OOP MIDTERM
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Java
created by James Gosling at Sun MicroSystems (subsidiary of Oracle Corporation) and released in 1995
initially “Greentalk” by James Gosling and its file extension is .gt then after that “Oak”
in 1995, it was renamed “Java” due to trademark by Oak Technologies
Features of Java
Simple
Object Oriented
Platform Independent
Secured
Robust
Architectural Normal
Portable
High Performance
Distributed
Multi-threaded
Dynamic
Variable
Something that can store a piece of data
Can also be called as a container that holds any value\
Two Type of Types
Class Types
Primitive Types
Class Types
A type for objects with both data and methods
Primitive types
A simple, indecomposable values
Constants
are identifiers whose values never change once declared. The general syntax for declaring constants is:
final <type> <identifier> = <literal>;
Casting
is the process of assigning a value or variable of a specific type to a variable of another type.
Example:
double x=10.0 , y=3.0;
int z;
z = (int) (x/y);
Primitive Data Types
string
boolean
char
byte
short
int
long
float
Assignment Statements
is to assign a value to a variable
Use of assignment operator “=”
Syntax: Variable_name = expression;
Operators
are symbols that perform logical or mathematical functions on operands such as variables, constants, and objects.
Unary Operators
require only one operand. In Java, there are at least four unary operators: negation (-), bitwise complement (~), increment (++), and decrement (--). These operators change the value of their operand without using an assignment operator (=).
Arithmetic Operators
+ Addition
- Subtraction
* Multiplication
/ Division
% Modulo
++ Increment
-- Decrement
Comparison / Relational Operators
>
>=
<
<=
==
!=
Conditional / Logical Operators
! NOT
|| Logical OR
&& Logical AND
Shortcut Assignment Operators
+= Assignment with Addition
-= Assignment with Subtraction
*= Assignment with Multiplication
/= Assignment with Division
%= Assignment with Modulo
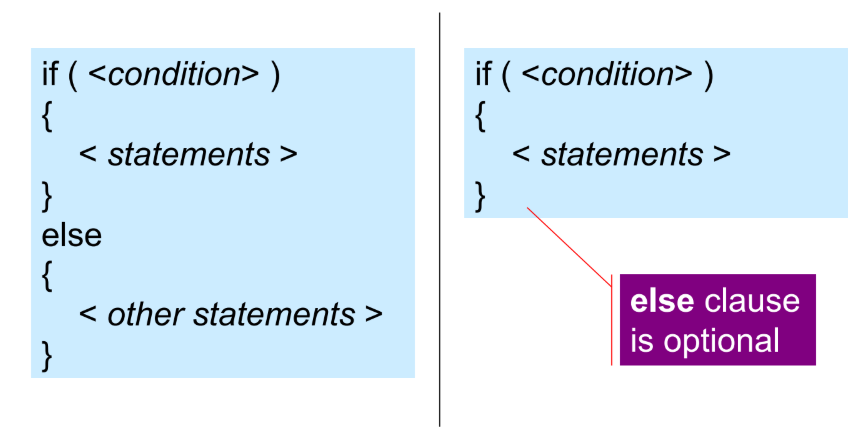
if-else Statement
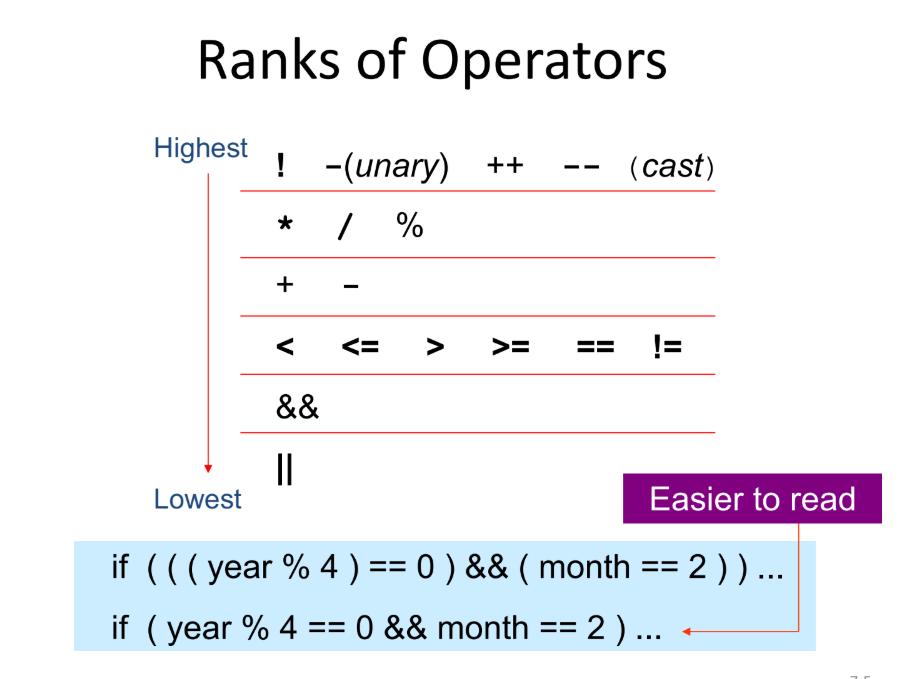
Rank of Operators
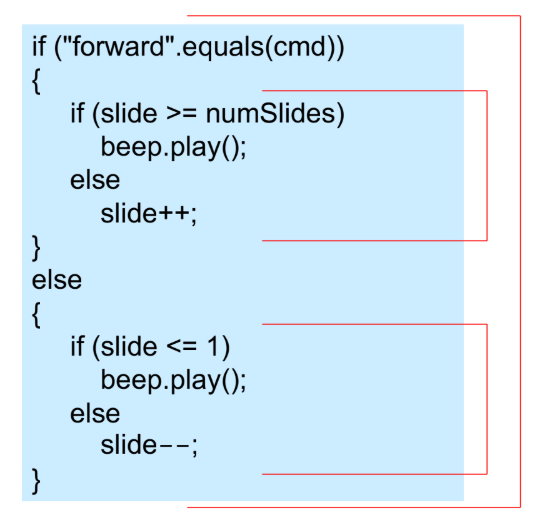
Nested if-else
if-else-if

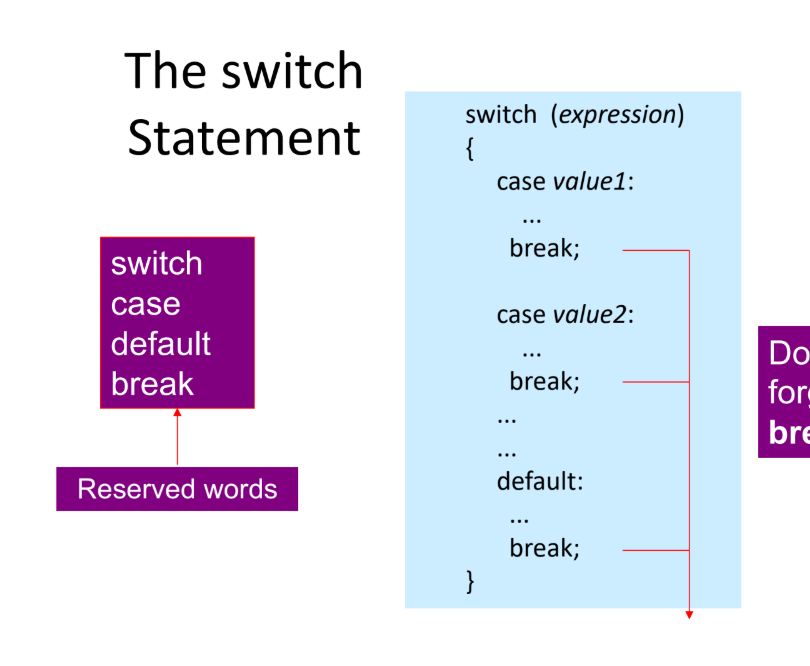
The Switch Statement
Iterations
Repeating the same code fragment several times
Java provides three control statements for
iterations (a.k.a. loops): for, while, and
do-while.
The while loop
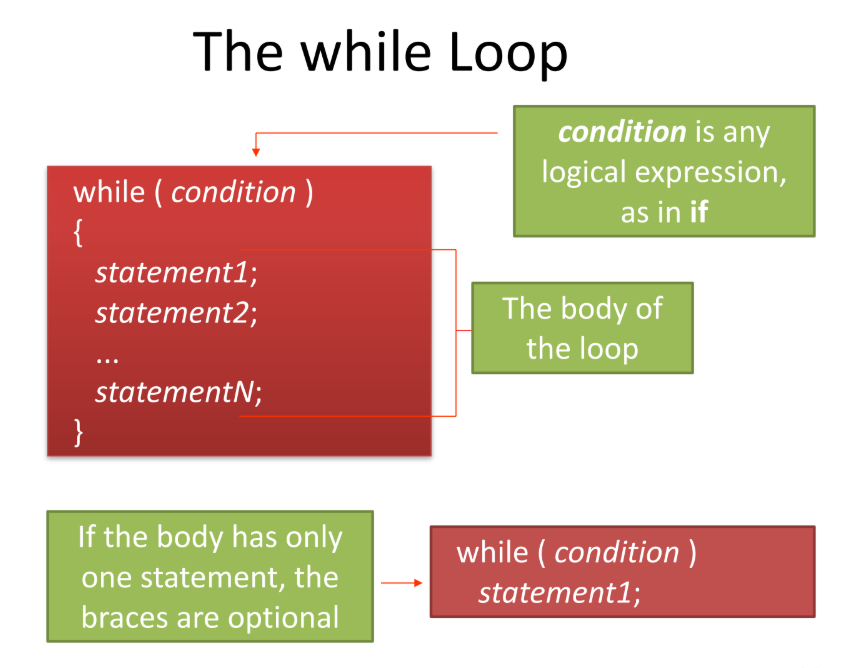
The while loop
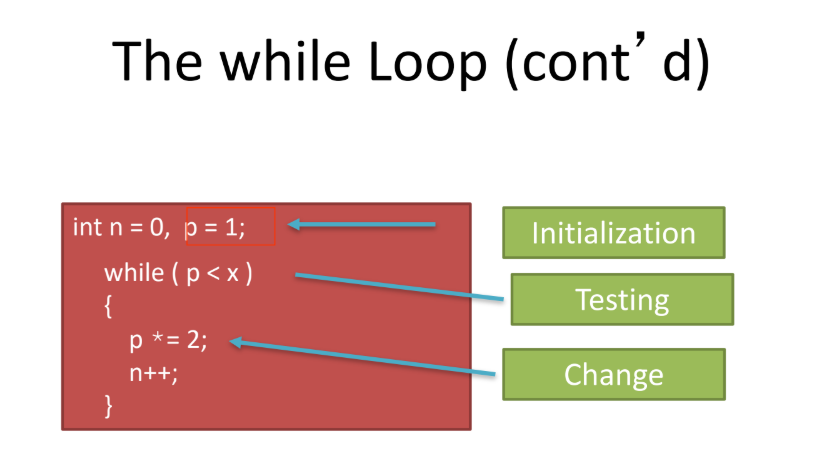
The for loop
is a shorthand that combines in one statement initialization, condition, and change:

The do-while loop
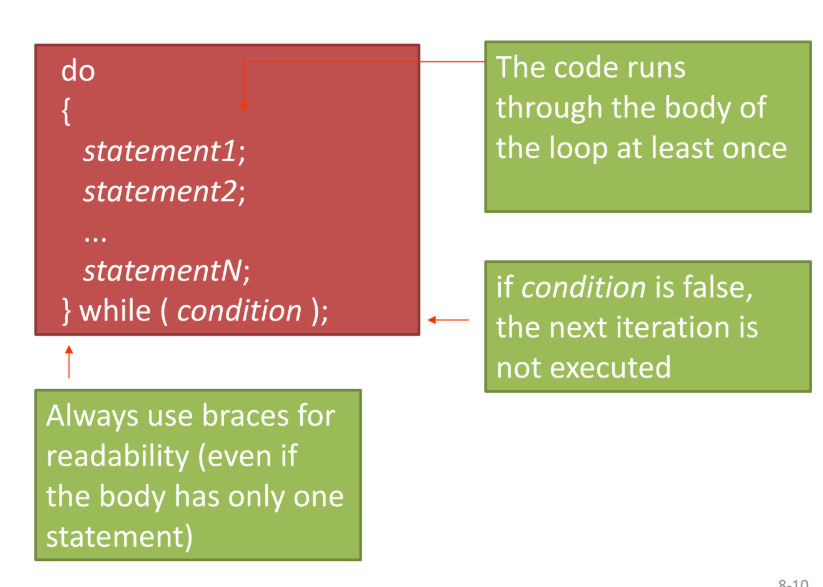
break
instructs the program to immediately quit the current iteration and go to the first statement following the loop.
return
instructs the program to immediately quit the current method and return to the calling method.
Nested Loops
A loop within a loop