Ceutics Exam 2: Buffer Solution
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
A critical physicochemical property of a drug is
ionization
ionization
is a process by which a neutral molecule gains or loses a proton and thereby acquires a positive or negative electrical charge.
charged species formed thru ionization are called
ions
can conduct an electrical current, and so substances that form ions in solution are called electrolytes.
ions
a compound that does not ionize when dissolved in water, and exists solely as the neutral, uncharged species.
nonelectrolyte
Many drug compounds do not ____ under physiological conditions and are considered to be _______.
ionize, nonelectrolytes
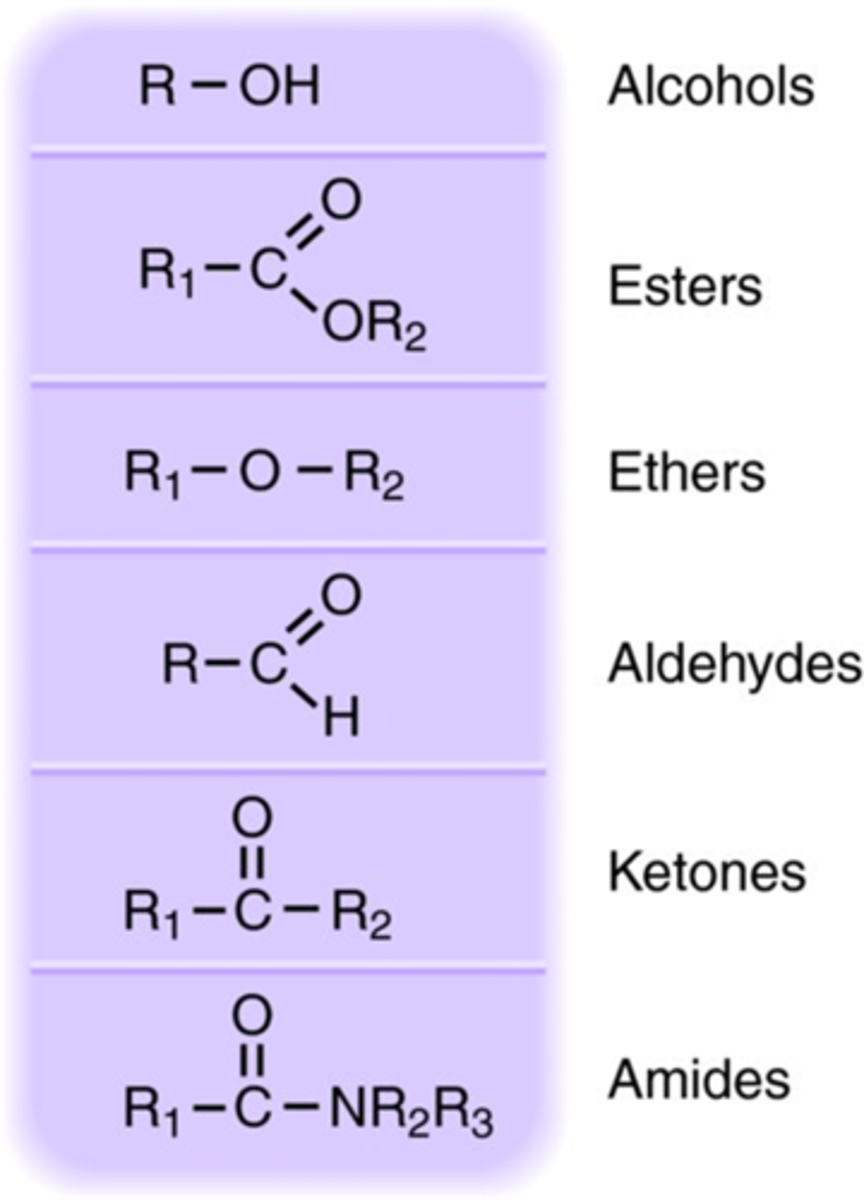
Compounds with the following functional groups do not generally ionize in aqueous solution:
Alcohols and sugars
Ethers
Esters
Ketones
Aldehydes
The majority of amides
Structures of some common nonelectrolyte functional groups.
alcohols, estes, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, amides
a strong electrolyte ionizes _____ when dissolved in water
completely
a strong electrolyte exists ____ in the form of positive and negative ions in solution
soley
what is an example of a strong electrolyte
sodium chloride (NaCl)
sodium chloride ionizes to form
Na+ and Cl- in aqueous solution
weak electrolyte
is ionizable, but ionizes partially; a fraction of dissolved molecules remain un-ionized, while others acquire a positive or negative charge.
examples of weak electrolytes
acetic acid and ammonia
importance of ionization of weak electrolytes
The properties of ionized (charged) and un-ionized (uncharged) forms of a drug or biologically active compound are dramatically different from each other, even though the only change in structure is the gain or loss of a proton, and the presence or absence of a charge.
charged and uncharged forms will be
Absorbed and distributed differently.
Will bind to receptors differently…
And may be metabolized and eliminated differently.
for a drug that can ionize, the proportion of ionized and un-ionized forms in the body is critical in determining
behavior.
why is the ionization of drugs in the drug product is also important,
influencing route of administration and shelf life of the drug product.
what is a drug that is a good example of the importance of ionization in drug design
indomethacin
what type of drug is Indomethacin
oral anti-inflammatory
- weak electrolyte
the ionized form of a drug dissolves more _____ and to a _____ extent than the un-ionized form
rapidly, greater
to enter the blood stream, the drug need to cross
lipophilic cell barriers
to be able to cross lipophilic cell barriers what is required
at least some molecules to be in the un-ionized form in the intestines
once indomethacin has reached its site of action, only the _____ form binds to the receptor
ionized
both _____ and _____ forms are important for different aspects of ADME and pharmacodynamics of indomethacin
ionized and un-ionized
According to the Bronsted–Lowry theory of acids and bases, an acid is
a compound that can donate a proton
According to the Bronsted–Lowry theory of acids and bases, a base is
a compound that can accept a proton
based on bronsted-lowry there has to be ____ compound present to _____ the proton from the acid, or to ____ the proton to the base
another compound, receive, provide
in almost all situations the other compound involved in the bronsted-lowry concept is
water
why is water a remarkable solvent
it can behave as both an acid and a base
ampholytes
compounds with the dual property of being able to act as both an acid and a base
The water molecule possesses a ____ giving it the ability to accept or donate a positively charged proton
dipole
dipole
two electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by a small distance
hydronium ion
hydrogen ion combines with a water molecule to form a hydronium ion, H3O(+)
the pH od body fluids ranges between
1 and 8
the ____ is the most acidic region of the body
acidic
stomach pH
1 - 3
the normal pH of intestinal fluids is
6-7
the pH of blood is ____ which corresponds to a [H+] of ____
7.4, 40 nM
the value of [H+] can only vary from ______ to ______ with out serious metabolic consequences
37 to 43
Local pH in various tissues depends on _______ and _______ of each tissue, and rarely exceeds ____
composition and function
8
a drug can be expected to encounter physiological environments that vary between pH 1_____and ____ which makes ionization in this pH range of the _____ interest
1 and 8, greatest
if a drug does not have a function group that ionizes in the pH region of 1-8 then it behaves as a _________. what does this mean?
nonelectrolyte, remains un-ionized over the entire physiological pH range
why from a formulation perspective is it important to control pH of a product
1)To minimize drug degradation
2)To improve patient comfort and compliance
3) …or to improve delivery.
what type of dosage form can have a pH outside of the 1-8 range
liquids ( solutions, suspensions, and emulsions)
why are higher pH values of pharmaceutical liquids often required
to make the drug more soluble, or to maintain good stability and an adequate shelf life
when a strong acid is added to water hydrogen ion concentration in solutions ______ and pH _____
increases, decreases
what happens because a strong acid dissociates completely
The molar concentration of H+ is equal to the molar concentration of acid added for a monoprotic acid (HCl), and twice the molar acid concentration for a diprotic acid (H2SO4
example of a strong base
hydroxide ion OH-
what happens when a strong base reacts with H+ in water
the concentration of H+ will decrease and the solution of pH will increase
The molar decrease in H+ concentration will be equal to the molar concentration of _____ added
NaOH
Although strong acids and bases are often used in pharmaceutical products to adjust the pH of liquids, there are _____ strong acid or strong base drug.
no
main difference between strong acid and bases compared to weak acid and bases
weak acids and bases are only partially dissociated in water because of their diminished ability to donate or accept protons
what are the 2 forms that weak acids exist in
uncharged, un-ionized species and negatively charged ions
when a weak base is dissolved in water
only a fraction of molecules accept protons
what are the 2 forms that weak bases exist in
uncharged, un-ionized species and positively charged ions
Typical weak acids have the following functionalities:
Carboxylic acids
Sulfonic acids
Phenols
Thiols
Imides
conjugate acid-base pair
An acid and base that can be represented by an equilibrium in which the two species differ only by a proton
Ka
acid dissociation constant
- A- is the conjugate base of the acid HA
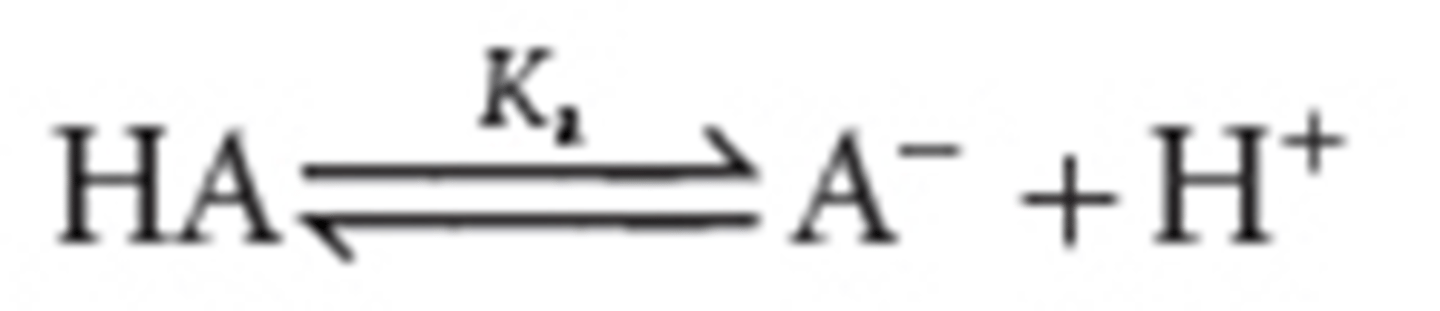
what is the conjugate base of base B in Ka equation
BH+
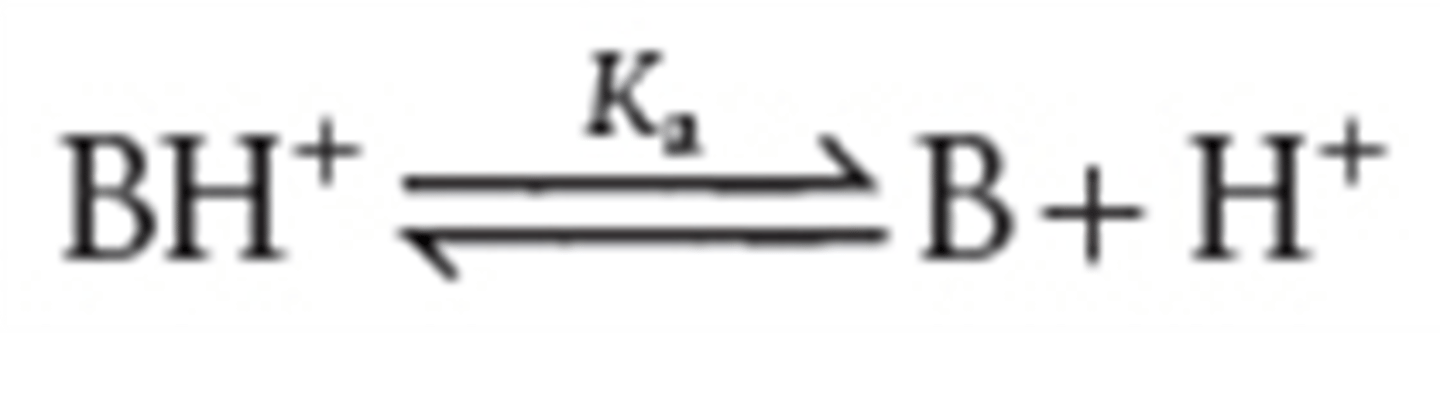
how do we understand or predict the behavior of ions
Because ions behave differently from uncharged molecules, we are interested in what proportion of a weak acid or weak base is un-ionized or ionized in a given situation
law of mass
describes the dissociation of a weak acid and of the conjugate acid of a weak base.
It states that at equilibrium the product of the concentrations on one side of an equation, when divided by the product of concentrations on the other side of the equation, is a constant regardless of the individual concentrations
the larger the Ka the ______ the acid HA and the _____ its conjugate base A-
stronger, weaker
Ka is a property of the conjugate acid-base pair and gives is information about the
strengths of both forms
define Ka for the conjugate acid of a weak base
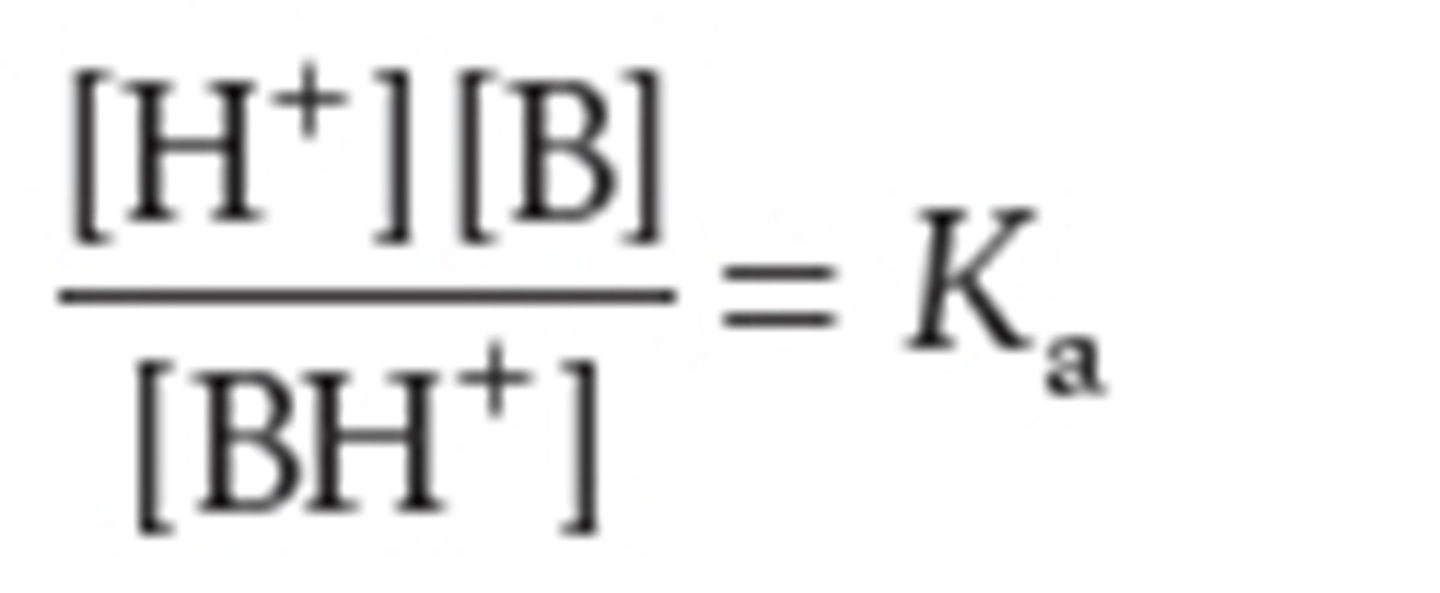
the larger of the value of Ka the ______ BH+ dissociates to ____ protons
more, donate
the larger Ka the _____ the conjugate acid BH+ and the _____ the base B
stronger, weaker
weak acids or conjugate acids of weak bases with a large Ka have a _____ pKa
small
weak acids with a small Ka have a _____ pKa
large
does the pKa value itself tell us whether a drug is a weak acid or base
no
a weak acid with a pKa of 3 is a ________ acid than a weak acid with a pKa of 4
stronger
the higher the pKa of a compound the ________ is the basic form of the conjugate acid-base pair
stronger
a weak base of pKa 8 is a _________ base than a weak base of pKa 7
stronger
weak acid and base drugs are frequently available as their
salts
weak acid naproxen is also available as its sodium form
sodium, naproxen
the weak base clonidine is available in its salt form
clonidine hydrochloride
how is the salt of a weak acid usually obtained
reacting it with a strong base such as NaOH
reacting the salt of a weak acid with a strong base results in
sodium salt
reacting the salt of a weak base with a strong acid such as HCL results in
hydrochloride salt
why are salts themselves strong electrolytes
dissociate completely into their constituent ions in water
ions generated do not remain _________________ if one of the components of the salt is a weak acid or base
completely ionized
pharmaceutical companies often develop the salt form of a __________ rather than the original weak acid or base form for several reasons- why
drug
salts can be more readily crystallized into stable, easy to manufacture crystals
salt form of a drug dissolve ______ in aqueous solution
faster
salt form of a drug are more ____ on storage, and are ______ to handle during processing
stable, easier
salts of ______ drugs are preferred over the weak base form
amine
amines are
volatile and unstable
amines have a short shelf life as
solids
stability and shelf life improve dramatically if an amine is converted to the
hydrochloride salt
The relative concentrations of the ionized and un-ionized forms depend not only on the _____ of the weak acid or base, but also on the _____ of the aqueous solution in which it is dissolved.
pKa, pH
buffered solution
one that resists changes in its pH when small amounts of acid or base are added, or when the solution is diluted
buffer solutions contain an acid to react with added
OH-
buffer solutions contain a base to react with added
H+
buffered solutions can be any weak acid-weak base pair, but are usually
conjugate acid-conjugate base pair
the pH of the buffer depends on the
pKa of the buffering substance and on the relative concentrations of conjugate acid and base
pH value of acidic buffer solutions
7
acidic buffer solutions are commonly made from a
weak acid and one of its salts- often a sodium salt
pKa of buffer solution of acetic acid
4.75
an example of a buffered solution of
acetic acid and sodium acetate
If additional hydrogen ions are added to this solution, they are consumed in the reaction with CH3COO−, and the equilibrium shifts to the
left
- [H+] and pH of the solution remain constant
![<p>left<br>- [H+] and pH of the solution remain constant</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/51903a27-dbaa-429a-8b83-2eb4b5b1a269.png)
what is the pH of an alkaline buffer solution
7