Psychology 202: Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:36 AM on 12/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
1
New cards
What is the Prisoner’s Dilemma? What does it tell us about the prevalence of cooperation?
Prisoner's dilemma
* Game theory model for understanding cooperation and competition
* Two suspects in custody and separated
* What happened with your pair’s points over trials?
* Some cooperate the whole time (maximize points)
* Defect every time (might lose, but if I win, I’ll get 5)
* Partner starting defecting too
* Strategies?
* Does cooperation and kindness towards someone happen in humans?
* Yes, but cooperation is hard to get
* Element in trust in cooperation
* Prisoner's dilemma
* Models why cooperation can be rare
* Influence of trust
* Game theory model for understanding cooperation and competition
* Two suspects in custody and separated
* What happened with your pair’s points over trials?
* Some cooperate the whole time (maximize points)
* Defect every time (might lose, but if I win, I’ll get 5)
* Partner starting defecting too
* Strategies?
* Does cooperation and kindness towards someone happen in humans?
* Yes, but cooperation is hard to get
* Element in trust in cooperation
* Prisoner's dilemma
* Models why cooperation can be rare
* Influence of trust
2
New cards
What is the tit-for-tat strategy?
* Tit-for-tat an effective strategy
* Do whatever to your partner that they did to you for the prior round
* Do whatever to your partner that they did to you for the prior round
3
New cards
What is altruism? Why is its existence hard to explain, in terms of evolutionary theory?
* Behavior towards another person that benefits other, at potential cost to self
* Ex.) Firefighter into burning building to save a child
* Why is altruism hard to explain?
* Evolutionary theory: promote your own genes; operates on selfishness
* Organism does things to promote its own survival and reproductive potential
* Ex.) Firefighter into burning building to save a child
* Why is altruism hard to explain?
* Evolutionary theory: promote your own genes; operates on selfishness
* Organism does things to promote its own survival and reproductive potential
4
New cards
What are the three explanations for altruism? Be able to provide examples for each explanation.
Selfishness, inclusive fitness, and reciprocal altruism
5
New cards
What is the selfishness explanation to altruism?
* Selfishness: Helping actually benefits yourself
* Evidence for selfishness hypothesis
* Ferguson et al. (2008): Beliefs in personal benefit predicted actual future blood donation better than beliefs in societal benefit
* “If I donate blood into the blood bank, I might get help from that”
* If you offer people a sticker saying they donated blood, they are more likely to do it
* I want to help people, but I am doing it because I am now viewed as a good person
* Sticker proves to everyone else that I am a good person, I did something good
* Evidence for selfishness hypothesis
* Ferguson et al. (2008): Beliefs in personal benefit predicted actual future blood donation better than beliefs in societal benefit
* “If I donate blood into the blood bank, I might get help from that”
* If you offer people a sticker saying they donated blood, they are more likely to do it
* I want to help people, but I am doing it because I am now viewed as a good person
* Sticker proves to everyone else that I am a good person, I did something good
6
New cards
What is the inclusive fitness explanation to altruism?
* Inclusive fitness: help relatives
* Evidence for inclusive fitness hypothesis
* Adoption patterns in Oceania (Silk, 1980)
* Oceania – geographic area in south pacific
* Indigenous people there
* Many cultures practiced adoption where they adopted kids into their families that weren’t their own kids
* These aren’t my children, but I'm going to take them into my family and take care of them
* Fitting the evolutionary hypothesis
* Makes sense because its inclusive fitness
* The most common types of children that got adopted was a relative (25% relatedness)
* There are some kids that are adopted that aren’t related a lot or it is unknown
* Kids that tended to be in this category were adopted into small families that didn’t have a lot of children
* Wanted more children to help with the subsistence farming
* We love these children, but they are also helping us out
* Alarm calls in Belding’s ground squirrels
* Specific call that means watch out, predator near
* If I give an alarm call, I’m making myself very obvious to the predator
* Doing to benefit to rest of group
* Animals were more likely to call when relatives were near by
* Animals were less likely to call when relatives were not around, animals around weren’t related to them
* Evidence for inclusive fitness hypothesis
* Adoption patterns in Oceania (Silk, 1980)
* Oceania – geographic area in south pacific
* Indigenous people there
* Many cultures practiced adoption where they adopted kids into their families that weren’t their own kids
* These aren’t my children, but I'm going to take them into my family and take care of them
* Fitting the evolutionary hypothesis
* Makes sense because its inclusive fitness
* The most common types of children that got adopted was a relative (25% relatedness)
* There are some kids that are adopted that aren’t related a lot or it is unknown
* Kids that tended to be in this category were adopted into small families that didn’t have a lot of children
* Wanted more children to help with the subsistence farming
* We love these children, but they are also helping us out
* Alarm calls in Belding’s ground squirrels
* Specific call that means watch out, predator near
* If I give an alarm call, I’m making myself very obvious to the predator
* Doing to benefit to rest of group
* Animals were more likely to call when relatives were near by
* Animals were less likely to call when relatives were not around, animals around weren’t related to them
7
New cards
What is the reciprocal altruism explanation of altruism?
* Reciprocal altruism: help others in return for future help for yourself
* Blood meal donation in vampire bats
* Problem they have --> maintain metabolism
* In order to fly, they need a high metabolism
* Go out at night to get blood meal, but not always successful
* If a bat doesn't eat in 36 hours, they will die
* Bats comes back into cave, and if they didn’t eat they will go up to another bat and beg for a blood meal
* Donor bat will regurgitate some of their blood to the bat that didn’t eat
* If I do a favor for you today, I know I will get repaid in the future
* Bat that was begging before will reciprocate the favor to the donor bat
* Rare phenomenon because it requires a lot of trust
* Evolves in tight, well-structured social groups where you are likely to rencounter another individual
* Blood meal donation in vampire bats
* Problem they have --> maintain metabolism
* In order to fly, they need a high metabolism
* Go out at night to get blood meal, but not always successful
* If a bat doesn't eat in 36 hours, they will die
* Bats comes back into cave, and if they didn’t eat they will go up to another bat and beg for a blood meal
* Donor bat will regurgitate some of their blood to the bat that didn’t eat
* If I do a favor for you today, I know I will get repaid in the future
* Bat that was begging before will reciprocate the favor to the donor bat
* Rare phenomenon because it requires a lot of trust
* Evolves in tight, well-structured social groups where you are likely to rencounter another individual
8
New cards
What types of psychological studies were spurred by the murder of Kitty Genovese?
* Murder of Kitty Genovese (1964)
* Bartender in Queens, New York
* When going home to apartment, perpetrator started assaulting her in the parking lot
* She got away from him and got into lobby of building, but he followed
* Over course of 30 minutes, he stabbed her to death
* Almost 40 people witnessed her dying, but no one called the police
* After the news broke, explanations were put forward
* This is a sure sign of urban decay
* Shows that if you live in an urban environment, social rules fall apart
* Nobody cares anymore
* Being a new yorker that made it happen
* New Yorkers are uncaring people, not friendly, they don’t help
* Psychologists looked into what really happened
* Bystander effect
* Lots of inaccuracies in the reporting in what originally happened
* Turns out lots of people did try to help
* Tried to call police, but they didn’t get through
* Resident in building did not help because he was gay, so he could’ve gotten arrested for just being gay
* Bartender in Queens, New York
* When going home to apartment, perpetrator started assaulting her in the parking lot
* She got away from him and got into lobby of building, but he followed
* Over course of 30 minutes, he stabbed her to death
* Almost 40 people witnessed her dying, but no one called the police
* After the news broke, explanations were put forward
* This is a sure sign of urban decay
* Shows that if you live in an urban environment, social rules fall apart
* Nobody cares anymore
* Being a new yorker that made it happen
* New Yorkers are uncaring people, not friendly, they don’t help
* Psychologists looked into what really happened
* Bystander effect
* Lots of inaccuracies in the reporting in what originally happened
* Turns out lots of people did try to help
* Tried to call police, but they didn’t get through
* Resident in building did not help because he was gay, so he could’ve gotten arrested for just being gay
9
New cards
What is the bystander effect? What factors influence the strength of the bystander effect?
* Bystander effect
* As the number of people present increases, the likelihood of helping decreases
* Bystander effect: influencing factors (what factors will motivate someone to help)
* Ambiguity
* More helping if clearer that the person truly needs help
* Situation is not ambiguous
* Disabled person with a cane falls down
* Person already has mobility issues, they clearly need help
* Cohesiveness
* More helping if member of established group; social responsibility norm
* As the number of people present increases, the likelihood of helping decreases
* Bystander effect: influencing factors (what factors will motivate someone to help)
* Ambiguity
* More helping if clearer that the person truly needs help
* Situation is not ambiguous
* Disabled person with a cane falls down
* Person already has mobility issues, they clearly need help
* Cohesiveness
* More helping if member of established group; social responsibility norm
10
New cards
What is diffusion of responsibility?
* Diffusion of responsibility
* Assume someone else will help, especially if large group of bystanders
* Explanation for why large members of bystanders don’t help
* Assume someone else will help, especially if large group of bystanders
* Explanation for why large members of bystanders don’t help
11
New cards
What are some sex differences in the expression of aggression?
* Sex differences: sexual dimorphism
* Sexual dimorphism – males look different than females in some sort of way
* Lions - Size, presence of manes
* Birds - Different coloring and size
* Monkeys – presence of cheek pads and size
* Useful to males to access females for reproduction
* Sex differences
* Males more aggressive than females in many species
* Aggression helps males to get access to more females by fighting other males
* Sex differences in children
* Boys and girls equally verbally aggressive
* Boys use more physical aggression
* Girls use more indirect (relational) aggression
* Spreading rumors
* Gossiping
* Sexual dimorphism – males look different than females in some sort of way
* Lions - Size, presence of manes
* Birds - Different coloring and size
* Monkeys – presence of cheek pads and size
* Useful to males to access females for reproduction
* Sex differences
* Males more aggressive than females in many species
* Aggression helps males to get access to more females by fighting other males
* Sex differences in children
* Boys and girls equally verbally aggressive
* Boys use more physical aggression
* Girls use more indirect (relational) aggression
* Spreading rumors
* Gossiping
12
New cards
What is the intrauterine position effect, and how does it demonstrate the effect of testosterone on aggression?
Intrauterine position effect: natural testosterone exposure in utero in rodents
Compare females that are:
O M
Females on both sides, surrounded by no males
1 M
Female on one side and male on the other side
2 M
Males on both sides, surrounded by no males
Matters because testosterone is going to be circulating through the uterus
Look at aggressive behavior once female is born when in the presence of an intruder female
2M females are more aggressive than the 1M or 0M
Level of exposure of testosterone in the womb impacts how aggressive you are
Compare females that are:
O M
Females on both sides, surrounded by no males
1 M
Female on one side and male on the other side
2 M
Males on both sides, surrounded by no males
Matters because testosterone is going to be circulating through the uterus
Look at aggressive behavior once female is born when in the presence of an intruder female
2M females are more aggressive than the 1M or 0M
Level of exposure of testosterone in the womb impacts how aggressive you are
13
New cards
What are some aggression correlates of low serotonin levels?
* Low serotonin correlated with:
* Higher scores on standard aggression tests
* Impulsive arson
* Animal abuse
* Higher scores on standard aggression tests
* Impulsive arson
* Animal abuse
14
New cards
How does observational learning influence aggression?
* Effects of observational learning: Do children pick up aggressive behavior from adults?
* Bandura’s Bobo doll study
* If adults modeled aggression with the doll, children would mimic that
* Bandura’s Bobo doll study
* If adults modeled aggression with the doll, children would mimic that
15
New cards
How did Lee et al. (2013) investigate the effects of spanking on child aggression? What were the main results?
* Spanking: Lee et al. (2013)
* Mothers' and fathers’ self-report of frequency of spanking within prior month; child age 3
* Child aggression at age 5: Aggression subscale of Child Behavior Checklist
* Child argues a lot
* Child is cruel
* Child bullies or is mean to others
* Child destroys things
* Child gets in fights
* Child threatens people
* Results:
* Being spanked 2+ times at age 3 by mother or father associated with increased risk of aggression at age 5
* Greatest risk when both parents spanked more than twice in prior month
* Mothers' and fathers’ self-report of frequency of spanking within prior month; child age 3
* Child aggression at age 5: Aggression subscale of Child Behavior Checklist
* Child argues a lot
* Child is cruel
* Child bullies or is mean to others
* Child destroys things
* Child gets in fights
* Child threatens people
* Results:
* Being spanked 2+ times at age 3 by mother or father associated with increased risk of aggression at age 5
* Greatest risk when both parents spanked more than twice in prior month
16
New cards
What is catharsis?
* Does catharsis (‘venting’) help?
* Catharsis: releasing, and thereby providing relief from, strong or repressed emotions
* Studies have shown this doesn’t work
* Catharsis: releasing, and thereby providing relief from, strong or repressed emotions
* Studies have shown this doesn’t work
17
New cards
How did Bushman (2002) investigate the effect of catharsis on the expression of aggression? What were the main results?
* Bushman (2002):
* Anger participants in lab setting, Then: IV = activity type
* Punching bag + rumination (think about person that angered you)
* catharsis situation
* Punching bag + distraction (think about becoming physically fit)
* No punching bag (control)
* DV = intensity and duration of noise blast administered to person who initially angered the participant
* If you win trial, you have noise blast machine, and you get to pick how loud and long this noise blast will be in the other persons headphones
* Way to operationalize aggression
* Results:
* Ps in rumination group were more aggressive than Ps in other two groups
* Ps in rumination group also felt angrier than Ps in other two groups
* Anger participants in lab setting, Then: IV = activity type
* Punching bag + rumination (think about person that angered you)
* catharsis situation
* Punching bag + distraction (think about becoming physically fit)
* No punching bag (control)
* DV = intensity and duration of noise blast administered to person who initially angered the participant
* If you win trial, you have noise blast machine, and you get to pick how loud and long this noise blast will be in the other persons headphones
* Way to operationalize aggression
* Results:
* Ps in rumination group were more aggressive than Ps in other two groups
* Ps in rumination group also felt angrier than Ps in other two groups
18
New cards
What is the difference between instrumental and relational aggression?
* Instrumental aggression is the intentional harm, usually physical, done to others to obtain a goal, such as attacking a person to steal a wallet or purse.
* Relational aggression harms another person’s social standing through behaviors such as ignoring, excluding, and gossiping.
* Relational aggression harms another person’s social standing through behaviors such as ignoring, excluding, and gossiping.
19
New cards
What are some effects of testosterone on aggression, beyond the intrauterine position effect?
* Prenatal exposure to high levels of androgens, which can occur naturally or because of medications occasionally given to pregnant women, increases the aggressive play of both male and female preschoolers
* Adult men with higher levels of prenatal testosterone exposure score higher on standardized questionnaires of aggression.
* Testosterone levels on the high end of the typical range in teen and adult males are positively correlated with delinquency, drug abuse, and aggression
* Testosterone levels for both male and female criminals correlate with the violent nature of the crimes for which they were sentenced, as well as the dominance and violence that they demonstrate while in prison
* Testosterone appears to affect aggressive behavior by increasing the sensitivity of the amygdala to threatening stimuli, such as angry faces
* When feeling threatened, a person might engage in more aggressive behavior as a preemptive strike.
* Adult men with higher levels of prenatal testosterone exposure score higher on standardized questionnaires of aggression.
* Testosterone levels on the high end of the typical range in teen and adult males are positively correlated with delinquency, drug abuse, and aggression
* Testosterone levels for both male and female criminals correlate with the violent nature of the crimes for which they were sentenced, as well as the dominance and violence that they demonstrate while in prison
* Testosterone appears to affect aggressive behavior by increasing the sensitivity of the amygdala to threatening stimuli, such as angry faces
* When feeling threatened, a person might engage in more aggressive behavior as a preemptive strike.
20
New cards
What is the difference between stress and stressors?
* Stressors: specific events or chronic pressures that place demands on a person or threaten the person’s well-being
* Stress: physical and psychological response to internal or external stressors
* Both can have immediate and cumulative effects on health
* Stress: physical and psychological response to internal or external stressors
* Both can have immediate and cumulative effects on health
21
New cards
What are the main components of Selye’s General Adaptation Response model?
* Selye’s General Adaptation Response (GAS)
* Alarm reaction: fight or flight; mobilize resources
* When stressor hits immediately
* Resistance: Cope with stressor
* Figure out the stressor, how will I handle this?
* High resistance --> coping better with the stressor
* Exhaustion: Reserves depleted
* Coping with stressor for a long time, at a time I run out of resources to deal with it
* Won’t be able to cope anymore
* Alarm reaction: fight or flight; mobilize resources
* When stressor hits immediately
* Resistance: Cope with stressor
* Figure out the stressor, how will I handle this?
* High resistance --> coping better with the stressor
* Exhaustion: Reserves depleted
* Coping with stressor for a long time, at a time I run out of resources to deal with it
* Won’t be able to cope anymore
22
New cards
What role does the amygdala play in the regulation of the fear response?
* Fear circuit – helps us to rapidly assess a particular situation
* Amygdala is helping you rapidly assess the situation
* What do I need to do?
* If you damage amygdala, rats are unable to properly respond to fear stimuli
* Amygdala is helping you rapidly assess the situation
* What do I need to do?
* If you damage amygdala, rats are unable to properly respond to fear stimuli
23
New cards
How do the SAM (sympathetic adrenal medullary) system and the HPA (hypothalamic pituitary adrenal) axis respond differently to stress?
* SAM
* Yellow Side
* Triggering your sympathetic nervous system
* Response to acute stressor
* Fight or flight response
* Pupils dilating
* Rapid breathing
* Releasing adrenaline and norepinephrine
* HPA Axis
* Blue Side
* Chronic stress
* Cortisol release
* Related to giving you an energy boost because you need to deal with this longer-term stressor
* Related to feelings of being stressed
* Yellow Side
* Triggering your sympathetic nervous system
* Response to acute stressor
* Fight or flight response
* Pupils dilating
* Rapid breathing
* Releasing adrenaline and norepinephrine
* HPA Axis
* Blue Side
* Chronic stress
* Cortisol release
* Related to giving you an energy boost because you need to deal with this longer-term stressor
* Related to feelings of being stressed
24
New cards
What did the Abbott et al. (2003) study find about the relationship between social status and cortisol in primates?
* Abbott et al. (2003): Are subordinates more stressed than dominants?
* Comparative study of primate species
* Species with a dominant hierarchy
* Everyone has their place
* Dominant controls everything
* Dominance status and cortisol
* Found results are around the board
* Results across species highly variable
* Subordinated had higher cortisol than dominants
* Dominant had higher cortisol than subordinates
* Dominants and subordinates had same cortisol levels
* Predictors of higher cortisol in subordinates?
* Higher rates of stressors
* Decreased opportunities for social support
* Comparative study of primate species
* Species with a dominant hierarchy
* Everyone has their place
* Dominant controls everything
* Dominance status and cortisol
* Found results are around the board
* Results across species highly variable
* Subordinated had higher cortisol than dominants
* Dominant had higher cortisol than subordinates
* Dominants and subordinates had same cortisol levels
* Predictors of higher cortisol in subordinates?
* Higher rates of stressors
* Decreased opportunities for social support
25
New cards
Is ‘Type A’ behavior a risk for heart disease?
* Intensity, drive, anger and hostility linked to increased rates of heart disease
* Type A behavior pattern: tendency toward easily aroused hostility, impatience, a sense of time urgency, and competitive achievement striving
* But: Hostility more predictive of heart disease than competitiveness
* Higher hostility ratings correlated with more CHD incidents
* Type A behavior pattern: tendency toward easily aroused hostility, impatience, a sense of time urgency, and competitive achievement striving
* But: Hostility more predictive of heart disease than competitiveness
* Higher hostility ratings correlated with more CHD incidents
26
New cards
What are some ways in which people interpret stress?
* Primary appraisal: the interpretation of a stimulus as stressful or not
* Secondary appraisal: determining whether the stressor is something you can handle/have control over or not
* Negative appraisal: the response to a stressor as a threat
* Positive appraisal: the response to a stressor as a challenge
* Leads to better coping
* Secondary appraisal: determining whether the stressor is something you can handle/have control over or not
* Negative appraisal: the response to a stressor as a threat
* Positive appraisal: the response to a stressor as a challenge
* Leads to better coping
27
New cards
What are some strategies people use to cope with stress?
Mind management, body management, and situation management
28
New cards
What is mind management?
* Repressive coping: avoiding situations or thoughts that are reminders of a stressor; maintaining an artificially positive viewpoint
* Push it down
* When a stressor is really overwhelming, repressive coping may be the way to go
* Rational coping: facing a stressor and working to overcome it
* Deal with it
* Problem-focused coping: address specific problems by finding solutions
* Emotion-focused coping: target negative emotions
* Relationship-focused coping: Maintain and protect social relationships
* Importance of perceived control:
* Perceived control of stressful events can be related to more effective coping
* Perceived lack of control can add to stress
* Whether or not you have control over the situation is less important than how you perceive your control
* Reframing: Finding a new or creative way to think about a stressor that reduces its threat
* Stress Inoculation Training (SIT): A therapy that helps people to cope with stressful situations by developing positive ways to think about the situation
* Push it down
* When a stressor is really overwhelming, repressive coping may be the way to go
* Rational coping: facing a stressor and working to overcome it
* Deal with it
* Problem-focused coping: address specific problems by finding solutions
* Emotion-focused coping: target negative emotions
* Relationship-focused coping: Maintain and protect social relationships
* Importance of perceived control:
* Perceived control of stressful events can be related to more effective coping
* Perceived lack of control can add to stress
* Whether or not you have control over the situation is less important than how you perceive your control
* Reframing: Finding a new or creative way to think about a stressor that reduces its threat
* Stress Inoculation Training (SIT): A therapy that helps people to cope with stressful situations by developing positive ways to think about the situation
29
New cards
What is body management?
* Relaxation therapy: a technique for reducing tension by consciously relaxing muscles of the body
* Biofeedback: the use of an external monitoring device to obtain information about a bodily function and possibly gain control over that function
* Learn to slow down heartrate/breathing
* Aerobic exercise: promotes stress relief and psychological well-being
* May increase serotonin and endorphins
* Biofeedback: the use of an external monitoring device to obtain information about a bodily function and possibly gain control over that function
* Learn to slow down heartrate/breathing
* Aerobic exercise: promotes stress relief and psychological well-being
* May increase serotonin and endorphins
30
New cards
What is situation management?
* Changing your life situation to reduce stress
* Social support: aid gained through interacting with others
* Women are more likely to seek support under stress (“tend and befriend response”)
* Social support: aid gained through interacting with others
* Women are more likely to seek support under stress (“tend and befriend response”)
31
New cards
What is the importance of perceived control to coping effectiveness?
* Reframing things can directly have impacts on your body
* Thinking of stress as helpful can decrease health risks
* Heart pounding getting more oxygen to brain
* Body is preparing me to get ready to face challenge
* Social Support
* Oxytocin is helpful hormone in dealing with stress
* Reaching out to others when under stress
* Thinking of stress as helpful can decrease health risks
* Heart pounding getting more oxygen to brain
* Body is preparing me to get ready to face challenge
* Social Support
* Oxytocin is helpful hormone in dealing with stress
* Reaching out to others when under stress
32
New cards
What is positive psychology?
* Approach that emphasizes normal behavior and human strengths
* What are factors that create resilience?
* What helps us find happiness?
* What are factors that create resilience?
* What helps us find happiness?
33
New cards
What is positive psychotherapy?
* Treatment for depression that focuses on increasing positive emotion, engagement and meaning
* Differs from targeting negative symptoms
* Differs from targeting negative symptoms
34
New cards
What are some examples of positive psychology exercises?
* Obituary/biography
* Imagine what you would want your obituary to say at the end of a long and positive life
* Write a brief essay on what you would like to be remembered for the most
* Active/constructive responding
* React in a visibly positive and enthusiastic way to good news from someone else
* Respond actively and constructively to someone you know at least once of day
* Savoring
* Once a day, take the time to enjoy something you usually hurry through
* Examples: eating, talking with family, walking to class
* Then, write down what you did differently and how it felt
* Blessings
* Each evening, write down three good things that happened
* Write down why you think they happened
* Different than focusing on negative events and recording event and recording efforts to change them
* Gratitude visit
* Think of someone to whom you are grateful, but have never properly thanked them
* Write a letter to them describing your gratitude
* Read or give the letter to them
* Imagine what you would want your obituary to say at the end of a long and positive life
* Write a brief essay on what you would like to be remembered for the most
* Active/constructive responding
* React in a visibly positive and enthusiastic way to good news from someone else
* Respond actively and constructively to someone you know at least once of day
* Savoring
* Once a day, take the time to enjoy something you usually hurry through
* Examples: eating, talking with family, walking to class
* Then, write down what you did differently and how it felt
* Blessings
* Each evening, write down three good things that happened
* Write down why you think they happened
* Different than focusing on negative events and recording event and recording efforts to change them
* Gratitude visit
* Think of someone to whom you are grateful, but have never properly thanked them
* Write a letter to them describing your gratitude
* Read or give the letter to them
35
New cards
How can stress produce cross-generational effects?
* Stress because of disasters can produce long-range and cross-generational effects.
* Researchers identified women who witnessed the 9/11 attacks in New York while pregnant and who subsequently developed PTSD (Yehuda et al., 2005).
* One year later, the women and their infants showed indications of long-term, chronic stress.
* Researchers identified women who witnessed the 9/11 attacks in New York while pregnant and who subsequently developed PTSD (Yehuda et al., 2005).
* One year later, the women and their infants showed indications of long-term, chronic stress.
36
New cards
How do the effects of stress vary according to gender?
* Women are more likely to tend-and-befriend in response to stressors.
* Soothing frightened children, hiding, and forming social alliances for further protection might be more effective strategies.
* Research support for tend-and-befriend includes a study showing that after being stressed, women, but not men, demonstrated an increase in caretaking motivation in response to videos showing crying infants.
* Instead of the traditional hormones associated with fight-or-flight, a tend-and-befriend response is more closely associated with the release of oxytocin, a hormone related to social bonding
* Soothing frightened children, hiding, and forming social alliances for further protection might be more effective strategies.
* Research support for tend-and-befriend includes a study showing that after being stressed, women, but not men, demonstrated an increase in caretaking motivation in response to videos showing crying infants.
* Instead of the traditional hormones associated with fight-or-flight, a tend-and-befriend response is more closely associated with the release of oxytocin, a hormone related to social bonding
37
New cards
How do the effects of stress vary according to socioeconomic status?
* The poor experience more noise, more toxins, more carcinogens, more violence, fewer resources, less health care, higher levels of drugs and alcohol abuse, less exercise, more anger, less control, and less trust.
* The items on this long list have something in common—all of these factors are associated with high stress.
* Residents of low-income neighborhoods reported higher rates of perceived stress, which in turn was related to more risky health-related behaviors, such as smoking and lower physical activity
* The items on this long list have something in common—all of these factors are associated with high stress.
* Residents of low-income neighborhoods reported higher rates of perceived stress, which in turn was related to more risky health-related behaviors, such as smoking and lower physical activity
38
New cards
How does stress produce epigenetic effects?
* We defined epigenetics as the influence on traits by factors that determine how genes perform.
* For example, we observed how both rats and human children who were well nurtured by their mothers showed more resilience to stress later in life.
* The nurture received from the mother had influenced how the genes responsible for producing and reacting to stress hormones behaved during later stressful experiences
* Severe stress early in life produces lasting challenges, including increased HPA axis responses to stress, hyperactivity of the norepinephrine system, reduced volume in the hippocampus, and heightened responses by the amygdala to threat stimuli, such as negative facial expressions
* Genes and life stress also interact to produce MDD.
* The rate of expression of genes linked to MDD interacts with an individual’s quality of social experience, from adversity to support
* For example, we observed how both rats and human children who were well nurtured by their mothers showed more resilience to stress later in life.
* The nurture received from the mother had influenced how the genes responsible for producing and reacting to stress hormones behaved during later stressful experiences
* Severe stress early in life produces lasting challenges, including increased HPA axis responses to stress, hyperactivity of the norepinephrine system, reduced volume in the hippocampus, and heightened responses by the amygdala to threat stimuli, such as negative facial expressions
* Genes and life stress also interact to produce MDD.
* The rate of expression of genes linked to MDD interacts with an individual’s quality of social experience, from adversity to support
39
New cards
How does stress affect the immune system?
* Short-term bursts of stress can have a beneficial effect on many biological systems, including the immune system, your body’s frontline defense against infection and cancer
* However, the immune system does not perform as well in the face of long-term, chronic sources of stress.
* If stressors persist long enough, an overall reduction in immune response occurs.
* As a result, stress can lead to greater frequency and severity of viral illnesses
* Stress hormones directly suppress the activity of lymphocytes
* However, the immune system does not perform as well in the face of long-term, chronic sources of stress.
* If stressors persist long enough, an overall reduction in immune response occurs.
* As a result, stress can lead to greater frequency and severity of viral illnesses
* Stress hormones directly suppress the activity of lymphocytes
40
New cards
How does stress affect mood, sleep, and weight?
* Long-term, chronic stress can begin a cascade of changes in mood, sleep, and appetite that compromise well-being.
* Disruptions of sleep because of stress are particularly hazardous to health because we need sleep to restore our bodies after the challenges of the day.
* Both sleep quantity and sleep quality are associated with both overall health and cognitive outcomes
* Stress frequently serves as a trigger for a depressed mood.
* Self-reports of daily stressors, like having an argument with a friend, were correlated with the participants’ mood
* The ability of stress to alter levels of circulating cortisol, discussed earlier in this chapter, might form the basis for this connection between stress and depressed mood
* Cortisol is released in large quantities early in the morning, contributing to wakefulness.
* As the day progresses, cortisol levels drop off, reducing wakefulness and setting the stage for sleep.
* If you experience a big jolt of cortisol because of a stressor late in the evening, getting to sleep is going to be difficult, even when you’re tired
* Mood and sleep can both affect appetite.
* Among the criteria for MDD are changes in appetite.
* Some people who are depressed lose weight without dieting, while others gain weight.
* By now, it shouldn’t surprise you to learn that stress, along with depression, also can contribute to obesity.
* In response to stress-related hormones, fat cells behave differently, growing in both size and number
* Disruptions of sleep because of stress are particularly hazardous to health because we need sleep to restore our bodies after the challenges of the day.
* Both sleep quantity and sleep quality are associated with both overall health and cognitive outcomes
* Stress frequently serves as a trigger for a depressed mood.
* Self-reports of daily stressors, like having an argument with a friend, were correlated with the participants’ mood
* The ability of stress to alter levels of circulating cortisol, discussed earlier in this chapter, might form the basis for this connection between stress and depressed mood
* Cortisol is released in large quantities early in the morning, contributing to wakefulness.
* As the day progresses, cortisol levels drop off, reducing wakefulness and setting the stage for sleep.
* If you experience a big jolt of cortisol because of a stressor late in the evening, getting to sleep is going to be difficult, even when you’re tired
* Mood and sleep can both affect appetite.
* Among the criteria for MDD are changes in appetite.
* Some people who are depressed lose weight without dieting, while others gain weight.
* By now, it shouldn’t surprise you to learn that stress, along with depression, also can contribute to obesity.
* In response to stress-related hormones, fat cells behave differently, growing in both size and number
41
New cards
What is resilience, and how does it affect the response to stress?
* People differ in resilience, or the ability to adapt to life’s challenges in positive ways.
* Low resilient people have higher levels of perceived stress
* Resilient people do not ignore feelings of sadness or stress, but like Holocaust survivor Viktor Frankl, they remain optimistic and confident about their abilities to cope with adversity.
* In contrast, when people lack resilience, they feel overwhelmed, helpless, and victimized.
* They become more vulnerable to the use of negative coping strategies, including alcoholism and drug abuse, to escape their problems.
* The personality trait of hardiness contributes to resilience
* Compared to less hardy people, people with high hardiness experience less threat or disruption in response to the normal stressors of life.
* Hardiness combines commitment, control, and challenge
* People with high commitment see the world as interesting and seek involvement rather than withdrawal.
* Control refers to individuals’ belief in their ability to influence events.
* Challenge is a state of mind that sees change and new experiences not as negative stressors, but as opportunities for learning and personal growth.
* Maintaining a flexible approach to meeting your life’s goals is far less likely to create stress
* Other protective factors contributing to individual differences in resilience are cognitive skills, social skills, and flexibility in response to new situations
* Individual differences in resilience might also have their roots in emotion.
* People who are generally more positive in mood tend to build the resources that they need, including strong social networks, to sustain them at difficult times
* Low resilient people have higher levels of perceived stress
* Resilient people do not ignore feelings of sadness or stress, but like Holocaust survivor Viktor Frankl, they remain optimistic and confident about their abilities to cope with adversity.
* In contrast, when people lack resilience, they feel overwhelmed, helpless, and victimized.
* They become more vulnerable to the use of negative coping strategies, including alcoholism and drug abuse, to escape their problems.
* The personality trait of hardiness contributes to resilience
* Compared to less hardy people, people with high hardiness experience less threat or disruption in response to the normal stressors of life.
* Hardiness combines commitment, control, and challenge
* People with high commitment see the world as interesting and seek involvement rather than withdrawal.
* Control refers to individuals’ belief in their ability to influence events.
* Challenge is a state of mind that sees change and new experiences not as negative stressors, but as opportunities for learning and personal growth.
* Maintaining a flexible approach to meeting your life’s goals is far less likely to create stress
* Other protective factors contributing to individual differences in resilience are cognitive skills, social skills, and flexibility in response to new situations
* Individual differences in resilience might also have their roots in emotion.
* People who are generally more positive in mood tend to build the resources that they need, including strong social networks, to sustain them at difficult times
42
New cards
What are some examples of using positive psychology to examine happiness?
* Happiness is associated with a long list of positive outcomes, including longevity
* Psychologists approach happiness from two different perspectives
* A hedonic approach focuses on obtaining pleasure and avoiding pain.
* A eudaimonic approach focuses on meaningfulness and self-realization.
* Happiness often seems fleeting or transient.
* The primary reason for this elusiveness is that happiness is typically relative
* Research with identical twins suggests that we have a happiness “set point” that is largely influenced by genetics
* Happiness can be improved by thinking carefully about what things interfere with our happiness, such as allowing ourselves to stay mad at a partner following an argument, and working to avoid these things.
* One critical factor in people’s happiness is the strength of their interpersonal relationships.
* Happiness is also contagious, spreading out along networks of social contact
* Happiness and Marriage
* Among interpersonal relationships, the institution of marriage is particularly likely to contribute to happiness
* In a large-scale study that followed 13,000 adults for five years, people who remained married experienced higher well-being than those who separated or divorced
* Among the benefits of marriage are reduced infidelity, longer-lasting relationships, and longer life
* People who are married and living with their spouse enjoy a significantly lower death rate than those who are unmarried.
* The positive effects of marriage on happiness are about twice as large for couples who consider their spouse to be their best friend
* A major factor in satisfaction with a relationship is how you think your partner sees you
* Happiness and Wealth
* At both national and individual levels, being poor does appear to be correlated with being unhappy.
* However, once basic needs are met, additional money does not guarantee happiness
* In addition, how people use their wealth can influence happiness
* People who are less materialistic report being happier than people who are materialistic
* People who spend money on experiences rather than materialistic goods experience improved well-being
* Psychologists approach happiness from two different perspectives
* A hedonic approach focuses on obtaining pleasure and avoiding pain.
* A eudaimonic approach focuses on meaningfulness and self-realization.
* Happiness often seems fleeting or transient.
* The primary reason for this elusiveness is that happiness is typically relative
* Research with identical twins suggests that we have a happiness “set point” that is largely influenced by genetics
* Happiness can be improved by thinking carefully about what things interfere with our happiness, such as allowing ourselves to stay mad at a partner following an argument, and working to avoid these things.
* One critical factor in people’s happiness is the strength of their interpersonal relationships.
* Happiness is also contagious, spreading out along networks of social contact
* Happiness and Marriage
* Among interpersonal relationships, the institution of marriage is particularly likely to contribute to happiness
* In a large-scale study that followed 13,000 adults for five years, people who remained married experienced higher well-being than those who separated or divorced
* Among the benefits of marriage are reduced infidelity, longer-lasting relationships, and longer life
* People who are married and living with their spouse enjoy a significantly lower death rate than those who are unmarried.
* The positive effects of marriage on happiness are about twice as large for couples who consider their spouse to be their best friend
* A major factor in satisfaction with a relationship is how you think your partner sees you
* Happiness and Wealth
* At both national and individual levels, being poor does appear to be correlated with being unhappy.
* However, once basic needs are met, additional money does not guarantee happiness
* In addition, how people use their wealth can influence happiness
* People who are less materialistic report being happier than people who are materialistic
* People who spend money on experiences rather than materialistic goods experience improved well-being
43
New cards
What is flow?
* During activities that contribute to the good life, people experience flow, in which they are absorbed in their current activity, usually related to work, problem solving, or creativity
* The word flow was chosen to describe this experience on the basis of interviews in which people spontaneously used the metaphor to explain their own experiences.
* These experiences may qualify as altered states of consciousness and are usually perceived as highly positive.
* Time appears to stand still for people who are immersed in flow.
* The word flow was chosen to describe this experience on the basis of interviews in which people spontaneously used the metaphor to explain their own experiences.
* These experiences may qualify as altered states of consciousness and are usually perceived as highly positive.
* Time appears to stand still for people who are immersed in flow.
44
New cards
What are the roles of the id, ego and superego, according to Freud?
* Psychodynamic (Freud)
* Id: Primitive drives; present at birth
* Ego: The Self that others see
* Superego: Internalized rules for right and wrong; conscience
* Ego attempts to balance demands of id and superego
* Self is trying to balance out urges and moral sense (angel and devil)
* Id: Primitive drives; present at birth
* Ego: The Self that others see
* Superego: Internalized rules for right and wrong; conscience
* Ego attempts to balance demands of id and superego
* Self is trying to balance out urges and moral sense (angel and devil)
45
New cards
What are the roles of the unconscious, preconscious, and conscious?
* Unconscious: Id
* Preconscious: Ego and Superego
* Conscious: Ideas, thoughts and feeling of which you are aware
* Preconscious: Ego and Superego
* Conscious: Ideas, thoughts and feeling of which you are aware
46
New cards
What is the function of a defense mechanism? What are some examples of Freud’s defense mechanisms?
* Protective behaviors of the ego
* Manage threats to the balance of id and superego
* Picture describing different examples
* Examples:
* Denial: refusing to acknowledge source of anxiety
* Repression: excluding source of anxiety from awareness
* Projection: attributing unacceptable qualities of the self to someone else
* Reaction formation: warding off an uncomfortable thought by overemphasizing its opposite
* Rationalization: Concocting a seemingly logical reason or excuse for behavior that might otherwise be shameful
* Displacement: shifting the attention of emotion from one object to another
* Sublimation: channeling socially unacceptable impulses into constructive, even admirable, behavior
* Manage threats to the balance of id and superego
* Picture describing different examples
* Examples:
* Denial: refusing to acknowledge source of anxiety
* Repression: excluding source of anxiety from awareness
* Projection: attributing unacceptable qualities of the self to someone else
* Reaction formation: warding off an uncomfortable thought by overemphasizing its opposite
* Rationalization: Concocting a seemingly logical reason or excuse for behavior that might otherwise be shameful
* Displacement: shifting the attention of emotion from one object to another
* Sublimation: channeling socially unacceptable impulses into constructive, even admirable, behavior
47
New cards
What is Freud’s theory of psychosexual development?
* How developing personality deals with sexual impulses of id
* Where are you getting pleasure from?
* Stages:
* Oral (0-18 months): pleasure centers on the mouth - sucking, biting, chewing
* Anal (18-36 months): pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination; coping with demands for control
* Phallic (3-6 years): pleasure zone is the genitals; coping with incestuous sexual feelings (oedipus complex)
* Latency (6 - puberty): dormant sexual feelings identification process - gender identity
* Genital (puberty on): maturation of sexual interests
* Where are you getting pleasure from?
* Stages:
* Oral (0-18 months): pleasure centers on the mouth - sucking, biting, chewing
* Anal (18-36 months): pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination; coping with demands for control
* Phallic (3-6 years): pleasure zone is the genitals; coping with incestuous sexual feelings (oedipus complex)
* Latency (6 - puberty): dormant sexual feelings identification process - gender identity
* Genital (puberty on): maturation of sexual interests
48
New cards
What is a Freudian slip?
Verbal or memory mistake linked to the unconscious mind
49
New cards
What ideas from Freud are still used today? Not used?
* Ideas no longer used
* Psychosexual development
* Too much emphasis on sexual issues as root of personality types and psychological problems
* Ideas of still used
* Unconscious (but not as important as Freud believed)
* Defense mechanisms
* Psychosexual development
* Too much emphasis on sexual issues as root of personality types and psychological problems
* Ideas of still used
* Unconscious (but not as important as Freud believed)
* Defense mechanisms
50
New cards
How did the neo-Freudians differ from Freud, in terms of their approach to explaining personality and development?
* Social competence instead of sexuality as major motivation for behavior
* Carl Jung: Collective unconscious; introversion and extroversion
* Humanity has shared unconsciousness
* Karen Horney: Different views from Freud on men and women
* Founder of feminist approach
* Carl Jung: Collective unconscious; introversion and extroversion
* Humanity has shared unconsciousness
* Karen Horney: Different views from Freud on men and women
* Founder of feminist approach
51
New cards
How does the humanistic approach view personality development?
* Learning as a major influence on personality
* Example: Learn to be conscientious through operant conditioning
* Example: Learn to be conscientious through operant conditioning
52
New cards
How does the behaviorist approach view personality development?
* Response to psychodynamic and learning approaches
* Views behavior as basically good
* De-emphasize abnormal behavior; focus instead on success
* Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
* Everyone strives for self-actualization
* Achieving one's full potential
* Personality develops because we're striving towards self-actualization
* Views behavior as basically good
* De-emphasize abnormal behavior; focus instead on success
* Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
* Everyone strives for self-actualization
* Achieving one's full potential
* Personality develops because we're striving towards self-actualization
53
New cards
What is trait theory?
* Trait theory
* Trait – personality characteristic that meets three criteria
* Stable
* Consistent
* Varies from person to person
* Interested in individual differences in traits
* Clusters of characteristics to help explain individual differences in personality
* Factor analysis
* Trait – personality characteristic that meets three criteria
* Stable
* Consistent
* Varies from person to person
* Interested in individual differences in traits
* Clusters of characteristics to help explain individual differences in personality
* Factor analysis
54
New cards
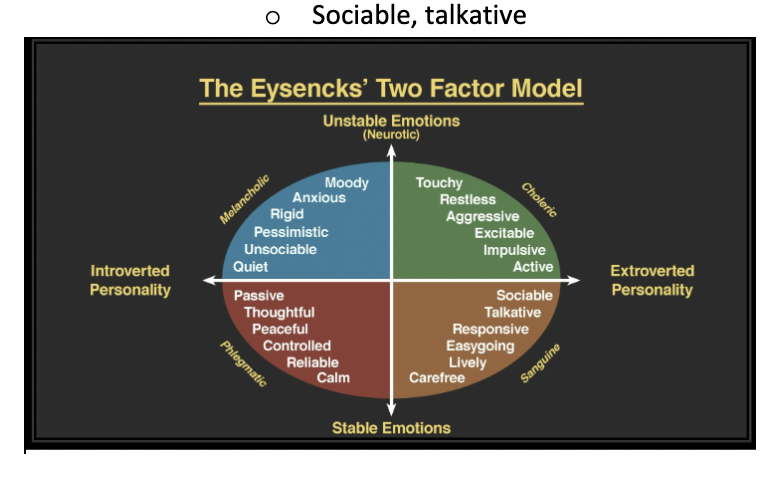
What are the main dimensions of Eysenck’s personality model?
* Two dimensions:
* Introversion/extroversion
* Neuroticism/stability
* Introverted neurotic
* Moody, anxious, quiet
* Extroverted neurotic
* Touchy, restless, aggressive
* Introverted stable
* Passive, thoughtful
* Extroverted stable
* Sociable, talkative
* Introversion/extroversion
* Neuroticism/stability
* Introverted neurotic
* Moody, anxious, quiet
* Extroverted neurotic
* Touchy, restless, aggressive
* Introverted stable
* Passive, thoughtful
* Extroverted stable
* Sociable, talkative
55
New cards
What are the main dimensions of The Big Five model?
* Openness: imaginative vs. down to earth, variety vs. routine, independent vs. conforming
* Conscientiousness : organized vs. disorganized, careful vs. careless, self-disciplined vs. weak-willed
* Extroversion: social vs. retiring, fun-loving vs. sober, affectionate vs. reserved
* Agreeableness: softhearted vs. ruthless, trusting vs. suspicious, helpful vs. uncooperative
* Neuroticism: worried vs. calm, insecure vs. secure, self-pitying vs. self-satisfied
* Continuum, each person falling somewhere on it
* Conscientiousness : organized vs. disorganized, careful vs. careless, self-disciplined vs. weak-willed
* Extroversion: social vs. retiring, fun-loving vs. sober, affectionate vs. reserved
* Agreeableness: softhearted vs. ruthless, trusting vs. suspicious, helpful vs. uncooperative
* Neuroticism: worried vs. calm, insecure vs. secure, self-pitying vs. self-satisfied
* Continuum, each person falling somewhere on it
56
New cards
What types of evidence exist for a biological basis to personality?
Temperament, genetics, evolutionary approaches
57
New cards
How does temperament provide evidence for biological basis to personality?
* Recall Kagan’s reactivity test
* High reactivity – cry and get upset at any new stimulus
* Low reactivity – not fazed by new stimuluses
* Differences that early tells us that there is biological predisposition to temperament, which turns into personality
* Individual differences in activity level, emotionality, sociability
* High reactivity – cry and get upset at any new stimulus
* Low reactivity – not fazed by new stimuluses
* Differences that early tells us that there is biological predisposition to temperament, which turns into personality
* Individual differences in activity level, emotionality, sociability
58
New cards
How does genetics provide evidence for biological basis to personality?
* Measures of heritability
* Heritability:
* Degree of variation in a personality trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in the population
* Ranges between 0-100%
* How much of a difference is due to genetic differences?
* Everybody has same hair color; heritability is 0% because there is no variation
* Monozygotic (MZ) vs. Dizygotic (DZ) twins
* Identical twins (MZ) vs. Fraternal twins (DZ)
* If it is genetic, MZ should rank higher than DZ
* MZ had higher correlation than DZ
* Big 5 traits showed this pattern
* Therefore there is genetic component
* Adoption studies
* MZ twins – identical twins
* Twins similar in traits regardless of whether they were raised together
* Adopted siblings are no more alike in personality than randomly selected persons
* Not strong environmental difference
* Personalities of adopted children largely unrelated to those of adoptive parents
* Heritability:
* Degree of variation in a personality trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in the population
* Ranges between 0-100%
* How much of a difference is due to genetic differences?
* Everybody has same hair color; heritability is 0% because there is no variation
* Monozygotic (MZ) vs. Dizygotic (DZ) twins
* Identical twins (MZ) vs. Fraternal twins (DZ)
* If it is genetic, MZ should rank higher than DZ
* MZ had higher correlation than DZ
* Big 5 traits showed this pattern
* Therefore there is genetic component
* Adoption studies
* MZ twins – identical twins
* Twins similar in traits regardless of whether they were raised together
* Adopted siblings are no more alike in personality than randomly selected persons
* Not strong environmental difference
* Personalities of adopted children largely unrelated to those of adoptive parents
59
New cards
How does the evolutionary approach view personality?
* View personality traits as adaptive
* Roots of personality in animal temperaments
* Roots of personality in animal temperaments
60
New cards
What is the difference between a self-report inventory and a projective test? What are some examples of each?
* Direct observation
* High reliability (consistent measurement), But:
* Time-consuming, expensive
* Some aspects of personality can be concealed (social desirability)
* Self-report inventories
* Personality inventories
* Must be tested for reliability and validity
* Rely on self-report: problems with social desirability
* MMPI (Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory)
* Projective tests
* Standard series of ambiguous stimuli designed to elicit responses that reveal inner aspects of an individual’s personality
* Ps “project” personalities as they describe what they see
* Ex.) Rorschach Inkblot Test
* Describe what you see in the inkblot
* Is this too ambiguous, doea it really tell us anything about a person?
* High reliability (consistent measurement), But:
* Time-consuming, expensive
* Some aspects of personality can be concealed (social desirability)
* Self-report inventories
* Personality inventories
* Must be tested for reliability and validity
* Rely on self-report: problems with social desirability
* MMPI (Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory)
* Projective tests
* Standard series of ambiguous stimuli designed to elicit responses that reveal inner aspects of an individual’s personality
* Ps “project” personalities as they describe what they see
* Ex.) Rorschach Inkblot Test
* Describe what you see in the inkblot
* Is this too ambiguous, doea it really tell us anything about a person?
61
New cards
What is locus of control?
* If you have an external locus of control (locus means “place” in Latin), you expect that most of your outcomes occur because of chance, luck, opportunity, or other factors beyond your control.
* However, if you have an internal locus of control, you believe that most of your outcomes are due to your own talent and effort.
* People with an internal locus of control manage stress more effectively, floss their teeth more regularly, are more likely to seek shelter in response to tornado warnings, use their seat belts more consistently while driving, and are more likely to practice effective birth control
* However, people with an internal locus of control tend to be less sympathetic with the plight of others, viewing their troubles as due to their choices and behavior as opposed to outside forces they can’t control
* However, if you have an internal locus of control, you believe that most of your outcomes are due to your own talent and effort.
* People with an internal locus of control manage stress more effectively, floss their teeth more regularly, are more likely to seek shelter in response to tornado warnings, use their seat belts more consistently while driving, and are more likely to practice effective birth control
* However, people with an internal locus of control tend to be less sympathetic with the plight of others, viewing their troubles as due to their choices and behavior as opposed to outside forces they can’t control
62
New cards
What is reciprocal determinism?
* Reciprocal determinism - A social– cognitive learning theory of personality that features the mutual influence of the person and that of the situation on each other.
* Bandura believed that observation of others’ behavior played an important role in the development of personality
* Bandura believed that observation of others’ behavior played an important role in the development of personality
63
New cards
What are different ways to define ‘disorder’?
* What qualifies as a disorder?
* Statistical abnormality?
* Bell curve
* Middle is normal
* On the ends are the extremes
* Deviation from ‘ideal’ behavior?
* Abnormal behavior as distressing and harmful to self and others
* Statistical abnormality?
* Bell curve
* Middle is normal
* On the ends are the extremes
* Deviation from ‘ideal’ behavior?
* Abnormal behavior as distressing and harmful to self and others
64
New cards
What are the two main systems used for diagnosing disorders?
* Two main systems for diagnosis:
* DSM (American Psychiatric Association)
* Thick book of diagnosing characteristics of particular disorders
* ICD (World Health Organization)
* DSM (American Psychiatric Association)
* Thick book of diagnosing characteristics of particular disorders
* ICD (World Health Organization)
65
New cards
How does labeling tie into diagnosis?
* Labeling and diagnosis:
* Facilitates professional communication
* But:
* Can stigmatize and lead to self-fulfilling prophecies
* Labeling and language
* Person-first vs. Identity first
* Person with autism vs. Autistic person
* Facilitates professional communication
* But:
* Can stigmatize and lead to self-fulfilling prophecies
* Labeling and language
* Person-first vs. Identity first
* Person with autism vs. Autistic person
66
New cards
Why are personality disorders not diagnosed in children?
* You can’t consider anyone under the age of 18 to have personality
* It is considered temperament
* There are parallel disorders that children can be diagnosed with
* It is considered temperament
* There are parallel disorders that children can be diagnosed with
67
New cards
What are the symptoms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD)? Why is it considered a ‘wide spectrum’ disorder?
* Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) - pulling into yourself, trapped in your own world
* Wide spectrum of impairment
* Symptoms can range from being not severe to very severe
* Impairment in:
* Social ability and interpretation of social situations
* Communication skills; language delays
* Sometimes cognitive impairments
* Theory of Mind
* Not do very well in TOM tasks
* Common Behavior:
* Repetitive behavior: rocking, spinning, hand movements
* Coping mechanism to shut the world out
* Stimming – repetitive behavior
* Sensitivity to environmental stimuli
* Loud sounds physically hurt to hear
* Touch hurts
* Desire for routine
* Do not like change
* Wide spectrum of impairment
* Symptoms can range from being not severe to very severe
* Impairment in:
* Social ability and interpretation of social situations
* Communication skills; language delays
* Sometimes cognitive impairments
* Theory of Mind
* Not do very well in TOM tasks
* Common Behavior:
* Repetitive behavior: rocking, spinning, hand movements
* Coping mechanism to shut the world out
* Stimming – repetitive behavior
* Sensitivity to environmental stimuli
* Loud sounds physically hurt to hear
* Touch hurts
* Desire for routine
* Do not like change
68
New cards
What is savantism?
* Savant syndrome is a rare condition in which persons with various developmental disorders, including autistic disorder, have an amazing ability and talent.
* Autistic savants
* Relatively rare
* Remarkable abilities in a narrow area: art, memory, arithmetic, music, spatial skills
* Autistic savants
* Relatively rare
* Remarkable abilities in a narrow area: art, memory, arithmetic, music, spatial skills
69
New cards
What are causal factors for ASD?
* Causes of ASD
* Primarily biological: Concordance rates for MZ twins between 70-90%
* If one twin has autism what is the likelihood the other one has it too
* Parental age a risk factor
* Differences in brain structure
* Brian growth during the first two years tends to be very fast but becomes abnormally slow during adolescence
* NOT due to Vaccinations
* Are rates of ASD increasing?
* Autism is not increasing, but ability to diagnose it is better
* Primarily biological: Concordance rates for MZ twins between 70-90%
* If one twin has autism what is the likelihood the other one has it too
* Parental age a risk factor
* Differences in brain structure
* Brian growth during the first two years tends to be very fast but becomes abnormally slow during adolescence
* NOT due to Vaccinations
* Are rates of ASD increasing?
* Autism is not increasing, but ability to diagnose it is better
70
New cards
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), and how is it used in the treatment of autism?
* Applied Behavioral Analysis (ABA)
* Moderately to severely affected
* Improves communication and social skills
* Developed by Ivar Lovaas and colleagues; based on operant conditioning
* Rewarded for good behavior right away
* Intensive therapy: requires a minimum of 40 hours/wk. of treatment
* Accessibility issues:
* Very expensive
* Moderately to severely affected
* Improves communication and social skills
* Developed by Ivar Lovaas and colleagues; based on operant conditioning
* Rewarded for good behavior right away
* Intensive therapy: requires a minimum of 40 hours/wk. of treatment
* Accessibility issues:
* Very expensive
71
New cards
What are the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
* Impulse control disorder
* Restless, impulsive, inattentive
* Can have inattention + hyperactivity or just one
* Difficulty in following instructions, maintaining attention on tasks, maintaining friendships
* Estimated that 11% of boys and 4% of girls have ADHD in U.S.
* But: possibility of overdiagnosis (psychologist vs. educational setting)
* Don't want to sit still in class at young age, but that doesn’t mean they have ADHD, could just be an active kid
* Restless, impulsive, inattentive
* Can have inattention + hyperactivity or just one
* Difficulty in following instructions, maintaining attention on tasks, maintaining friendships
* Estimated that 11% of boys and 4% of girls have ADHD in U.S.
* But: possibility of overdiagnosis (psychologist vs. educational setting)
* Don't want to sit still in class at young age, but that doesn’t mean they have ADHD, could just be an active kid
72
New cards
What are causal factors for ADHD?
* Biological: MZ twin concordance rate of 55%
* Impairment in the connection between frontal lobes and the limbic system
* Limbic system deals with immediate responses --> makes sense why it would be problems with impulse control
* Enviornmental risk factors: Lead contamination; low birth weight; prenatal exposure to alcohol, tobacco
* Impairment in the connection between frontal lobes and the limbic system
* Limbic system deals with immediate responses --> makes sense why it would be problems with impulse control
* Enviornmental risk factors: Lead contamination; low birth weight; prenatal exposure to alcohol, tobacco
73
New cards
Why are stimulant medications used to treat ADHD?
* Medications: Ritalin, Dexedrine, Adderall
* Meds increase dopamine, norepinephrine
* Why are stimulants used?
* Underactivity in frontal lobes controlling impulsivity
* Seeking out more things to stimulate frontal lobe
* Stimulants make it more active, so person doesn’t have to act out
* Medication helped them have more positive behaviors and less negative behaviors
* Meds increase dopamine, norepinephrine
* Why are stimulants used?
* Underactivity in frontal lobes controlling impulsivity
* Seeking out more things to stimulate frontal lobe
* Stimulants make it more active, so person doesn’t have to act out
* Medication helped them have more positive behaviors and less negative behaviors
74
New cards
What are some behavioral therapies for ADHD?
* Treatment using operant conditioning
* Simple tasks, working on specific behavior
* Shape the behavior
* Parent training
* How can parents help out
* Classroom management
* Simple tasks, working on specific behavior
* Shape the behavior
* Parent training
* How can parents help out
* Classroom management
75
New cards
What are the main components of the diathesis-stress model? How can this model help us to understand causal factors for many disorders?
* Diathesis-stress model
* General framework for understanding causes of disorders
* Diathesis: predisposing factors
* Genetics, personality traits, environment, early and prolonged stressors
* Stress: Precipitating or triggering factors
* Stressful major life events associated with the onset of psychopathological symptoms in adulthood
* General framework for understanding causes of disorders
* Diathesis: predisposing factors
* Genetics, personality traits, environment, early and prolonged stressors
* Stress: Precipitating or triggering factors
* Stressful major life events associated with the onset of psychopathological symptoms in adulthood
76
New cards
What is anxiety?
* Strong negative emotions
* Physical tension because of anticipation of danger
* Physical tension because of anticipation of danger
77
New cards
What are the symptoms of GAD?
* Excessive anxiety and worry more days than not for 6 months
* Person finds it difficult to control the worry
* Anxiety/worry associated with at least 3 of the following symptoms:
* Restlessness/feeling keyed up or on edge
* Being easily fatigued
* Difficulty concentrating or mind going blank
* Irritability
* Muscle tension
* Sleep disturbance
* Sleep too much or too little
* Normal sleep patterns disrupted
* Person finds it difficult to control the worry
* Anxiety/worry associated with at least 3 of the following symptoms:
* Restlessness/feeling keyed up or on edge
* Being easily fatigued
* Difficulty concentrating or mind going blank
* Irritability
* Muscle tension
* Sleep disturbance
* Sleep too much or too little
* Normal sleep patterns disrupted
78
New cards
What are the symptoms of panic disorder?
* Panic disorder: sudden occurrence of multiple physiological symptoms that contribute to a feeling of stark terror; panic attack
* Sympathetic nervous system responses (racing heart, sweating, breathing heavily)
* Agoraphobia: an extreme fear pf venturing into public or open spaces; correlates with panic disorder
* Panic disorder can occur with or without agoraphobia
* Approximately 22% of the US population reports having at least one panic attack
* Sympathetic nervous system responses (racing heart, sweating, breathing heavily)
* Agoraphobia: an extreme fear pf venturing into public or open spaces; correlates with panic disorder
* Panic disorder can occur with or without agoraphobia
* Approximately 22% of the US population reports having at least one panic attack
79
New cards
What are the symptoms of phobic disorders?
* Phobia: Excessive fear of an object or situation
* Specific phobias: snakes, heights, elevators, germs, etc.
* Social anxiety: fear of being scrutinized and criticized by others; meeting new people; public speaking
* Agoraphobia
* Specific phobias: snakes, heights, elevators, germs, etc.
* Social anxiety: fear of being scrutinized and criticized by others; meeting new people; public speaking
* Agoraphobia
80
New cards
What are the symptoms of OCD?
* Obsessions: repetitive, intrusive thoughts
* Fear based
* Cognitive part
* Compulsions: Ritualistic behaviors designed to fend off obsessions
* OCD example
* Already had disorder, stress of having child triggered her to not be able to control it
* Fear based
* Cognitive part
* Compulsions: Ritualistic behaviors designed to fend off obsessions
* OCD example
* Already had disorder, stress of having child triggered her to not be able to control it
81
New cards
What are the symptoms of PTSD?
* Occurs after traumatic event
* Hypervigilance
* Avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma
* Flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, nightmares
* Hypervigilance
* Avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma
* Flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, nightmares
82
New cards
What are causal factors for OCD?
* MZ twin concordance 63-87%
* Dysfunction in caudate nucleus of basal ganglia; involved in impulse suppression
* Not able to push down impulses
* Low serotonin
* Strep infection as a young child
* Dysfunction in caudate nucleus of basal ganglia; involved in impulse suppression
* Not able to push down impulses
* Low serotonin
* Strep infection as a young child
83
New cards
What is cognitive therapy?
* Cognitive therapy: Helping a client identify and correct distorted thinking about self, others or the world
* Cognitive restructuring/reframing: Teaches clients to question the automatic beliefs, assumptions, and predictions that often lead to negative thinking; replace with more realistic and positive beliefs
* Cognitive restructuring/reframing: Teaches clients to question the automatic beliefs, assumptions, and predictions that often lead to negative thinking; replace with more realistic and positive beliefs
84
New cards
What is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): A blend of cognitive and behavioral therapeutic strategies
85
New cards
What is systematic desensitization, and how is it used to treat anxiety disorders such as phobias?
* Example of behavioral therapy: systematic desensitization
* Change conditioned emotional response (CER) to anxiety-producing stimulus using classical conditioning
* Negative --> neutral --> positive
* Start very slowly (show picture of snake) and work up to more (touching a real snake)
* VR --> before ready to deal with real situation, give person virtual experience to expose them to virtual stimuli, then they can be put in the real situation
* Change conditioned emotional response (CER) to anxiety-producing stimulus using classical conditioning
* Negative --> neutral --> positive
* Start very slowly (show picture of snake) and work up to more (touching a real snake)
* VR --> before ready to deal with real situation, give person virtual experience to expose them to virtual stimuli, then they can be put in the real situation
86
New cards
What are some effective medications for anxiety disorders?
* Recall effect of neurotransmitter GABA: inhibitory
* Relaxes you
* GABA agonists ---> increase relaxation
* Medication for anxiety disorders often act to increase GABA (agonists)
* Example: Benzodiazepines (Valium, Xanax)
* Medication: SSRIs help with social phobia, but cognitive and behavioral methods are treatments of choice
* Panic disorder treatments often combine medication and CBT
* Combination of CBT and medicine proves to work best
* Treatment of OCD:
* OCD treatments blend medication and CBT with focus on Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
* Expose client to triggering stimulus
* Client learns not to engage in compulsion as response to trigger
* Relaxes you
* GABA agonists ---> increase relaxation
* Medication for anxiety disorders often act to increase GABA (agonists)
* Example: Benzodiazepines (Valium, Xanax)
* Medication: SSRIs help with social phobia, but cognitive and behavioral methods are treatments of choice
* Panic disorder treatments often combine medication and CBT
* Combination of CBT and medicine proves to work best
* Treatment of OCD:
* OCD treatments blend medication and CBT with focus on Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
* Expose client to triggering stimulus
* Client learns not to engage in compulsion as response to trigger
87
New cards
What is most effective for treatment of anxiety disorders: medication, psychotherapy, or both?
* Both
* Medication correct imbalance
* Psychotherapy allows you to correct/challenge behaviors
* Medication correct imbalance
* Psychotherapy allows you to correct/challenge behaviors
88
New cards
What are the symptoms of major depressive disorder (MDD)?
* Profound, persistent period of depression for two or more weeks as indicated by:
* Depressed mood
* Markedly diminished interest and pleasure
* Significant weight loss or gain
* Insomnia or hypersomnia
* Psychomotor agitation or retardation (general activity level really high or really low)
* Fatigue or loss of energy
* Feelings of worthlessness and excessive guilt
* Diminished ability to think, concentrate and make decisions
* Recurrent thoughts of death or suicidal ideation
* Comorbidity of depression and anxiety
* Having one disorder linked up with another
* Depression and anxiety are comorbid
* Depressed mood
* Markedly diminished interest and pleasure
* Significant weight loss or gain
* Insomnia or hypersomnia
* Psychomotor agitation or retardation (general activity level really high or really low)
* Fatigue or loss of energy
* Feelings of worthlessness and excessive guilt
* Diminished ability to think, concentrate and make decisions
* Recurrent thoughts of death or suicidal ideation
* Comorbidity of depression and anxiety
* Having one disorder linked up with another
* Depression and anxiety are comorbid
89
New cards
What is dysthymia, and how is it different from MDD?
* Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia)
* Chronic (2+ years) of low grade depression
* Doesn’t meet criteria for MDD
* Differenced from MDD in intensity and level of functioning
* Don't have as severe of problems
* Two or more of the following symptoms:
* Poor appetite or overeating
* Insomnia or hypersomnia
* Low energy or fatigue
* Low self-esteem
* Poor concentration or difficulty making decisions
* Feelings of hopelessness
* Chronic (2+ years) of low grade depression
* Doesn’t meet criteria for MDD
* Differenced from MDD in intensity and level of functioning
* Don't have as severe of problems
* Two or more of the following symptoms:
* Poor appetite or overeating
* Insomnia or hypersomnia
* Low energy or fatigue
* Low self-esteem
* Poor concentration or difficulty making decisions
* Feelings of hopelessness
90
New cards
What is the differences between depression and bipolar disorder?
* Depression is unipolar (one side of mood spectrum)
* Bipolar disorders include both manic and depressive episodes (two sides of mood spectrum)
* Bipolar disorders include both manic and depressive episodes (two sides of mood spectrum)
91
New cards
What are the differences between Bipolar I and Bipolar II disorders?
* Bipolar 1
* History of manic episodes (highest of highs)
* History of depressive episodes
* Bipolar 2
* History of hypomanic episodes (less extreme that normal manic episode)
* History of major depressive episodes
* History of manic episodes (highest of highs)
* History of depressive episodes
* Bipolar 2
* History of hypomanic episodes (less extreme that normal manic episode)
* History of major depressive episodes
92
New cards
What occurs during a manic episode?
* Manic episode
* Distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive and/or irritable mood
* Manic episode indicated by three or more of the following:
* Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
* Decreased need for sleep
* More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking
* Racing thoughts
* Distractibility (attention too easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant stimuli)
* Increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation
* Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have a high potential for painful consequences (e.g., unrestrained buying sprees, sexual indiscretions)
* Distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive and/or irritable mood
* Manic episode indicated by three or more of the following:
* Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
* Decreased need for sleep
* More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking
* Racing thoughts
* Distractibility (attention too easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant stimuli)
* Increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation
* Excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have a high potential for painful consequences (e.g., unrestrained buying sprees, sexual indiscretions)
93
New cards
What occurs during a hypomanic episode?
* Hypomanic episode
* Restless, consumed with confidence, energized
* Not as prone to the gloom following mania
* Hypomanic states generate bursts of creative work
* Might not drop down so low after a manic episode
* Restless, consumed with confidence, energized
* Not as prone to the gloom following mania
* Hypomanic states generate bursts of creative work
* Might not drop down so low after a manic episode
94
New cards
How do a person's mental states change with bipolar disorder?
* Present mental state can be:
* A manic episode
* A mixed episode
* A major depressive episode
* Mixed episode: alternation between moos states within an episode
* Special case of rapid cycling
* Highest of highs to lowest of lows in a matter of minutes
* A manic episode
* A mixed episode
* A major depressive episode
* Mixed episode: alternation between moos states within an episode
* Special case of rapid cycling
* Highest of highs to lowest of lows in a matter of minutes
95
New cards
What is cyclothymic disorder?
Cyclothymic disorder: hypomanic + low-level depression)
96
New cards
What is Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)?
This type of depression is related to changes in seasons and begins and ends at about the same times every year.
97
New cards
What are the biological factors for mood disorders?
* Concordance higher for bipolar disorder than unipolar disorder
* Strong genetic component because of high MZ concordance rate
* Medications targeting norepinephrine and serotonin modulate mood
* Heritability estimates for MDD = 33-45%
* Depression related to diminished activity in left prefrontal cortex and increased activity in right prefrontal cortex
* Strong genetic component because of high MZ concordance rate
* Medications targeting norepinephrine and serotonin modulate mood
* Heritability estimates for MDD = 33-45%
* Depression related to diminished activity in left prefrontal cortex and increased activity in right prefrontal cortex
98
New cards
What are the situational factors for mood disorders?
* Negative reactions of others to depressed persons can produce rejection and isolation
* Importance of social support: may buffer and protect
* Importance of social support: may buffer and protect
99
New cards
What are the cognitive factors for mood disorders?
* Dysfunctional attitudes
* Helplessness theory: individuals who are prone to depression automatically attribute negative experiences to causes that are internal, stable, and global
* I didn’t get the job because I'm a bad person
* Persons with pessimistic, self-blaming thought patterns more likely to develop depression in response to stressful life events
* Recall the diathesis-stress model
* Diathesis – predispositional factors (biological and environmental)
* Stress – major life event that brings the disorder out
* Helplessness theory: individuals who are prone to depression automatically attribute negative experiences to causes that are internal, stable, and global
* I didn’t get the job because I'm a bad person
* Persons with pessimistic, self-blaming thought patterns more likely to develop depression in response to stressful life events
* Recall the diathesis-stress model
* Diathesis – predispositional factors (biological and environmental)
* Stress – major life event that brings the disorder out
100
New cards
What are the differences between the psychoanalytic, humanistic, and behavioral approaches in the treatment of mood disorders?
* Psychoanalysis (Freud)
* Goals: Insight, make the unconscious conscious, expand the ego’s control (become aware of what is really going on)
* More therapist-driven; interpretation
* Humanistic approaches
* Person-centered therapy
* Reflection; unconditional positive regard (make sure client knows whatever they say they are still a good person)
* Behavioral, cognitive and cognitive-behavioral (CBT)
* Change depressive thought patterns; learned optimism
* Goals: Insight, make the unconscious conscious, expand the ego’s control (become aware of what is really going on)
* More therapist-driven; interpretation
* Humanistic approaches
* Person-centered therapy
* Reflection; unconditional positive regard (make sure client knows whatever they say they are still a good person)
* Behavioral, cognitive and cognitive-behavioral (CBT)
* Change depressive thought patterns; learned optimism