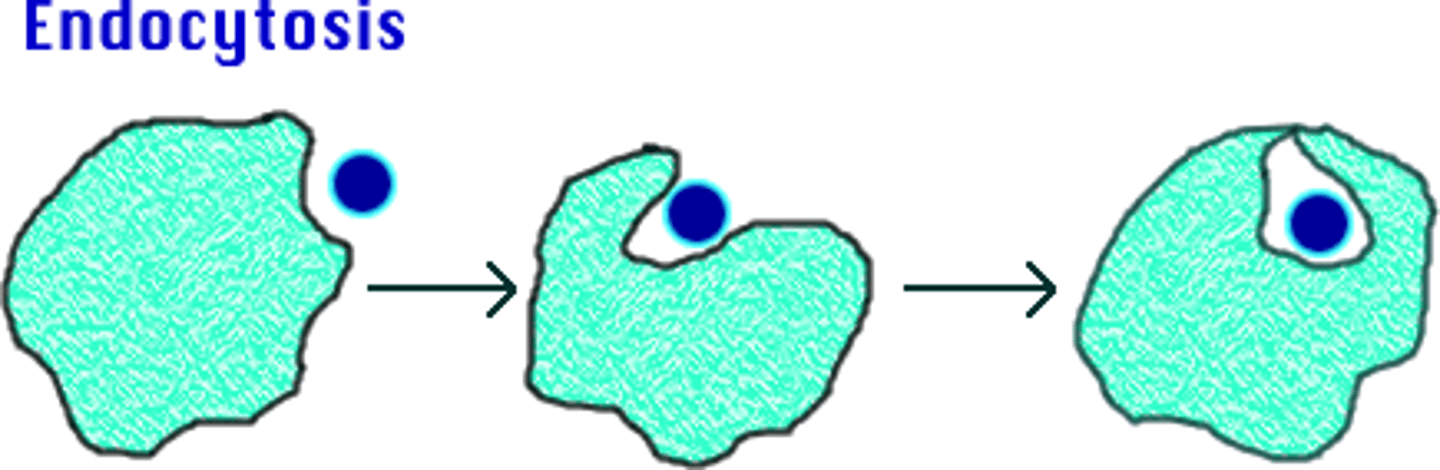
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane (type of active transport)
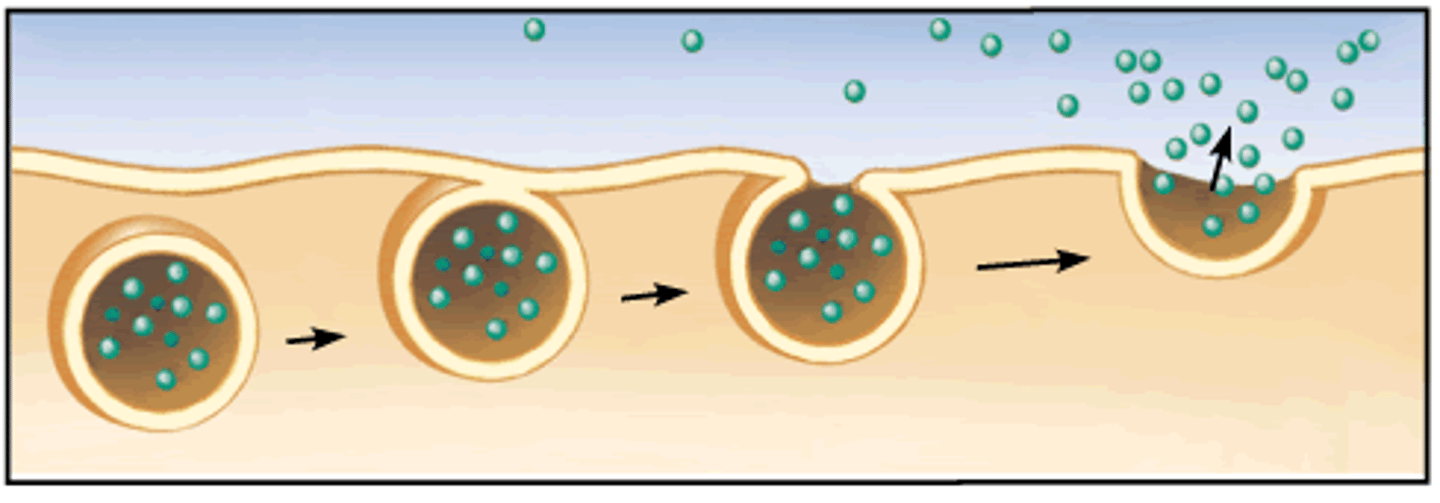
exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material (type of active transport)
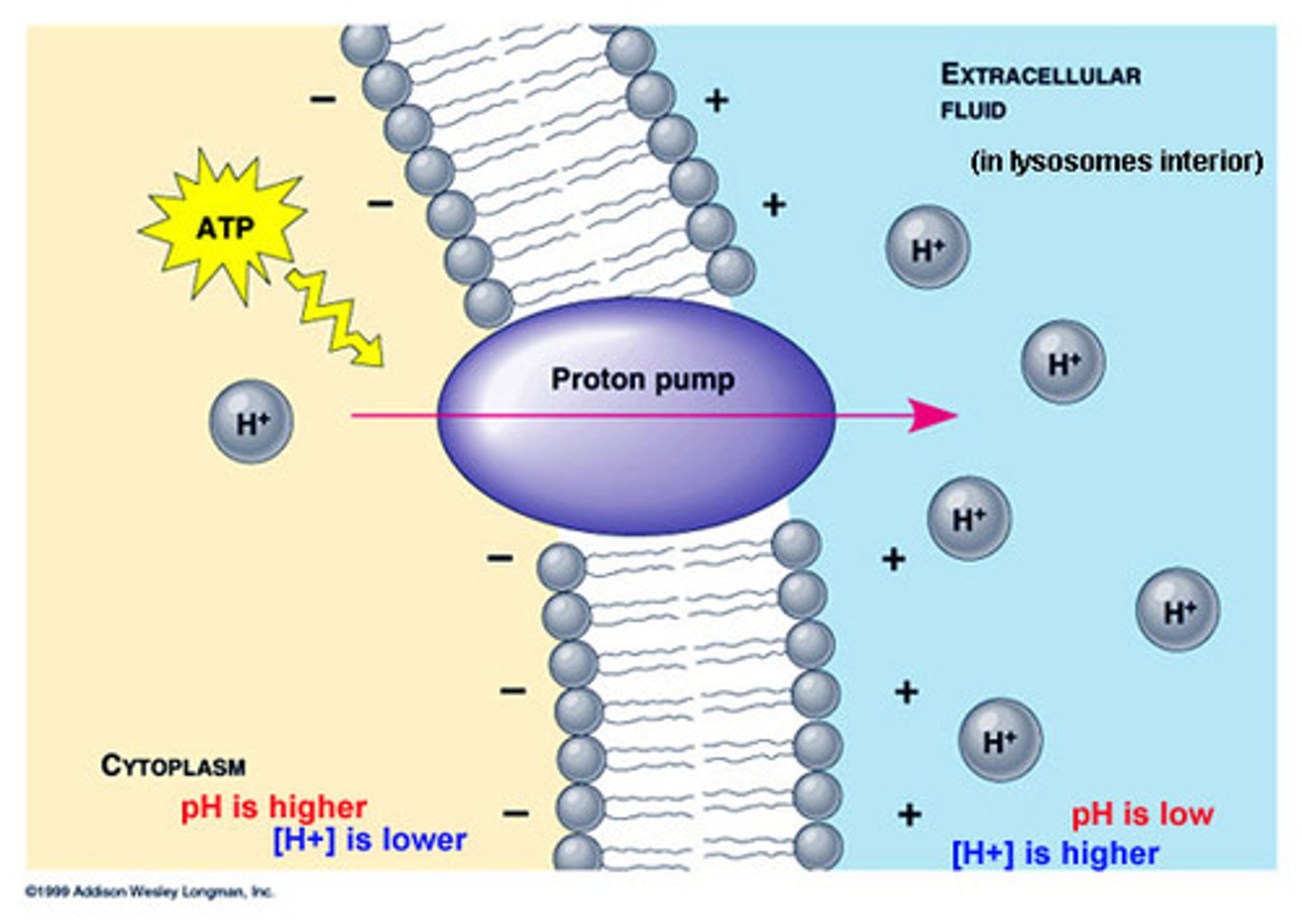
protein pumps (active transport)
transport proteins that require ATP energy to do work
concentration gradient
Is the difference in the concentration of a substance from on location to another.
semipermeable membrane
cell membrane that allows smaller molecules or molecules without an electrical charge to pass through it, while stopping larger or highly charged molecules
phospholipid
a lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes
ALL cells have ( both prokaryotes & eukaryotes)
cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes
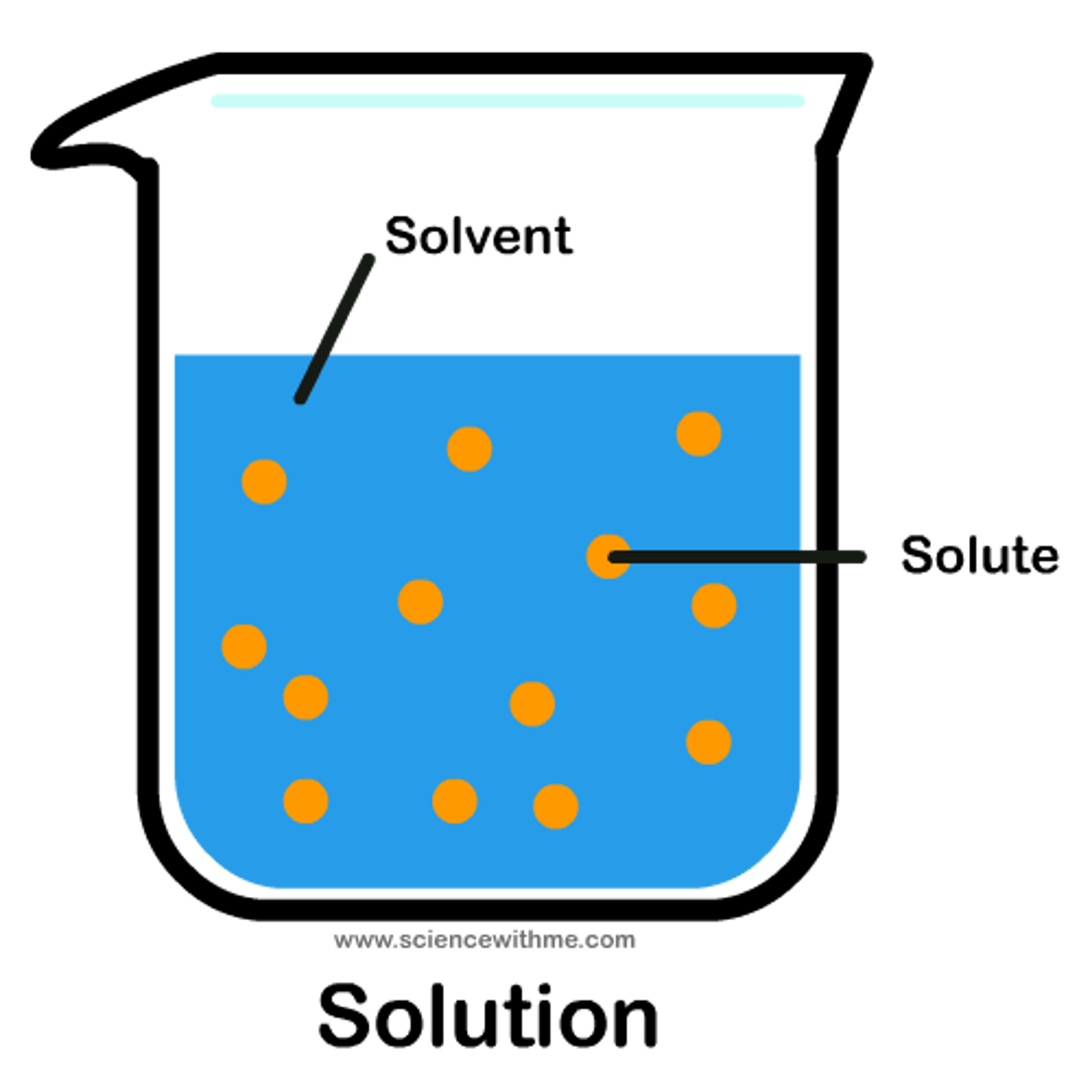
solution
a homogeneous mixture containing one or more solutes dissolved in a solvent (often water)