Lecture 9: Infectious Causes of Hepatitis/Drugs & Toxins
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Viral Hepatitis
Prodromal (Pre-icteric) Phase: Malaise, Nausea, Vomiting, Fever, RUQ pain
Icteric: Jaundice, dark urine
Very high AST & ALT (usually ≥ 400)
mild-moderate ↑ ALP
unless in liver failure, ↑ serum Bilirubin; Conjugated (Direct) is typically higher
urine + for Bilirubin
Lab values increase early in the prodrome, peak before jaundice is maximal, & fall slowly during the recovery phase
Urinary bilirubin usually precedes jaundice
Acute Hepatic Failure
massive hepatic necrosis; viral Hepatitis causes
caused by HAV + HEV
Carrier state
HBV only: + HBsAg, with no Anti-HBs, & normal Aminotransferases
Hepatitis A
Does NOT lead to chronic infection or carrier state; NOT a risk factor for cancer
Spread: Fecal-oral (close contact, contaminated food or water)
Virus Not cytopathic; Cytotoxic T-cells destroy infected cells
IgM Ab appears at onset of symptoms
IgG confers lifelong immunity
Causes Acute Liver Failure in newly infected (particularly those with other chronic liver disease)
Dx: IgM anti-HAV
vaccine
Hepatitis B Types of Clinical presentations
Clinical presentation determined by host immune response:
Acute Hepatitis followed by recovery & clearance of virus
Acute Hepatic Failure due to massive liver necrosis
Chronic Hepatitis (with or without progression to cirrhosis)
Asymptomatic “healthy” carrier state
Hepatitis B
Transmission: Parenteral; Blood (IV drugs sharing of needles, transfusions), sex, vertical (during childbirth)
HBsAg (surface Ag) → appears before symptoms; peaks in acute, symptomatic period;
HBsAg persistence beyond 6 months indicates chronicity
Anti-HBs (Antibody to HBsAg) → IgG begins to rise generally after disappearance of HBsAg → persists for life; confers immunity; basis of vaccine
In cases that progress to CHRONIC disease, ANTI-HBsAg IS NOT PRODUCED
Chronic disease: Positive HBsAg with Negative Anti-HBsAg
Anti-HBc (Antibody to Core Antigen) → IgM followed by IgG is present in both acute & chronic infections
Present in natural infections; absent in vaccinated
+ HBeAg or HBV quantitative PCR → high viral load/active viral replication
infectious to others (persistence indicates Chronic Hepatitis)
HBeAg-negative Hepatitis B (via mutational loss of e antigen) may also cause Chronic disease
Vaccine produces Anti-HBsAg only! (Anti-HBc is negative)
Chronic Hepatitis B
Persistent ↑ ALT, AST, HBeAg with HBsAg & No Anti-HBsAg
HBeAg, HBV-DNA, & HBV DNA Polymerase signify active viral replication
Some cases of Chronic infection (HBsAg +, Anti-HBsAg -), Transaminases ALT/AST become normal (Carrier state)
Hepatitis B Clinical Manifestations
Acute infection is mild or subclinical in majority
Anorexia, fever, jaundice, RUQ pain
Most cases resolve without treatment
Acute liver failure low
Infection persists & becomes chronic
risk of chronic infection is greatest in infants that acquired it vertically
Immune complex-mediated phenomena (from HBsAg-anti HBs immune complexes)
PAN (Polyarteritis Nodosa) & Glomerulonephritis (Membranous or Membranoproliferative) usually within a year after infection
Chronic infection (particularly if acquired at birth) is a risk factor for developing Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Vaccination is highly effective
Rx for Chronic disease: Interferon & antivirals but complete cure unlikely because HBV can integrate into host DNA
Hepatitis D
Entirely Dependent on HBV for its life cycle (occurs only as coinfection with HBV)
Defective RNA virus that can only produce infection in Hepatitis B infected hepatocytes because HDV requires encapsulation by HBsAg
Transmission: Parenteral
Virus only produces one protein, HDAg
Coinfection of healthy patient (HBV + HDV at same time): usually self-limited acute hepatitis with clearance of both viruses
Superinfection (chronic HBV carrier gets exposed): Higher risk of fulminant acute hepatitis & progression to cirrhosis & HCC
Dx: Total Anti-HD antibodies. Confirm with measurement of HDV RNA in serum.
Hepatitis C
Chronic Hepatitis
Transmission: Parenteral
Fluctuating elevations of Transaminases
Few individuals clear the virus
Many develop Cirrhosis over 20 to 30 years & have ↑ risk of HCC
Detectable HCV RNA in blood
Screen with anti-HCV (false negative very early in infection or in immunosuppressed)
HCV-RNA viral load test
Rx: specific & highly effective antiviral drugs available (virus does not integrate into host DNA; true cures possible)
Hepatitis C Complications
Cryoglobulinemia: Monoclonal or Polyclonal IgM cryoglobulins with Rheumatoid factor activity (bind FC of IgG) & Raynaud’s syndrome
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis
Vasculitis (cutaneous, leukocytoclastic)
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda due to Uroporphyrinogen Decarboxylase in the liver; blistering skin lesions that develop on sun-exposed skin (Photosensitivity)
Hepatitis E
Zoonotic disease with animal reservoirs; waterborne & fecal-oral transmitted
Most self-limited
Fulminant Acute hepatitis (liver failure) occurs in infected pregnant women
Chronic disease does not occur in the immunocompetent
No ↑cancer risk
Serology or PCR for viral RNA
IgM anti-HEV at onset of symptoms & rising transaminases
IgG anti-HEV persists
Morphology of Viral Hepatitis
Variable portal & lobular lymphoid infiltrates present
Acute: Apoptotic (with Acidophil bodies) or Necrotic (→ Acute Liver Failure)
Chronic: dense Portal Lymphocytic inflammation with “interface” activity (inflammation extends beyond the limiting plate of the Triads into the liver parenchyma)
Also called “piecemeal necrosis”
Fibrosis (portal → periportal → bridging → cirrhosis) develops
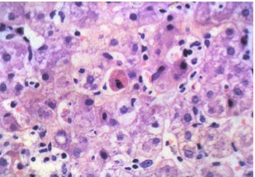
Acute hepatitis
Acidophil body (Apoptosis)
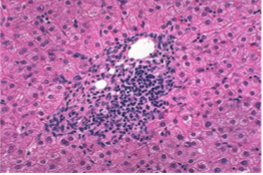
Chronic Hepatitis
portal lymphocytic inflammation with interface activity
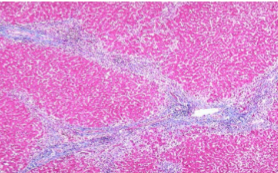
Chronic Hepatitis
Bridging fibrosis or Cirrhosis
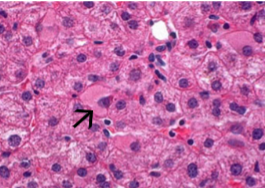
Hepatitis B: “Ground glass hepatocytes”
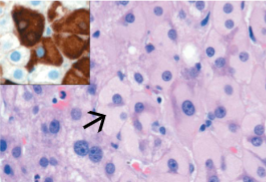
Hepatitis B: “Ground glass hepatocytes”
IHC staining for HBsAg
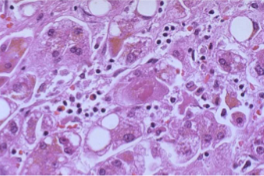
Hepatitis C: Steatosis
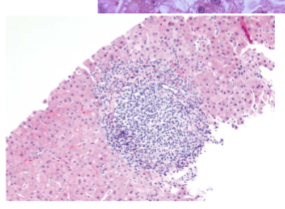
Both HBV & HCV: Portal track Lymphoid infiltration with interface activity
Recovery from Acute Hepatitis following necrosis
Recovery may be complete if Reticulin support network is not injured
Postnecrotic Cirrhosis if Reticulin is destroyed
May be due to causes other than viral, such as drugs, chemicals, mushrooms (Amanita phalloides)
Irregular sized nodules (Macronodular Cirrhosis)
Wide fibrous (collagenous) septae
Loss of hepatocytes
Regenerative nodules
Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Liver Abscesses
Due to mostly to pyogenic bacteria
via Portal vein seeding from appendicitis, diverticulitis, other contaminated abdominal surgeries
via Arterial dissemination (IV drugs, infective endocarditis)
by Ascending the biliary tract (Ascending Cholangitis)
via Direct extension from peritonitis of via Penetrating injury
Fever, RUQ pain, tender Hepatomegaly
Neutrophilia
↑ inflammatory biomarkers (CRP, ESR, Procalcitonin)
↑ ALP; var. ↑ AST/ALT, +/- Jaundice w/ biliary obstruction (↑ Direct Bili)
Frequent in elderly; symptoms less developed; Dx delayed
Large abscess: surgical drainage
Small abscesses: antibiotics
Mortality for large abscesses
Other causes of liver abscesses
hepatic infections are mostly due to Parasites:
Malaria
Schistosomiasis (Intrahepatic “Pipestem Fibrosis”)
Strongyloidiasis
Cryptosporidiosis
Leishmaniasis
Echinococcosis (Hydatid Cysts + calcified walls caused by the larva of small tapeworm)
Rx is surgical resection of the cyst. Liver Bx is contraindicated as accidental entry of cyst fluid into circulation → anaphylaxis
Amebiasis (Dx by serology)
Liver Flukes (live in lumen of bile ducts)
Autoimmune Hepatitis
Chronic Progressive Hepatitis with autoantibodies that responds to immunosuppression
Genetic predisposition; associated with other autoimmune disease; Female
Specific antibody to Liver unknown
Overlaps with other chronic hepatitis
Inflammation of Triads with interface activity; numerous Plasma cells are typical
Lymphs & plasma cells may be seen inside hepatocyte cytoplasm (Emperipolesis)
May see areas of necrosis; usually see fibrosis; may present with Cirrhosis
Autoantibodies, ↑ Serum IgG, liver Bx, Exclusion of other causes
Hepatitis with prominent plasma cells
“Typical for AIH”: Lymphoplasmacytic Portal infiltrate with Interface activity ("piecemeal necrosis")
Microvesicular Steatosis
Reye syndrome usually seen in children & teenagers with use of Aspirin (Salicylates) after viral infections with Varicella or Influenza
Can occur due to a metabolic fatty acid oxidation disorder
Aspirin metabolites inhibit Mitochondrial Beta-oxidation of Fatty Acids (primary path of FA breakdown)
Risk for Acute Hepatic Failure (without necrosis)
Aspirin use is Contraindicated if < 19 years of age (except for Kawasaki Disease)
Poor Px
Fatalities usually due to Encephalopathy
Cholestatic
Bland hepatocellular cholestasis w/o inflammation
Contraceptives/Estrogen; Anabolic steroids, Amoxicillin-Clavulinate, HART
Hepatocellular necrosis
Massive necrosis → Acetominophen; halothane
Chronic hepatitis → Isoniazid (for TB)
Fibrosis and cirrhosis
Periportal and pericellular
Alcohol; methotrexate; enalopril; vitamin A (retinoids)
Granuloma formation
Noncaseating epithelioid granulomas: Sulfonamides; amiodarone; Isoniazid
Fibrin ring granulomas: Allopurinol
Fatty liver
Large and small droplets: ETOH, corticosteroids, methotrexate, total parenteral nutrition
Microvesicular: Valproate; Tetracycline; ASA-Reye syndrome; ART
Steatohepatitis with Mallory-Denk bodies: EtOH; Amiodarone
Vascular lesions
Sinusoidal obstruction/veno-occlusion of central vein
High dose chemotherapy
Bush teas
Budd-Chiari
hepatic vein occlusion
Oral contraceptives
Hepatocellular Adenoma
Oral contraceptives; anabolic steroids
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
ETOH; thorotrast
Cholangiocarcinoma
Thorotrast
Angiosarcoma
Thorotrast, vinyl chloride; arsenic
Alcoholic Liver disease
3 types: steatosis (fatty change), alcoholic steato-hepatitis, fibrosis (→ Cirrhosis)
Excessive alcohol intake causes steatosis, dysfunction of mitochondria, microtubules, cellular membranes, & oxidative stress, → inflammation & hepatocyte death
Mediators of cell injury include Acetaldehyde (induces lipid peroxidation & binds to proteins to form adducts), ↑ CYP2E1 Enzyme (creates free radicals), & ↓ Glutathione antioxidant levels
Alcohol catabolism by Alcohol Dehydrogenase & Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase consume NAD+ to generate reduced
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (↑NADH + H+)
↓ NAD+ results in hepatic steatosis via ↓ fatty acid oxidation
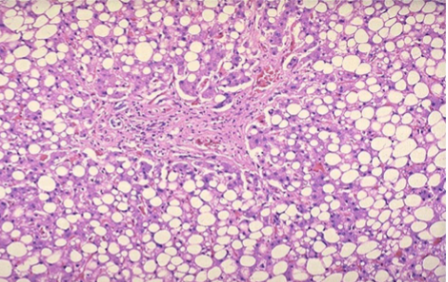
Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis
lipid accumulation coalesces into large droplets that distend hepatocyte & displace the nucleus (Macrovesicular Steatosis)
Liver is enlarged, yellow, greasy

Alcoholic Hepatitis
Hepatocyte swelling (Balloon cells) & necrosis in background of Steatosis
Mallory-Denk bodies: eosinophilic inclusions formed of damaged cytokeratins which are ubiquitinated
Neutrophilic infiltrate in lobules; variable mononuclear cells
Liver normal to increased size
May progress to alcohol related steatofibrosis → eventual Cirrhosis
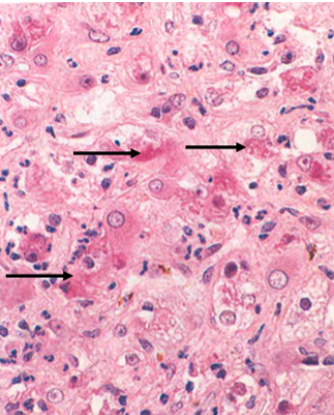
Numerous Mallory-Denk bodies
Composed of damaged aggregates of Keratins 8 & 18 which are Ubiquitinated

Alcoholic hepatitis with clustered inflammatory cells marking the site of a necrotic hepatocyte (arrowhead) & Mallory body (arrow)
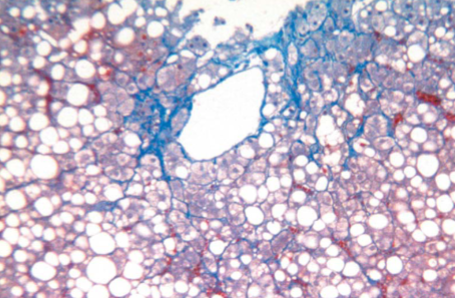
Alcoholic Steatohepatitis with early fibrosis
Steatohepatitis is often accompanied by perivenular & pericellular (Zone 3) fibrosis with a “chicken-wire” appearance
With continued injury can progress to periportal & bridging fibrosis & then to Cirrhosis
Alcoholic Cirrhosis is usually Micronodular (Laennec Cirrhosis)
Cirrhosis is rarely reversible
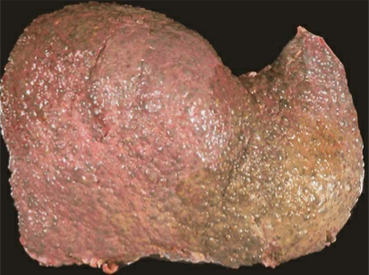
Alcohol-related Cirrhosis
Mostly Irreversible fibrosis; evolves slowly
End-stage: brown, shrunken < 1 kg
Nodular “hobnail” gross
Micronodules of trapped regenerative
hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous tissue
Microscopic (end-stage) may be indistinguishable from other causes of cirrhosis
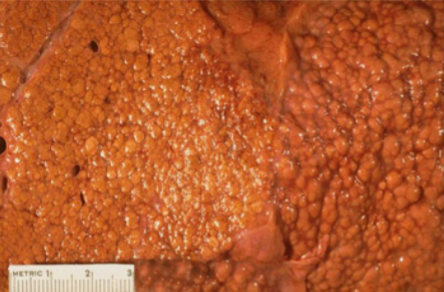
Alcoholic Cirrhosis
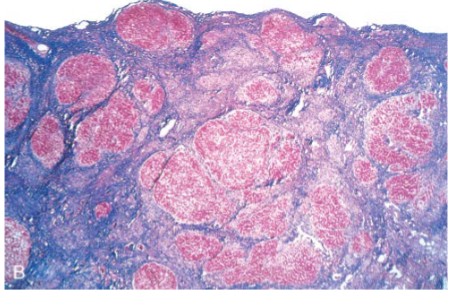
Alcoholic Cirrhosis
Alcoholic Liver disease Clinical features
Steatosis: Hepatomegaly, mild ↑ Bilirubin (mostly unconjugated), ALP & GGT; mild increases in Aminotransferases; Reversible Steatohepatitis: tends to appear acutely, after bout of heavy drinking: malaise, anorexia, upper abdominal discomfort, RUQ tenderness
↑ Bilirubin, ALP, & Aminotransferases; often neutrophilic leukocytosis
Serum AST:ALT ratio >2:1
With repeated bouts → Cirrhosis
With cessation, some may clear, but in others, hepatitis persists, & progress to Cirrhosis
May be clinically silent (Compensated) or progress to liver failure (Decompensated)
Portal Hypertension with ascites, esophageal varices; Hyperestrogenism
Liver failure (↓ Albumin, ↑PTT)
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease spectrum
Hepatic Steatosis (NAFLD): Steatosis in individuals who do not consume alcohol plus, two of: High BP, Dyslipidemia (↑ TG, LDL, or ↓ HDL), central obesity, Microalbuminuria
Associated with Obesity, Type 2 diabetes, Hyperlipidemia (metabolic syndrome)
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) refers to those of NAFLD that develop Steatohepatitis
NASH ↑risk of developing Cirrhosis
NASH complications- decompensated cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma
In the cirrhotic stage, the Fat may be lost (“burned out NASH”)
Most Isolated Fatty Liver
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Insulin resistance ↑ release of Free Fatty acids from somatic adipocytes
Results in increased FFA uptake in liver, stored as TG
↑ serum ALT/AST
Dx of NASH is by Liver Bx + Clinical history to exclude Alcohol
Fatigue or RUQ discomfort (caused by hepatomegaly)
NASH +/- advanced fibrosis/Cirrhosis
↑ risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
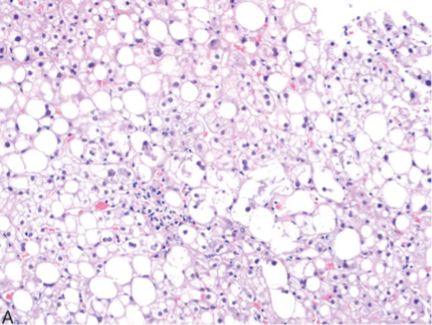
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Fat droplets- small/medium/large; balloon cells; inflammatory infiltrates
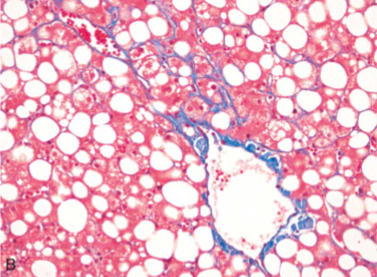
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Perisinusoidal fibrosis – chicken wire most prominent around central vein

Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Perisinusoidal fibrosis – chicken wire most prominent around central vein