
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Describe how coenzyme Q accepts electrons
Antioxidant because it can accept electrons from things so they don’t oxidise other things
Ubiquinone has a rign structure, this is where everything is sp2 hybridised
But it is not aromatic, in the ring there are only 4π electrons
Electron source can be accepted by an oxygen, this triggers a breaking of bonds throughout the molecule
This produces a negative charge on the oxygen that accepted the electron and forms a radical
Radical can accept another electron, producing another negative charge
This produces an aromatic product, the gain of aromaticity is the driving force in the reaction
Protons can be shuttles across the membrane to neutralise the O- charges
Can be oxidised back to the original molecule
Has a repeating unit, this aids membrane association.
Describe the 2 stage process of photosynthesis
Light dependent reaction
Building up molecules of ATP, producing oxygen - net oxidation from water, and we are reducing NADP+ --> NADPH, this gives us reducing equivalents
This uses energy from light
Dark reaction - this is light independent
Redyce carbon dioxide, hydrogen is used to redice the charge build up
Describe how chlorophyll absorbs light
Light absorption by the porphyrin ring around the magnesium centre
In the ring there is a large conjugated system
The energy gap for the homo-lumo is small, matching the energy of visible light
Describe b-carotene
Long conjugated system for the electrons to have a small energy gap, can absorb light
Describe the absorption spectra in the solar spectrum
Different molecules can absorb a large amount of different wavelengths, maximising their rate of photosynthesis
Combination of molecules act as an antenary complex
Describe the z scheme
P680 absorbs light, this excites electrons into thr LUMO (higher energy)
Electrons are transferred through a series of carriers, this is down a electrochemical gradient to a lower energy, this releases energy for proton pumping which allows ATP synthesis
P700 then excites the electrons again using energy from light absorption, they are passed to ferredoxin and then NADP+ reductase which produces NADPH
The electrons from P680 are replaced by oxidising water, as the P680 has a highest oxidising agent
P700 is the strongest reducing agent
Describe the reaction of rubisco
Conversion of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate to 3-phosphoglycerate
Kcat is 3/s, very slow but a key enzyme
For every carbon dioxide in, ypou get two molecules of 3phosphoglycerate
Describe the mechanism of Rubisco
Mg2+ is coordinated, 3 with active site residues that are negatively charged, one of these is a lysine hat has been carboxylated due to such a high concentration of CO2
If there are no substrates, 3 waters will also coordinate
Substrate enters and replaces two waters
Donate lysine lone pair, allos oxygn attack and deprotonation
Form an enolate that is coordinated to the magnesium
One histidine aids the deprotonation of the alcohol and a lysine aids alcohol formation
Flipping the sterochem
Forming the carbon-carbon bond
Enolate increases nucleophicity of the alkene
Water deprotonated to make a bettwe nucleophile
Attacks carbonyl and can form a tetrahedral intermediate
Tetrahedral intermediate forms
Reforms the carbonyl and break a C-C bond
Negative chartge is protonated by a protonated basic residue
Formed 2 x 3 phosphoglycerates
Describe the Calvin cycle with 3CO2
Incorporating 3CO2 means we've made 6G3P
If one carbon dioxide comes in, 2x3GP come out
For 3CO2, 1/6 G3P goes to central metabolic pathways and the other 5 go the rest of the pathway
How is fructose 6 phoshate regenerated?
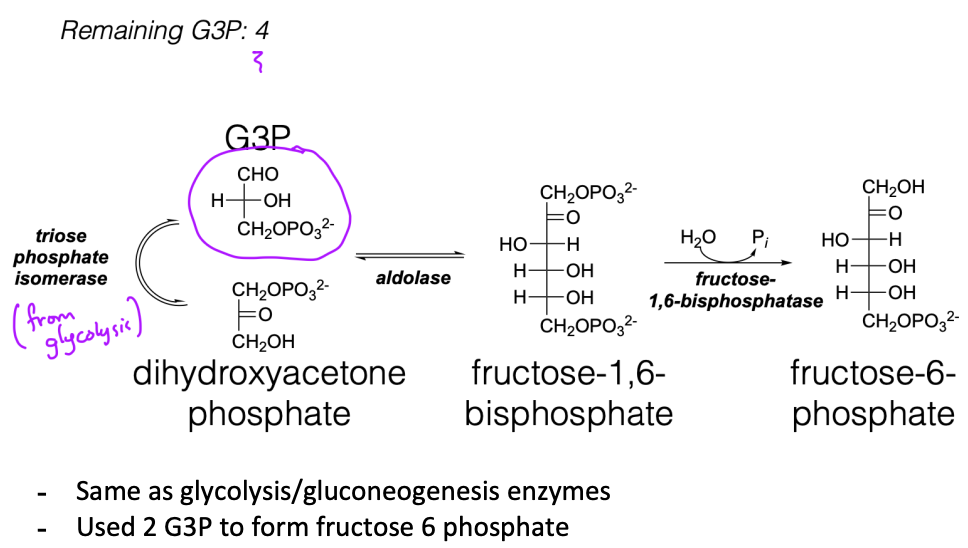
Describe the transketolase reaction
Another G3P is used with fructose 6phosphate to produce a 4C sugar and a 5C sugar
Describe the transketolase mechanism
TPP is an illid, -ve charge acts as a nucelophile and attacks the carbonyl
Can be protonated to form a protonated tetrahedral intermediate
Deprotonate alchol and reform the carbonyl.
Then kcik out LG, electrons are accepted by the N+ on the TPP
TPP allows the breaking of the C-C bond
Have a 4C sugar and 2 carbons attached to the TPP intermediate
Nitrogen donates e- via resonance
Attacks aldehyde and protonates the oxygen
Tetrahedral intermediate forms
Deprotonate alcohol
Form ketone
Kick out TPP as a LG
Forms a 5C sugar
Describe the second aldolase reaction
Aldolase combins a 4C and 3C to a 7C sugar - sedoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphate
Describe the reaction of sedoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphate
Phosphatase cannot be used for SLP as not a good LG
Form an inorganic phosphate
Describe th second transketolase reaction with sedoheptulose 7 phosphate
Second transketonase allows two 5C molecules to be produced
Overall 3X5C sugars
Describe the conversion of ribose5phosphate to ribulose5phosphate
Conversion of ribose5phosphate (an aldose) to ribulose5phosphate (a ketone)
Isomerisation from an aldehyde to a ketone
Describe the conversion of xyulose5phosphate to ribulose5phosphate
Attempting to change the stereochemistry of a carbon
Deprotonate a-to carbonyl to give us an enolate
Then kick oxygen electrons down and reprotonates on the other side, produces the epimer
Once we have deprotonates, the carbon is not planar - so have to add to the opposite face to get the opposite stereoisomer
Describe the conversion of ribulose5phosphate to ribulose1,5bisphosphate
Phosphorylate using a kinase
Produced 3 molecules of ribulose1,5bisphosphate and have one G3P left for the central metabolic pathways
Why is rubisco slow?
Not overly selective
Can also do photorespiration
Enolate attacks oxygen and gives a peroxide compound