Care of High-Risk Pregnant Women
1/163
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Ma'am Baccay's PPT and Lecture Discussion
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
High-risk Pregnancy
A situation in which a mother, her fetus, or both are at higher risk for problems during pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum than in a typical pregnancy
Maternal age
Weight
Substance/alcohol abuse
Abused/battered women
Existing/pre-existing medical condition
What are the risk factors of a high-risk pregnancy?
FALSE; Both are risk factors of a high-risk pregnancy
TRUE or FALSE; Advanced maternal age is a risk factor of a high-risk pregnancy and adolescent pregnancy is not
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE: Both overweight and underweight women are at risk for high risk pregnancy.
Physical development is not yet complete
Developmental task is not yet fulfilled
Emotional maturity not yet been achieved
In adolescent pregnancy, what aspects of their growth are not yet achieved/fulfilled making them risky?
35 years old
What age is considered elderly primigravid?
9 years old
According to Ma’am Ken, what age is the recorded youngest mother (idk lang if here in the PH lang or worldwide)?
TRUE; It is under '“Existing/pre-existing medical condition”
TRUE or FALSE; Mental health problems are considered risk factors for high risk pregnancy
Identity vs. Role Confusion
What developmental task do adolescents need to fulfill?
Having an idealistic concept of love
Give an example of a manifestation that an adolescent’s emotional maturity has not yet been achieved
Lack of knowledge about conception and contraception
Indulgence in risk-taking behavior
Early sexual initiation
Inadequate coping mechanism
Lack of concern for long-term consequences
Need for immediate gratification
Increase in dysfunctional families
Give at least 3 contributing factors of adolescent pregnancy.
Drinking alcohol and smoking (they are also at higher risk for early sexual initiation)
What is an example of a risk-taking behavior of adolescents?
Early marriage to escape poverty (they are also at higher risk for early sexual initiation)
What is an example of an inadequate coping mechanism as a contributing factor to adolescent pregnancy?
TRUE; This is under “Lack of concern for long-term consequences”
TRUE or FALSE; Once you pop, you can’t stop
FALSE; First 15 years of life
TRUE or FALSE; Those who have father absence for the first 10 years of lives are at risk for adolescent pregnancy
PIH (Pregnancy induced hypertension)
May nabasa ako na the cause remains unknown daw, pero feeling ko dahil underdeveloped pa yung cardiovascular system nila so pag dumami yung blood volume due to pregnancy, mas sensitive sila sa complications
IDA (Iron deficiency anemia
Double requirements of iron (from 60 to 120 ang demand)
Premature labor
Weak pelvic muscles; kapag hindi na kaya, doon magcocontract
Low birth weight infants
‘Di nila kayang i-hold yung appropriate infant weight kaya naglalabor agad
Cephalopelvic disproportion
Hindi possible ang vaginal birth
Intimate partner abuse
No confidence to decide for themselves
Highly dependent on their partners (risk for statutory rape
Give at least 3 complications of adolescent pregnancy and a rationale for each.
Detailed health history
Privacy during abdominal assessment and pelvic exam
PGH: may dedicated schedule for check up
Look for danger signs in pregnancy
Assess the nutritional status
Give at least 3 parameters that you need to take or keep in mind in the prenatal assessment of adolescent pregnancy
Prenatal education (physiologic changes, birth plan, newborn care)
Saan pwede manganak? Bawal sa lying-in clinic
Teach them about good nutrition
Assess their activity and ensure adequate rest periods
Because pwedeng nasa school pa
Pwedeng magkaroon ng activity intolerance r/t Iron deficiency anemia
Identify support system
Postpartum family planning
Use contraceptive right after pregnancy
Finish their education
How do you manage adolescent pregnancy?
Abortion
Ectopic Pregnancy
What are the two (2) first trimester bleeding conditions?
0 to 13 weeks
When is the first trimester?
Abortion
This is defined as the Expulsion of the product of conception or termination of pregnancy before the fetus is viable
Before the 20th week of gestation
Less than 500 g birth weight
Give 2 criteria to consider that a fetus is not viable
Spontaneous Abortion
Recurrent Abortion
Induced Abortion
What are the three classifications of abortion?
Before 16 weeks
In spontaneous abortion, when is it considered an early miscarriage?
Between 16 to 20 weeks
In spontaneous abortion, when is it considered a late miscarriage?
Threatened Abortion
Assessment: closed cervix, scanty to bright red vaginal bleeding, (+) uterine contractions
(A type of Spontaneous Abortion)
Threatened Abortion
Suggests an increased risk of miscarriage (50%)
Notify physician
FHT is assessed and TV UTZ exam is done
Limit sexual activity or avoid strenuous activity
Count number of perineal pads used
Observe for drainage with foul odor
What are included in the therapeutic management of threatened abortion?
Imminent or Inevitable Abortion
Assessment: Profuse vaginal bleeding, open cervix, (+) ruptured BOW (bag of water), (+) contractions
(A type of Spontaneous Abortion)
Imminent or Inevitable Abortion
In this type of spontaneous abortion, abortion is almost certain.
Natural expulsion of uterine content
Dilation and evacuation
What are included in the Therapeutic Management of Imminent/Inevitable Abortion?
Vacuum curettage [aka Vacuum Aspiration Abortion or Suction Curettage (?) ]
How do you perform dilation and evacuation in imminent abortion?
Complete Abortion
Type of Spontaneous Abortion: Products of conception are expelled spontaneously
Complete Abortion
Type of Spontaneous Abortion: All fetal and placental material is expelled from the uterus before 20 weeks of gestation
Observe the mother for signs of bleeding
Provision of emotional support
How do you manage complete abortion?
Incomplete Abortion
Type of Spontaneous Abortion: Clinical manifestations include active uterine bleeding and severe abdominal cramping
Incomplete Abortion
Type of Spontaneous Abortion: Some products of pregnancy are still in the uterus
Dilation and curettage (suction curettage)
What is the treatment for Incomplete Abortion?
Missed Abortion
A type of Spontaneous Abortion: Early pregnancy failure - fetus died in utero but is not expelled
Missed Abortion
Assessment: closed cervix, (+) spotting
(A type of Spontaneous Abortion)
Blighted ovum
What do you call it when the pregnancy sac is empty? (Missed Abortion)
UTZ will reveal that the fetus has died
How do you diagnose Missed Abortion?
Labor induction
Provision of emotional support
How do you treat/manage Missed Abortion?
Recurrent Abortion
Type of Abortion: Three or more consecutive spontaneous abortion
Discover the cause of Abortion
How do you manage Recurrent Abortion?
Chromosomal anomaly
Endocrinal or autoimmune disorder
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome (APAS)
Altered immune system
Deviations of the uterus
Involving septum in the uterus (may septum sa gitna kaya na-didivide eon into two separate parts) — A congenital anomaly among women
What are the possible causes of Recurrent Abortion? (CEAD)
Induced Abortion
A Type of Abortion: Elective termination of pregnancy
Induced Abortion
A Type of Abortion: Voluntary method to end a pregnancy at the request of the woman but not for reasons of impaired maternal health or fetal disease
Mifepristone
Misoprostol
Methotrexate
Vacuum aspiration with curettage
Dilation and curettage
* They can be done orally or through the vagina
* They induce contraction
Give 3 methods of pregnancy termination in Induced Abortion
Hemorrhage
Sepsis
What are the complications of Induced Abortion relating to Maternal Mortality?
Ectopic pregnancy
pinilit mo kasing paalisin yung nauna eh, edi yung sumunod tatakas/magtatago
Spontaneous abortion
Low birth weight infants
Fertility
Baka hindi na magbuntis kahit gusto pa
What are the complications of Induced Abortion relating to Impact on future pregnancies?
TRUE po
TRUE or FALSE: An induced abortion of more than 20 weeks AOG is considered murder
FALSE: Government hospitals
TRUE or FALSE: When induced abortion has been documented, especially in private hospitals, a police report should be made
Monitor vital signs, amount and type of bleeding, pain, emotional response to loss
Complete bed rest
Facilitate diagnostic tests
Assist and support during dilatation and curettage
Institute measures to alleviate fear and anxiety
WOF: hypovolemic shock, infection
Administer oxygen support if necessary
Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance
Monitor condition of uterus
Administer Rho-gam to Rh negative client after abortion
Facilitate physiologic reality but allow to undergo grieving process
Educate on follow-up care
What are included in the nursing management for Induced Abortion?
Ectopic Pregnancy
Occurs when a fertilized ovum becomes implanted on any tissue other than the uterine lining
scanty; sharp, stabbing
Ectopic pregnancy is characterized by _________ bleeding with ________, ___________ pain
Ampulla part of the oviduct
Common site of ectopic pregnancy
Interstitial part of the oviduct
pinaka-nakakatakot kasi maraming blood vessels
Most dangerous site of ectopic pregnancy
Salphingitis
Peritubal adhesions
Structural abnormalities of the fallopian tube
Previous ectopic pregnancy
Previous tubal surgery, pelvic, and abdominal
Multiple previous induced abortions
Tumors distorting the tube
IUD
Smoking
STI
Give at least 3 Risk Factors of Ectopic Pregnancy
FALLS (woosh woosh)
TRUE or FALSE; IUD is recommended for nulligravid in relation to ectopic pregnancy
Antibiotics for both mother and father
How is STI managed in Ectopic Pregnancy
Sharp, stabbing pain in lower abdomen
Radiating pain in the scapula
Vaginal spotting or bleeding (konti lang; hindi ganon kalakas)
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Fainting
Nausea and vomiting
S/Sx of hypovolemic shock (bleeding sa loob)
Give at least 3 clinical manifestations of Ectopic Pregnancy
Sonography
HCG level
Serum progesterone level (>25ng/mL)
Laparoscopy
What are the diagnostic tests for Ectopic Pregnancy?
Menstrual pattern
Vaginal bleeding pattern, nature, and amount
Pain
Vital signs
LOC
What should you assess in the management of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Adequate pain management
Identification and prevention of hypovolemic shock
Acceptance and resolution of grief and pregnancy loss
Increased knowledge on ectopic pregnancy
Perioperative care
What are the goals of care in the management of Ectopic Pregnancy?
FIRST TRIMESTER BLEEDING CONDITIONS
Abortion
Spontaneous Abortion
Threatened
Imminent
Complete
Incomplete
Missed
Recurrent Abortion
Induced Abortion
Ectopic Pregnancy
BONUS: Click to see the whole outline of the first trimester bleeding conditions
No, dapat UTZ pa rin ang gamit to confirm
Is Beta HCG a reliable indication of pregnancy?
Hydatidiform Mole (Molar Pregnancy)
Premature Cervical Dilatation
What are the second trimester bleeding conditions?
14 to 26 weeks
When is the second trimester of pregnancy?
Hydatidiform Mole (Molar Pregnancy)
Abnormal conceptions with excessive placental, and little or no fetal development
Hydatidiform Mole (Molar Pregnancy)
Placenta contains grape-like vesicles
Hydatidiform Mole (Molar Pregnancy)
Can lead to gestational trophoblastic neoplasia
Partial Mole
Type of Molar Pregnancy: Includes some fetal tissues and membranes
Complete Mole
Type of Hydatidiform Mole: Composed only of enlarged villi
FALSE; There are more chances that a cancer will develop in partial mole than in complete mole
TRUE or FALSE: There are more chances that a cancer will develop in complete mole than in partial mole
Maternal age
Paternal age
Prior molar pregnancy
Prior miscarriage
Family history
Racial factors: 17.5/1000 women
Diet and nutrition: decrease carotene and animal fat
What are the factors affecting Hydatidiform Mole conception?
35 years old
What maternal age is considered at risk for Hydatidiform Mole conception?
45 years old
What paternal age is considered at risk for Hydatidiform Mole conception?
TRUE
Prevalence rate in Japan = 16.5/1000 women
Prevalence rate in the Philippines = 17.5/1000 women
TRUE or FALSE: Asians are at higher risk of developing molar pregnancy
Beta-HCG: 1-2 Million U/mole
Normal HCG Factor: 50,000 U/mole
Soaper dami beh kaya nagcacause ng hyperemesis gravidarum (ikaw ba naman halos 20 to 40 times more than normal yung Beta-HCG, hindi ka ba naman magsuka nang magsuka)
Ultrasound
Will confirm grape-like structures
What are the diagnostic studies for Hydatidiform Mole?
Uterus larger than expected length of pregnancy
Like 12 weeks pa lang pero mukha nang 16 weeks
No palpable fetal parts
Kapag nag-Leopold’s Maneuver ka, hindi mo ma-aappreciate yung buttocks and extremities
Symptom of PIH and hyperemesis
Mataas yung BP (PIH)
Mataas din yung Beta-HCG (hyperemesis)
Vaginal bleeding containing grape-like tissue
Absence of fetal heart tones or activity
Confirmation by ultrasonography
What are the clinical manifestations of Molar Pregnancy (Hydatidiform Mole)?
Complete bedrest
Facilitate diagnostic studies
Assist and support during dilatation and curettage or total hysterectomy
Monitor the amount and type of bleeding
Institute measures to alleviate fear and anxiety
Monitor for side effects of prophylactic methotrexate
Monitor vital signs
Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance
Monitor the condition of the uterus
Educate on follow-up care
Support through loss of expected pregnancy
What are included in the nursing management for Hydatidiform Mole?
Methotrexate
There is a high chance that the partial mole will develop into a neoplasia
Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: Mataas (pataas nang pataas) pa rin yung Beta-HCG na nagliliead to Neoplasia
Binibigay sa mga feeling ng HCWs hindi na babalik sa hospital for monitoring
Usually 6 months minomonitor yung Beta-HCG
Adverse effect: Leukopenia
Bumababa ang WBC that is why important ang Reverse Isolation
Why is Prophylactic Methotrexate indicated for Molar Pregnancy?
After D&C (Dilation and Curettage) aka “Raspa”
Hindi pa pwedeng magbuntis agad kasi mataas pa ang Beta-HCG levels
After 6 months na consistent within normal levels ang Beta-HCG, doon na pwede magbuntis
Explain the follow-up care for Hydatidiform Mole
Premature cervical dilatation
Also known as incompetent cervix or cervical insufficiency
Premature cervical dilatation
Weak cervical tissue causes or contributes to premature birth or loss of an otherwise healthy pregnancy
Increased maternal age
Congenital structural defects
Trauma to the cervix
What are the risk factors of Premature cervical dilatation
Painless contractions in mid-trimester
Sa third trimester ma-tetest if competent ang cervix
Pink-stained vaginal discharge
Ruptured BOW
Pregnancy can still progress
What are the clinical manifestations of Premature cervical dilatation or Dysfunctional/Incompetent Cervix or Cervical insufficiency?
Bedrest in trendelenburg position
Observe for rupture of membranes or bleeding
If still intact pa
Monitor FHR with Doppler UTZ
Assist with therapeutic intervention
Cerclage procedure
Cesarean birth or cutting of suture for vaginal birth
What are included in the nursing management for Dysfunctional Cervix?
14 to 16 weeks AOG
In Cerclage Procedure, on what week of AOG is the cervix typically sutured?
37 to 38 weeks
In Cerclage Procedure, on what week of AOG is the suture in the cervix typically removed?
Placenta Previa
Abnormal Placental Attachments
Abruptio Placenta
What are the third trimester bleeding conditions?
27 weeks to the end of pregnancy or 27 to 38.5 weeks
When is the third trimester of pregnancy?
Placenta Previa
Implantation of the placenta at the lower uterine segment near the cervical os
Ultrasound
What is used to diagnose Placenta Previa?
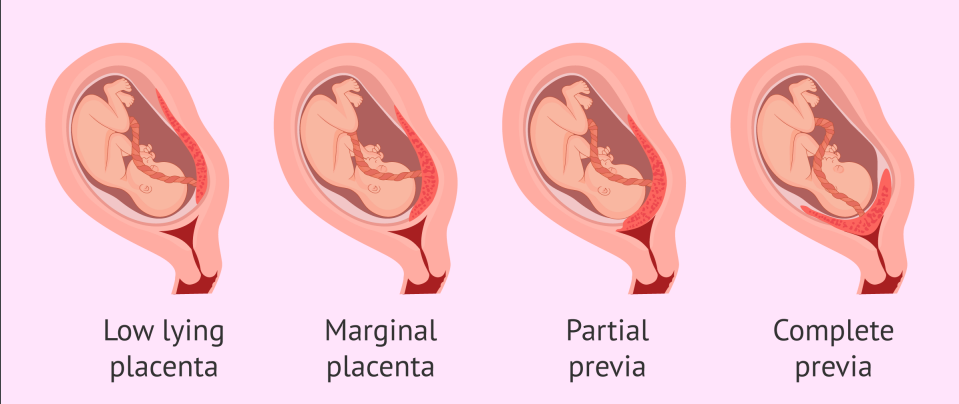
Total
Partial
Marginal
Low-Lying
What are the classifications of Placenta Previa?
Total
Classification of Placenta Previa: Totally obstructs cervical os
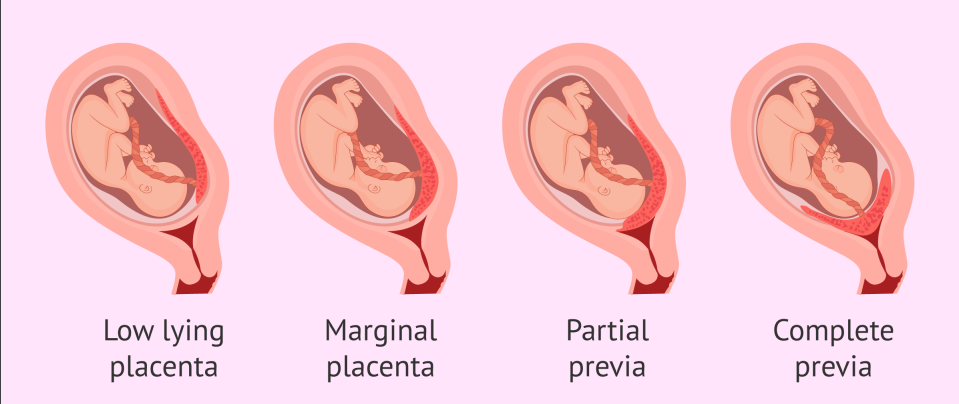
Partial
Classification of Placenta Previa: Partially occludes cervical os
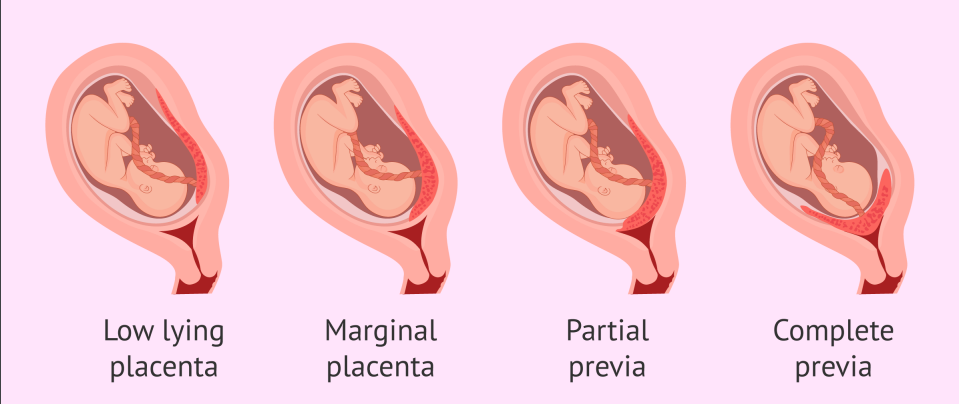
Marginal
Classification of Placenta Previa: Placental edge approaches cervical os
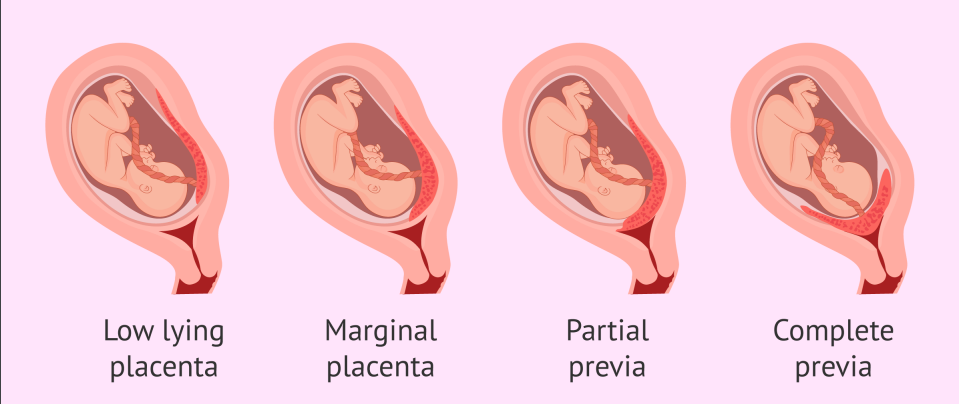
Low-lying
Classification of Placenta Previa: Lower portion of the uterus