Chapter 3: Nature of Materials
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Levels of Structure
Atom → Molecule/Crystal/Amorphous → Grain
Atoms
made of a dense nucleus consisting of protons and neutrons
Valence Electrons
electrons in the outermost shell that are involved with bonding
3 types of Primary Bonds
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
Ionic and Covalent bonds are typically found in _____ and _____
ceramics, polymers
Metallic bonds are typically found in ______ and ______
metals, alloys
Ionic bond
Electrons are transferred
Characteristics of materials joined by ionic bonds
High Density
Moderate to high strength
High hardness
Brittleness
High melting pint
LOW electrical + thermal conductivity
Covalent Bonds
Electron sharing
Characteristics of materials joined by covalent bonds
high strength
high melting point
brittle
conductivity depends on bond strength
Metallic bond
Valence electrons are not bound and free to move
Characteristics of materials joined by metallic bonds
highly mobile electrons
high electrical + thermal conductivity
bond strength, material strength, and melting point vary
low hardness
Van der Waals Forces
secondary/intermolecular bond formed between molecules that possess a nonsymmetrical distribution of electrical charge
Molecular Structures
Distinct number of atoms that are held together by primary bonds
Crystalline Structure
Atoms are arranged in a three-dimensional geometric arrays
Amorphous structures
Having a certain degree of local order, but no periodically ordered arrangement
Unit Cell
a unit building block that is repeated throughout space
Lattice
the arrangement of atoms in a three-dimensional geometric array
4 types of lattice structure
Simple Cubic (SC)
Body-centered cubic (BCC)
Face-centered cubic (FCC)
Hexagonal close-packed (HCP)
Packing efficiency of Simple Cubic
52%
Packing efficiency of Body-centered Cubic
68%
Packing efficiency of Face-centered Cubic
74%
Packing efficiency of Hexagonal close-packed
74%
Grains
small continuous regions of solid
Grain Boundaries
Surfaces that divide grains
Smallest unit of structure that can be observed by a light microscope
grains
(T/F) Small grain size can improve mechanical properties
True
Elastic Deformation
Temporary deformation of materials
Plastic Deformation
Permanent deformation of materials
Things mechanical properties are dependent on
Types of Lattice
Interatomic Forces (bond strength)
Spacing between adjacent planes
Density of atoms on various planes
Poisson’s Ratio
a measure of how much a material will shrink in one direction when it is stretched in another direction
Slip
sliding of blocks of crystal over one other along definite crystallographic planes
Dislocation
a type of defect within a crystal structure, specifically representing an irregularity in the arrangement of atoms
Line Type Defects
Localized imperfections in crystal
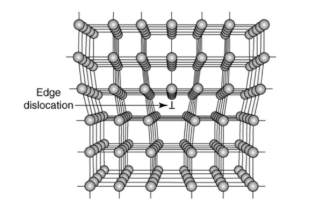
Edge Dislocation
The terminal edges of extra half-planes of atoms
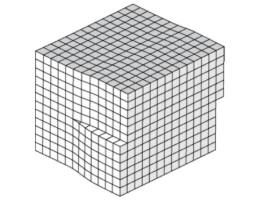
Screw Dislocation
partial tearing of the crystal plane
Point Defect
a localized imperfection in a crystal structure
Types of point defects
Vacancy
Interstitial
Substitutional
Vacancy
missing atoms
Interstitial
extra atoms
Substitutional
different atoms replace host atoms
Strain/Work Hardening
The strengthening of metals through plastic deformation
Anisotropic
properties that vary with direction (undesirable)
Isotropic
properties that are uniform in all directions
Fracture
a material has cracked or broken apart due to stress
2 types of fractures
ductile fracture
brittle fracture
Ductile Fracture
plastic deformation occurs before the material breaks
Brittle Fracture
the break occurs before plastic deformation
Recrystallization
the process of reducing the internal energy through new crystal formation
Cold working
metals are plastically deformed at temperature below their recrystallization
Hot working
metals are plastically deformed above their recrystallization temperature
(T/F) Mechanical properties increase as grain size increases
False
3 ways a metal might respond to the addition of another element
Insoluble
Some degree of solubility
Intermetallic compound
Insoluble
base metal and alloying addition each maintain their individual identities, structure and properties.
Some Degree of Solubility
Two materials form a solid solution, where alloying element dissolve in metal base
Interstitial Solid Solution
the alloy element atoms squeeze into open spaces between atoms of base metal lattice
Substitutional solid solution
the alloy element atoms occupy lattice site normally filled by atoms of base metal
Intermetallic compound
atoms of alloying element interact with atoms of base metal in
definite proportions and indefinite geometric relationships
Intermetallic Compound Characteristics
bonded w/ ionic or covalent
tend to be hard, brittle and high strength
Electrical Conductivity
the net movement of a charge through a material
Electrical Resistance depends on…
lattice imperfections and temperature
Doping
enhancing the electrical conductivity of intrinsic semiconductor by adding impurity atoms