Dentitions
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Tooth Eruption Mechanism
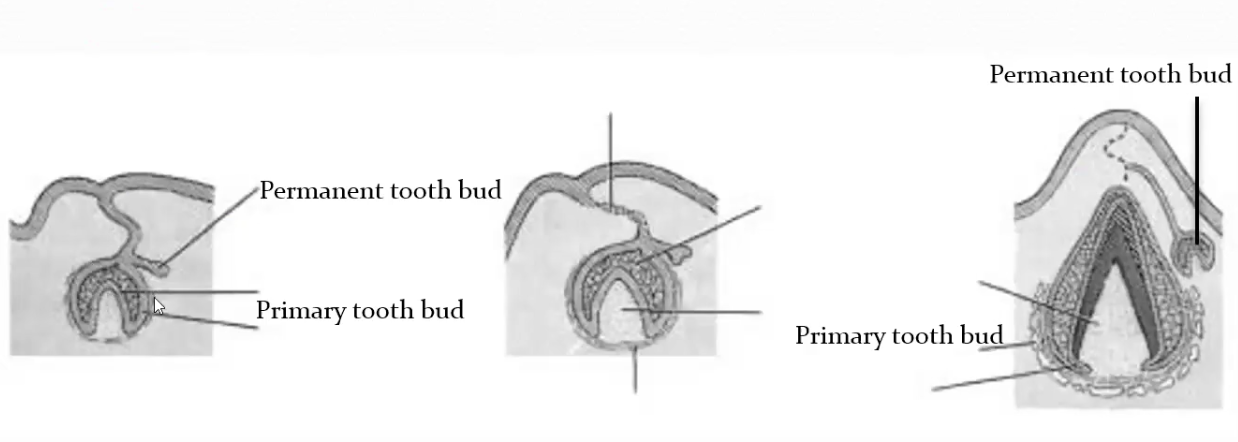
Dental sac is essential for tooth eruption
If not present, there is no eruption
If primary tooth is missing, permanent will be missing as well because it is attached lingually to the primary tooth bud
Erupt Lingually to primary
Coronal part regulates osteoclastogenesis needed for eruption
Basal half regulates osteogenesis needed for eruption
Dental follicle develops into PDL

Eruption sequence of
A/1: Central Incisor
B/2: Lat Incisor
C/3: Canine
D: Primary First Molar
4: First premolar
E: Primary second molar
5: Second Premolar
6: First Molar
7: Second Molar
Primary: A >B>D>C>E
Permanent Maxillary: 6>1>2>4>5>3>7
Permanent Mandibular: 6>1>2>3>4>5>7
How to determine the delay of tooth eruption
Based on age: ± 2 years of when it is supposed to erupt
Contralateral tooth: must erupt within 6 months of contralateral tooth eruption
HOW TO KNOW IT’S BEEN 6 MONTHS?: If the tooth has reached the occlusal plane, it has been 6 months
Causes of Tooth Eruption Delay
Primary: Eruption mechanism defect prevents eruption, not caused by lack of space
Cannot be fixed by ortho, will cause ankylosis
Secondary: Eruption mechanism is normal but there is not enough space to erupt
Can be corrected with ortho
Incisor eruption IMPA angle
What is the average change of mandibular incisor inclination relative to lower border of mandible
Mandibular plane mesial to maxillary plane is gonna move how much more than maxillary molars
90 degrees
Constant
Mandible moves 1.8mm more
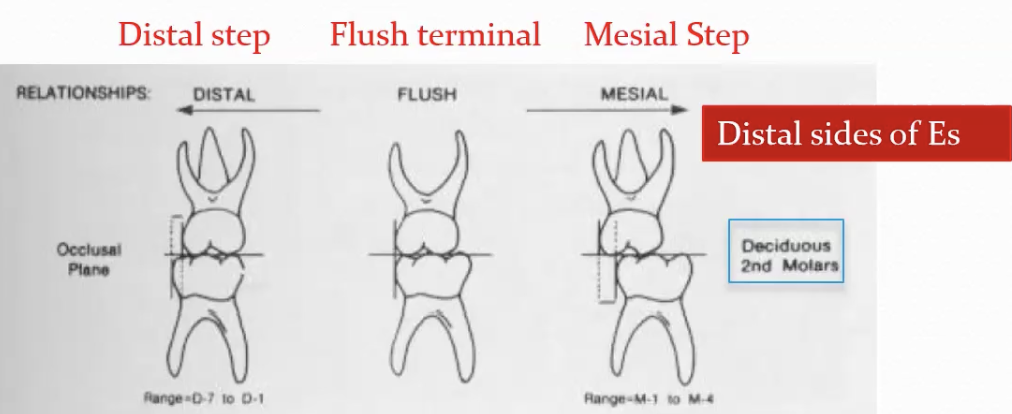
Molar Relationships in Primary Dentition
2nd Primary Molar: Compare to distal side
Flush: both molars align on distal side
Distal step: Mand molar is more distal
Mesial step: Mand molar is more mesial
Permanent 1st Molar in Mixed Dentition: Compare to mesial side
Flush: both molars align on mesial side
Distal Step: Mand molar is more distal
Mesial Step: Mand Molar is more mesial
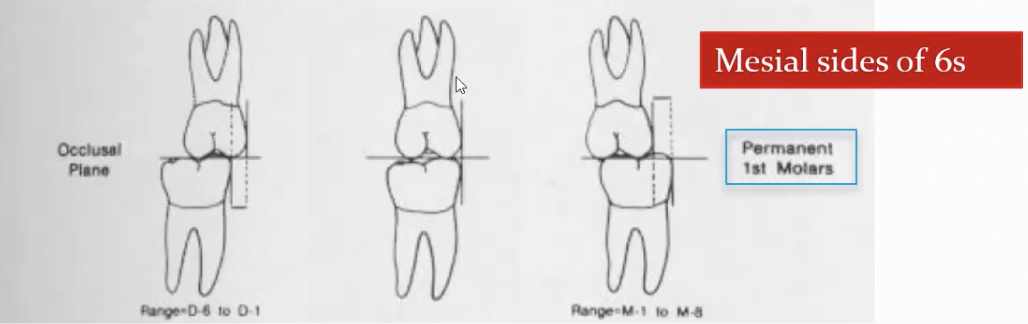
Flush → Leads to 55% Class I and 45% Class II
Distal step → Leads to 0% Class I and 100% Class II
MEsial step →
1mm leads to 75% Class I, 13% Class II and 1% Class 3
> 2mm leads to 61% Class I, 35% Class II and 4% Class III
Leeway Space
Primary molars occupy more space than permanent premolars, leaving some space [(C+D+E) -(3+4+5)]
Mandible: 2.4mm → DOUBLE
Maxilla: 1.2mm
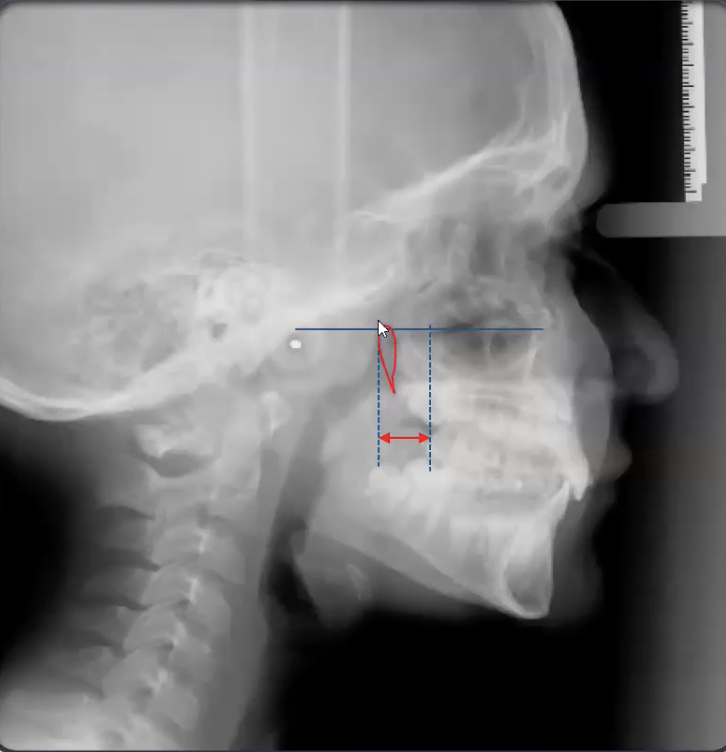
How do you know if 2nd max molars will fit ?
Measure from distal limit of pterygomaxillary fissure to distal limit of maxillary first molars
Age +3mm
Dental Arch Width changes from 6-45yr
6wk-13yo: increase in max and mand inter-canine and inter-molar widths
Boys do not have mand intercanine width increase, otherwise their increases are bigger
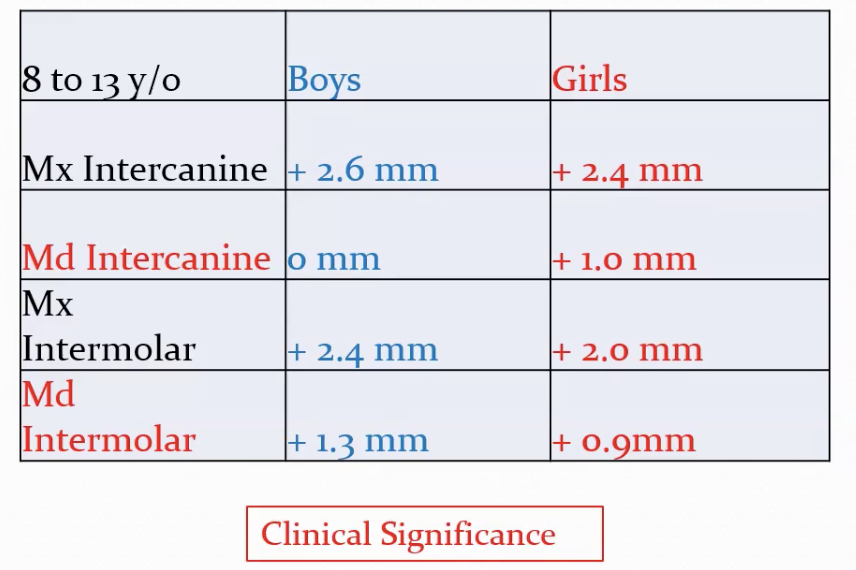
after 13yo: slight decrease in inter-canine width; stable inter-molar width
Why may untreated normal occlusion result in crowding from 9-20 yo
Decrease in arch length (anterior and posterior segment)
Increase in overjet and overbite
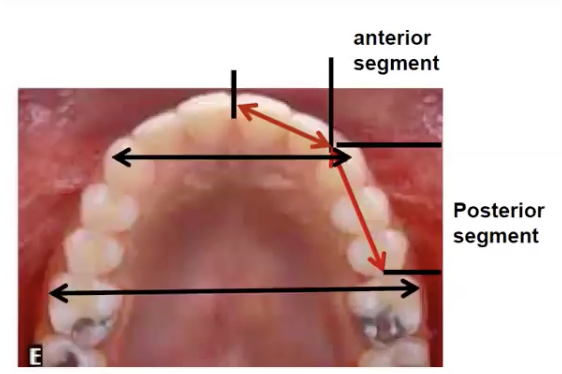
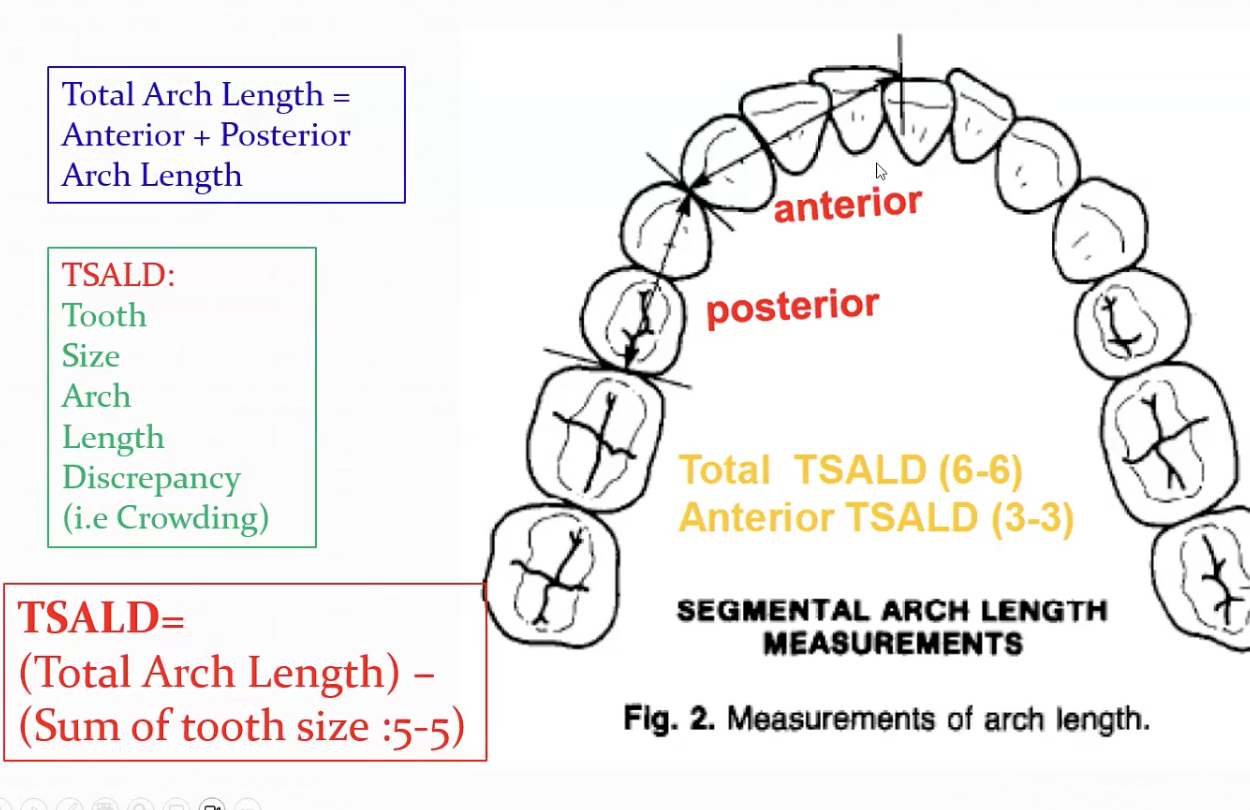
Vertical growth increase
Not related to 3rd molars
Causes of changes in occlusion 26-45yo
OJ: did not change
OB: increased significantly in females
Crowding is worse in mandibular
Mesial mgration of dentition