Materials and Methods Quiz 4
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Control Layers in a wall
Weather Barrier: for bulk water
Vapor Retarder: controls water vapor
Air Barrier: helps prevent infiltration
Weather Barrier
- Keeps out bulk water
- Protects structure
- Keeps insulation from getting wet
-helps reduce wind wash
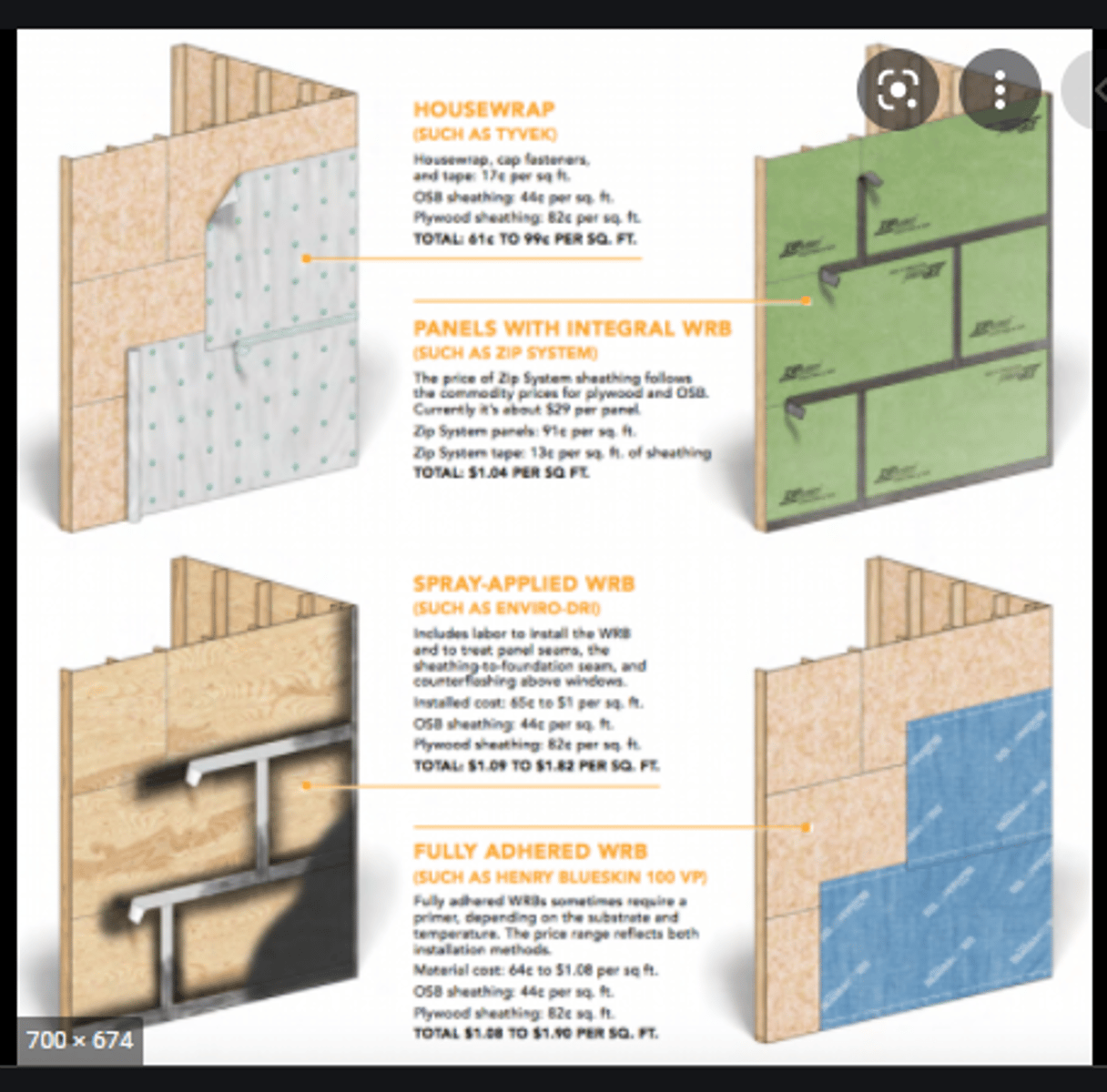
Vapor Retarder
- Prevents warm, moist air from being able to condense within the wall cavity.
- Always on warm side of wall
-not perfect
-measured in permeance

Air Barrier
- Prevents drafts.
- Helps to slow vapor movement by reducing the stack effect.
can be the same as weather barrier or vapor retarder
insulation (such as foam board) can also be used as air barrier
The "perfect" wall
Structure inside, control layers in middle, cladding outside
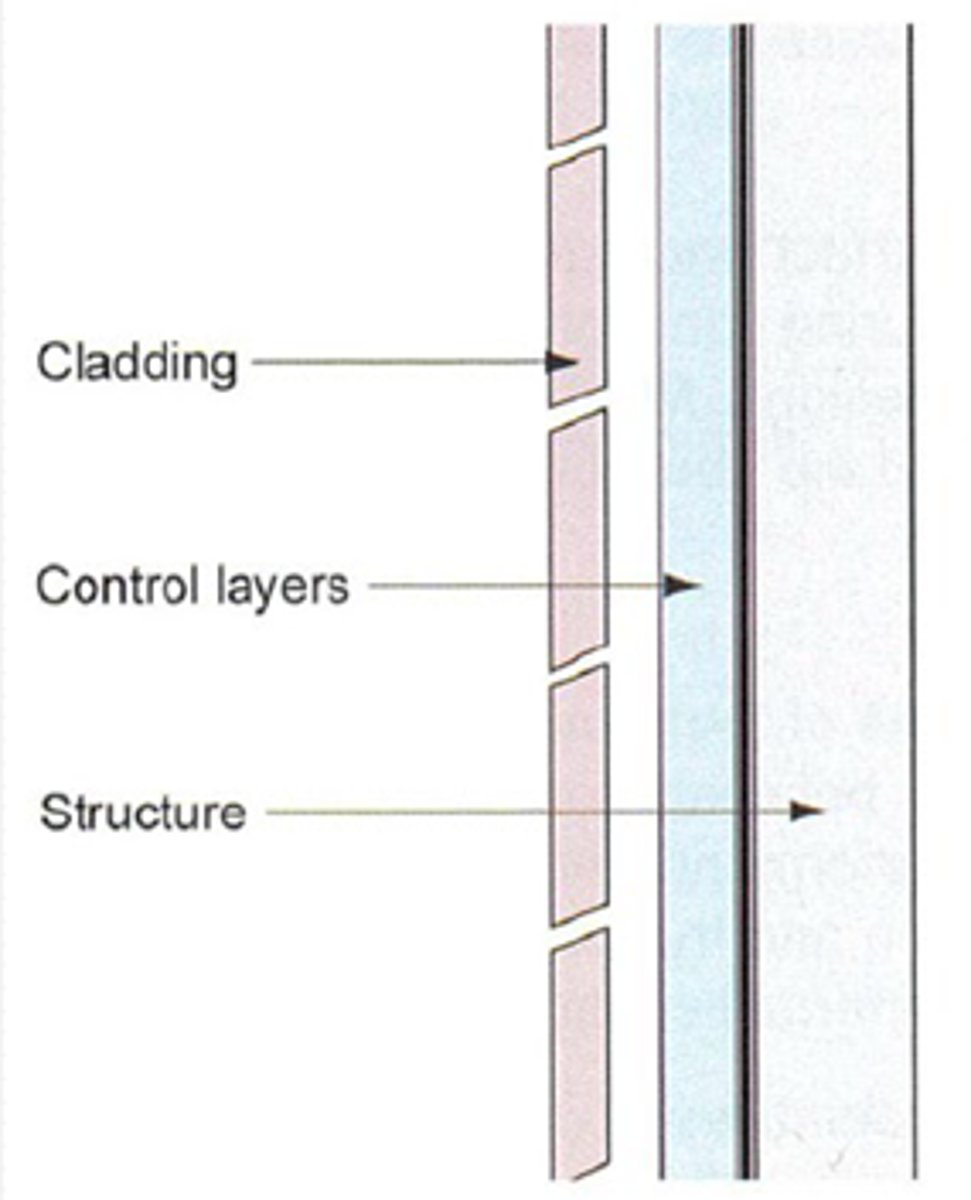
Airsealing
- the process of making the building air tight.
-necessary to control heat and vapor flow
-can be same as weather barrier and vapor retarder
-insulation can also be air barrier (foam board)
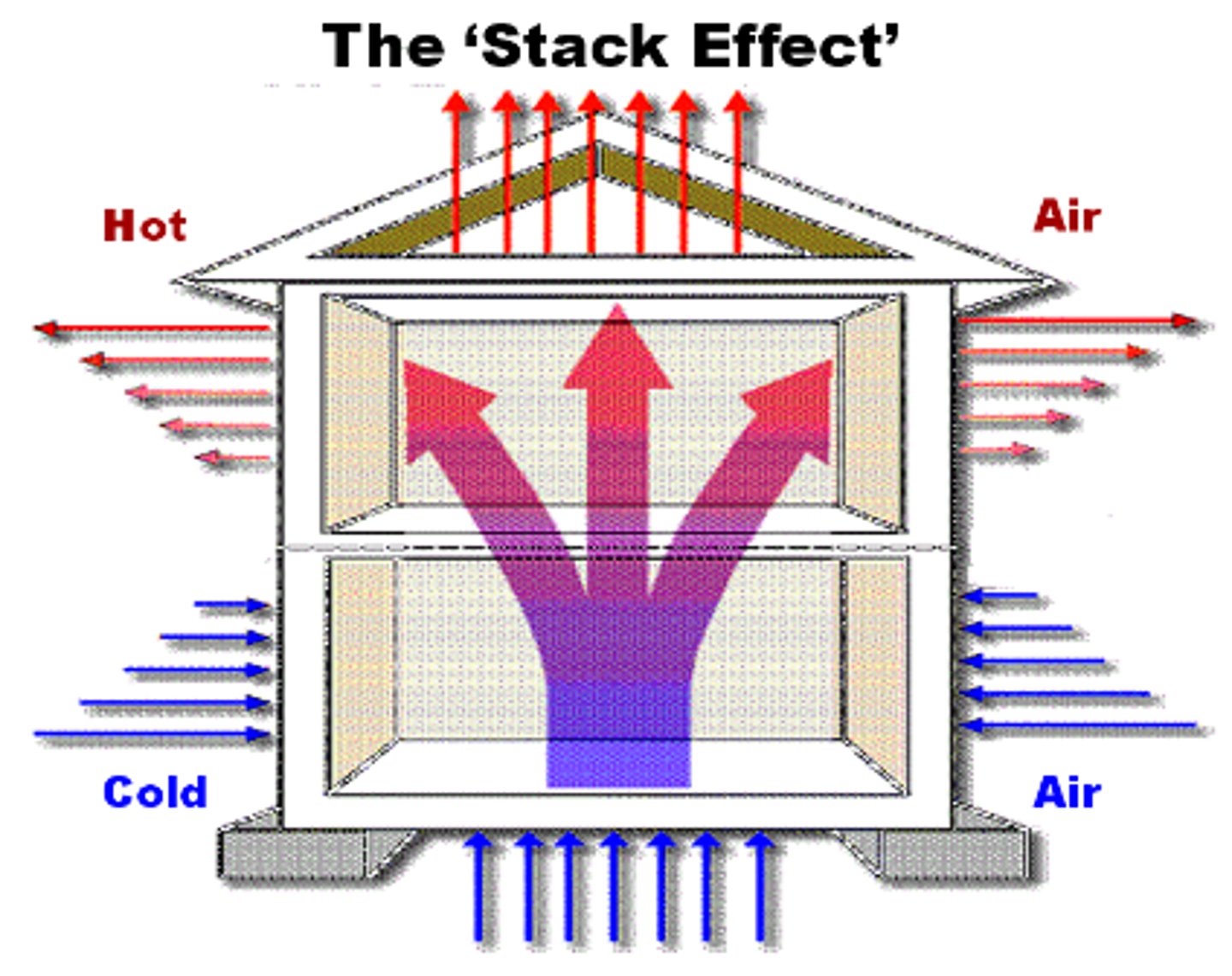
Stack effect
movement of air within a building caused by the difference in temperature between indoor and outdoor air, creating a pressure imbalance.
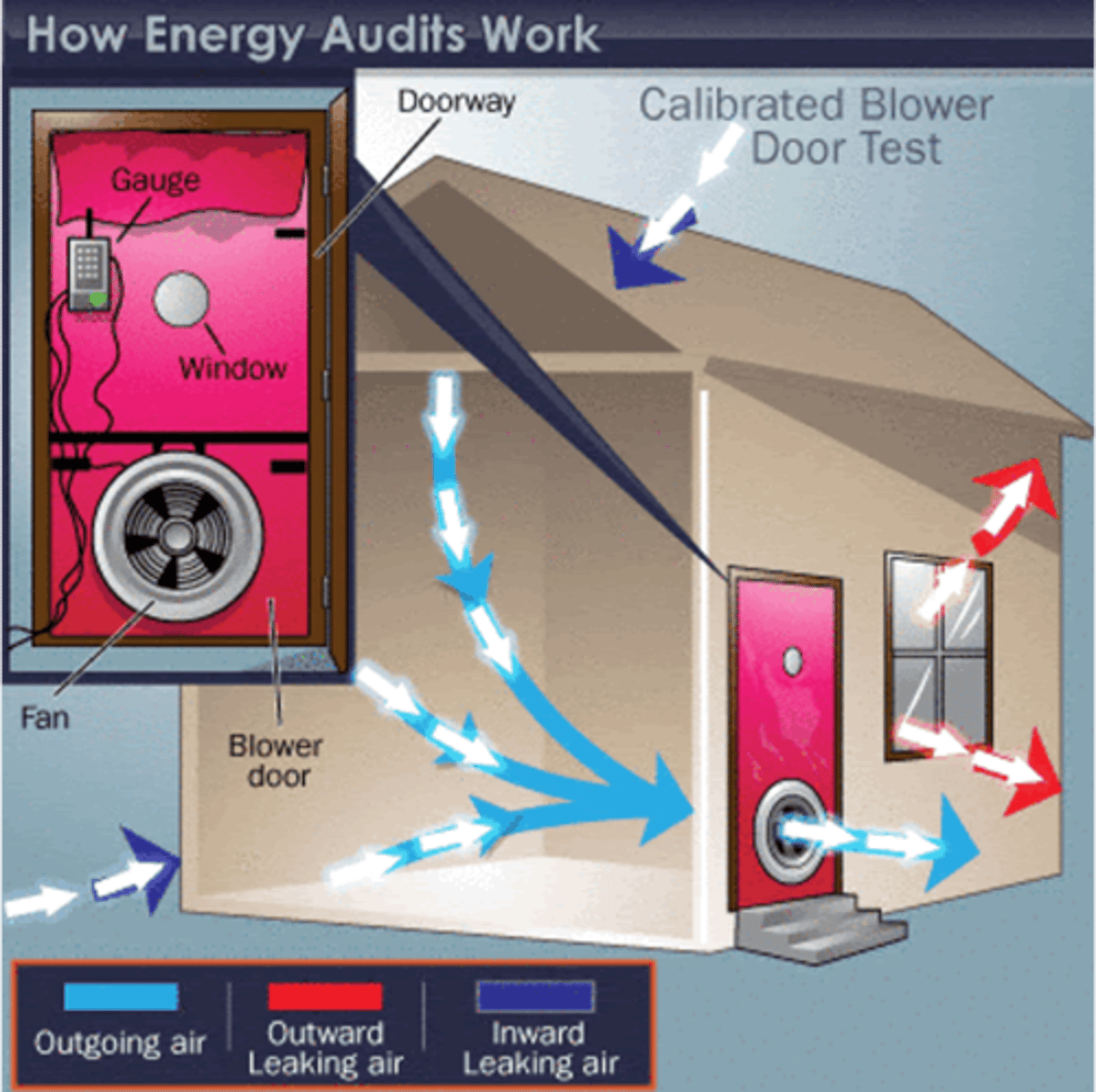
Blower Door Test
Used to measure airtightness of buildings by blowing air into or out of a building and creating a difference in pressure.
Ventilation
intentional process of exchanging indoor air with fresh outdoor air
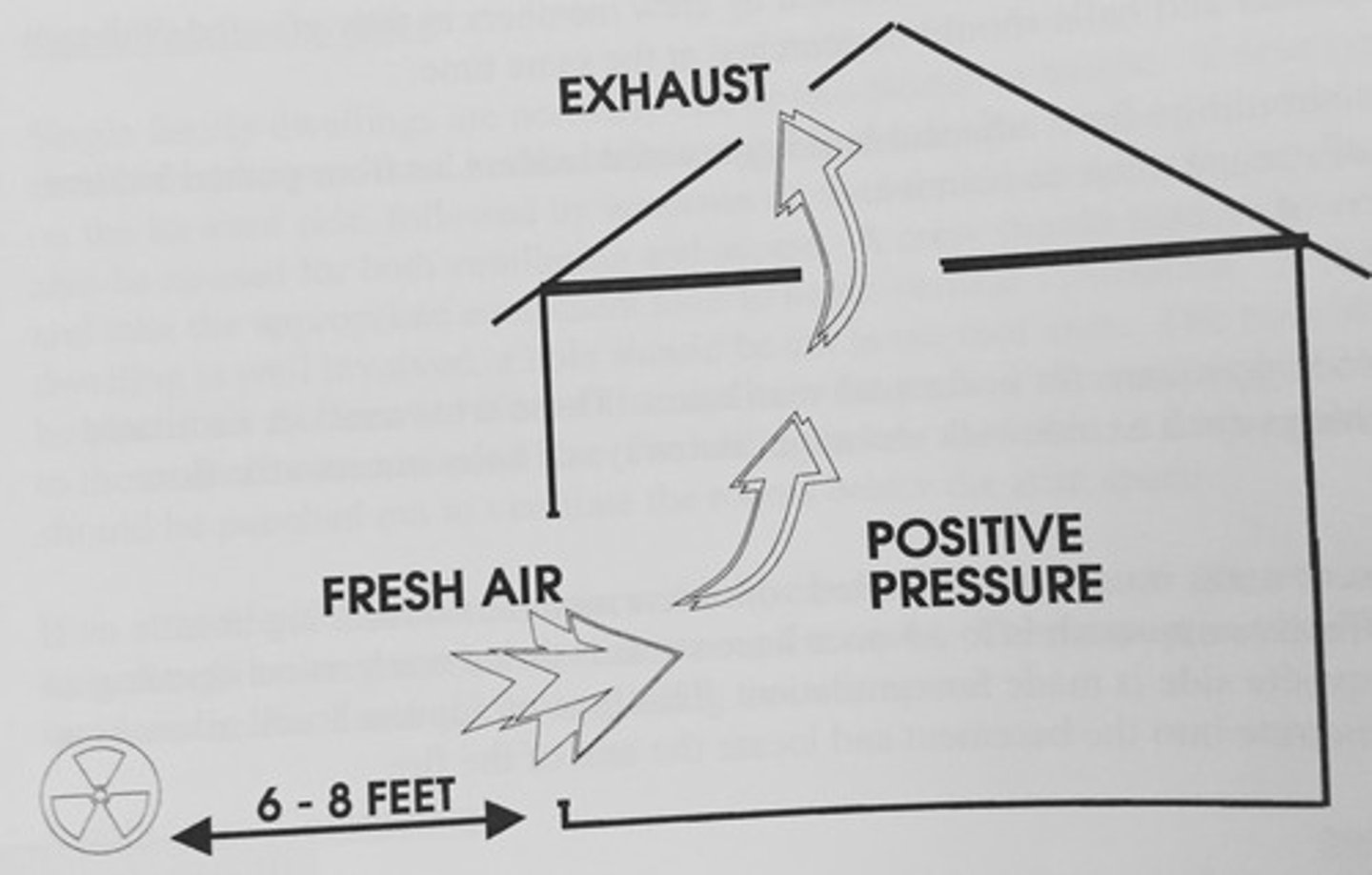
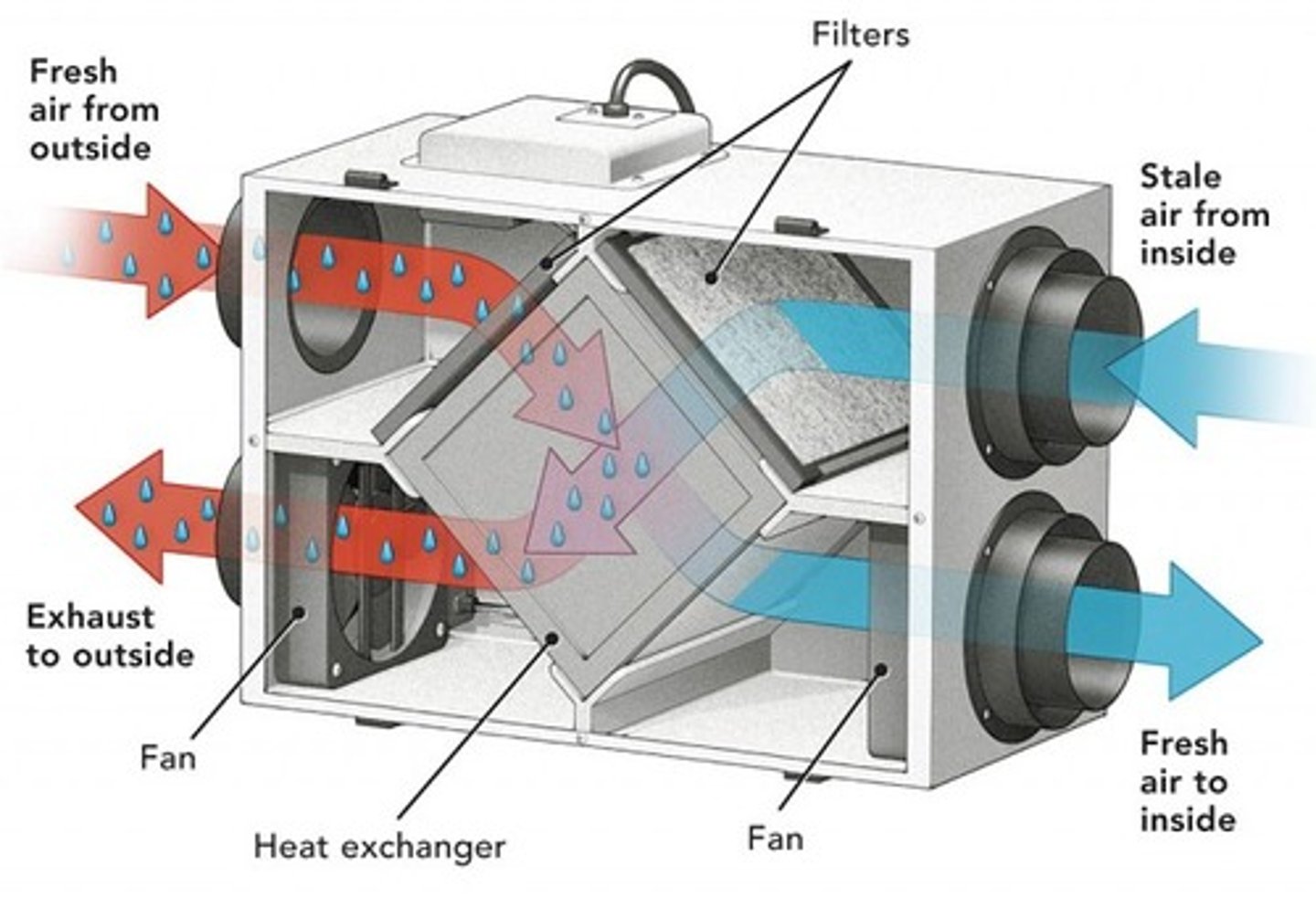
ERV
Energy Recovery Ventilator-transfers both heat and moisture between stale outgoing and fresh incoming air.
Ideal for humid or very dry climates
HRV
Heat Recovery Ventilator-Transfers heat between stale outgoing and fresh incoming air.
Ideal for cold climates
Permeance
measure of how easily water vapor can move through a material
Diffusion
Slow movement of water vapor through a material
Air Leakage
rapid movement of air through holes or gaps in a wall
Thermal Insulation
Material used to reduce heat transfer between inside and outside of a building, preventing excessive heat loss or gain
reduces energy required for comfort
R-value
-measure of resistance to heat flow
-higher value means better insulating properties
-depends on material type, density, and thickness
R-value units
-measured in F/Btu/hr (sf)
change in degrees Fahrenheit
per british thermal unit
per hour
for one square foot of material
U-value
-measures rate of heat flow
-lower value means better insulation
-typically used for assemblies (such as wall assembly or window)
-Inverse of R value: U=1/R
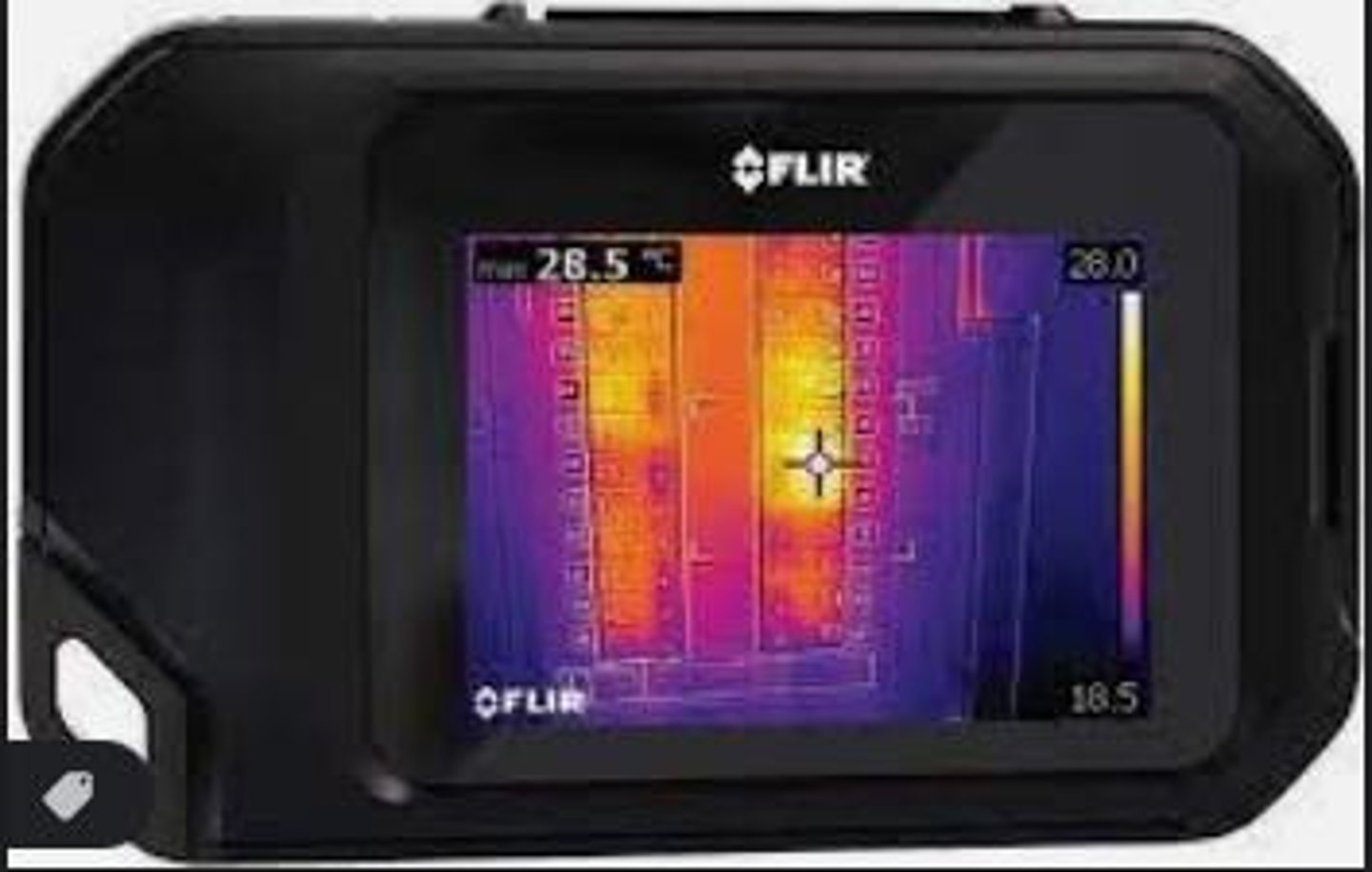
IR Camera
visualizes surface temperatures of materials. Can be helpful to show where heat is escaping or entering a building

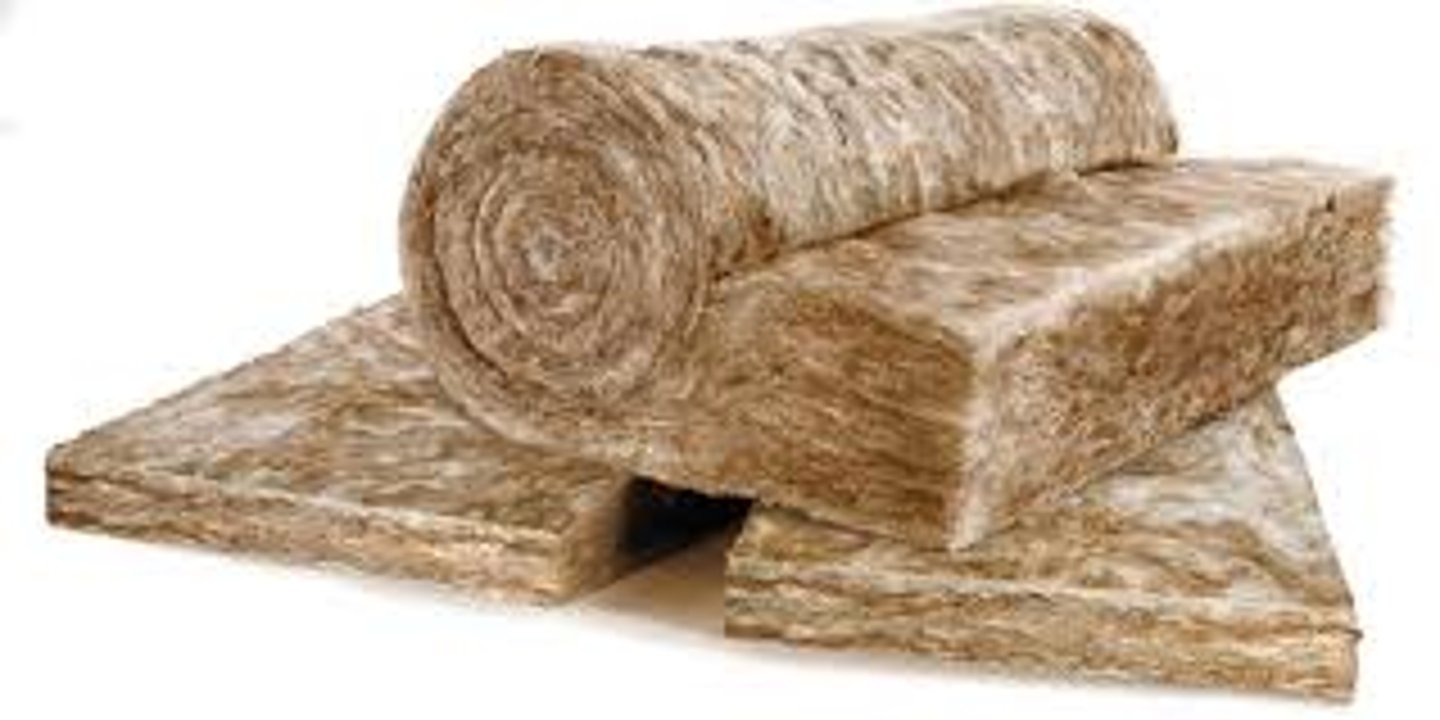
Fiberglass
Approximate R-Value: 3.5

Mineral Wool
Approximate R-Value: 4

Cellulose
Approximate R-Value: 3.8

Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
Approximate R-Value: 4

Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
Approximate R-Value: 5

Polyisocyanurate
Approximate R-Value: 6

Polyurethane spray foam
Approximate R-Value: 7
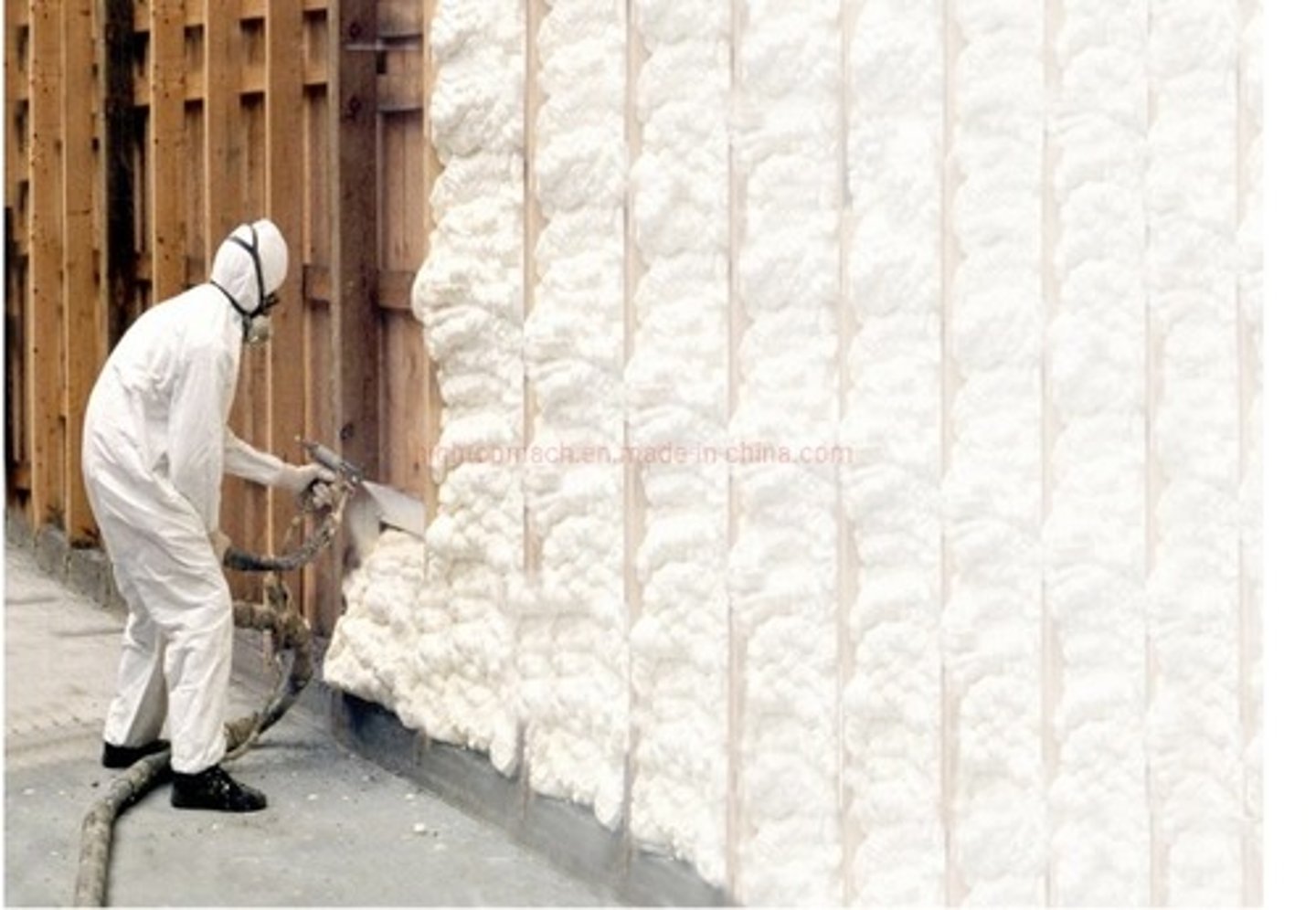

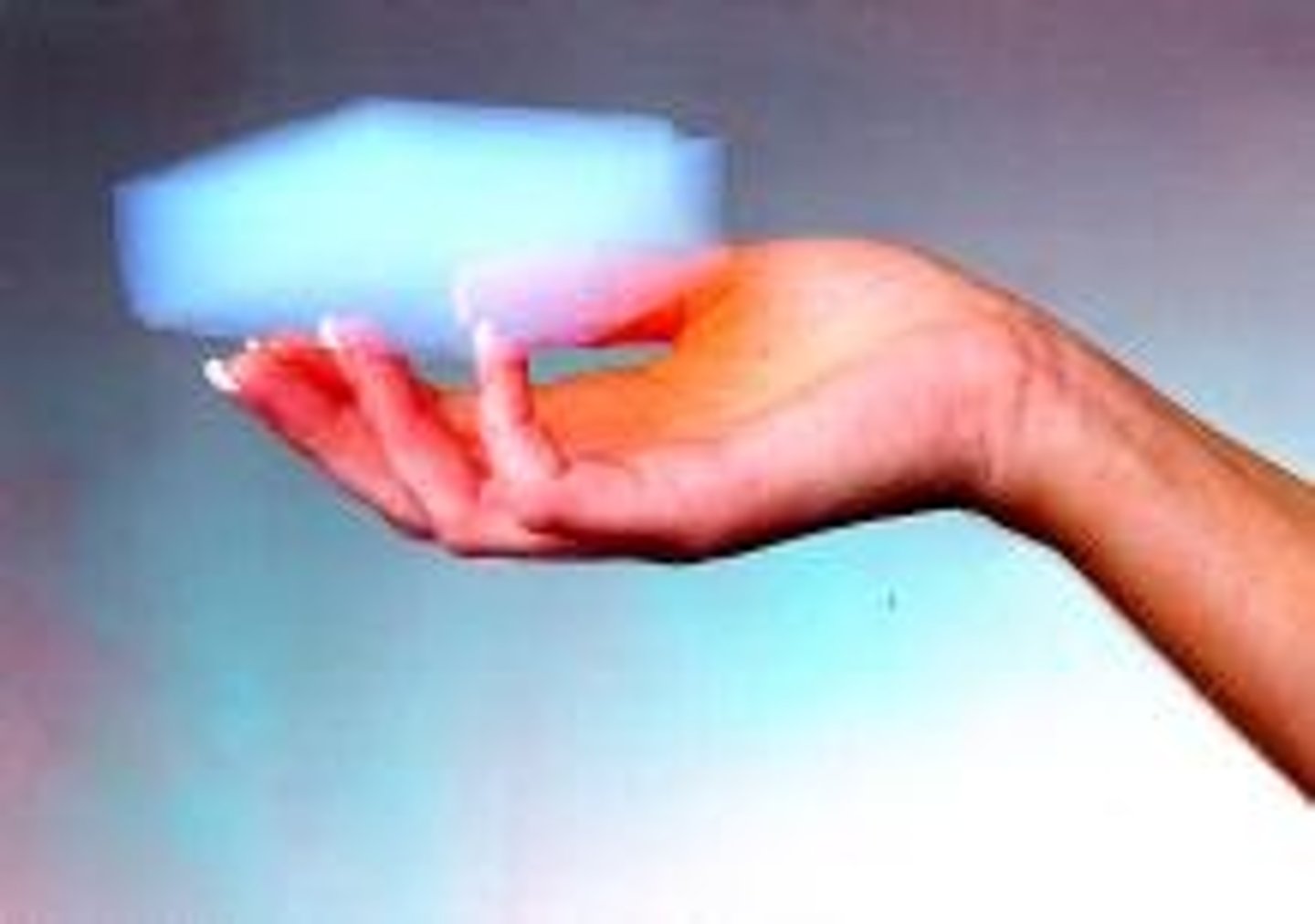
Aerogel
Approximate R-Value: 10.3

Vacuum Insulated Panels
Approximate R-Value: 29
Additive method of assembly R-value calculation
Calculate R-values of thickness of each material in the assembly then add them up
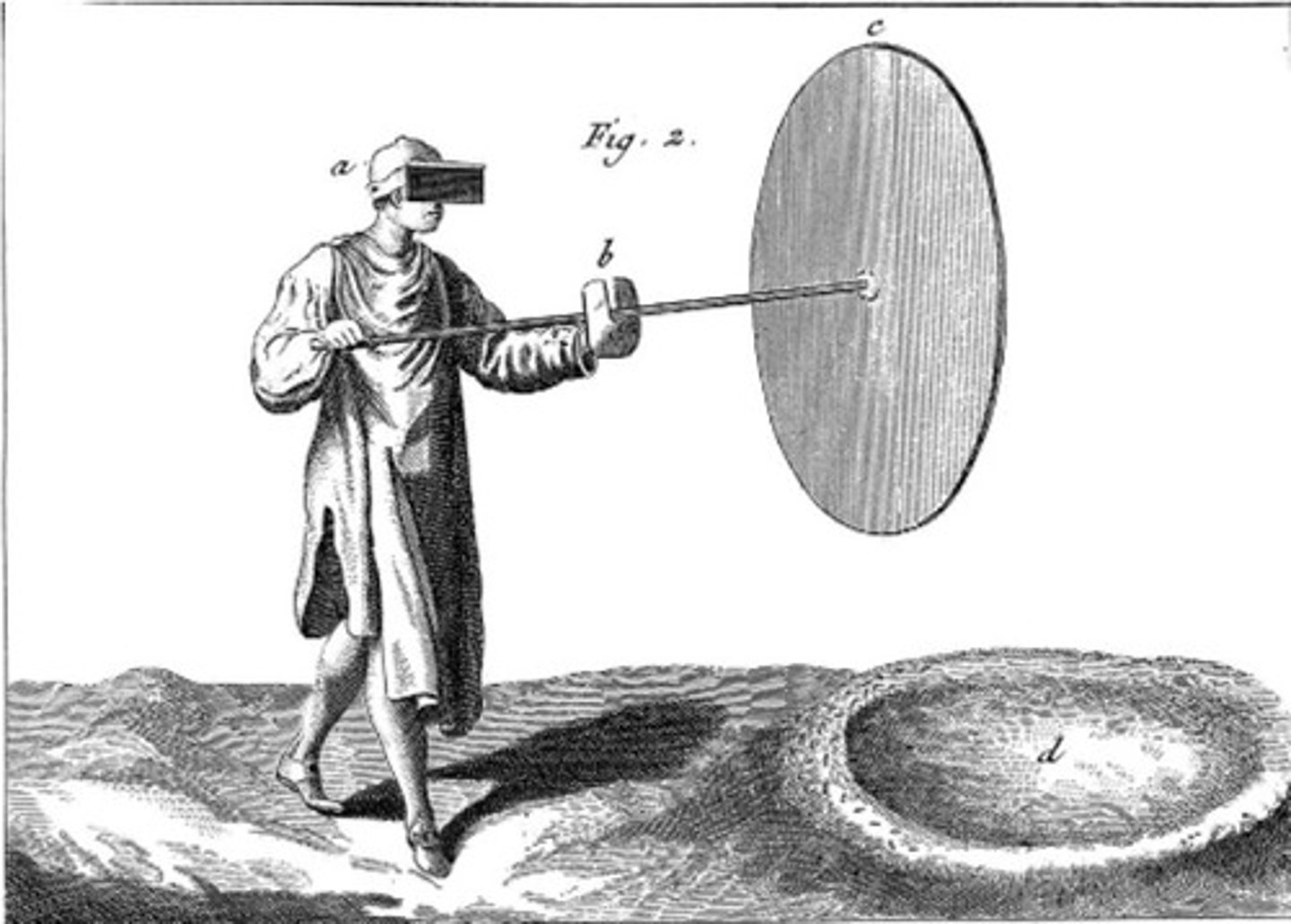
Crown Glass
An old form of window glass formed by blowing and whirling a hollow sphere of glass into a flat, circular disk
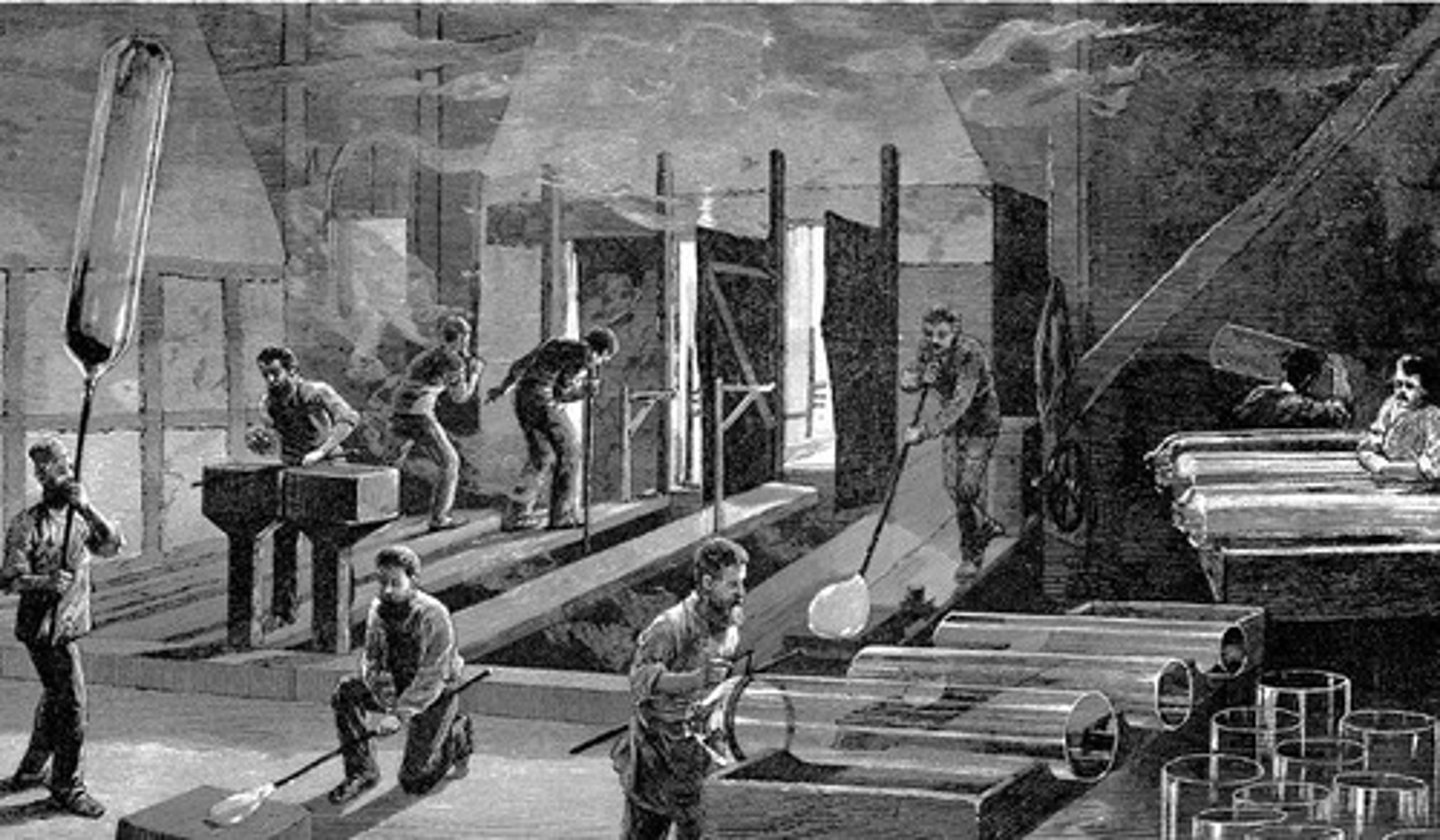
Cylinder Glass
glass sheet produced by blowing a large, elongated glass cylinder, cutting off its ends, slitting it lengthwise, and opening it into a flat rectangle
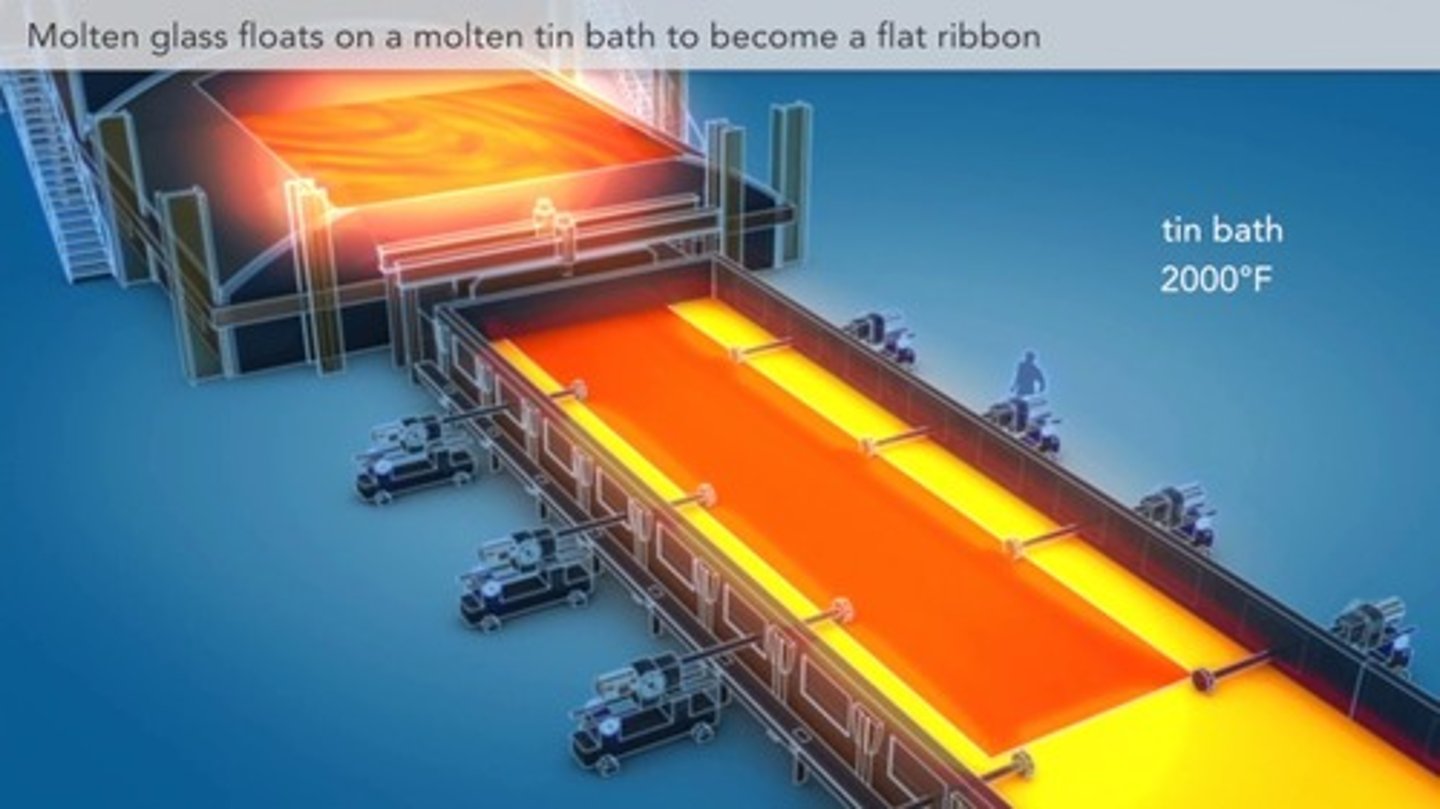
Float Glass
molten glass is poured onto a bath of molten tin, creating a continuous, flat ribbon of glass
Reflective coatings
Thin films of metal or metal oxide that are applied to standard glass.

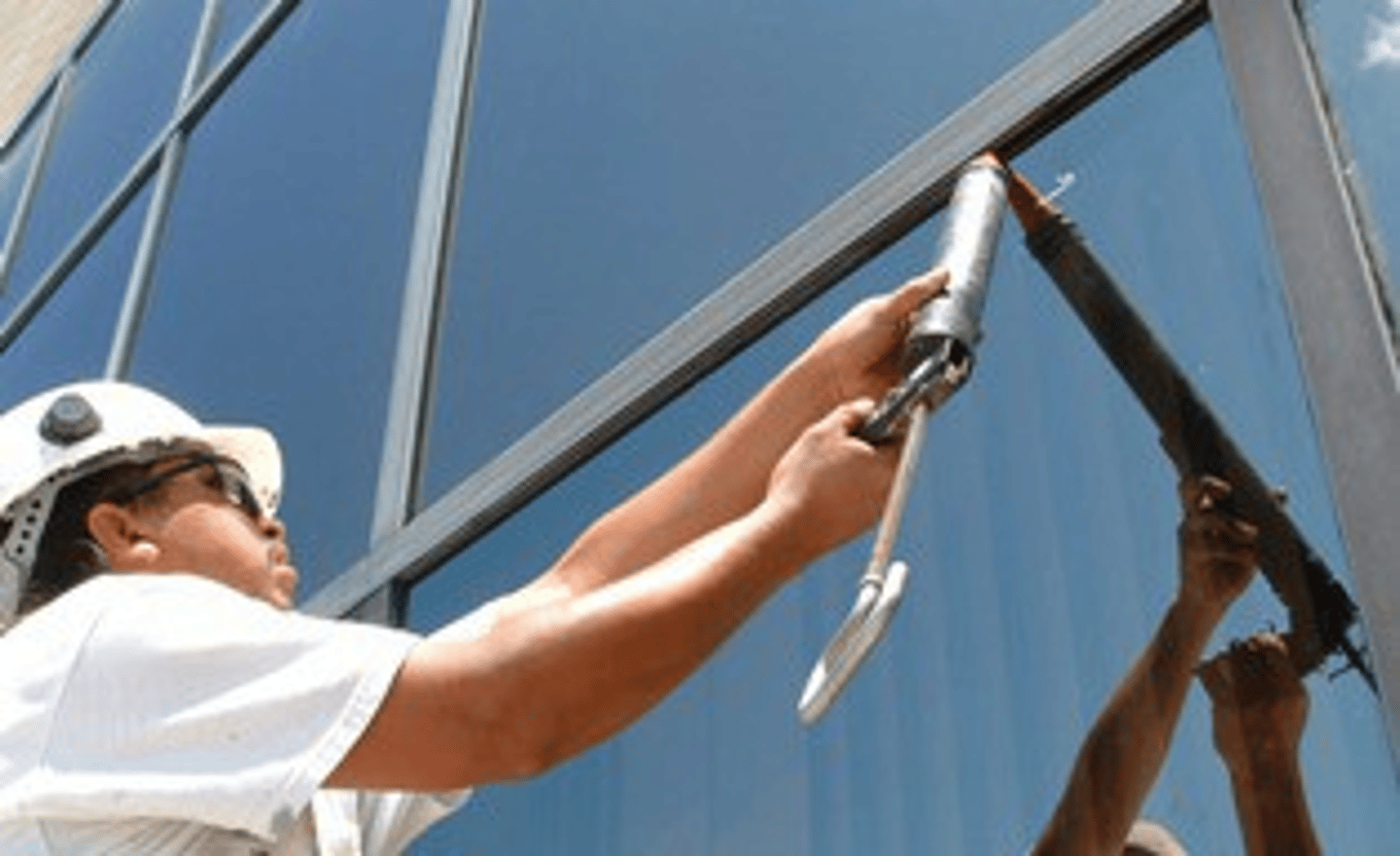
Wet Glazing
Applying silicone sealant to create watertight and airtight bond between glass and frame

Dry Glazing
Rubber or vinyl gasket compressed between glass and frame
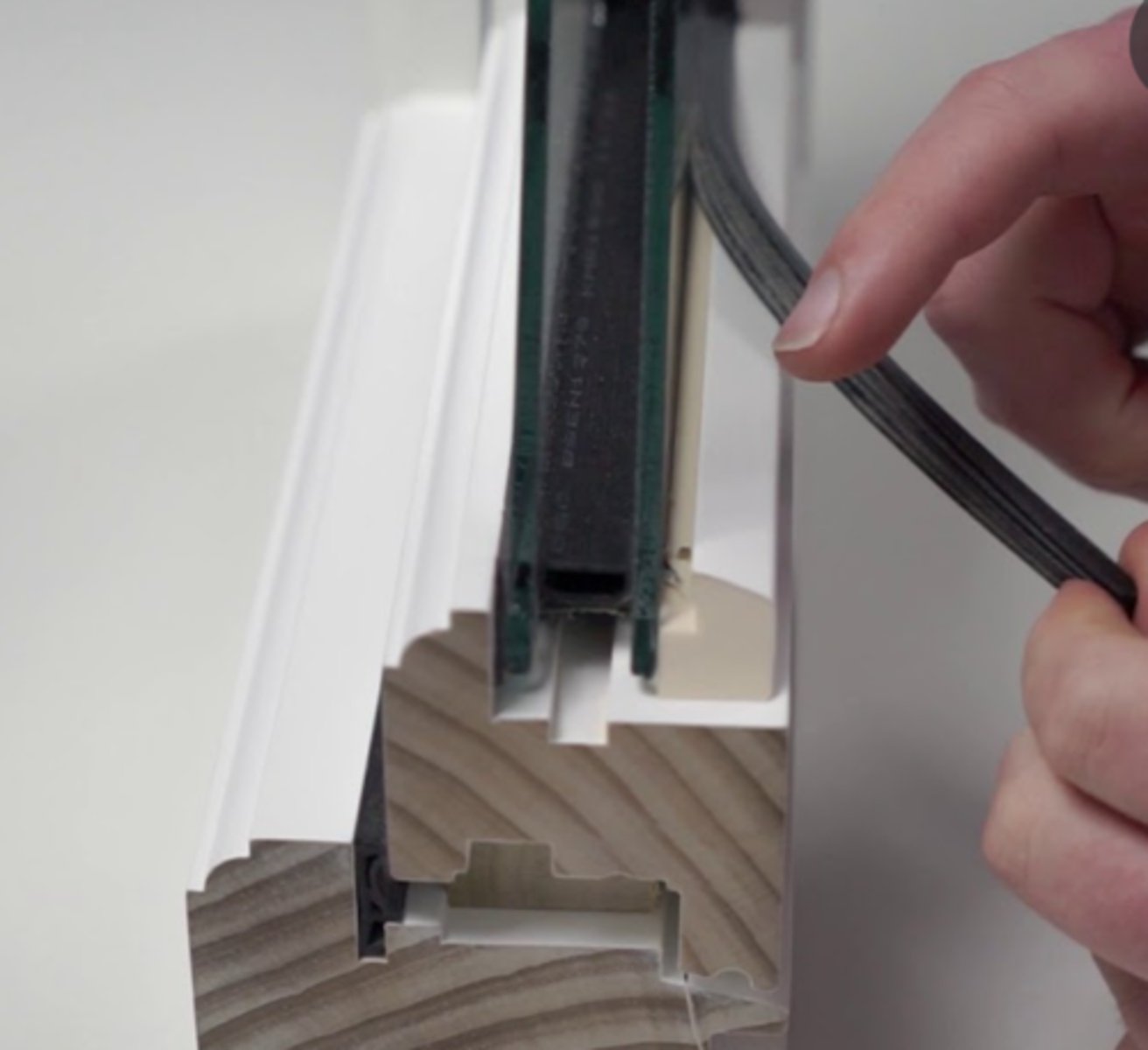
Extruded metal
Long pieces with section profiles designed to receive glazing units
Mullion
Vertical bar dividing window or door into sections
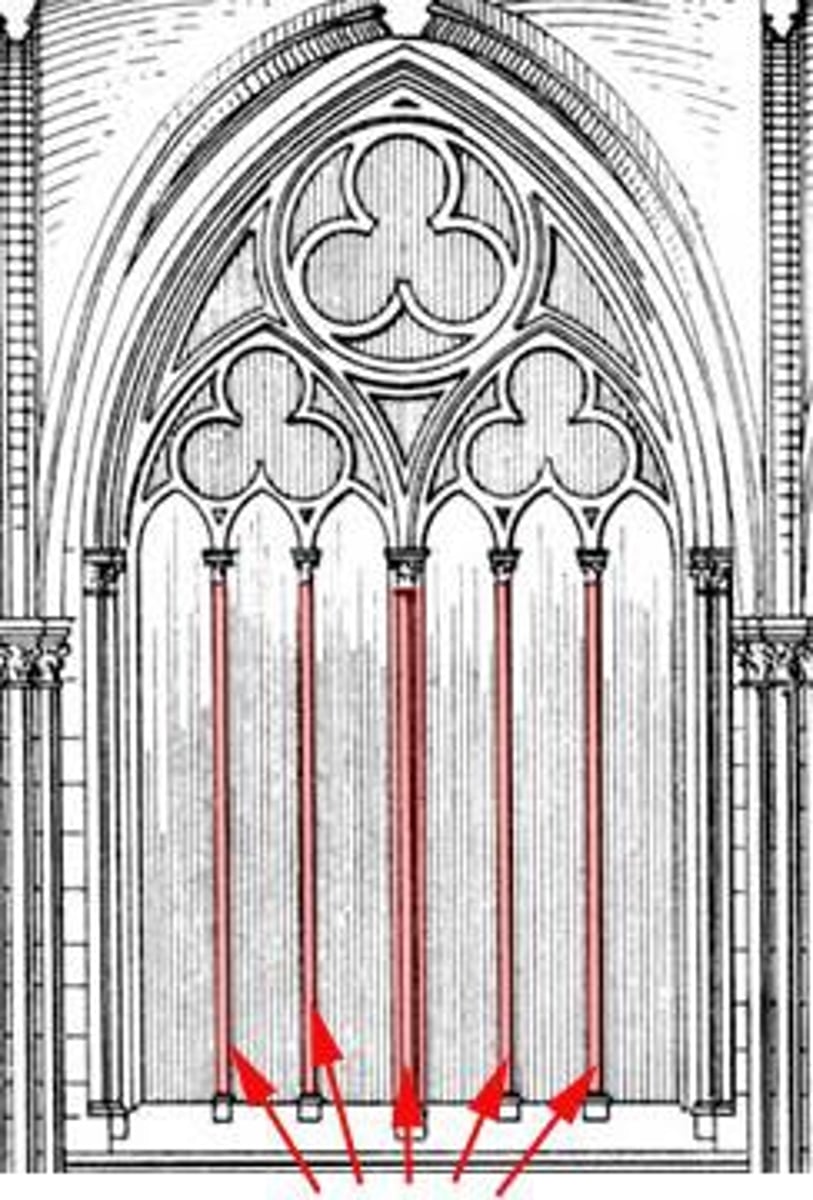

Thermal Break
break the path of heat flow through extruded metal that receives glazing
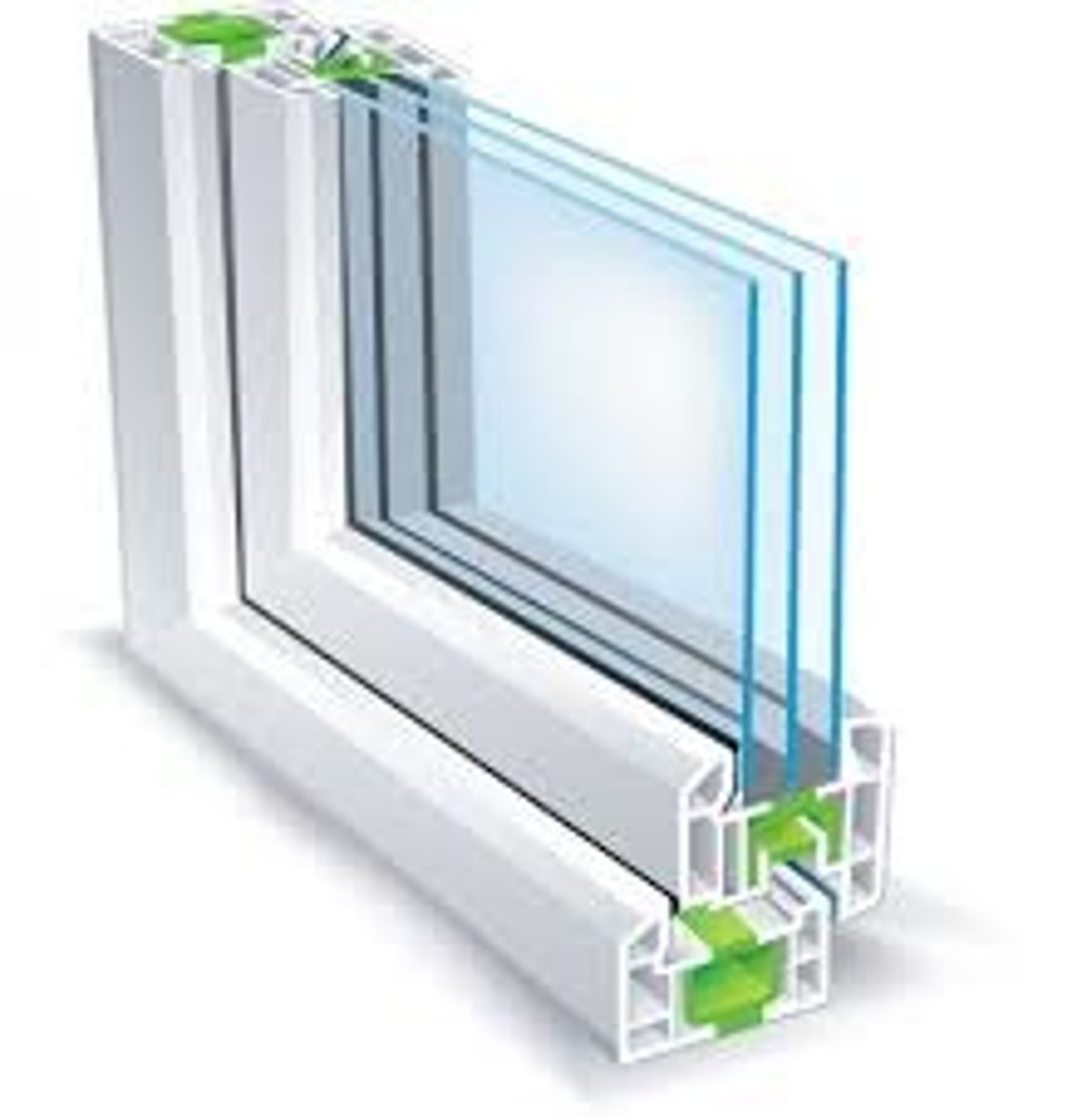

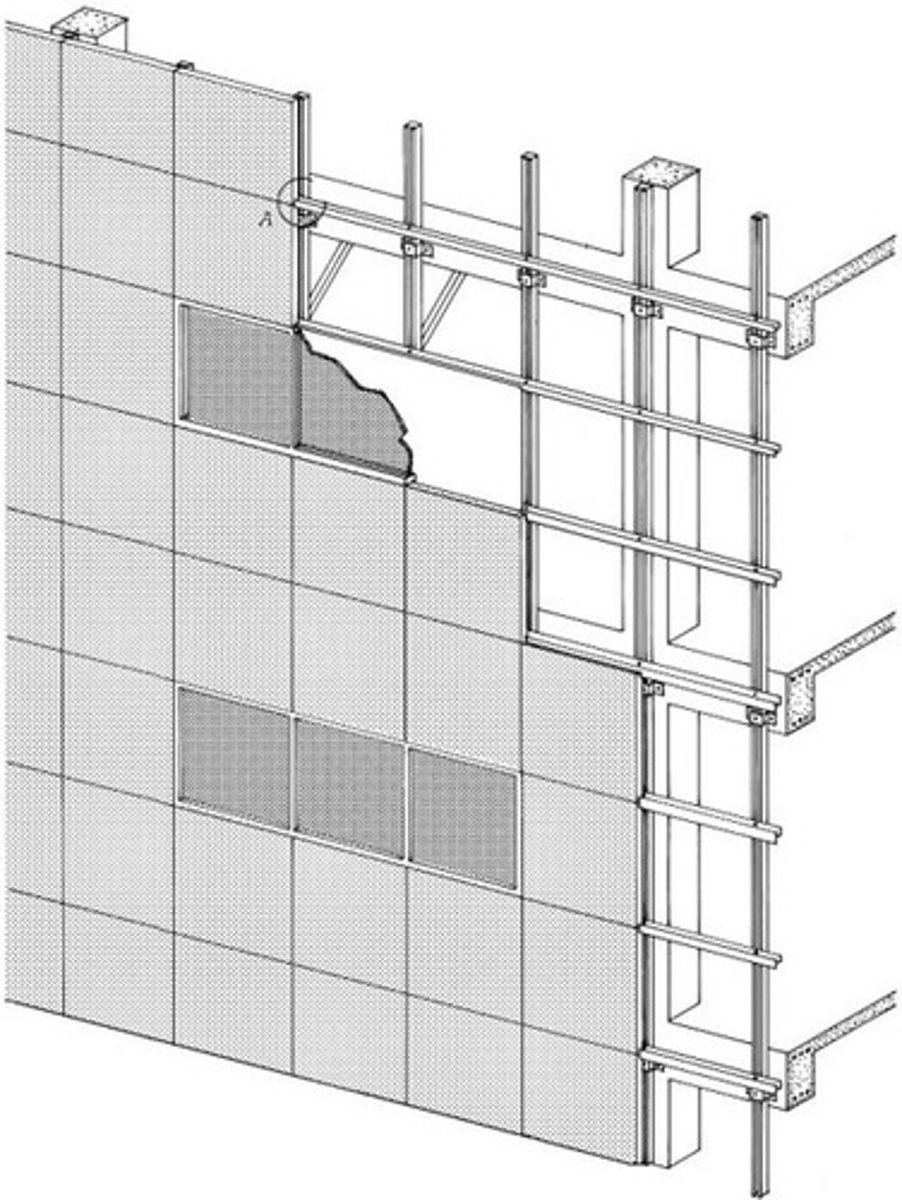
Curtainwall
Lightweight, self supporting cladding systems hung from the structure
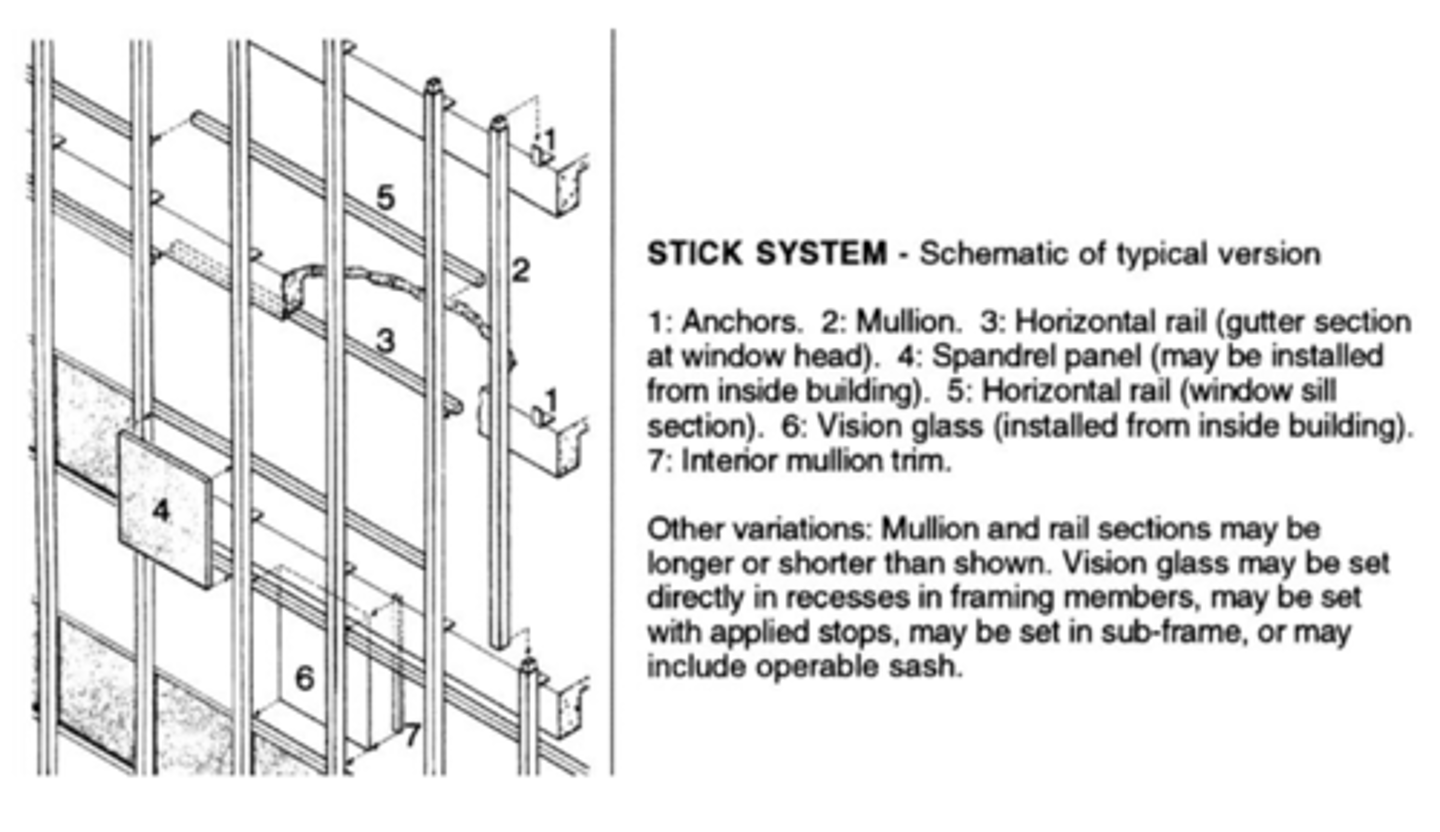
Stick system
A metal curtain wall system that is largely assembled in place
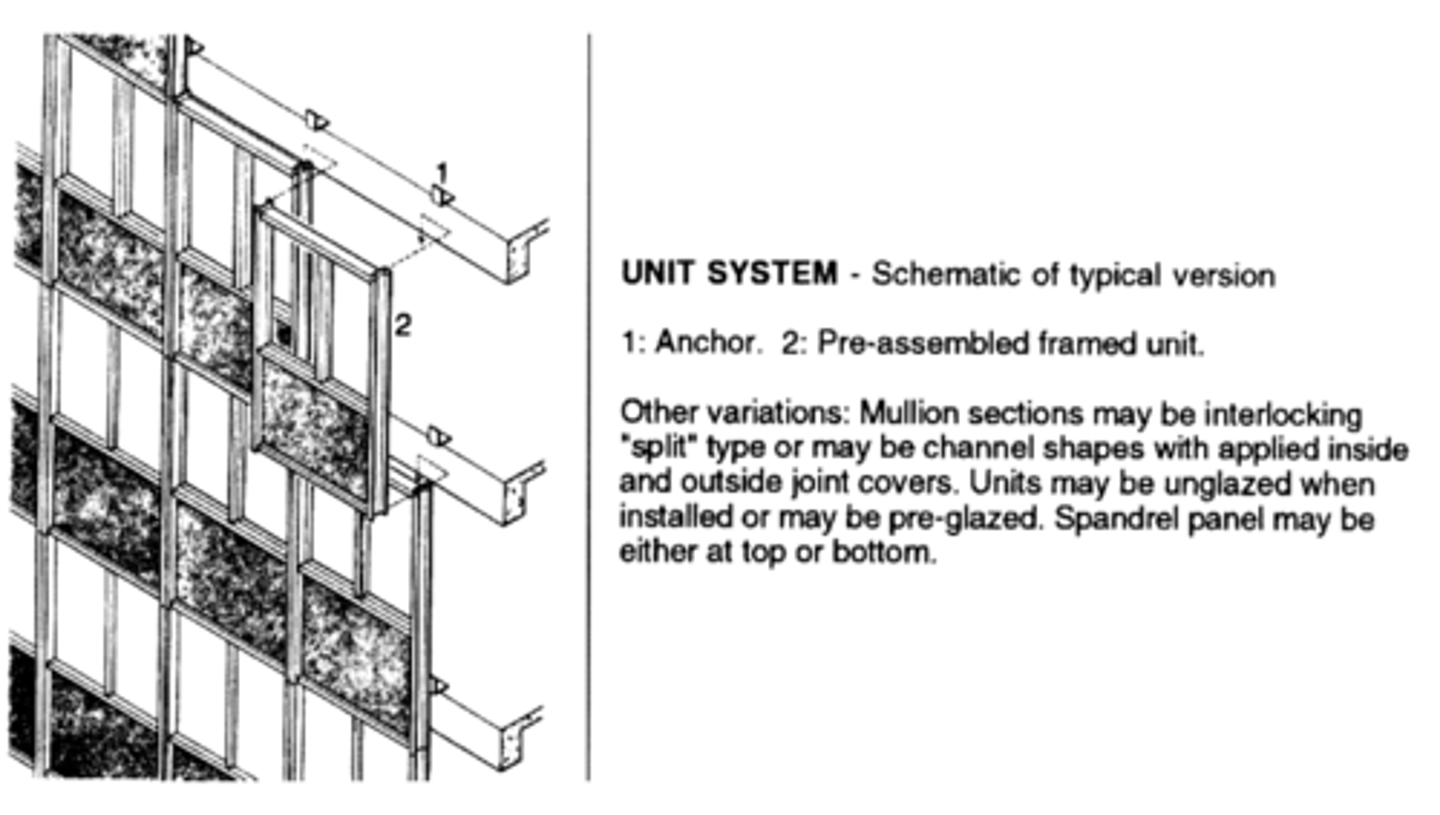
Unit System
utilizes prefabricated, framed curtain wall panels
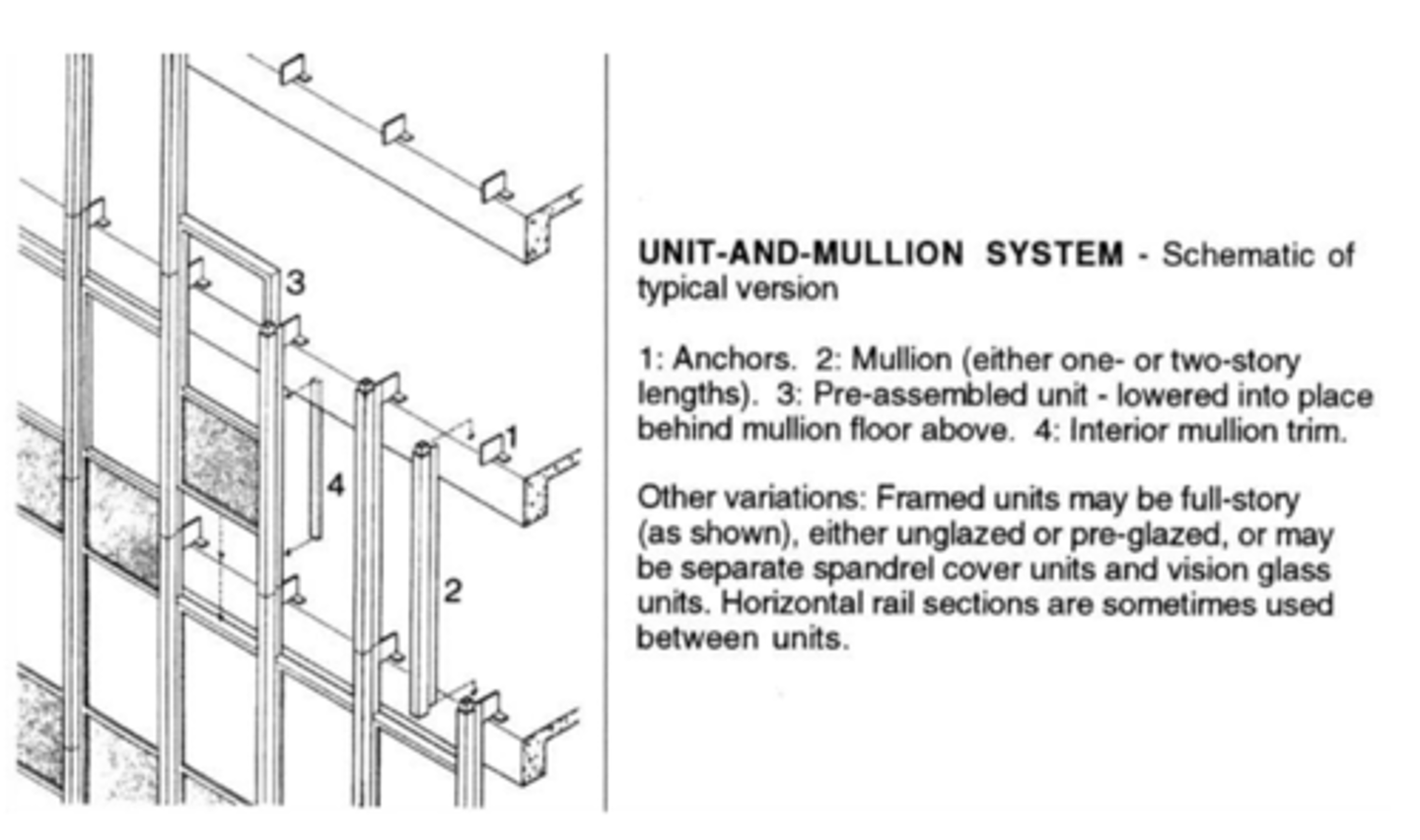
Unit and mullion systems
mullions are put in place first, then premade panels are lowered into place behind them
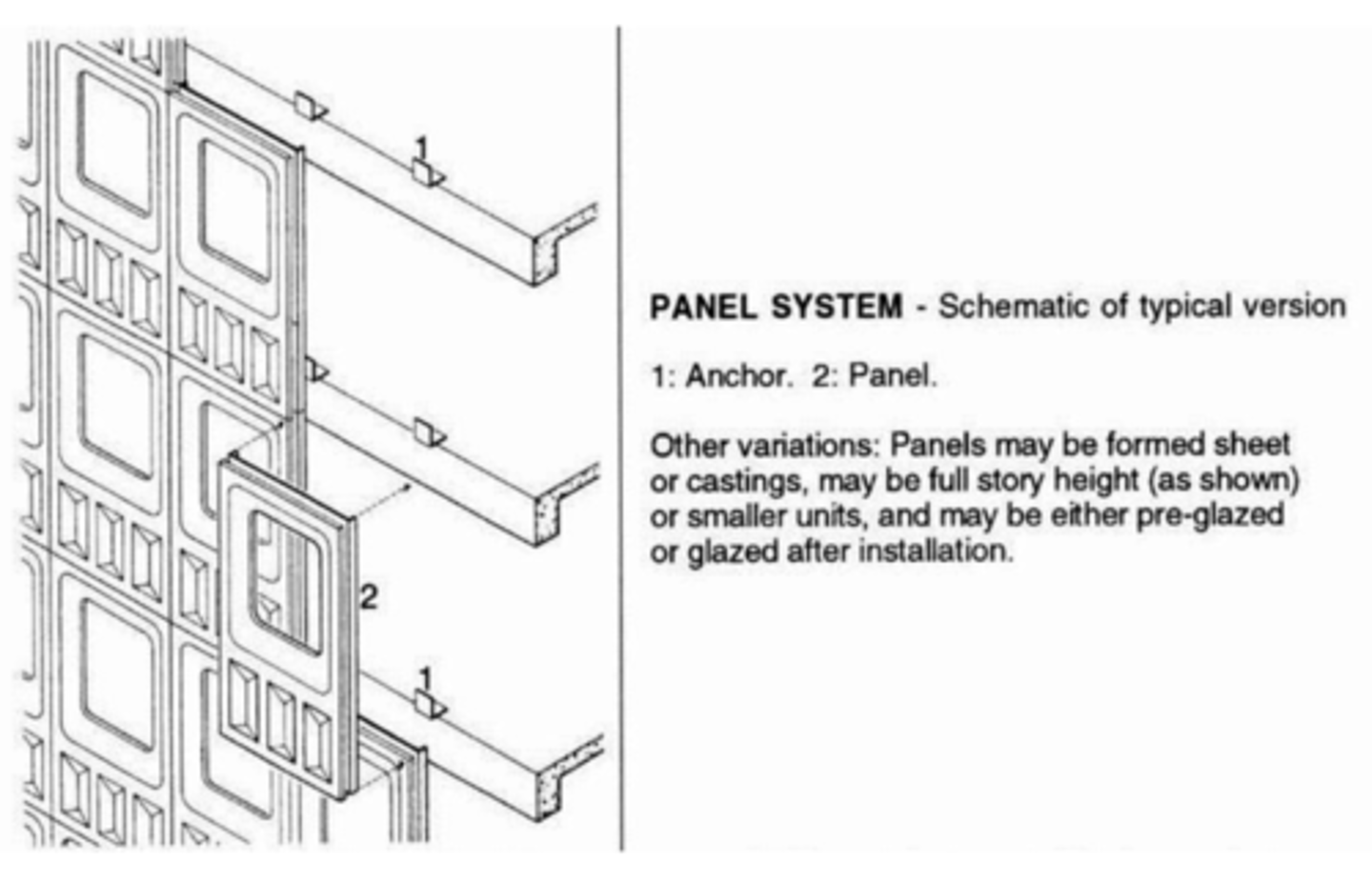
Panel System
A curtain wall system consisting of premade units
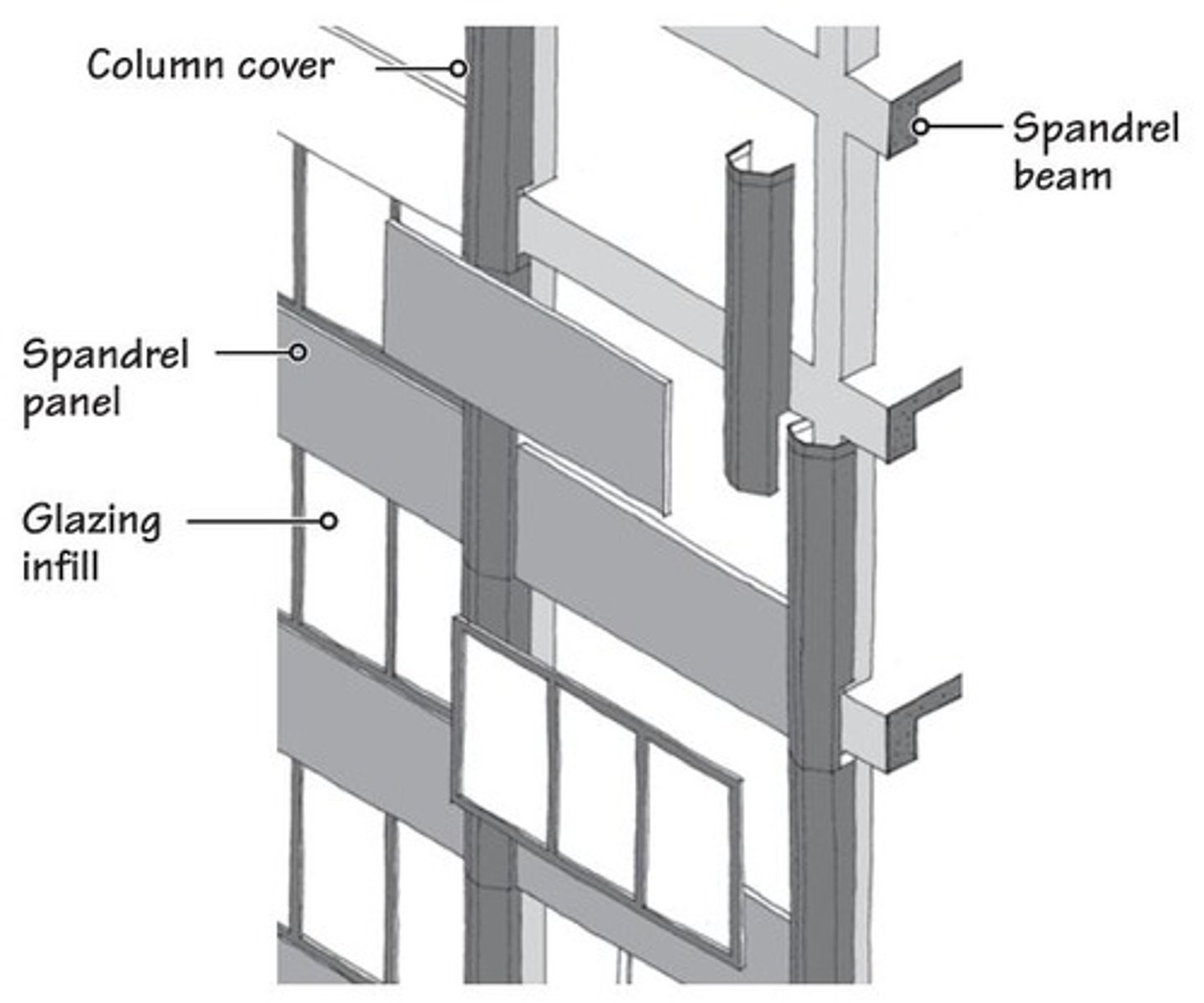
column cover and spandrel system
panels placed between columns then cap is put over columns.
Storefront vs curtain wall
storefront allows drainage out of mullion and is supported by building structure.
curtain walls are sealed to keep water out of mullions and are self supporting.
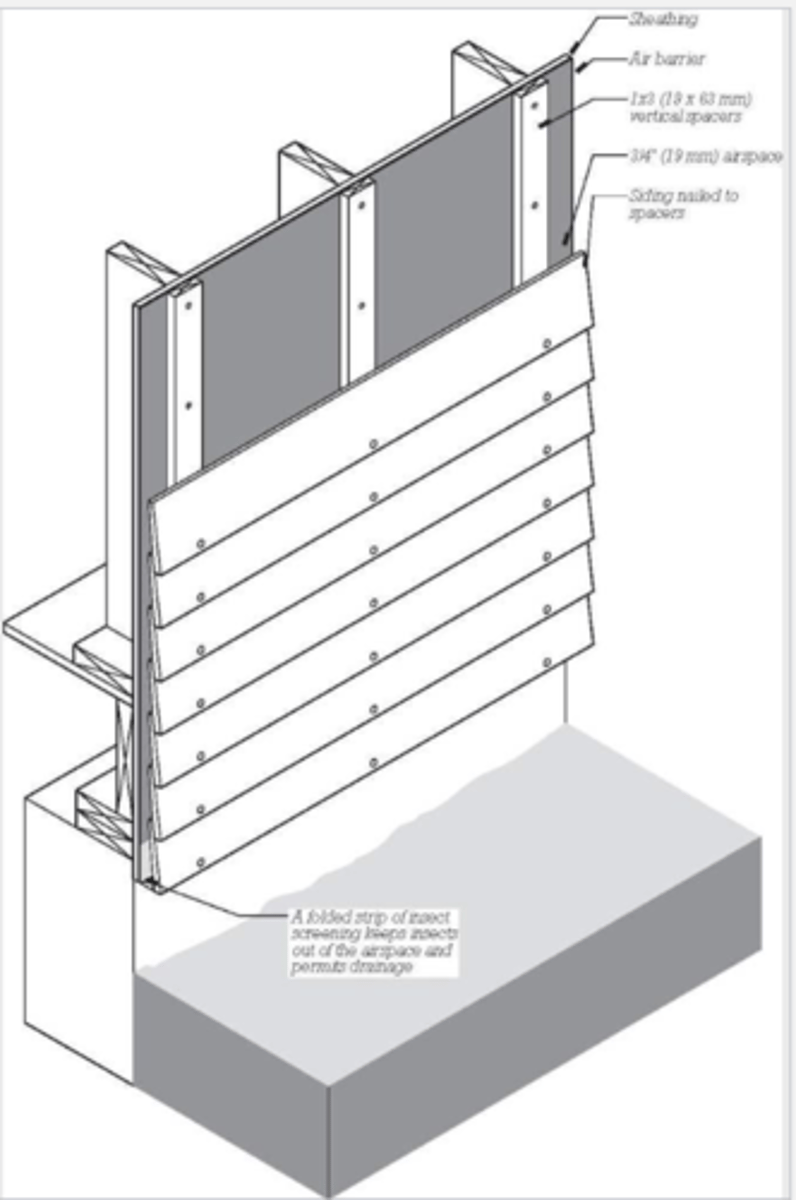
Pressure equalized rainscreen
Cladding system that uses gap behind cladding to balance air pressure on both sides of the cladding. This keeps water from being driven into the wall cavity
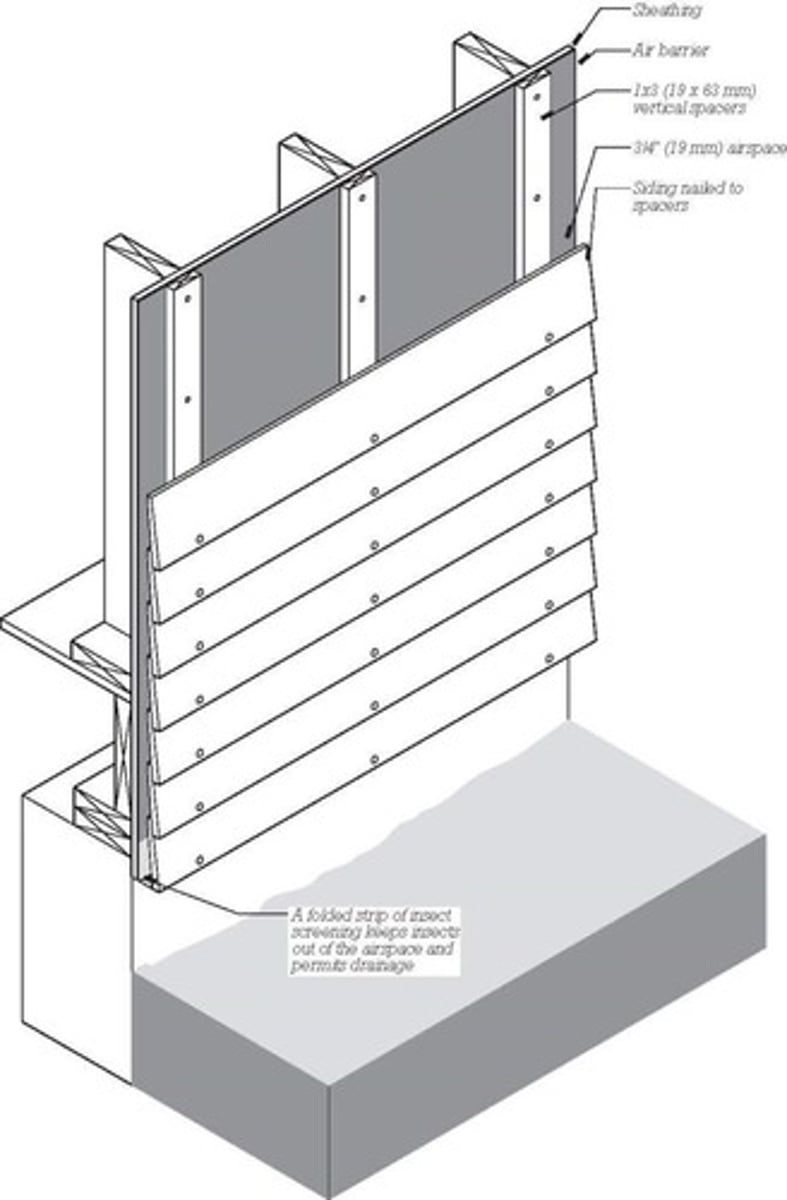
Pressure equalization chamber
reduces water and air infiltration by creating a sealed cavity. used in rainscreens and curtainwalls
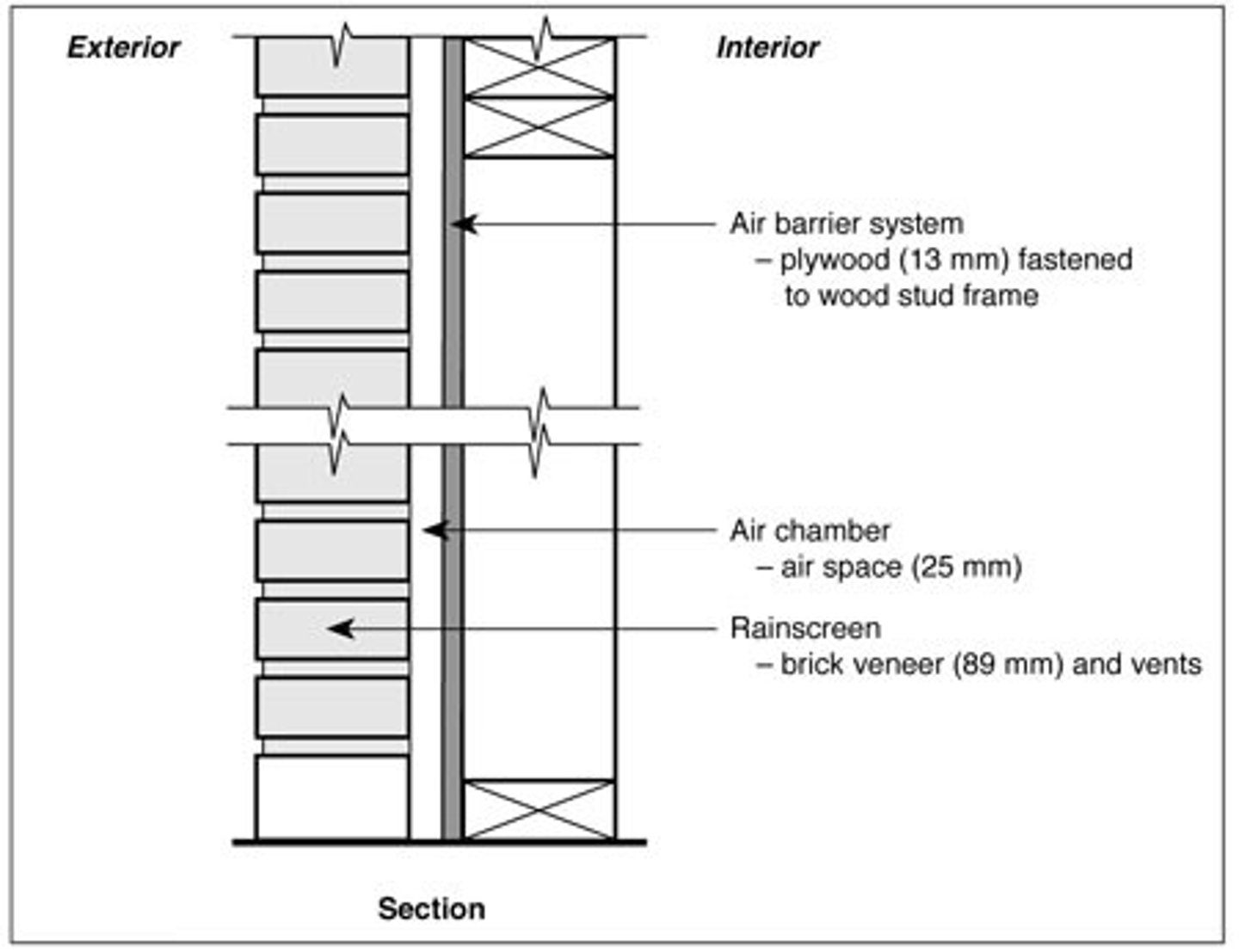
Rainscreen cladding
a wall assembly that protects a building from moisture by creating a ventilated air cavity between the outer cladding and the weather-resistant barrier. Cladding is used as rain barrier, while the cavity allows any infiltrating liquid water or vapor to escape
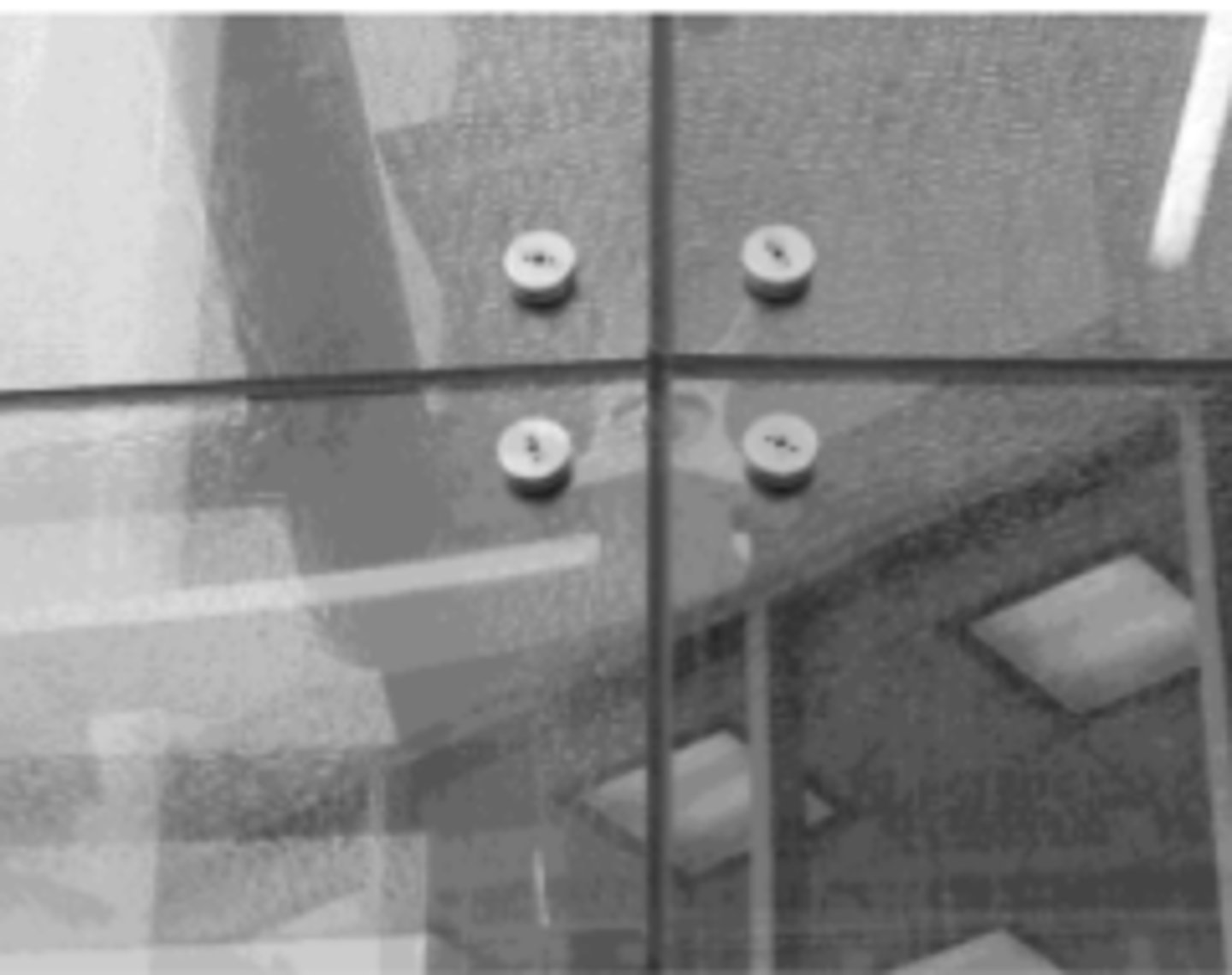
point supported glass system
holes are drilled into glass and are used to anchor the glass to mounts

precast veneer
concrete panels with stone or brick pattern
safing
high-density mineral wool material used as insulation because of its non-combustible qualities

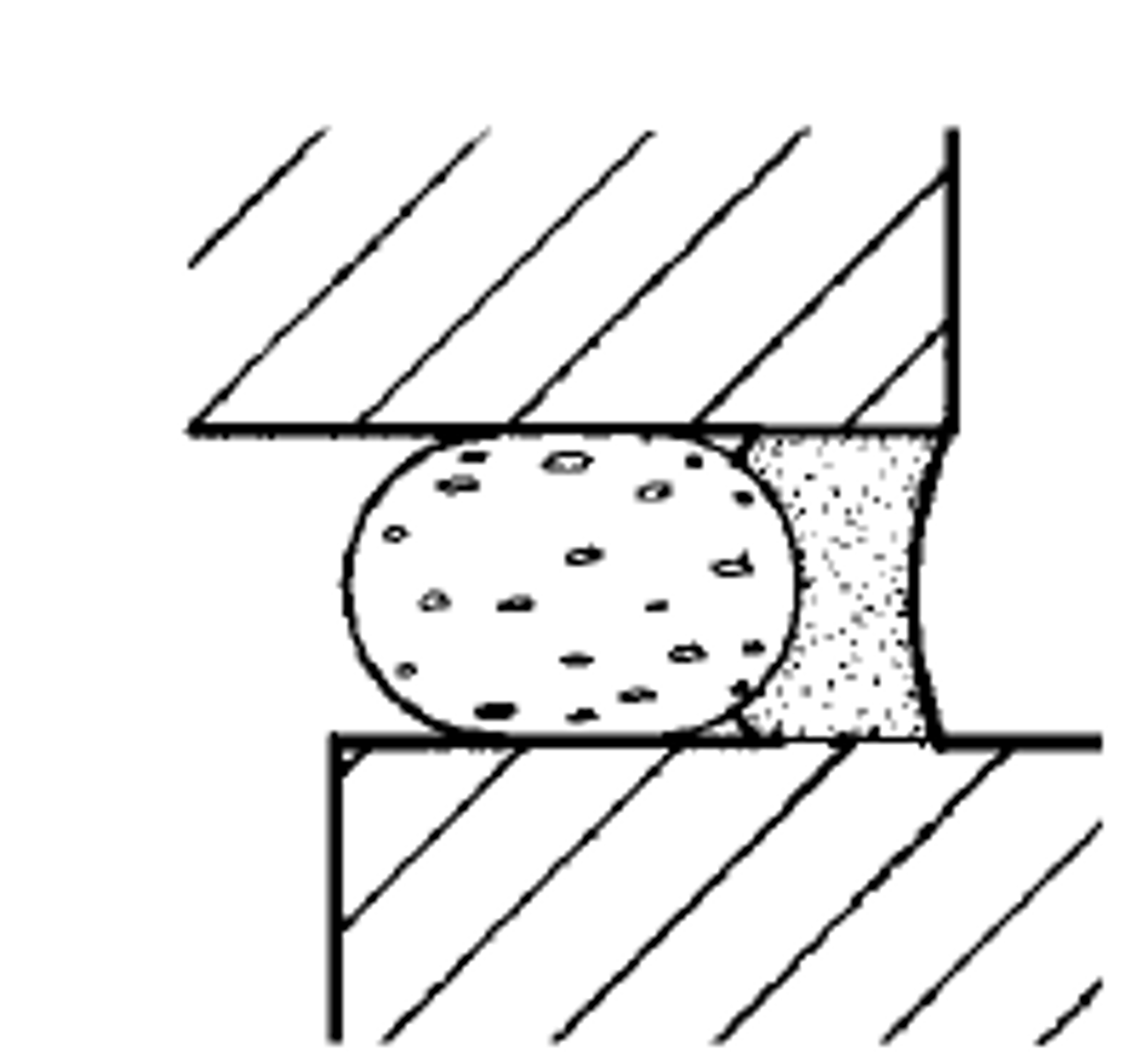
sealant and backer rod
backer rod: placed in crevice that has too much volume to use sealant efficiently
siding panels
large, sheet-like materials used as a protective and decorative covering for a building's exterior walls, shielding it from weather and enhancing its appearance

Wall shingles
overlapping pieces of material, typically wood, but also stone, asphalt, or slate, that are used to cover the exterior walls of a building for protection and decoration
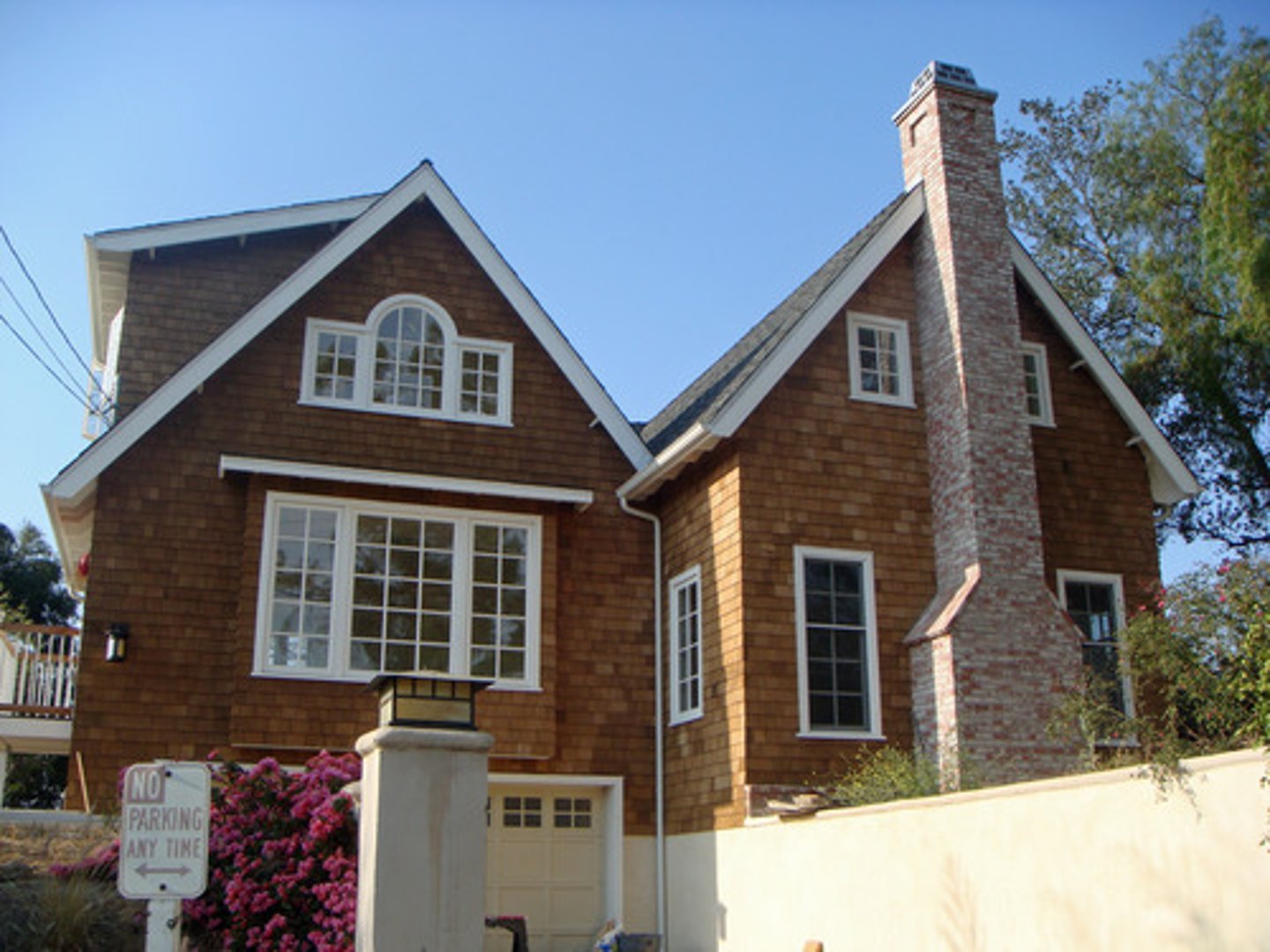

lap siding
horizontal siding style made of long, flat boards that overlap each other, creating a layered and visually appealing exterior.

fiber cement
composite building material made from cement, sand, water, and cellulose fibers, used primarily for exterior siding and cladding.

engineered wood siding
a durable composite material made from wood fibers, resins, and other binders, designed to look like natural wood while offering enhanced resistance to warping, rotting, and pests
