medical mycology intro
1/68
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Fungi
Eukaryotic cells; Living body is a mycelium made of hyphae; Grow as saprophytes and decompose dead organic matter.
Mycelium
The living body of a fungus, made up of a branching network of filaments.
Hyphae
Filaments that make up the mycelium of a fungus.
Saprophytes
Organisms that obtain nutrients from dead organic matter.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Used to ferment sugar to alcohol and carbon dioxide in the production of beer, wine, and bread.
Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus sojae
Used in the production of soy sauce and miso.
Mycoses
Diseases caused by fungi.
Superficial Mycoses
Affects only the outermost layers of skin and hair with little or no pathology.
Cutaneous Mycoses
Destruction of the keratin of skin, hair, and nails.
Subcutaneous Mycoses
Involves skin, muscle & connective tissue immediately below the skin
Systemic Mycoses
Involves the deep tissues and organs of the body.
Polyene Macrolides
Act by binding to the fungal cell membrane and causing the fungus to leak electrolytes.
Azoles
Inhibit the synthesis of ergosterol by blocking a specific enzymatic action.
Antimetabolites (5-Fluorocytosine)
A DNA substrate analog that leads to incorrect DNA synthesis.
Allylamines
Inhibit another enzyme in the pathway that leads to synthesis of ergosterol.
Glucan Synthesis Inhibitors
Inhibit glucan synthesis, a key component of the fungal cell wall.
Griseofulvin
Acts by disrupting the mitotic spindle.
Yeast
Single round to oval cells that usually bud to form daughter cells
Pseudohyphae
Chains of cells formed by budding that, when elongated, resemble true hyphae but are constricted at the septa
Mold
Composed of filaments that generally form a colony that may either be fuzzy, powdery, woolly, velvety, or relatively smooth
Hyphae
Tubular, thread-like structures of fungus
Mycelium
Many hyphae intertwined to form a thick mat
Aerial Hyphae
Above the agar surface; Usually support reproductive structures
Vegetative Hyphae
Food-absorbing portion that grows into the agar like roots
Aseptate Hyphae
No cross walls, wide and ribbon-like
Septate Hyphae
Cross walls very evident
Dimorphism
Quality of possessing two different appearances, or phases
Asexual Reproduction
Nuclear and cytoplasmic division, or mitosis, to produce two more identical cells; results in the formation of conidia (conidiogenesis)
Sexual reproduction
Fusion of two compatible haploid nuclei to form a zygote
Dueteromycetes
fungal imperfecti have asexual name and sexual name
Conidiogenesis
Asexual formation of conidia
Blastic Conidiogenesis
Parent cell enlarges, then a septum separates the enlarged portion into a daughter cell
Thallic Conidiogenesis
A septum forms first, and the growing point ahead of it becomes the daughter cell
Arthric Conidiogenesis
Daughter cells fragment within the hyphal strand (thallic)
Holo
All wall layers of the parent cell are involved in daughter conidium development
Entero-
Only inner cell wall layers are included
Blastoconidia
Holoblastic condia formed by budding along hyphae, pseudohyphae, or a single cell, as in yeasts
Poroconidia
Holoblastic conidia produced through a pore in the parent cell wall
Phialoconidia
Conidia arising from a phialide, which is a vase-shaped cell that may be ringed at the top by a cup-shaped collarette
Annelloconidia
Conidia arising from an annellide, which is a vase-shaped cell that exhibits a new ring of material as each conidium passes through
Chlamydoconidia
Thick-walled hyphal survival conidium formed during poor environmental conditions, which will germinate and produce conidia when a better climate occurs
Chlamydospore
thick wall vessicle of C. albians and some other yeast, which neither germinates nor produces conida when mature
Arthroconidia
Conidia produced by fragmentation of the hyphal strand through the septation points
Sporangia
Asexual sac-like structures at the tip of support stalk; contains sporangiospores
Microconidia
Smaller conidia in fungi that produce both large and small conidia
Macroconidia
Larger conidia in fungi that produce both may be single celled, but usually multicelled
Antheridium
male cell
Ascogonium
female cell
Ascus
zygote
Ascospores
formed by nuclear division within the ascus
Ascocarp
protective sac which houses the asci & ascospores
Cleistothecium
completely enclosed ascocarp
Basidium
club-shaped mother cell from which basidiospores arise
Basidiospores
sexual spore formed by the fusion of 2 compatible nuclei and cells into a zygote
Basidiocarp
protective structure which houses basidia and basidiospores
Zygophore
arm of hyphae that extends towards another compatible arm to produce a zygospore
Zygospore
sexual spore formed by fusion of 2 compatible hyphal arms
Zygosporangium
thick outer layer covering a zygospore
Mycelia Sterilia
No reproductive structures, just lots of hyphae
Cottony or Wooly Texture
Very high, dense aerial mycelium

Velvety Texture
Low aerial mycelium
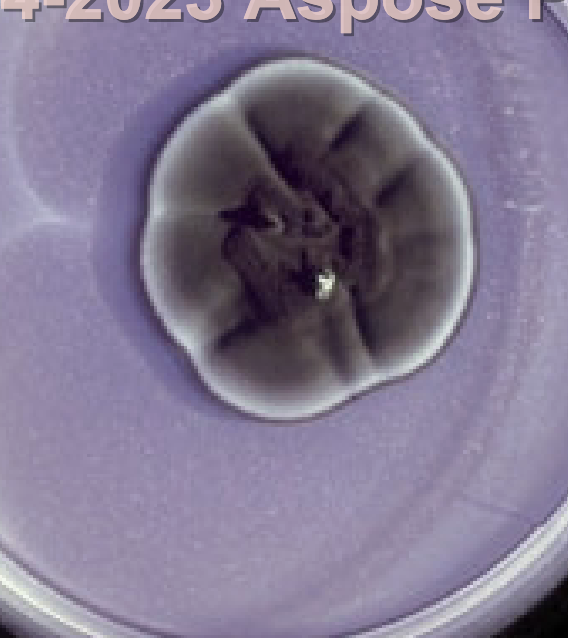
Granular or Powdery Texture
Dense production of conidia
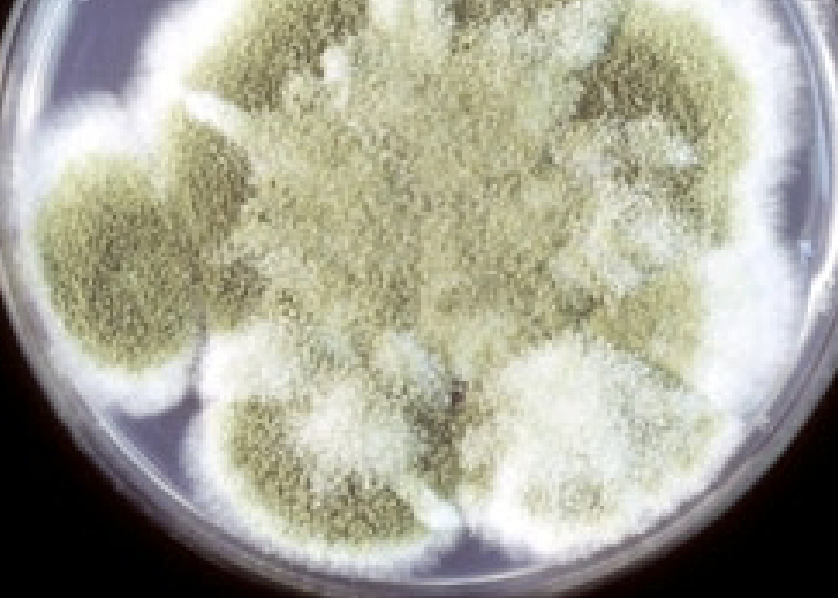
Glabrous Texture
Waxy, smooth, no aerial mycelium
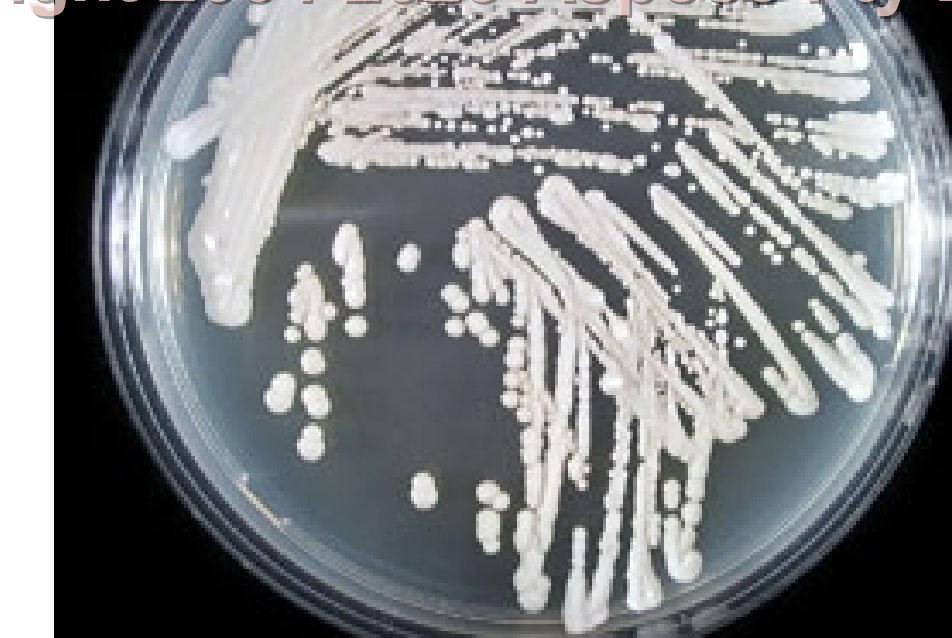
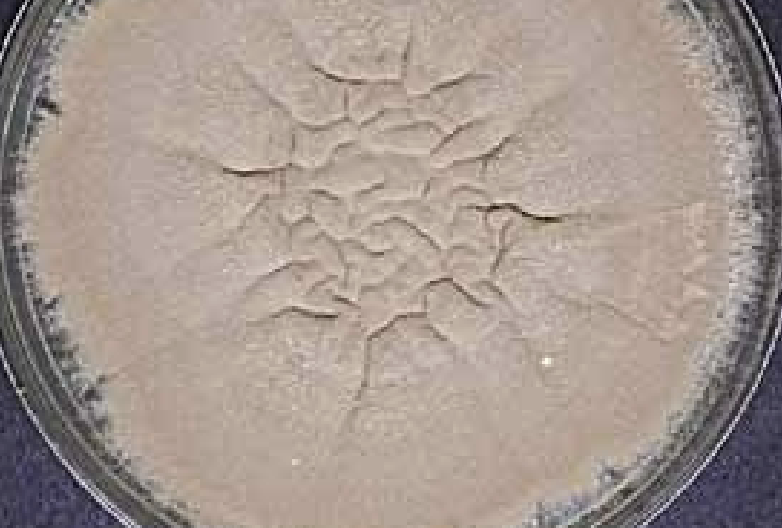
Rugose Topography
Deep furrows irregularly radiating from center
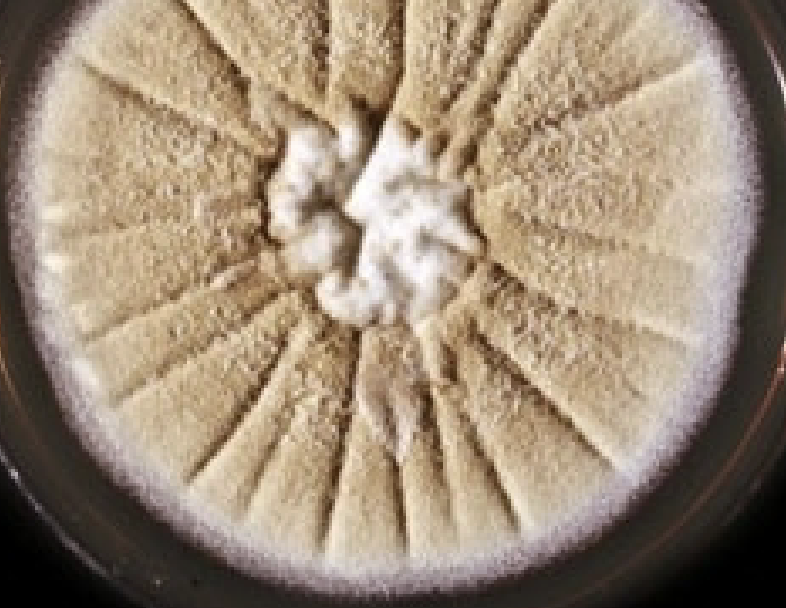
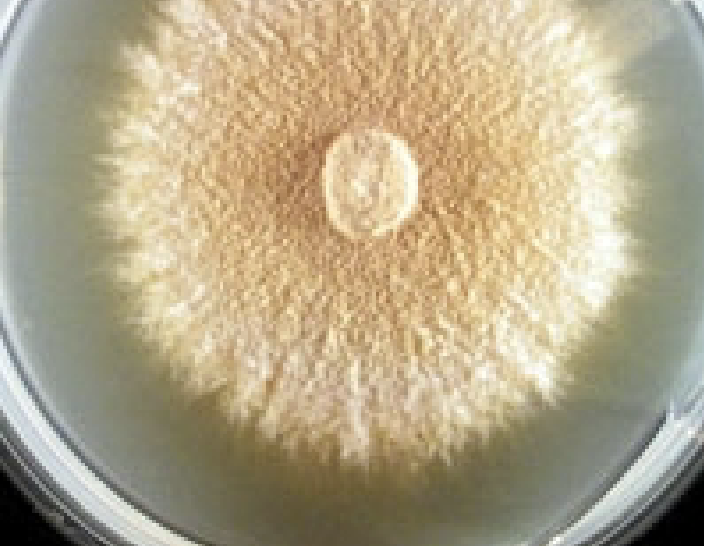
Umbonate Topography
Button-like central elevation
Verrucose Topography
Wrinkled, convoluted surface

Dematiaceous
Darkly colored conidia and hyphae
Hyaline
Lightly colored conidia and hyphae
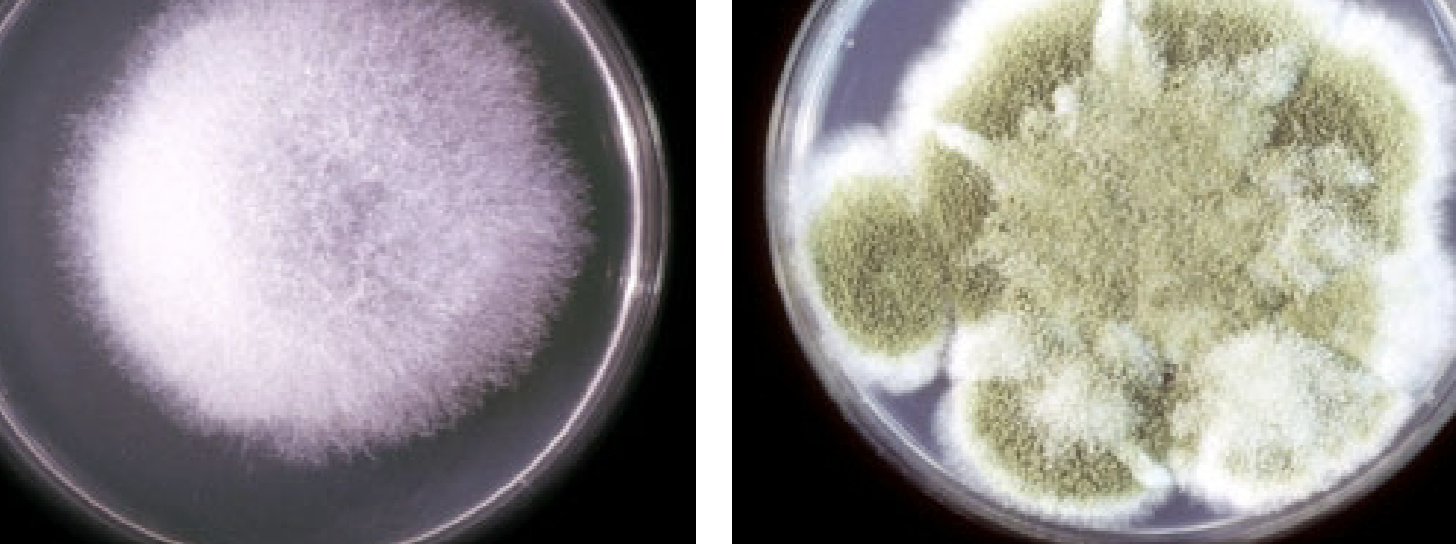
darkly colored condia and hyphae