Exam 2 Confocal Microscopy: Lec. 7 Brightfield, Phase Contrast, Polarized light, DIC
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
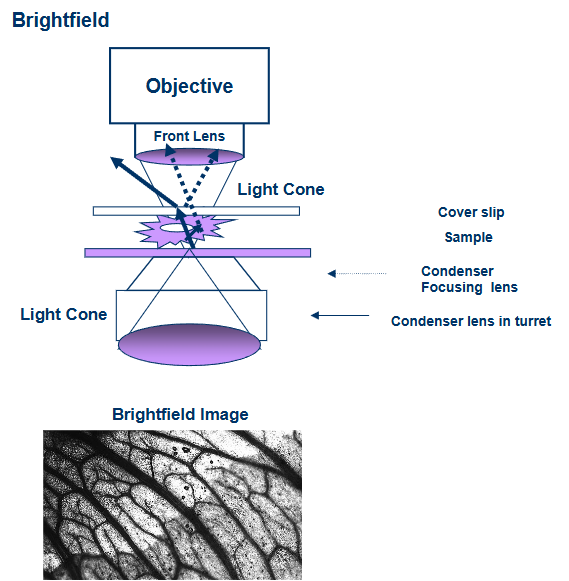
what are the four types of transmitted light imaging
1) brightfield
2) phase contrast
3) polarized light
4)differential interference contrast (DIC)
what is transmitted light image dependent on?
how light interacts with the sample
how light interacts with the specimen
how light interacts with the optics
visualizing the types of transmitted light
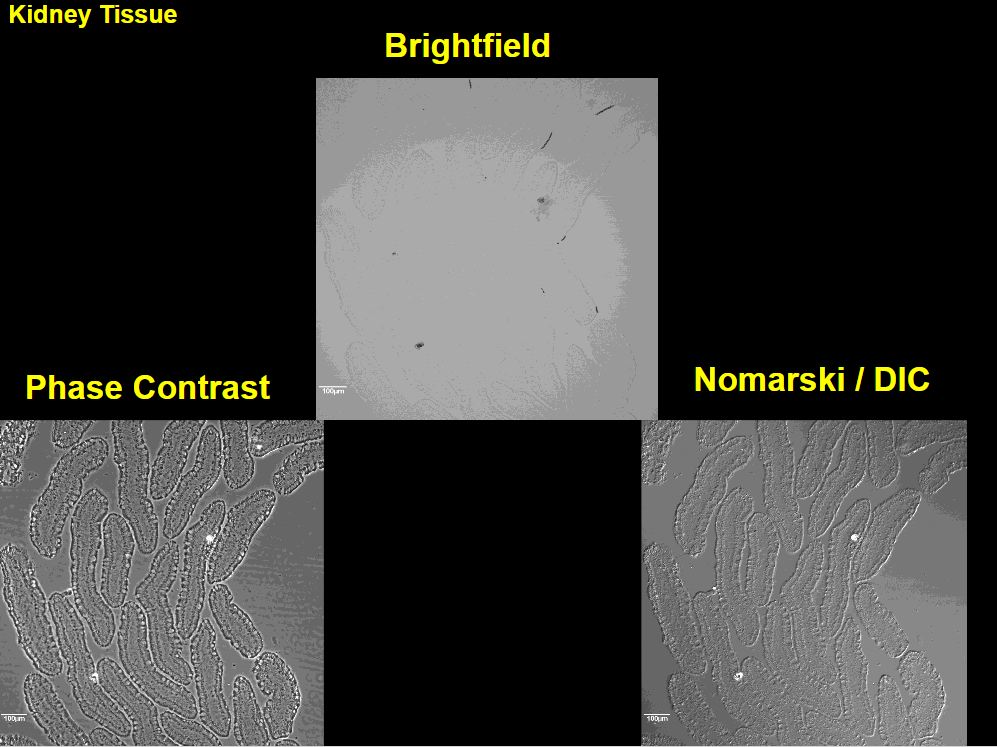

transmitted light interacting with sample
image formed when the undeviated background light is focused in the same image plane as the deviated light from the sample and interference takes place
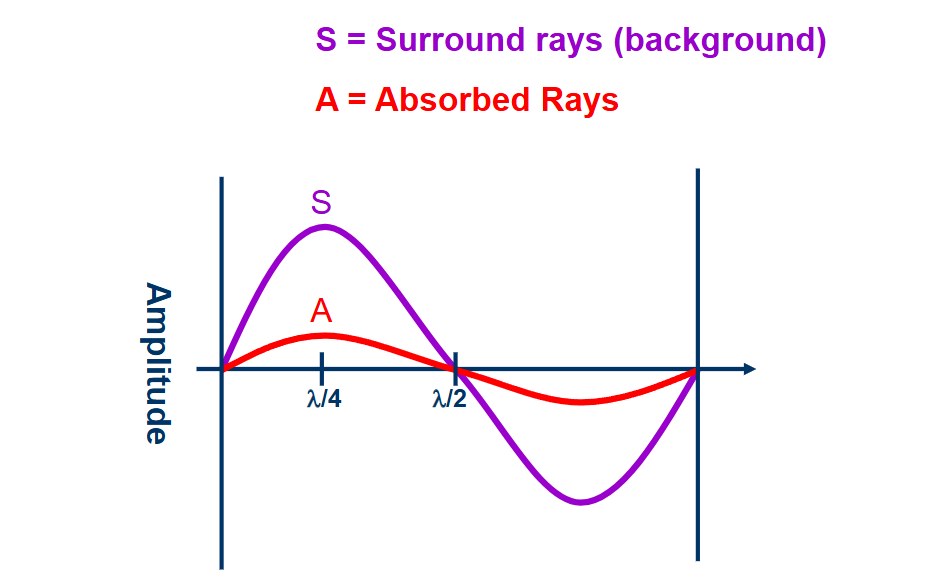
amplitutde
wave height
changes in amplitutde…
change in brightness
S and A waves
light passing through the sample is absorbed and therefore we see a decrease in intensity when compared to the brighter surrounding light
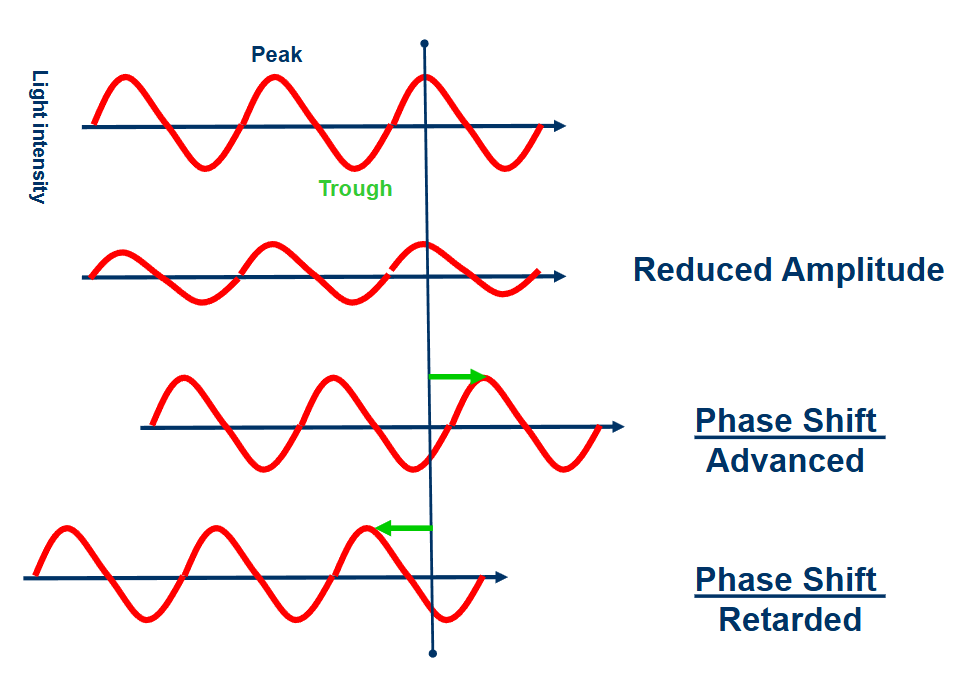
phase shifts
constructive intereference
when light waves combine, their intensities are added together
if peaks and troughs of both waves are near the same position constructive interefencce occurs (A+B=C)
the resulting ray (C) will be more intense (brighter) than the individual waves
destructive intereference
if peaks and troughs of both waves are in oppositve positions (out of phase), then deconstructive intereference occurs (A+B=c)
the resulting ray c will be less intense (darker) then the individual waves
D and S Wave definitions
S wave- undeviated or surround wave
D wave- deviated or diffracted wave
P waves
S+ D
When the waves recombine, they undergo interference and generate a resultant Particle wave
only when amplitutde of P is sign. different from S can we visually see the structures causing the interference
phase contrast optics: phase annulus in condenser
restricts illumination light to a ring
phase contrast optics: phase plate in objective
ring of low refractive index material
phase advances S waves only
phase contrast microscopy
optics enhance the phase shift between the undeviated surrounding light (S) and the deviated light (d) that interact with sample
deviated light is slowed (phase retarted) by interaction with the sample
S waves are faster (phase advanced) using optics with low refractive index
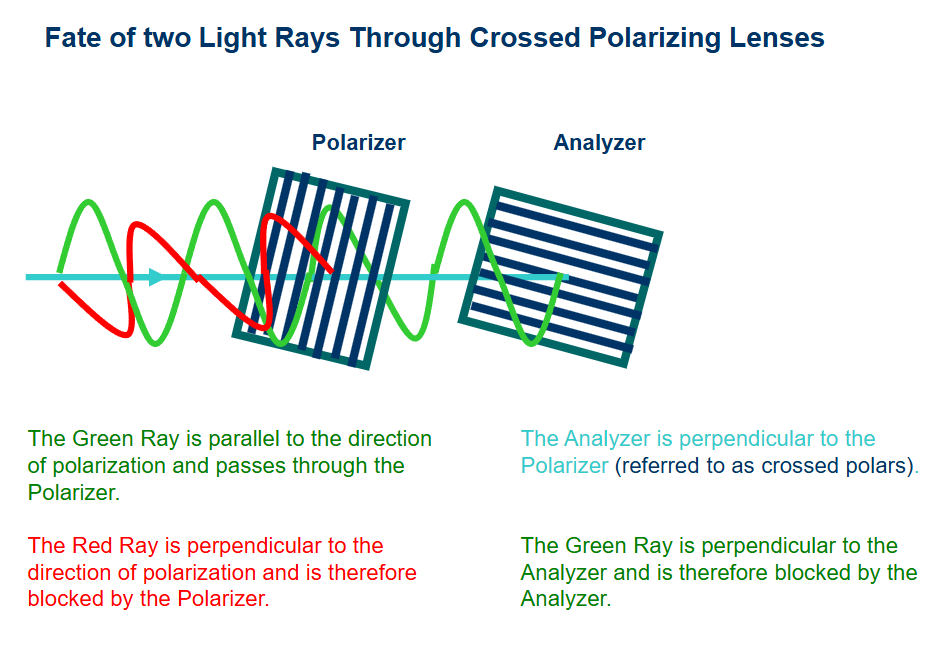
lineraly polarized light
when all light waves vibrate in a single plane, this is referred to as linearly polarized light
light from most illuminators - a halogen lamp is randomly polarized
randomly polarized light may also be referred to as unpolarized/non-polarized
polarizing lenses
birefringence
in some crystals (quartz, calcite) atoms are ordered in a precise geometic arrangement
ordered arrangment can result in direction-dependent differences in refractive index within a crysal
birefringence occurs when light entering the crystal lattice is refracted into two polarized rays
birefringence-onlique incident light results in O and E rays that
are linearly polarized
have perpendicular vibration planes to each other
have different trajectories (path) through the crystal
are phase shifted to each other
examples of birefringence in biology
most ordered macromolecular assemblies - lipid bilayers, bundles of microtubules, plant cell walls, starch granules
pretty uncommon in biology - more common for geology to have polarized light microscopy
Differential intereference contrast microscopy (DIC)
uses a birefringent crystal to generate the E and O rays
small difference s in refractive index and thickness of the sample will result in the E and O rays experincing a phase shift relative to each other
DIC picture
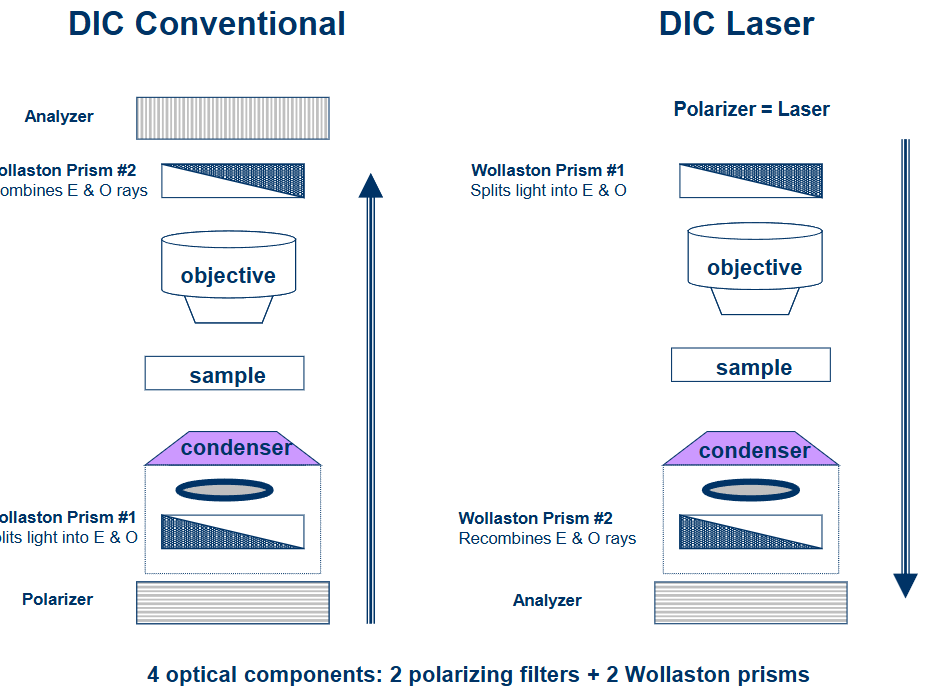
compare and contrast enhancing optics
both DIC and phase contast techniques depend on phase differences within the sample
DIC - amplitutde change due to phase shift of two perpendicullary polarized, deviated light rays (E and O waves)
phase contrast- amplitude change after destructive interference of deviated rays (D waves ) and undeviated rays (S wabes)