APES - Unit 5 - Population & Community & Conserving Biodiveristy
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
specialist species
Species with a narrow ecological niche. They may be able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions, or use only one type or a few types of food.
generalist species
species with a broad ecological niche
precautionary principle
a principle based on the belief that action should be taken against a plausible environmental hazard
indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded.
endemic species
species that are native to and found only within a limited area
keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
invasive species
plants and animals that have migrated to places where they are not native
habitat
the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
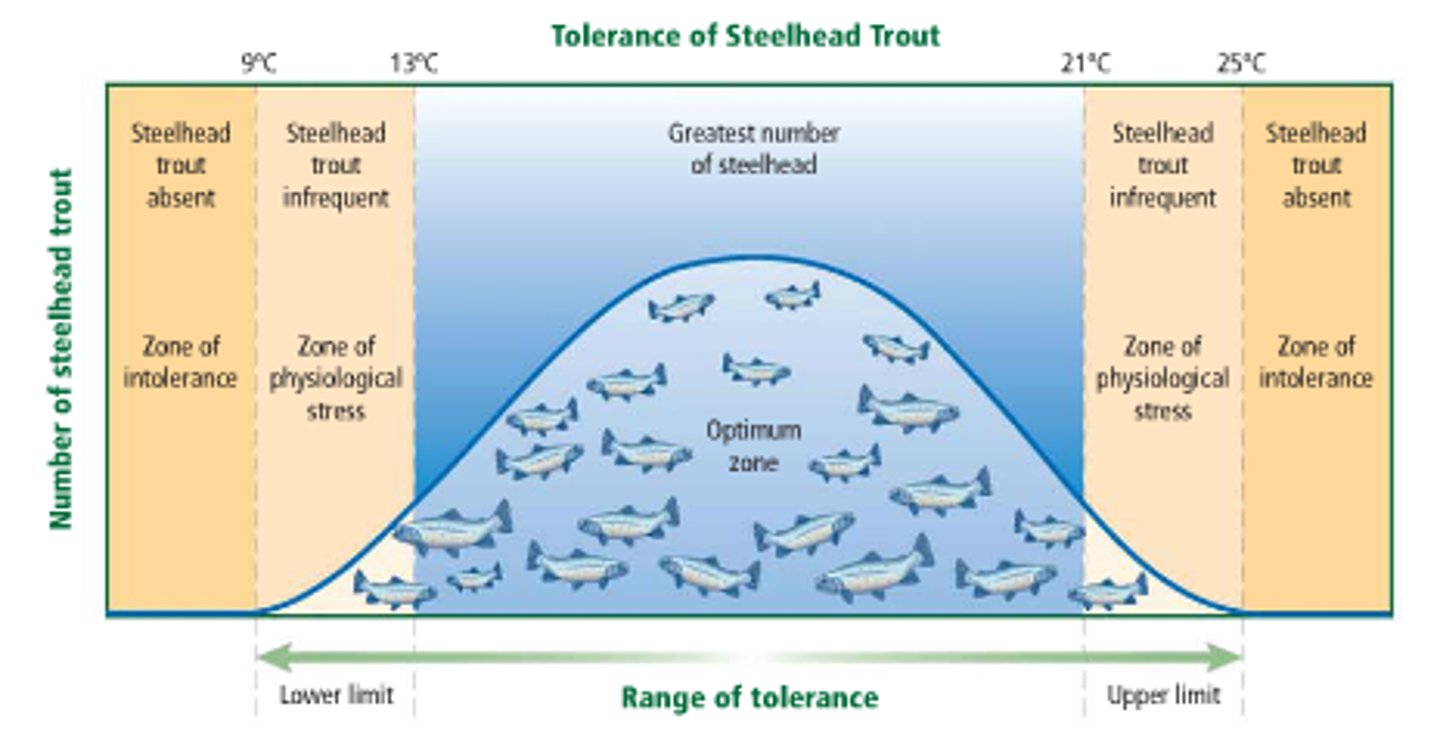
range of tolerance
the limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate
Niche
An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
competitive exclusion principle
Ecological rule that states that no two species can occupy the same exact niche in the same habitat at the same time
resource partitioning
The division of environmental resources by coexisting species such that the niche of each species differs by one or more significant factors from the niches of all coexisting species
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
prediation
a relation between animals in which one organism captures and feeds on others.
Parasitism
A relationship in which one organism lives on or in a host and harms it.
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
Symbiosis
A close relationship between two species that benefits at least one of the species.
community structure
the set of characteristics that shape communities
ecological succession
gradual change in living communities that follows a disturbance
primary succession
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
secondary succession
Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
climax forest
the oldest forests once considered by ecologists to have ended succession (now recognized that natural disturbances can reset to an earlier stage)
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Population range
the geographical area in which a specific species can be found
population spacing
how the organisms are arranged in a given area
clumped dispersion
The most common pattern of dispersion; individuals aggregated in patches.
uniform dispersion pattern
a pattern in which the individuals of a population are evenly distributed over an area
random dispersal
individuals in a population are spaced in an unpredictable way without a pattern. ex. dandelions that grow from windblown seeds might be randomly dispersed.
population size
the total number of individuals within a defined area at a given time
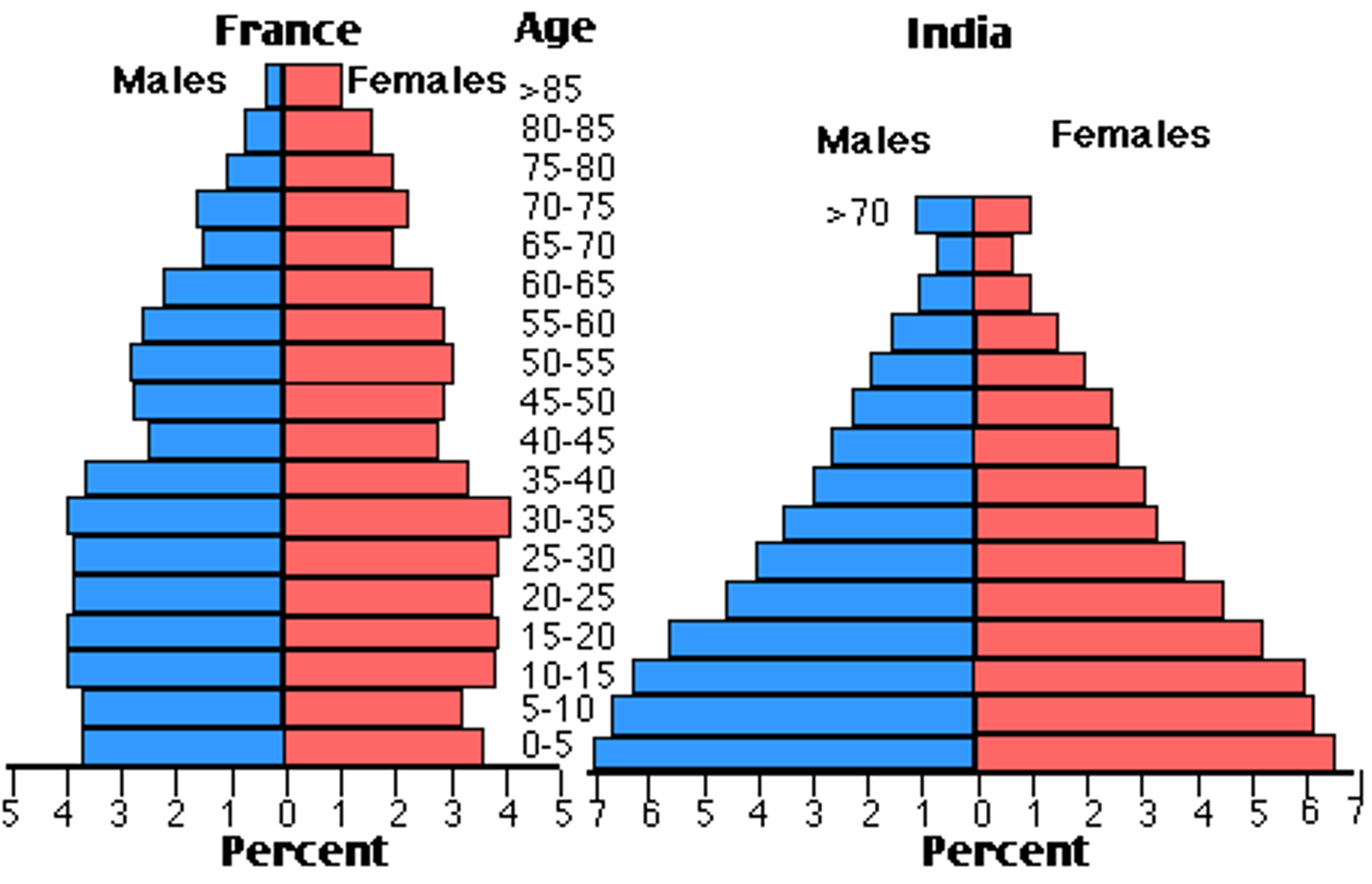
age structure
Percentage of the population (or number of people of each sex) at each age level in a population.
survivorship curve
a diagram showing the number of surviving members over time from a measured set of births
survivorship type 1
late loss, heavy parental care
survivorship type 2
relatively constant survivorship throughout life
ex. birds
survivorship type 3
Early loss; produce lots of offspring at once and many die right away
reproductive strategies
Behaviors or behavioral complexes that have been favored by natural selection to increase individual reproductive success. The behaviors need not be deliberate, and they often vary considerably between males and females.
K-selected species
Species that produce a few, offspring but invest a great deal of time and energy to ensure that most of those offspring reach reproductive age.
r-selected species
Species that reproduce early in their life span and produce large numbers of usually small and short-lived offspring in a short period.
Population growth formula
births - deaths + immigration - emigration
Exponential growth rate
Continuous increase in a population at a rate that is proportional to the number of individuals at a given time.
non-native species
A species that is not naturally found in an area. These organisms come from a different country or part of the world.
Logistic growth rate
S-shaped, slows or stops at the population's carrying capacity
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
conserving biodiversity
Conservation efforts focus on protecting entire ecosystems as well as single species, to insure that natural habitats and the interactions of many different species are preserved.
Extinction rates
Extinction rates right now are unprecedented, about 1000 times higher than the fossil record. Projected rates are another 10 times higher. There simply isn't room on the planet for so many humans living the way we do to maintain all the other species
endangered species
A species whose numbers are so small that the species is at risk of extinction
threatened species
A species that could become endangered in the near future
Regionally Extinct
a species is no longer found in part of its former range but still lives elsewhere.
functionally extinct
To the point at which species can no longer play a functional role in the ecosystem
HIPPCO
Habitat destruction, Invasive Species, Population growth, Pollution, Climate Change, Overexploitations
*habitat destruction is #1 threat to animals
Bioaccumulation
The accumulation of a substance, such as a toxic chemical, in various tissues of a living organism.
Overexploitation
overuse of species with economic value--a factor in species extinction
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species
International agreement between governments whose aim is to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals & plants does NOT threaten the survival of the species
Convention on Biological Diversity
An international treaty to help protect biodiversity
Endangered Species Act (ESA)
Protects species that are considered to be threatened or endangered. Includes migratory birds and their habitats.
Wildlife sanctuaries
Preserved land for living things