Organic Chemistry: Aldol, Claisen, and Michael Reactions Overview, chapter 21 & 22, ch 20, ch 19, ch 18 orgo chem, Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Functional Groups, and Stereochemistry
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
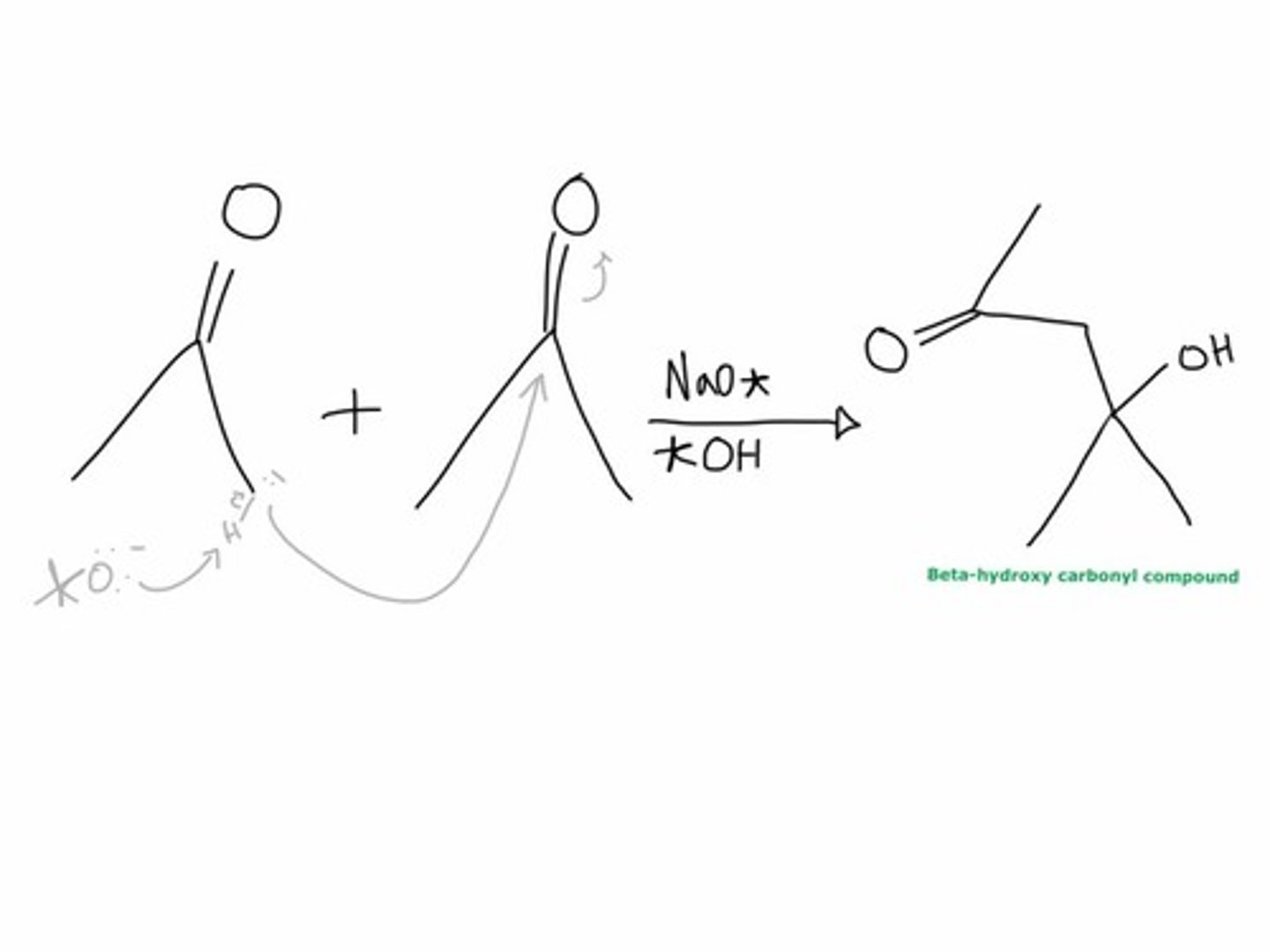
General Aldol reaction
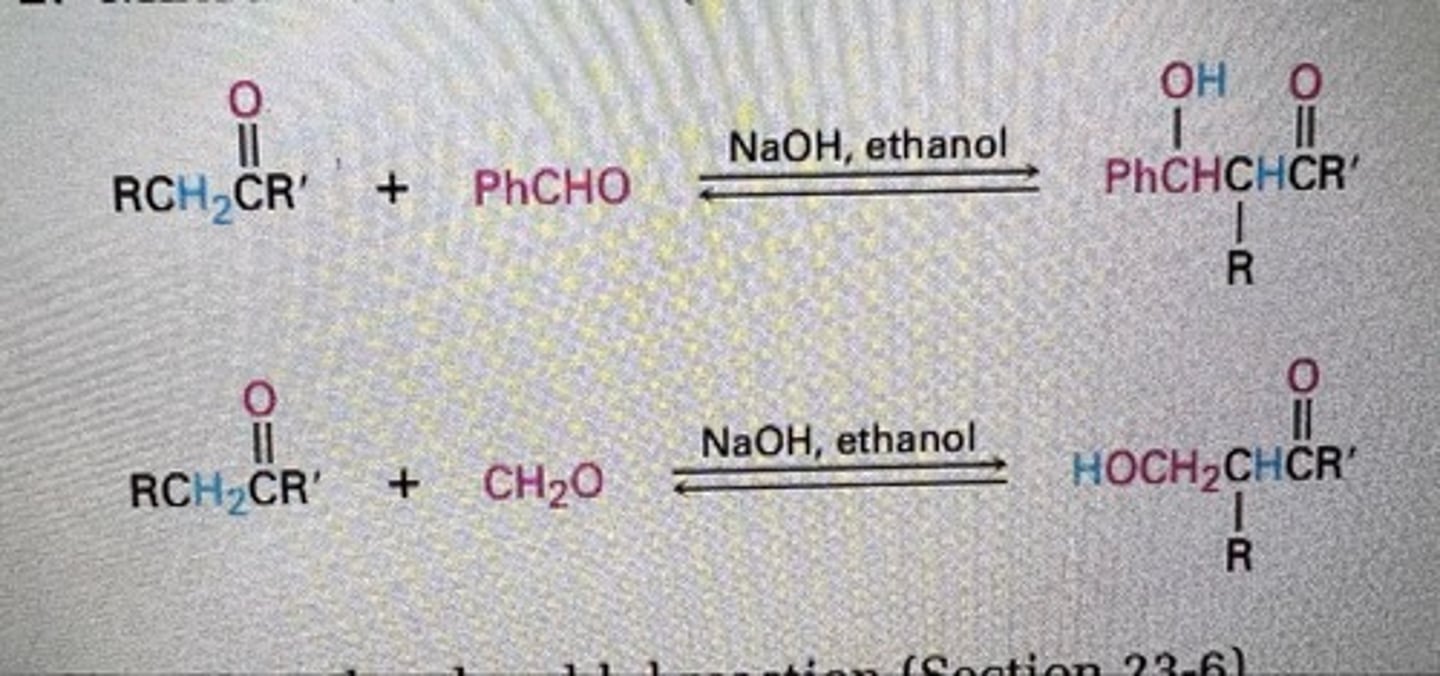
Mixed aldol reaction (Section 23-5)
Intramolecular aldol reaction
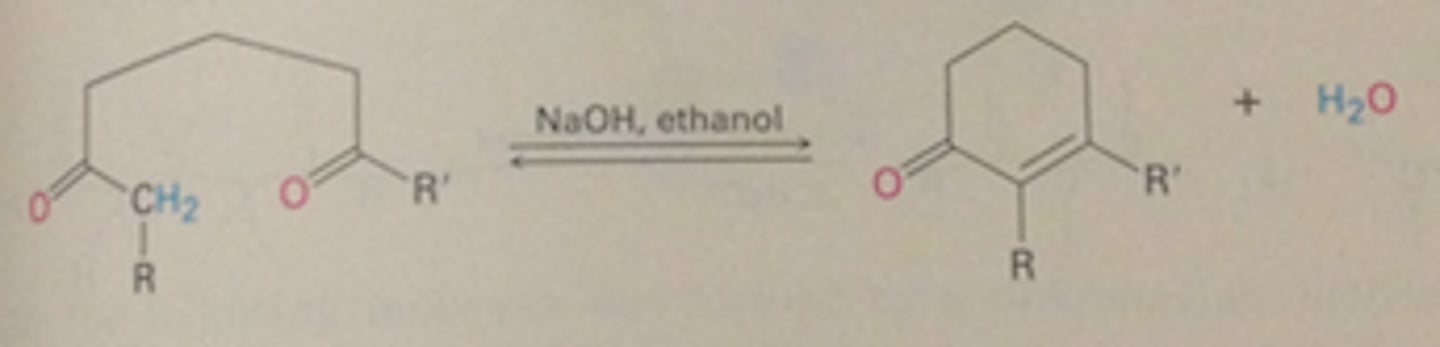
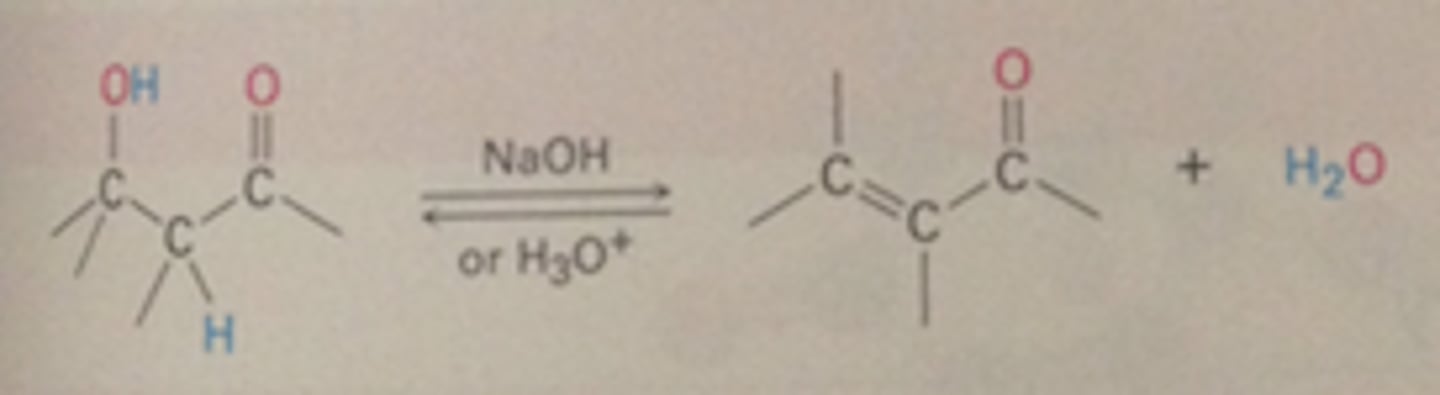
Dehydration of aldol products
Claisen condensation reaction (Section
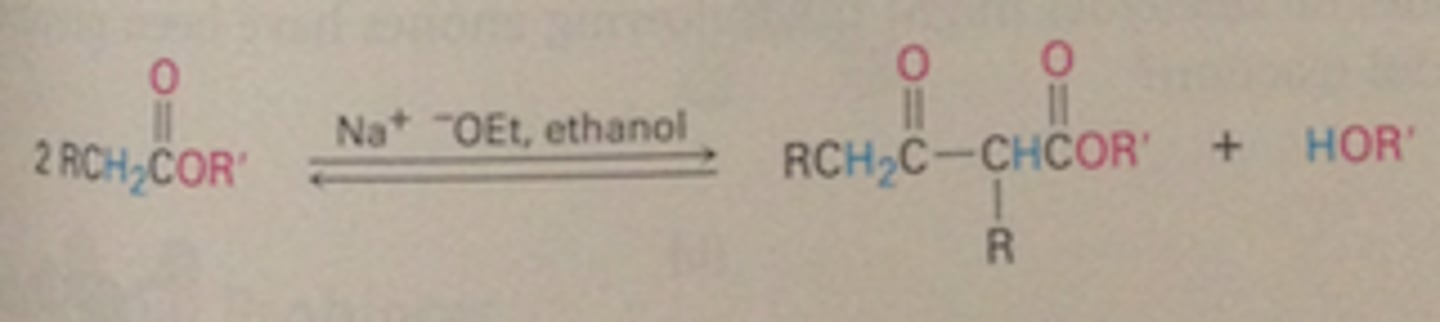
Mixed Claisen condensation reaction (Section

Intramolecular Claisen condensation (Dieckmann cyclization;

Michael reaction

Carbonyl condensations with enamines (Stork
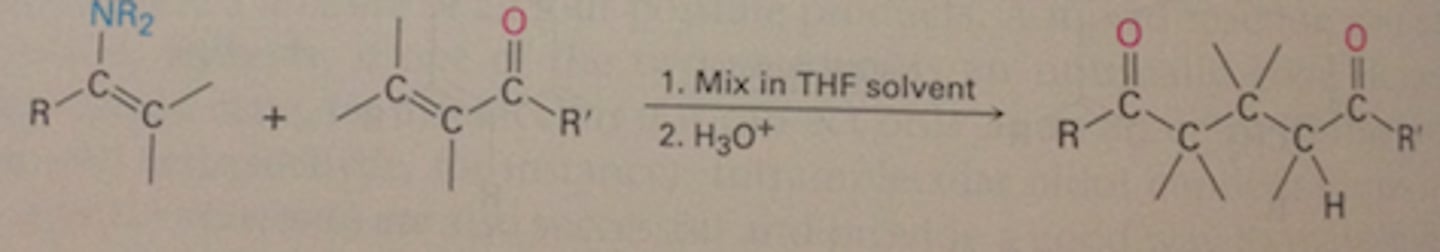
Naming Carboxylic acid
-ic acid
(-carboxylic acid)
Acid halide nomenclature
-oyl halide
(-carbonyl halide)
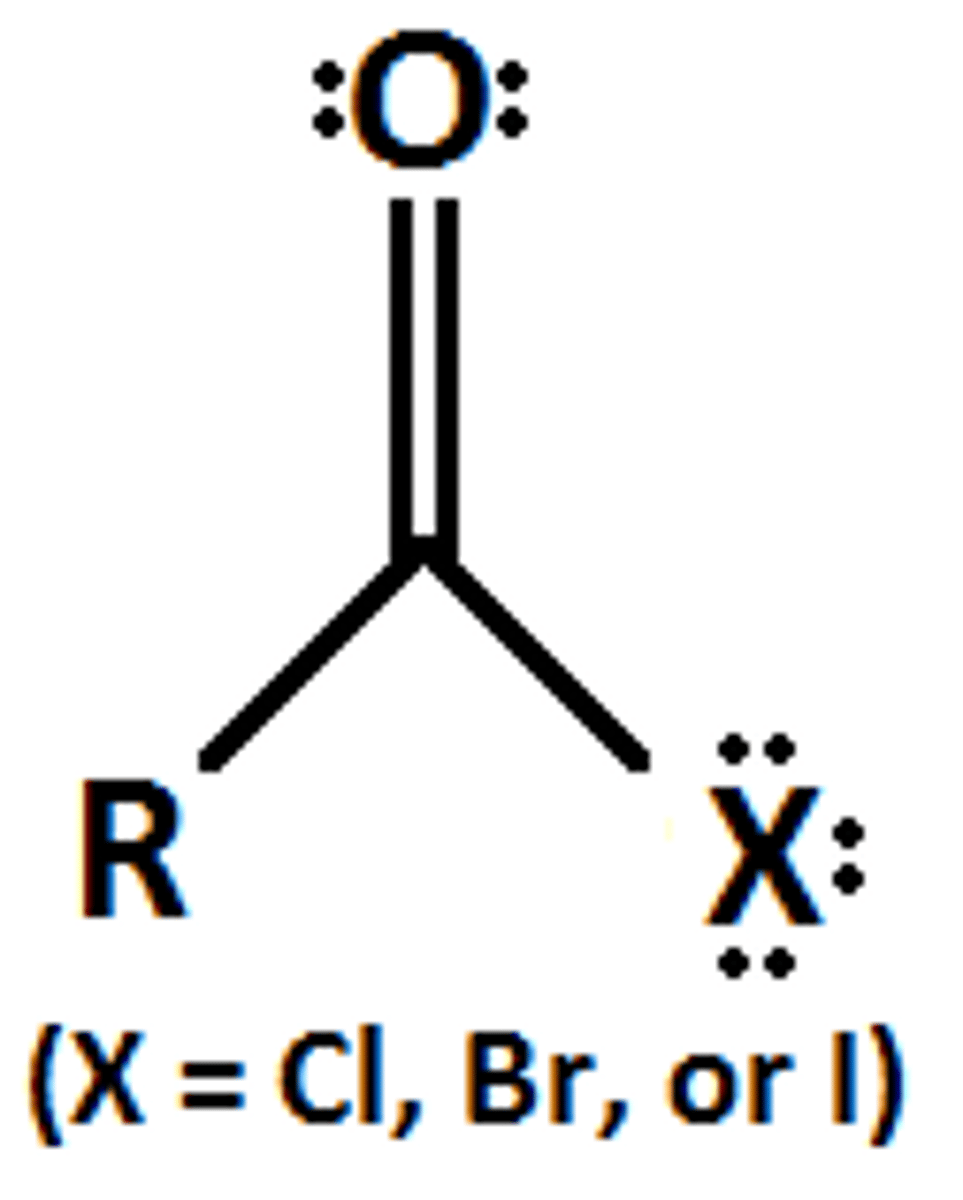
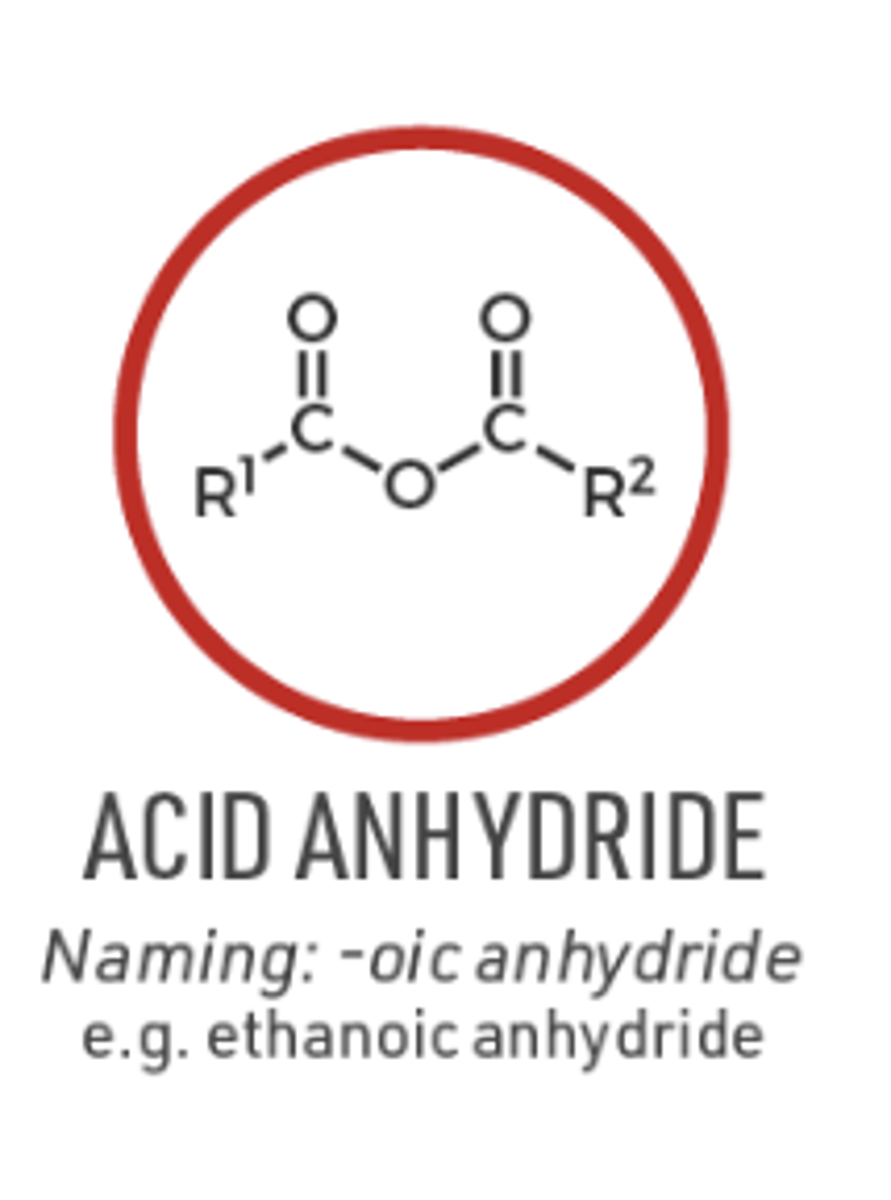
naming Acid anhydride
anhydride
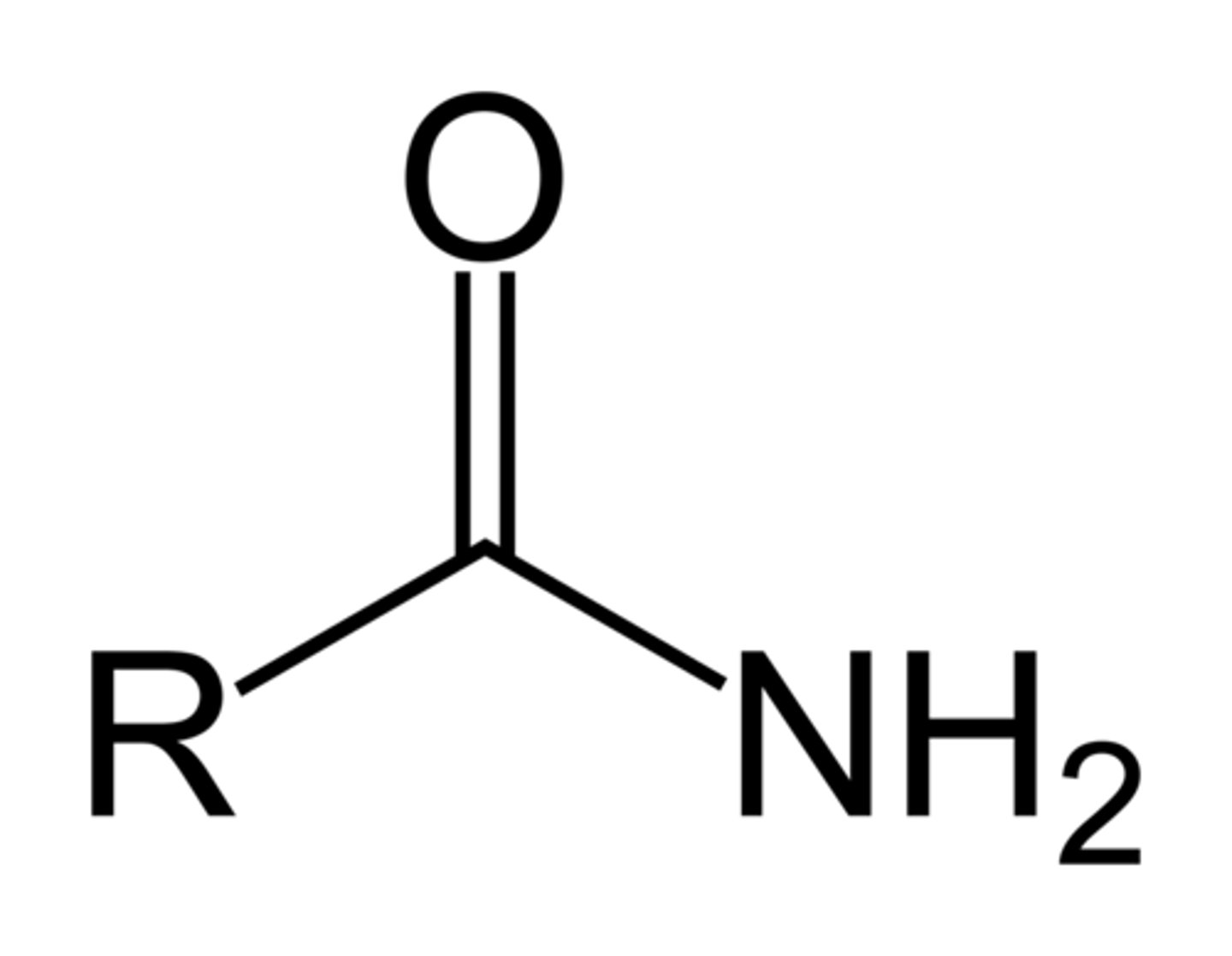
naming Amide
-amide
(-carboxamide)
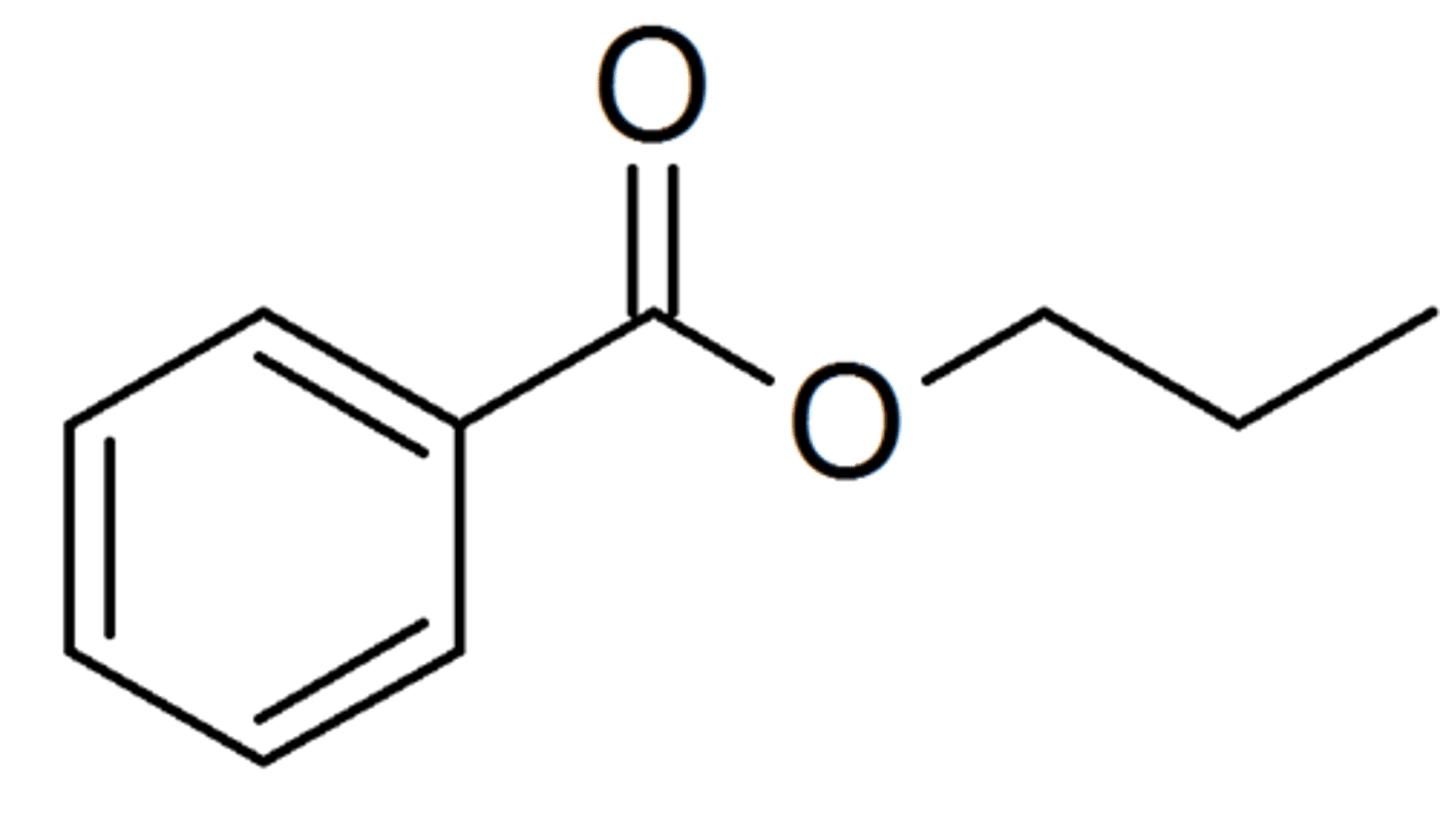
naming Ester
-oate
(-carboxylate)
naming Thioester
-thioate
(-carbothioate)

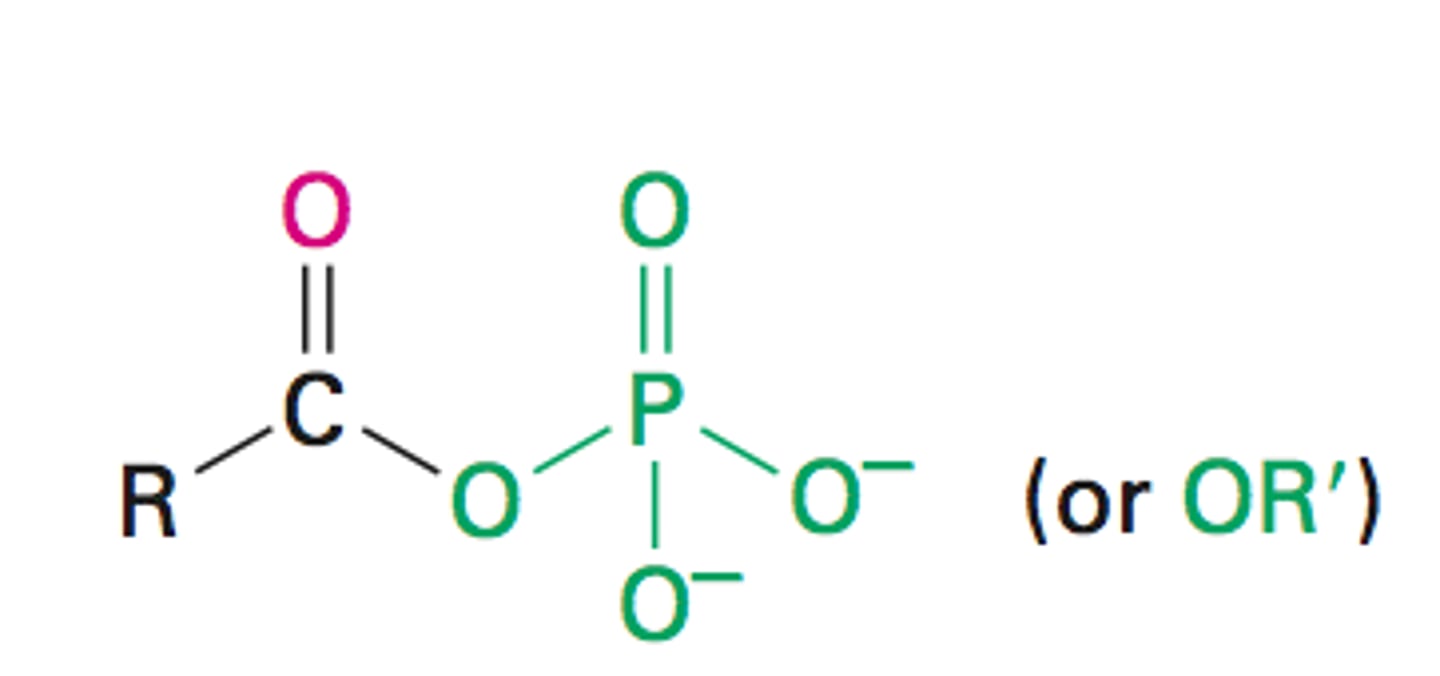
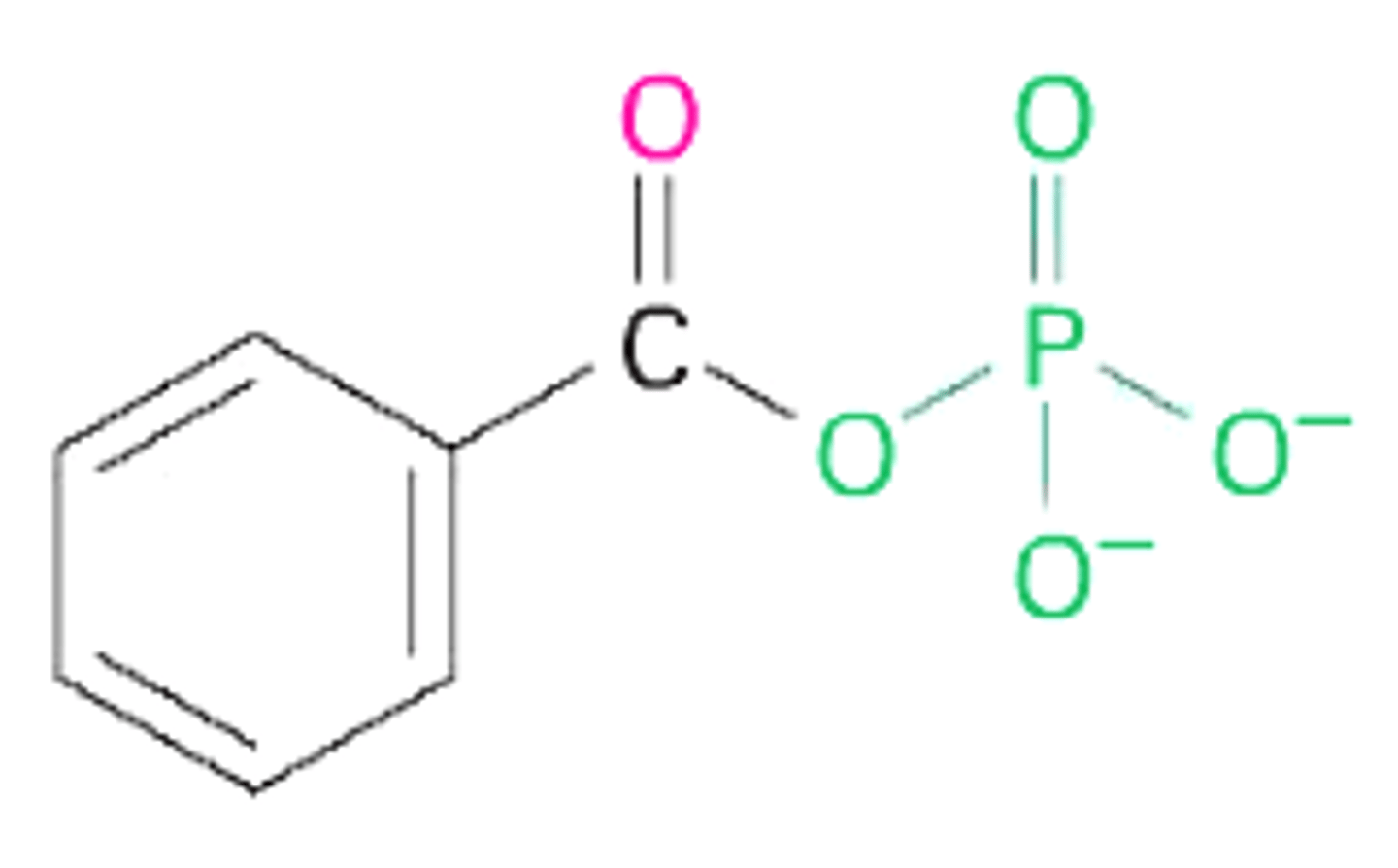
Naming Acyl phosphate
-oyl phosphate
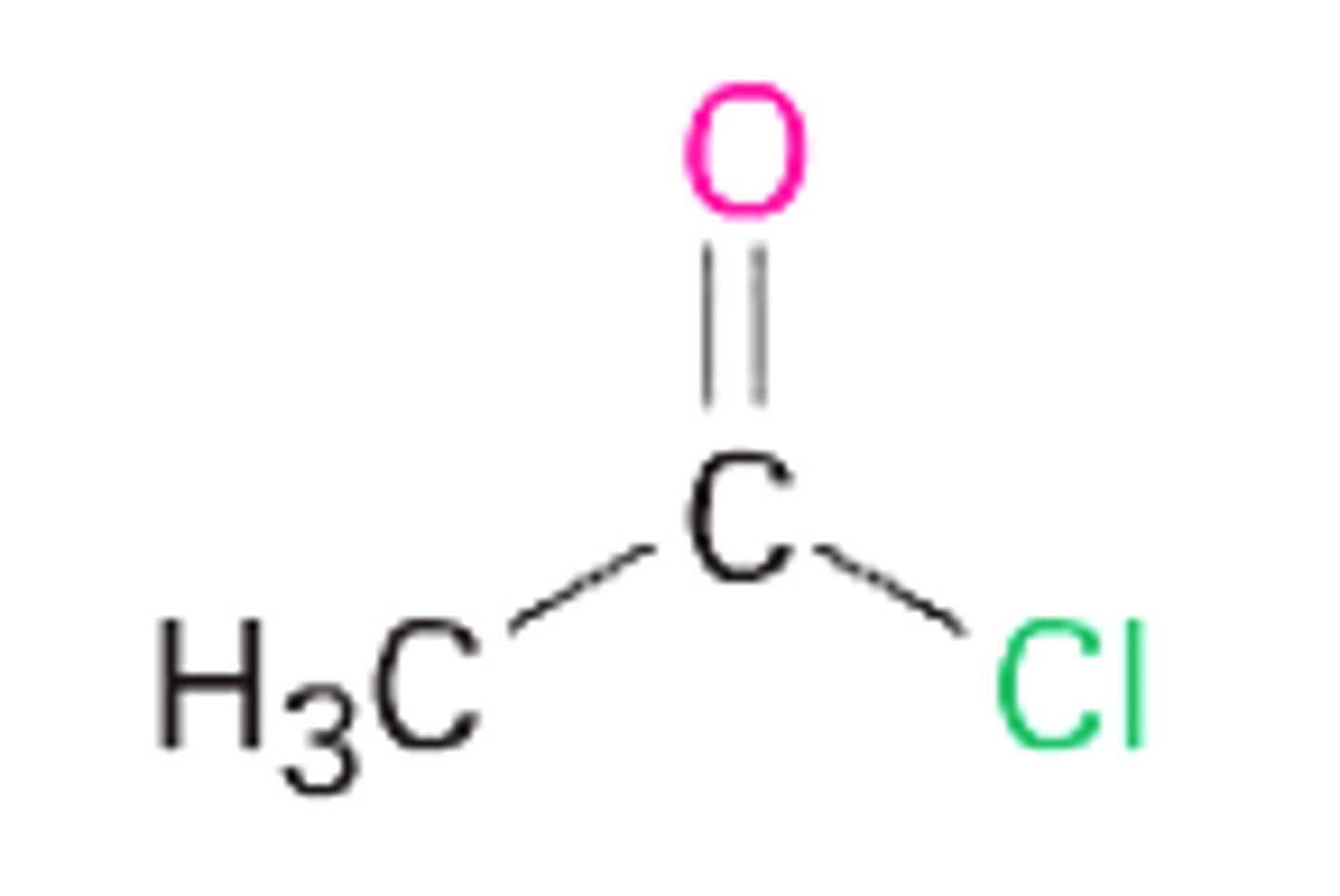
acetyl chloride
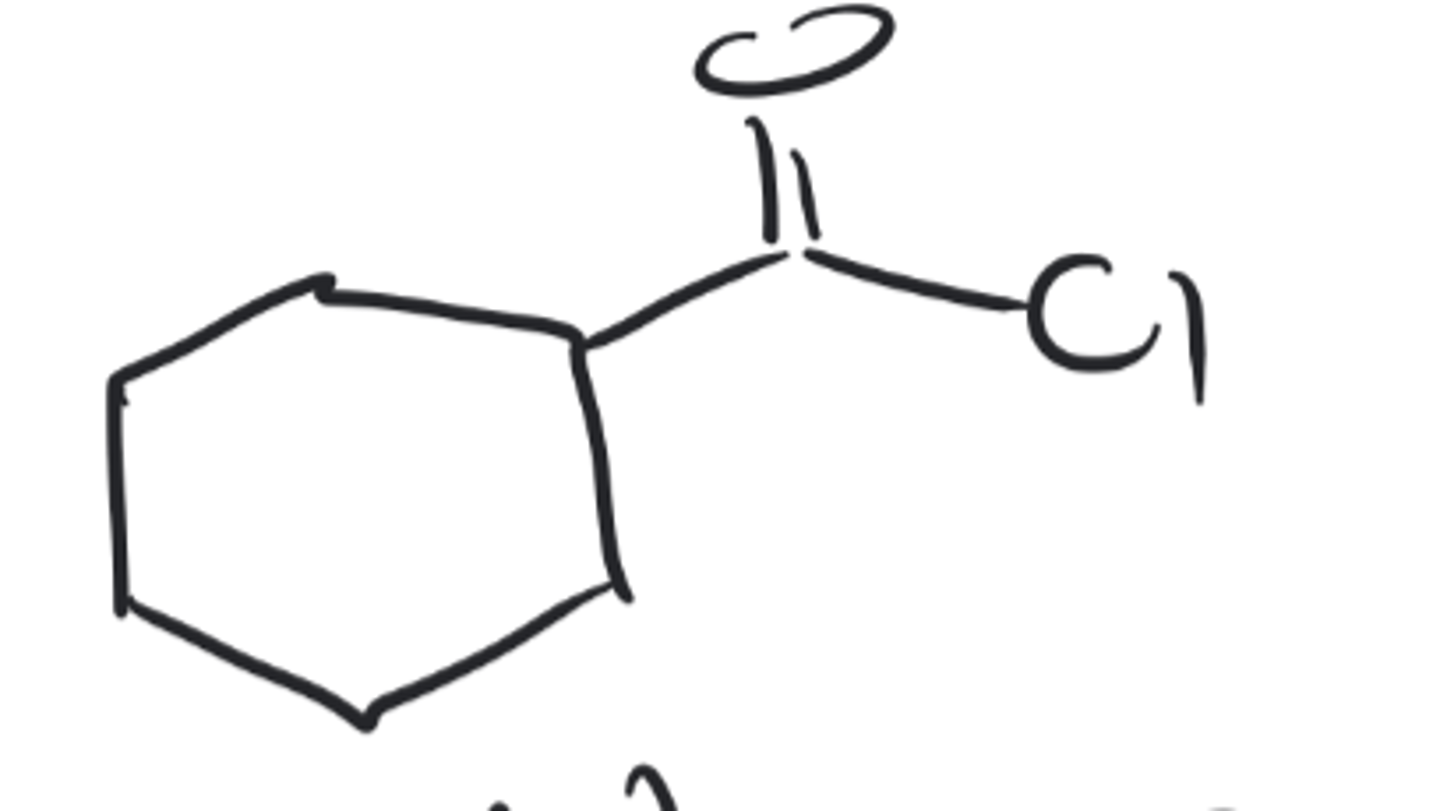
cyclohexane carbonyl chloride
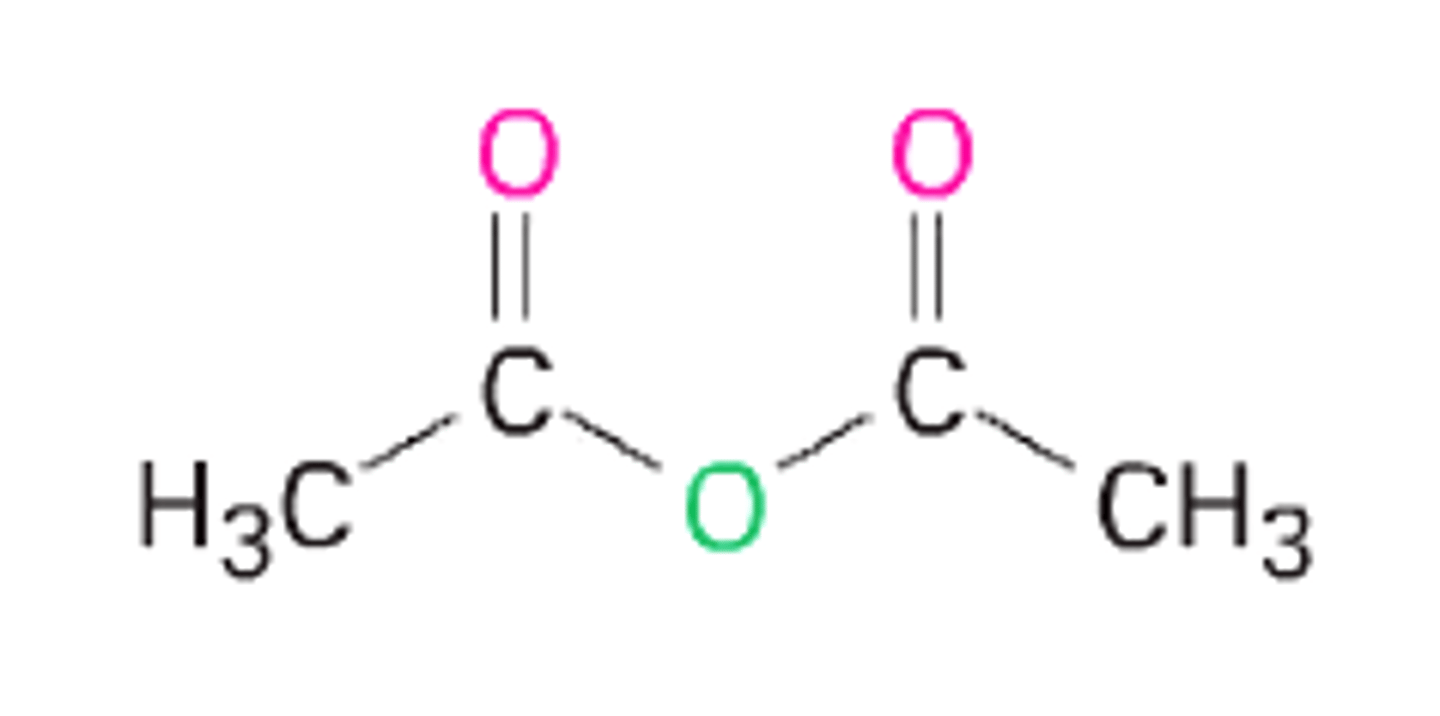
acetic anhydride
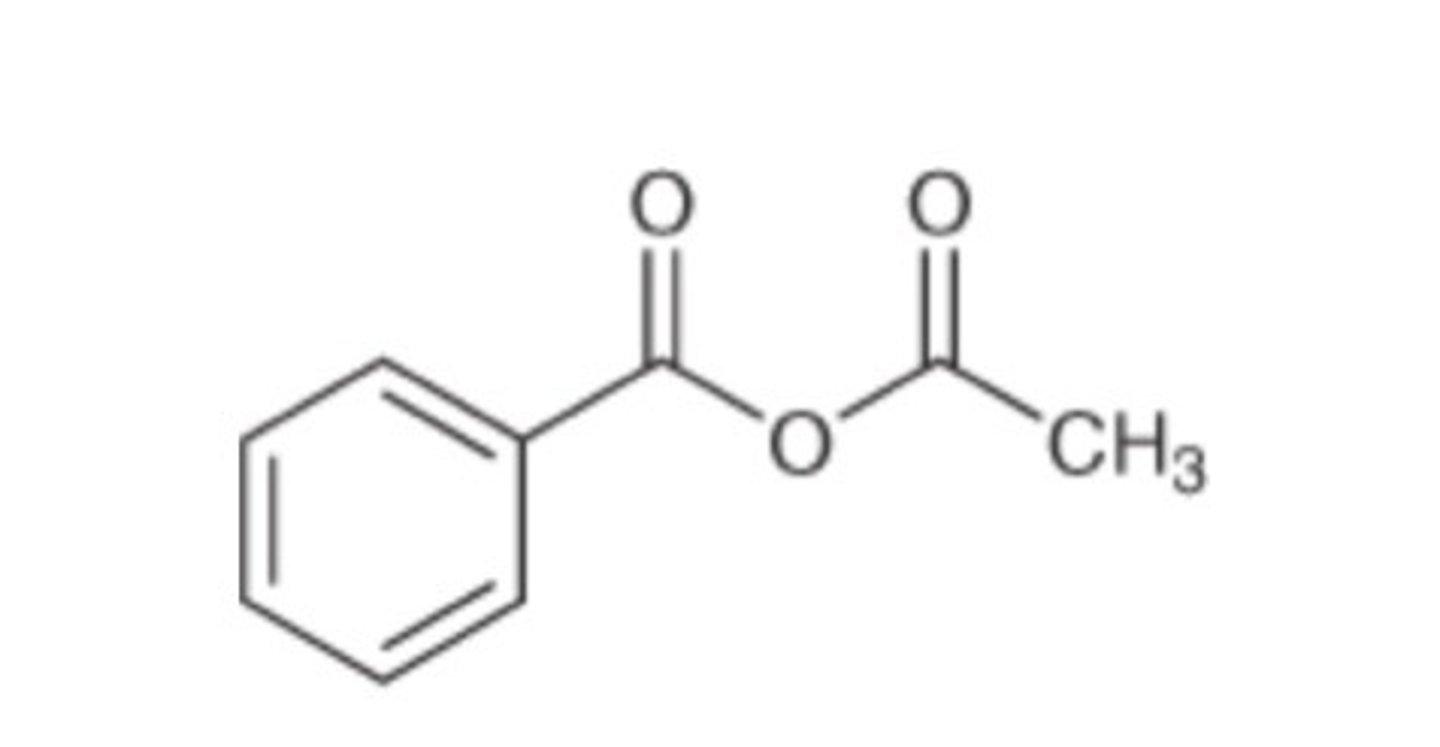
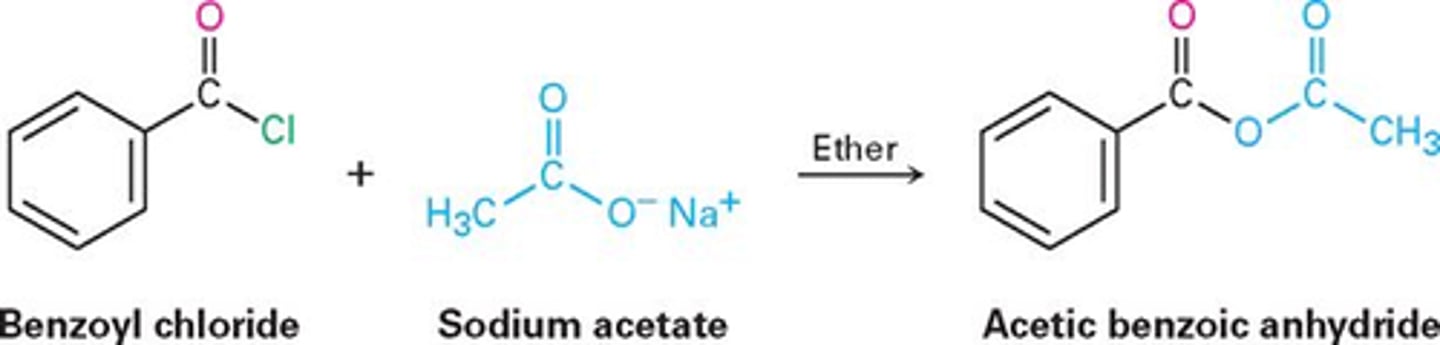
acetic benzoic anhydride
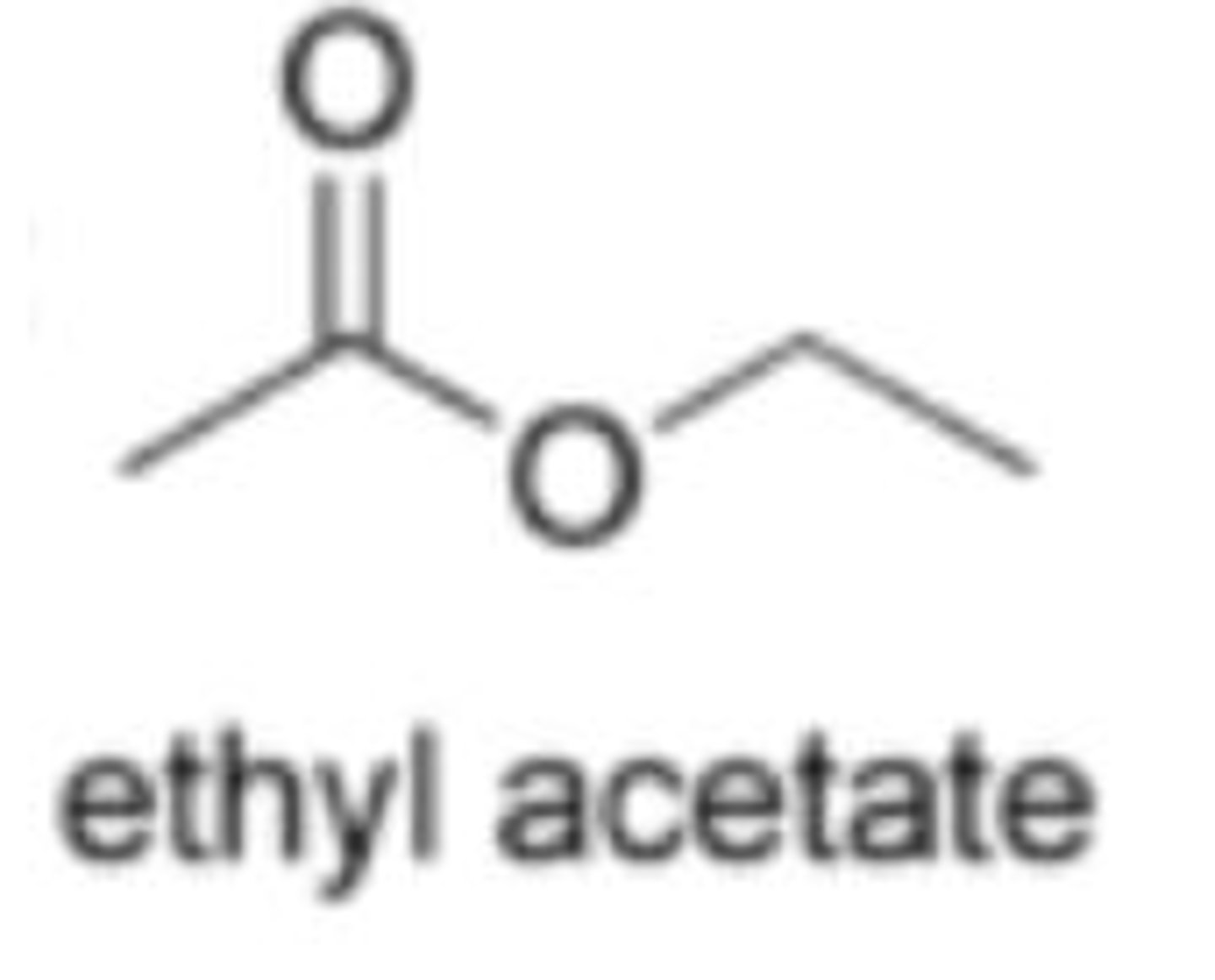
ethyl acetate
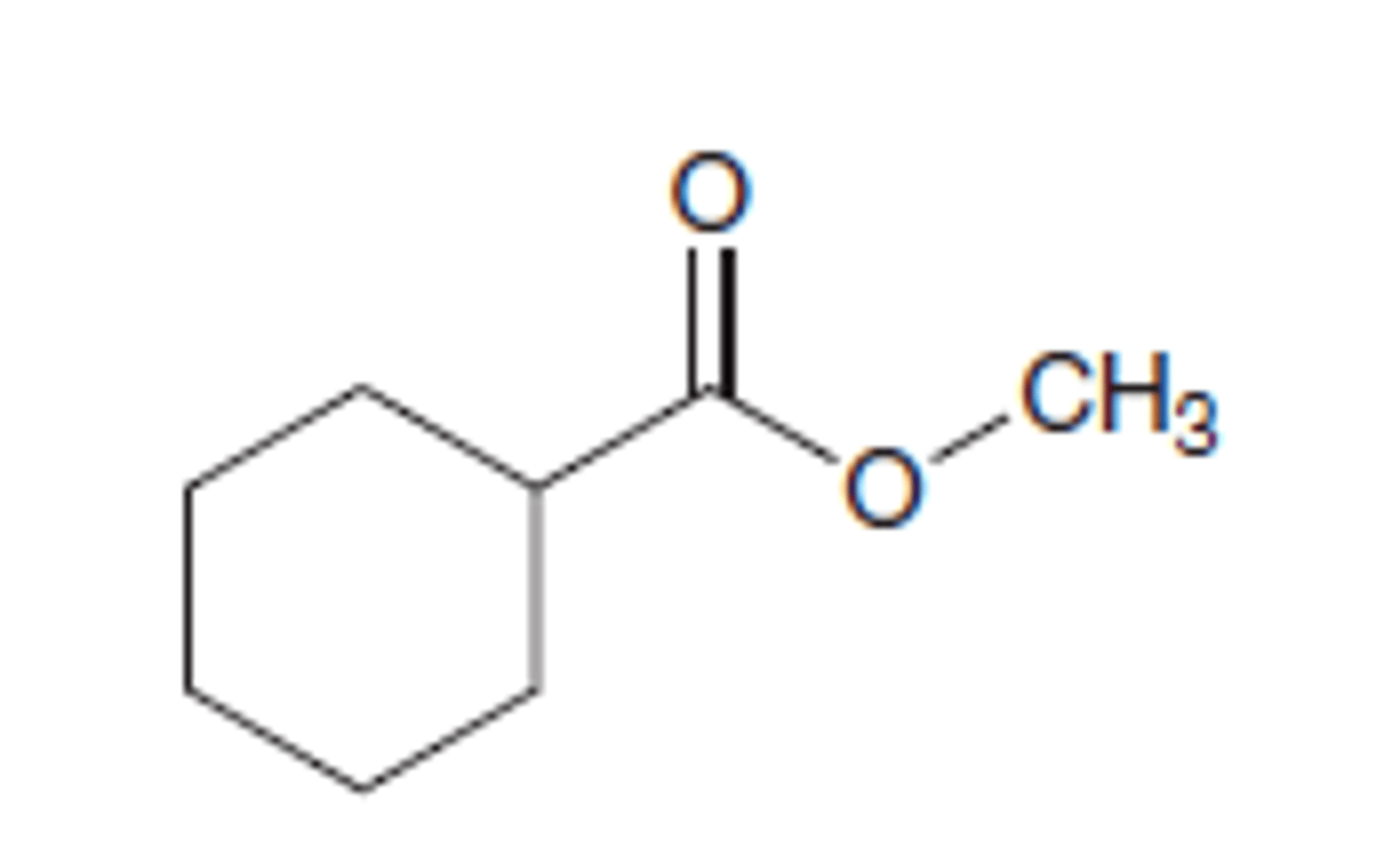
methyl cyclohexane carboxylate
acetamide
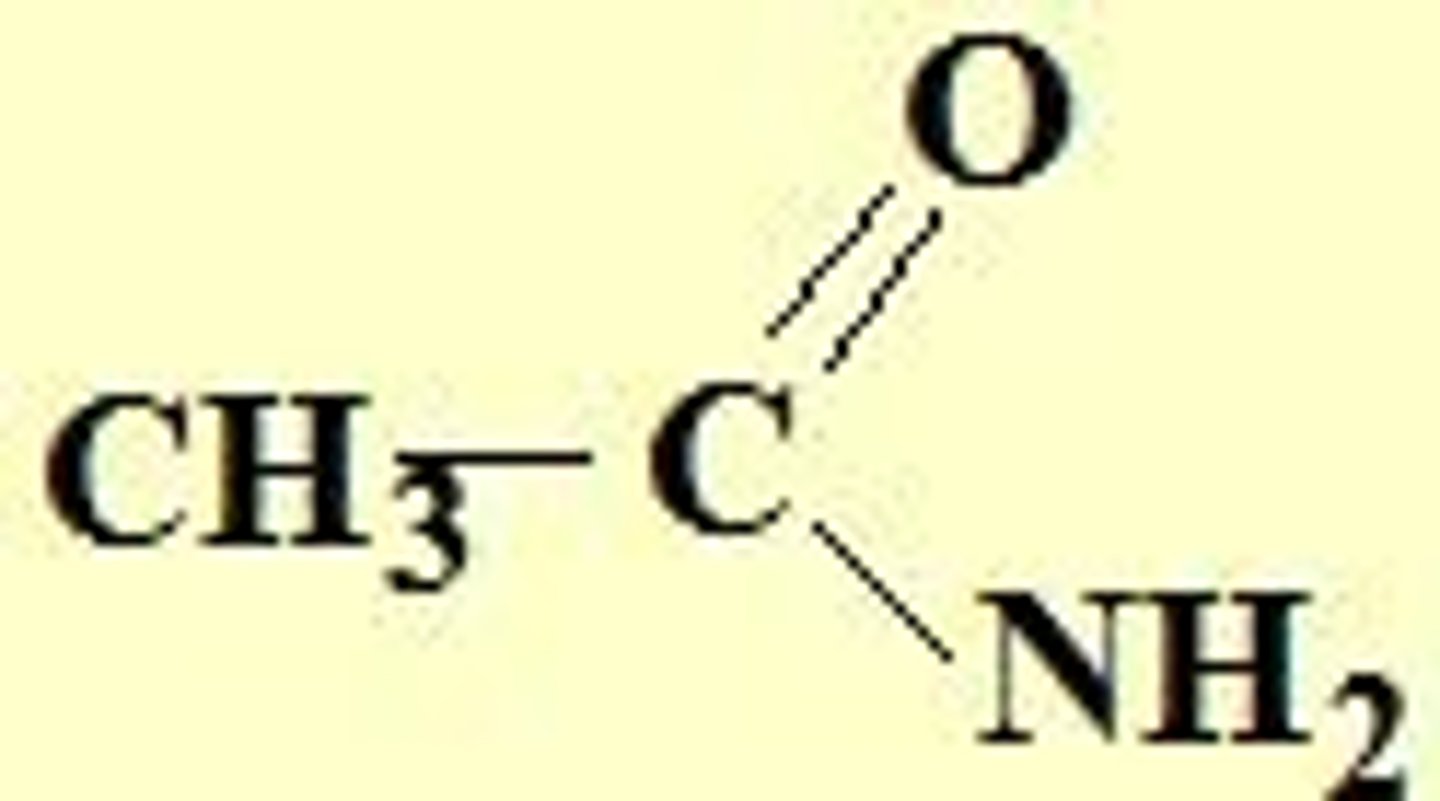
n-methyl propanamide

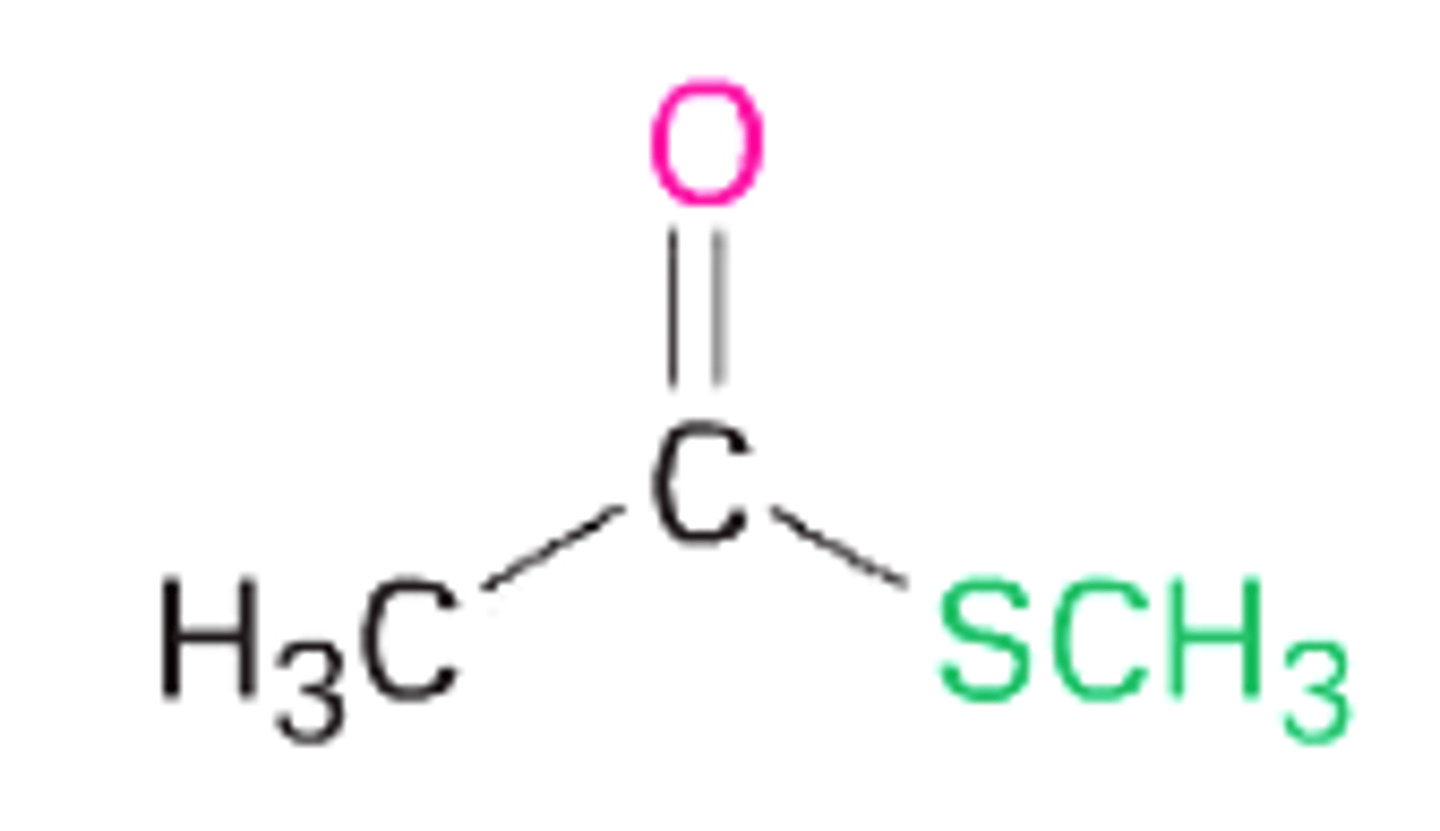
methyl thioacetate
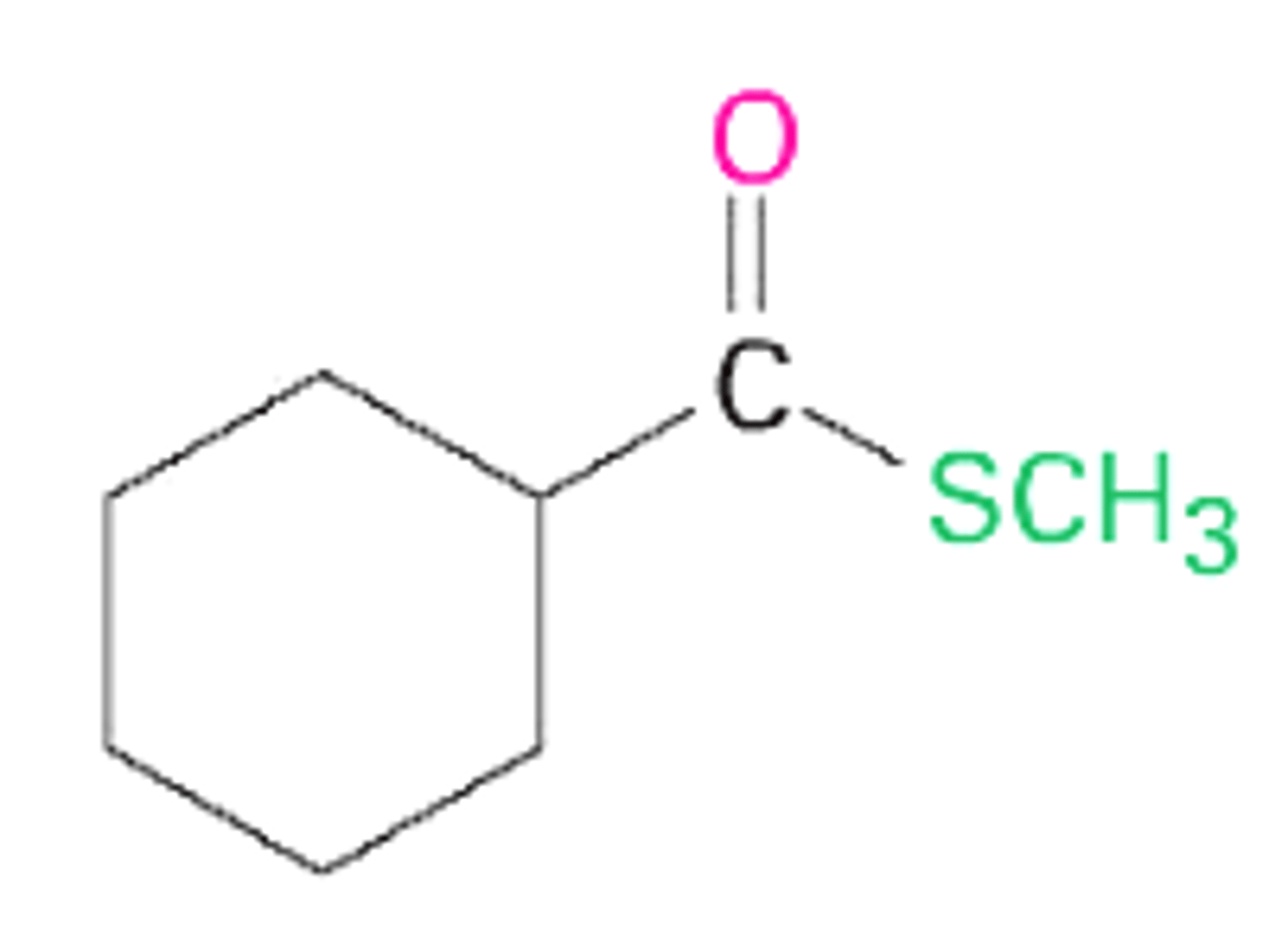
methyl cyclohexane carbothioate
benzoyl phosphate
reactivity rates with carboxylic acid derivatives
amide
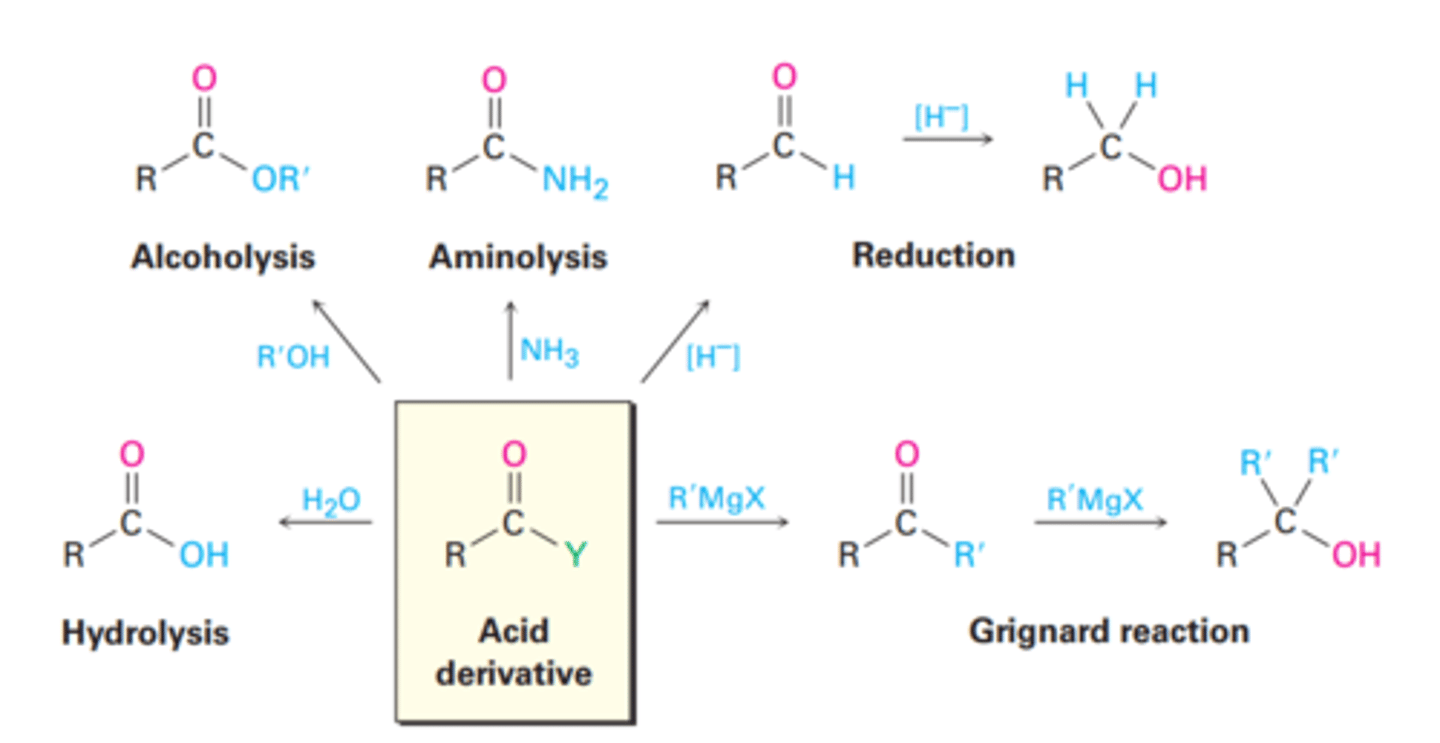
general Acid Halide rxns
- Hydrolysis Reaction
- Alcoholysis Reaction
- Aminolysis Reaction
- Reduction Reaction
- Grignard reaction
- Reaction with water to yield a carboxylic acid
- Reaction with an alcohol to yield an ester (in pyridine)
- Reaction with ammonia or an amine to yield an amide (must be 2 eqv unless it has a good base like NaOH/H2O and NR3 doesn't react)
- Reaction with a hydride reducing agent to yield an aldehyde or an alcohol
- Reaction with an organometallic reagent to yield a ketone and if used again to a 3° alcohol
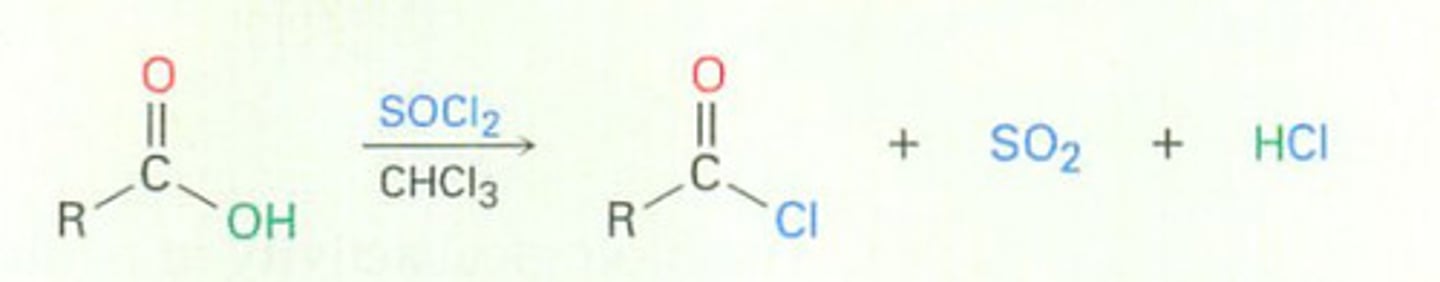
Conversion of Carboxylic Acids into Acid halides
can use PBr3/ ether too
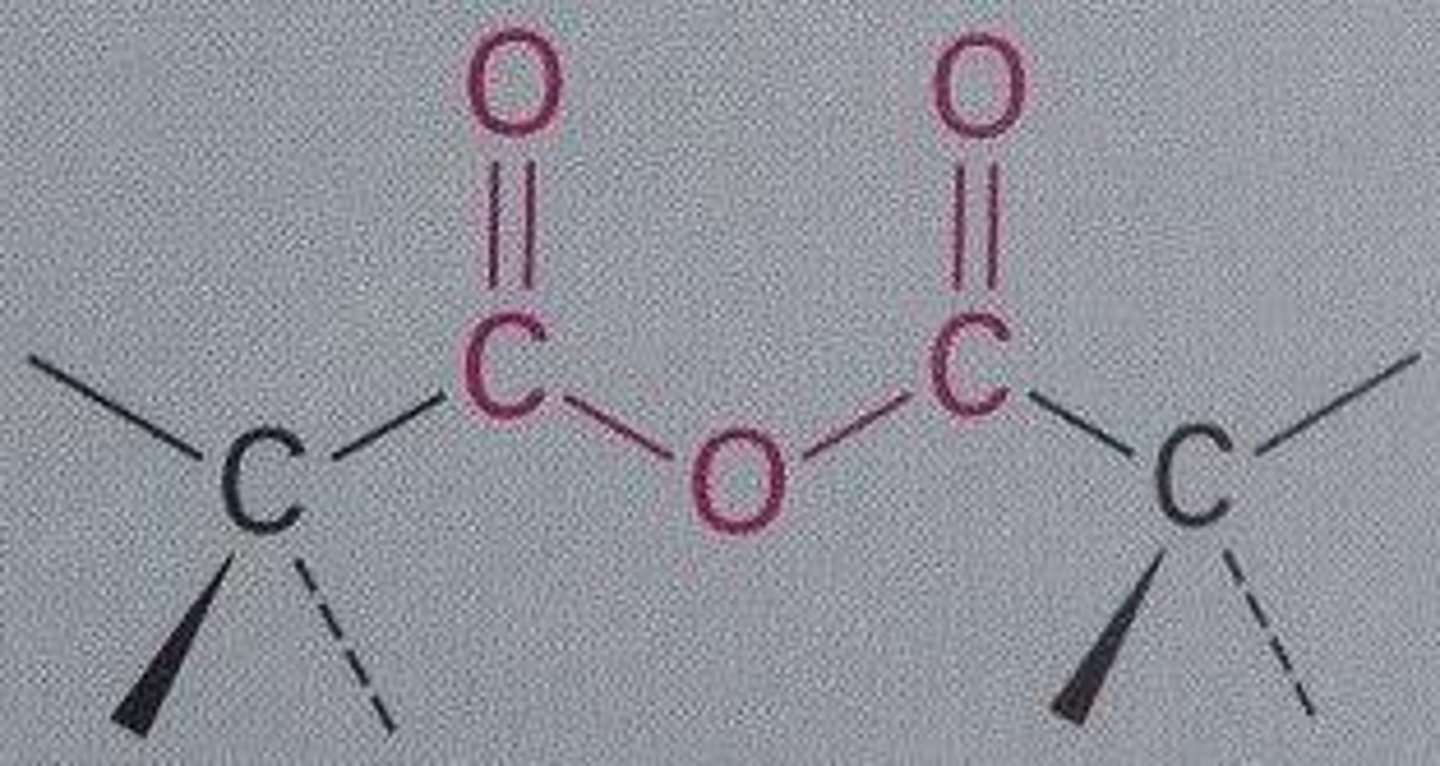
Conversion of Carboxylic Acids into Acid Anhydrides
using high heat (800C) can create two equivalents of carboxylic acids into one (an ester group forms)
Fischer esterification
can only be used with simple, low boiling alcohols
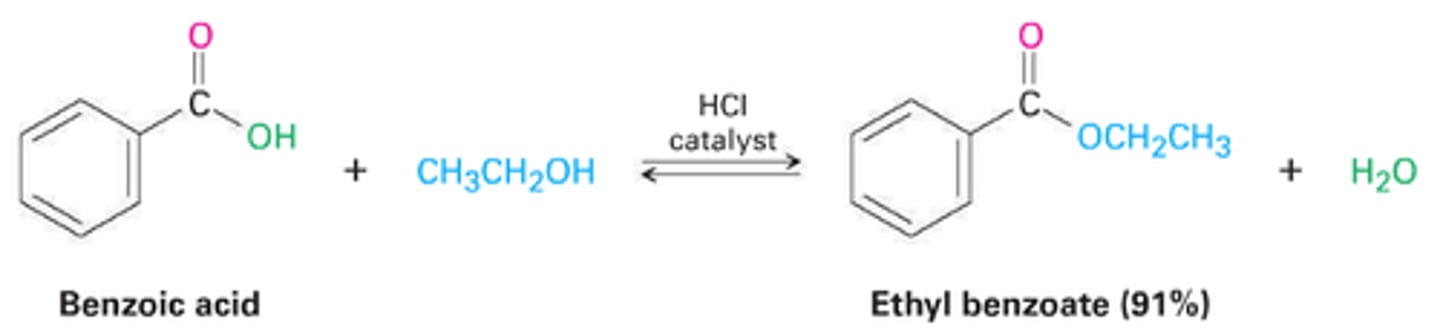
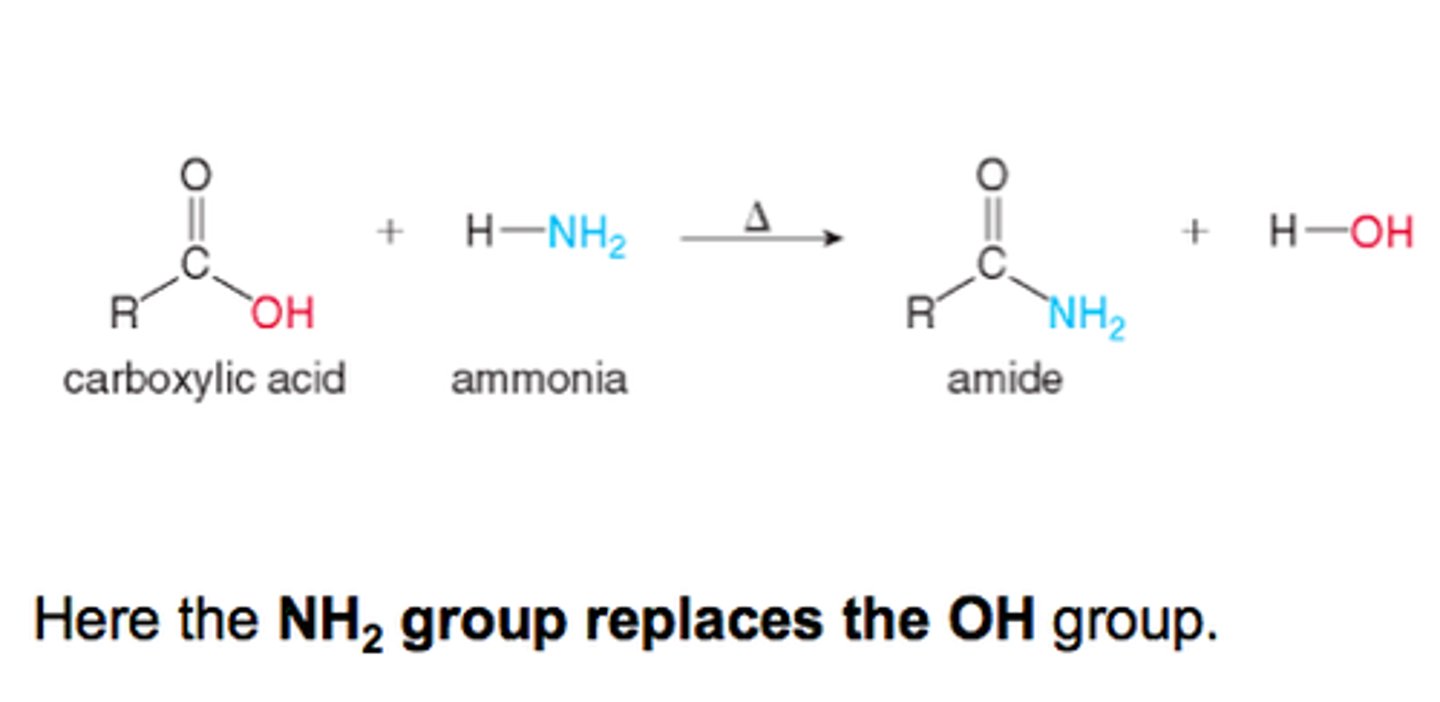
Conversion of Carboxylic Acids into Amides
can do in the picture of if the amine has an r group already make sure the entire amide is added together to make an enamide
CA's into primary alcohols
BH3/THF, H3O+ or LiAlH4/H3O+
Conversion of Acid Chlorides into Ketones:
Diorganocopper Reaction
ONLY with Acid chlorides does not react w any other carboxylic acid derivatives (esters, amides, or the carboxylic acids themselves)
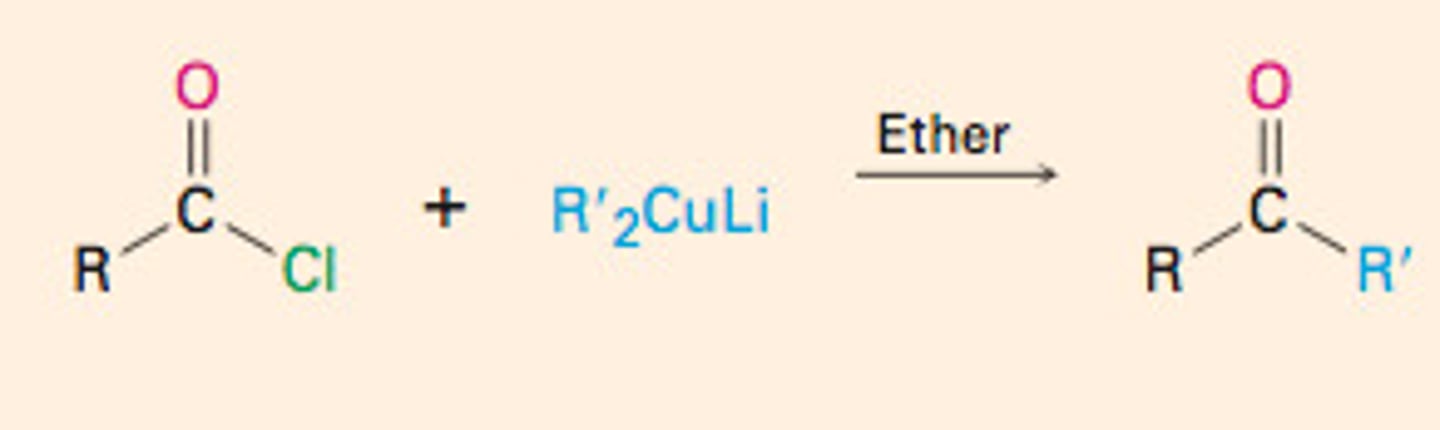
Nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of acidchloride with a carboxylate anion
Reactions of Acid Anhydrides
- Hydrolysis Reaction
- Alcoholysis Reaction
- Aminolysis Reaction
- Reduction Reaction
- rxn w water to CA's
- rxn w alchols into esters ( NaOH/H20 solvent)
- rxn w amines to amides ( NaOH/H20 solvent)
- reacts with nucleophiles (H-) to yield aldehydes than alcohols
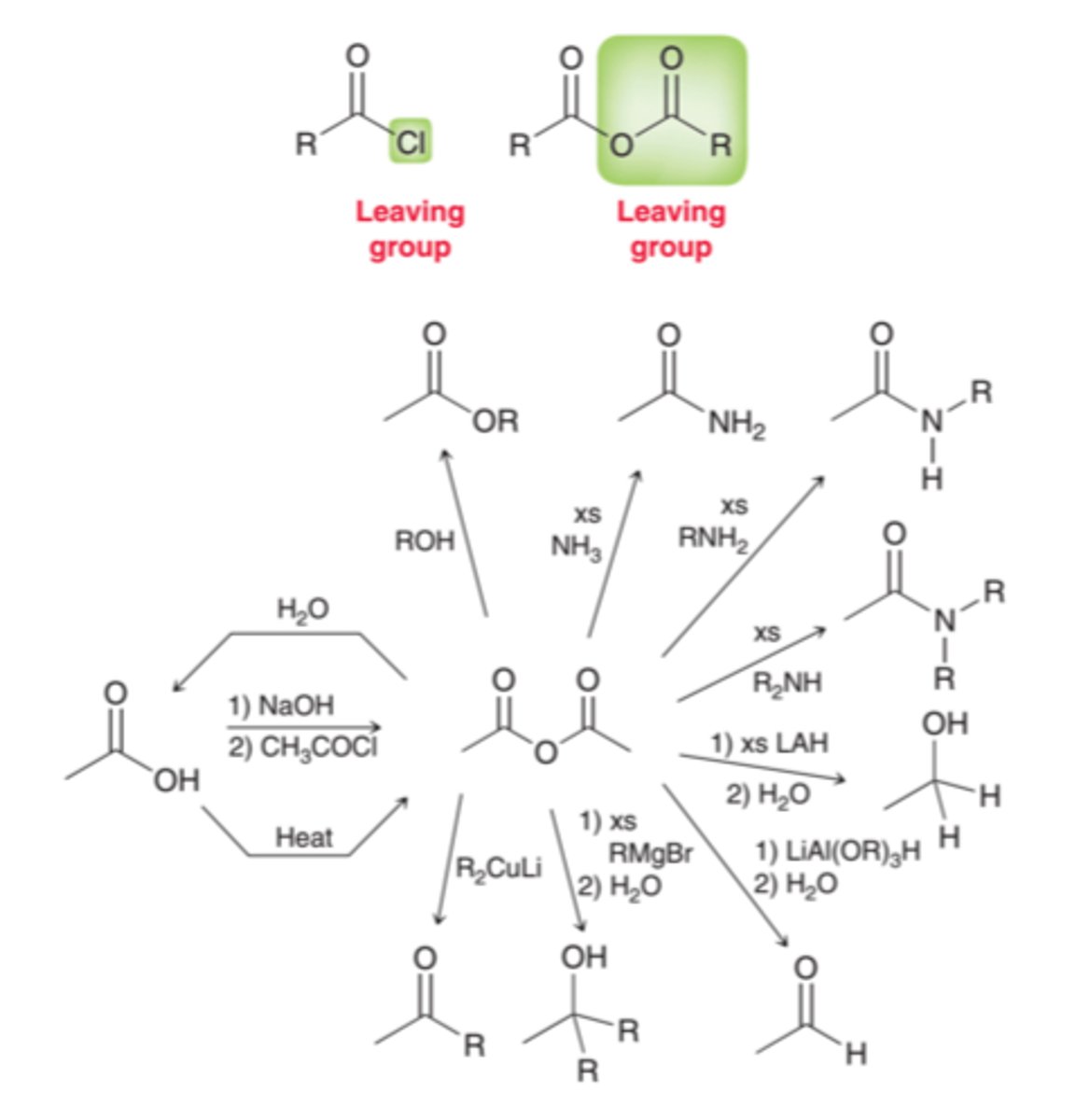
Preparation of Esters from CA's
1. 1.SOCl2/ 2. ROH, Pyridine
2. ROH/HCl
Method limited to simple alcohols
3. 1. NaOH/2. RX.
Method limited to primary alkyl halides
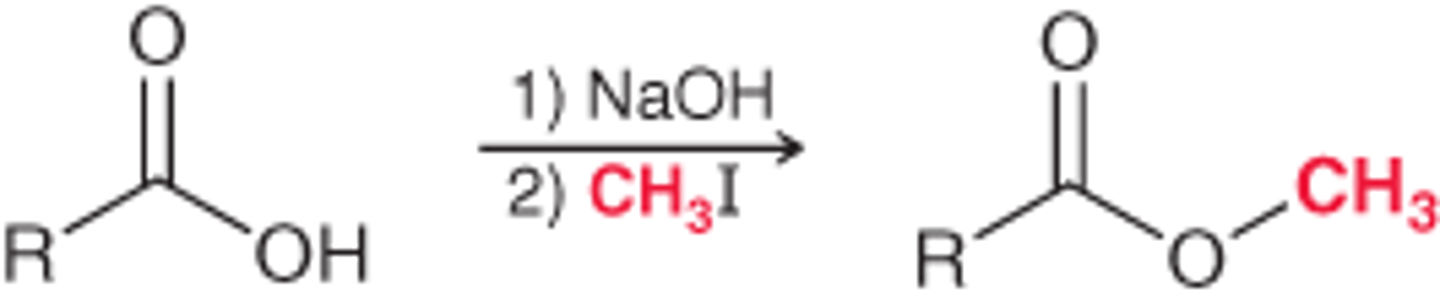
CONVERSION OF ESTERS INTO CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: HYDROLYSIS
H2O, NaOH
or H3O+ yields CA and a primary alcohol
the ether bond is broken and substituted with an OH
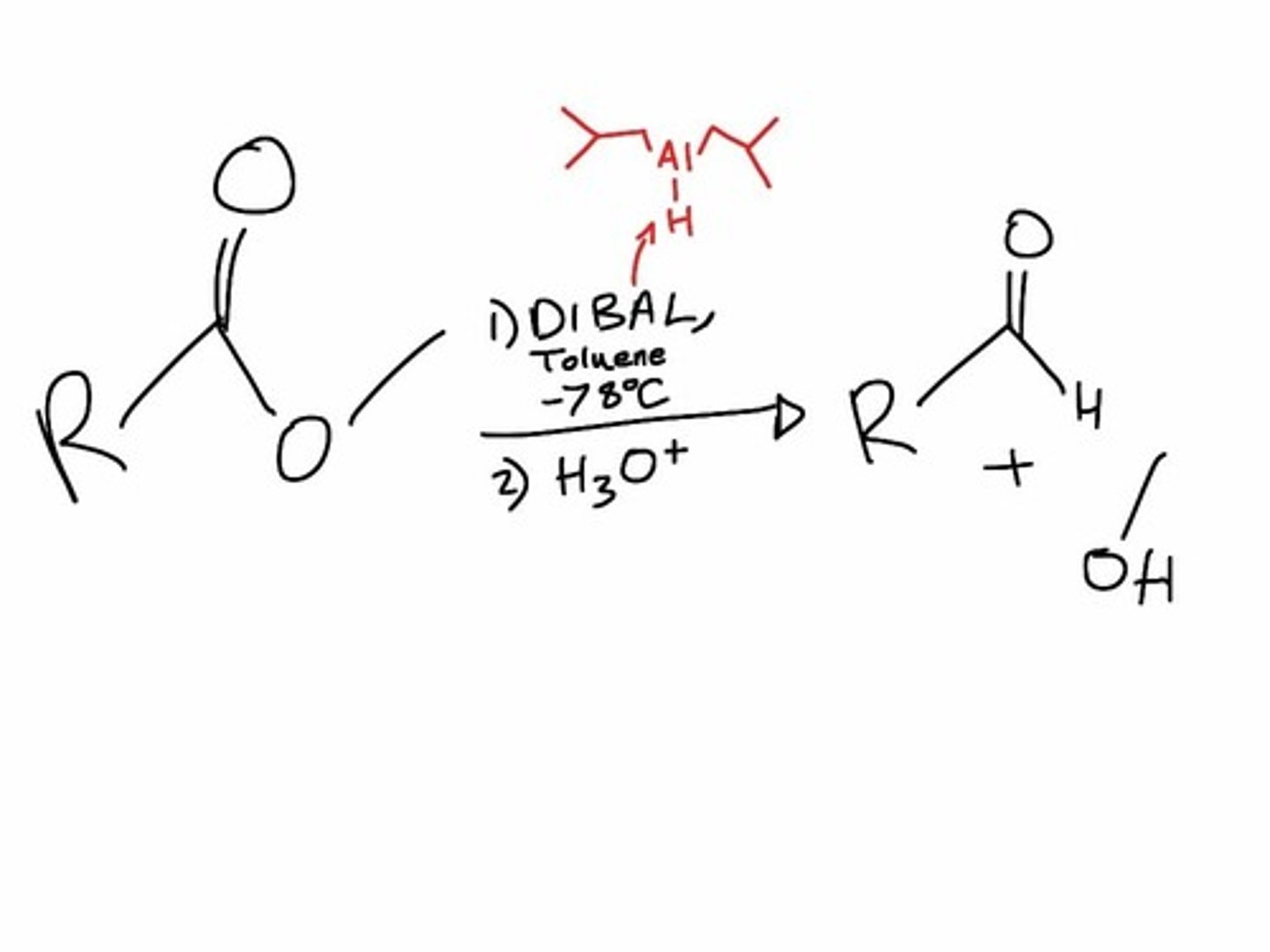
esters into aldehydes
or carboxylic acids into primary alcohols
1. DIBAH in toluene/2.H3o+
CONVERSION OF ESTERS INTO ALCOHOLS: GRIGNARD REACTION
Esters react with 2 equivalents of a Grignard reagent to yield a tertiary alcohol in which two of the substituents are identical
CONVERSION OF AMIDES INTO CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: HYDROLYSIS
amide + h30+/heat
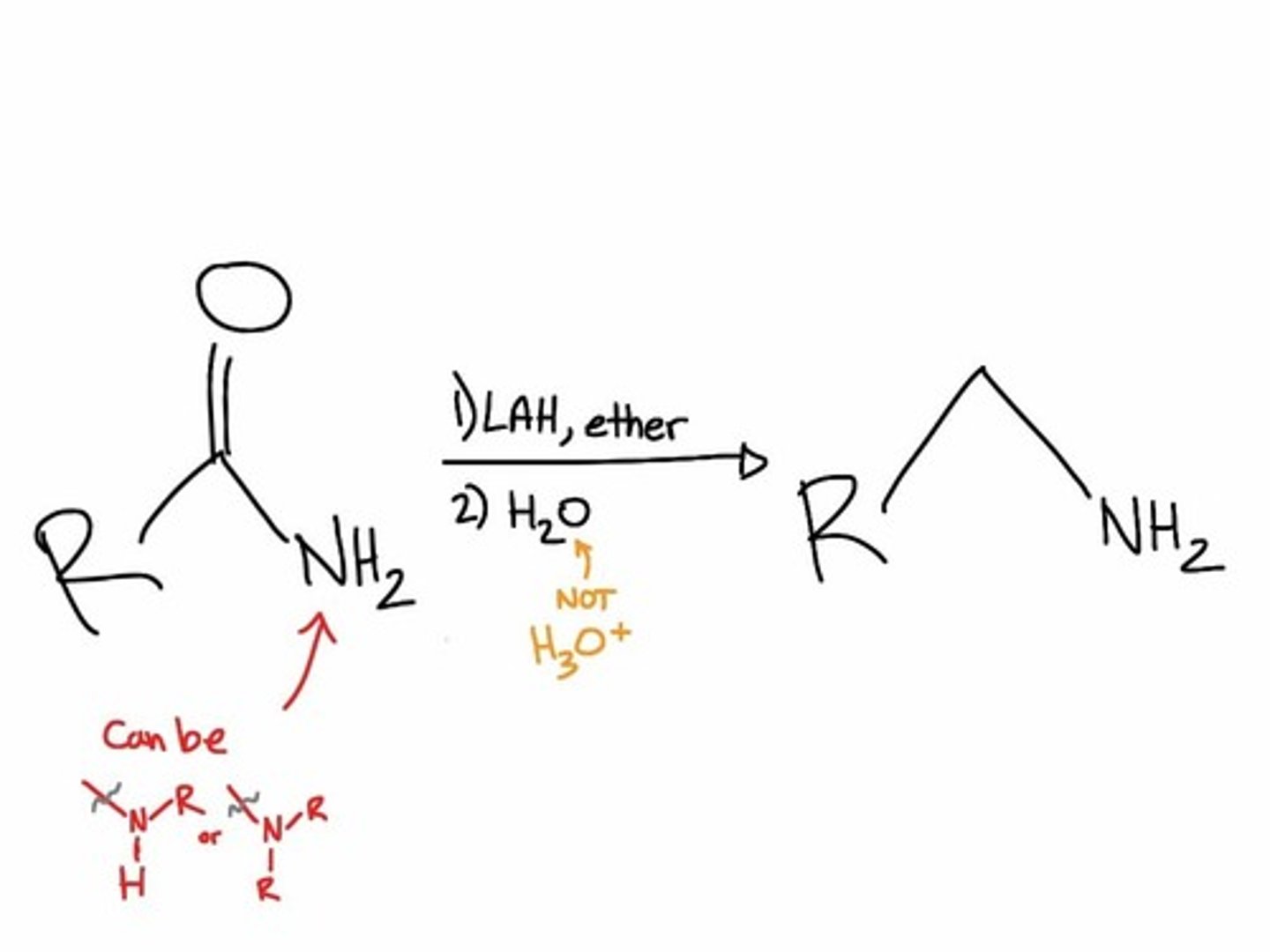
reduction of amides
only one that has a LiAlH4 /h20 reagent and doesnt reduce to alcohols, reduces to AMINES (no carbonyl group at allll)
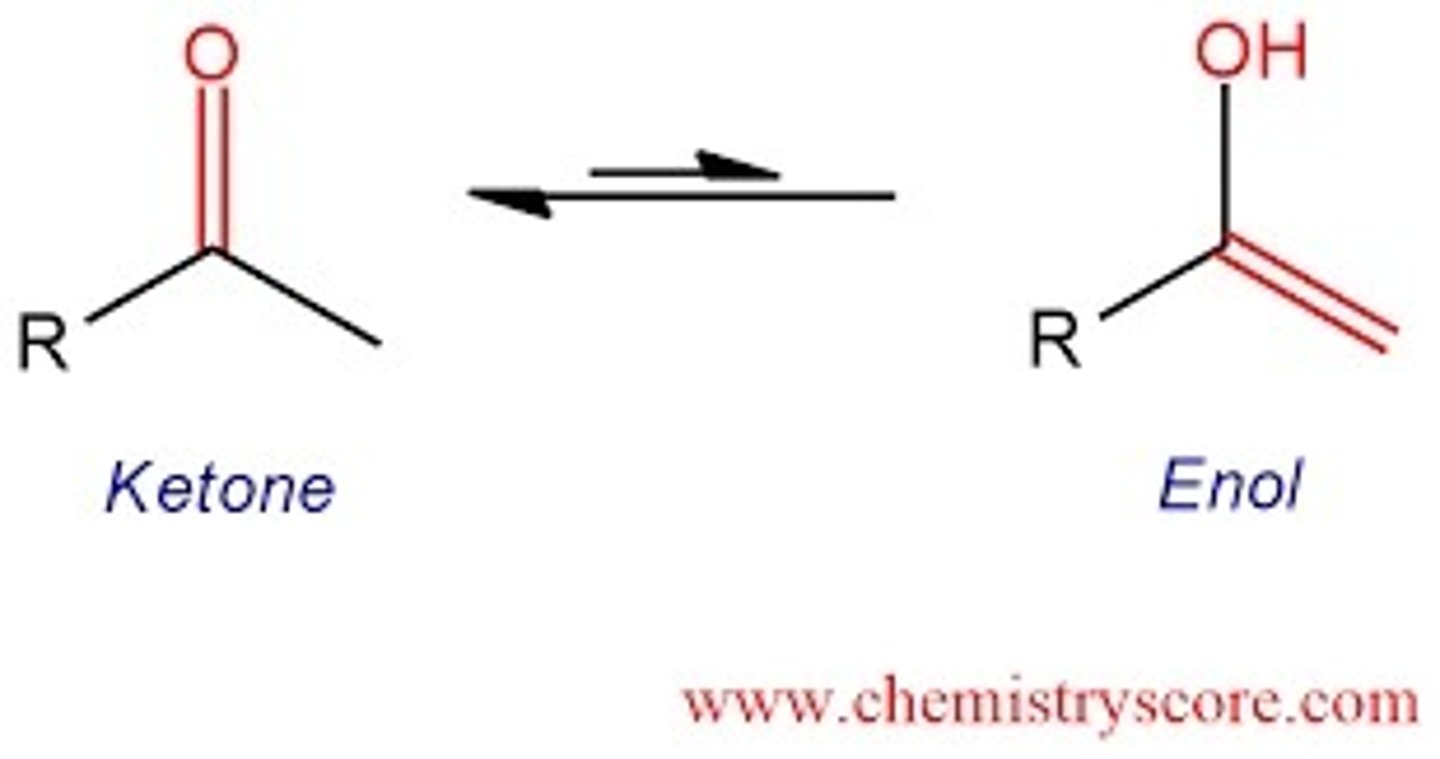
keto form and enol form
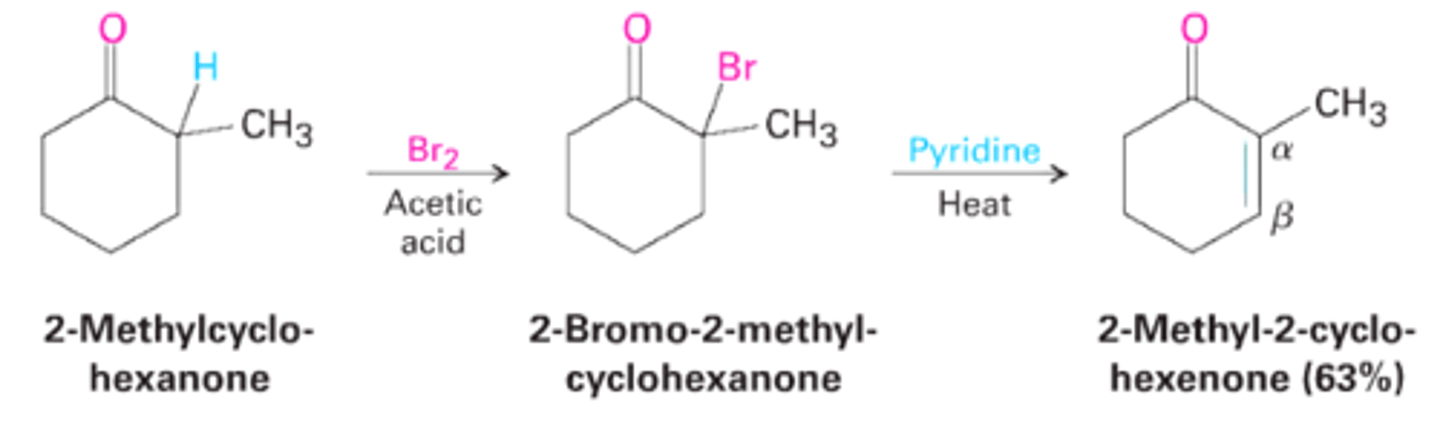
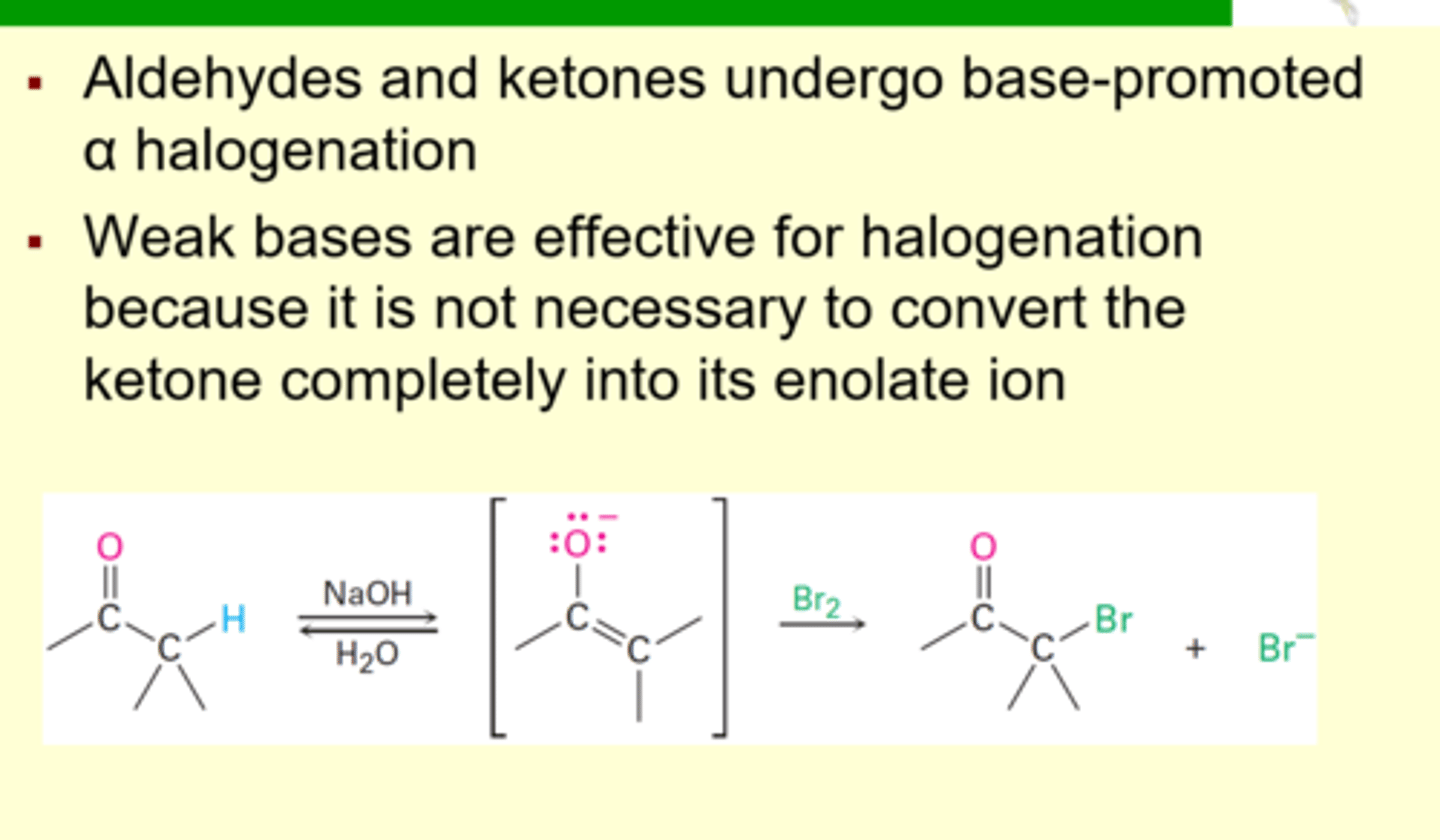
Alpha Halogenation of Aldehydes and Ketones
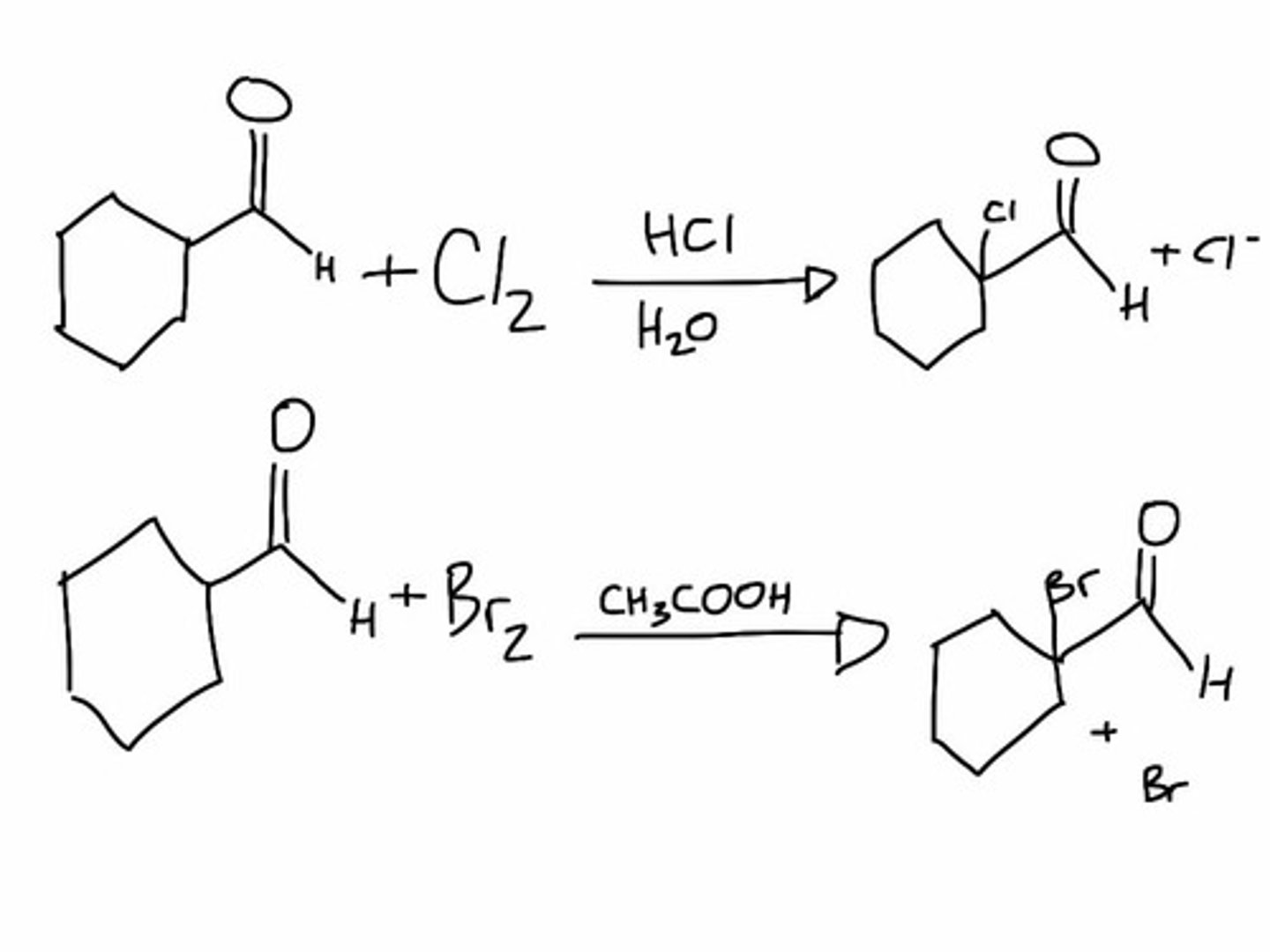
Elimination Reactions of-Bromoketones
Acids, esters, and amides do not react with Br2
they can onlyn work with a mixture of Br2 and PBr3(Hell-Volhard-Zelinskii reaction)
Reactivity of Enolate Ions
LDA/ THF can do this too
Malonic Ester Synthesis
- carboxylic acids that are trisubstituted at the alpha position.'
- Aryl halides
cant be used either
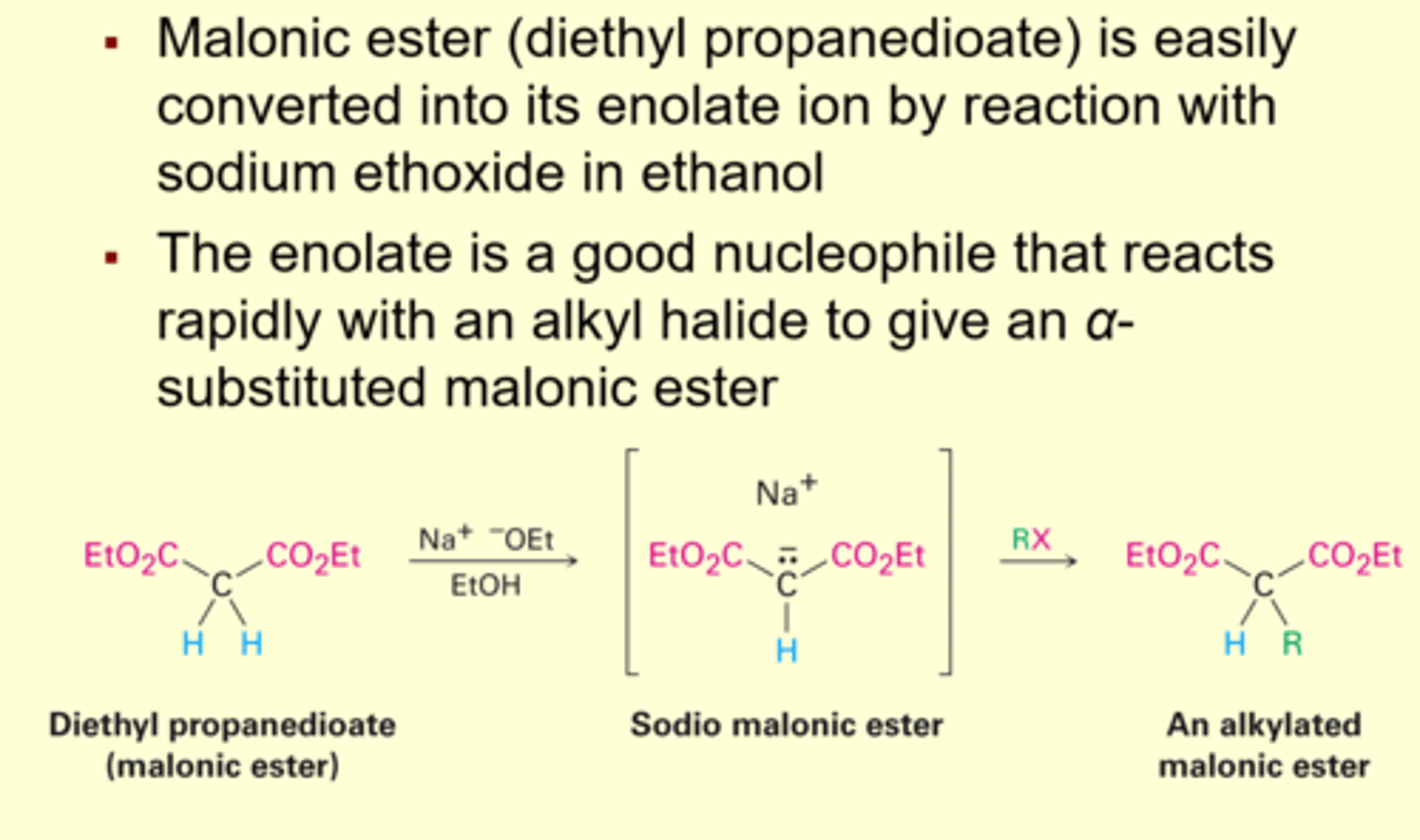
Hydrolysis and Decarboxylation
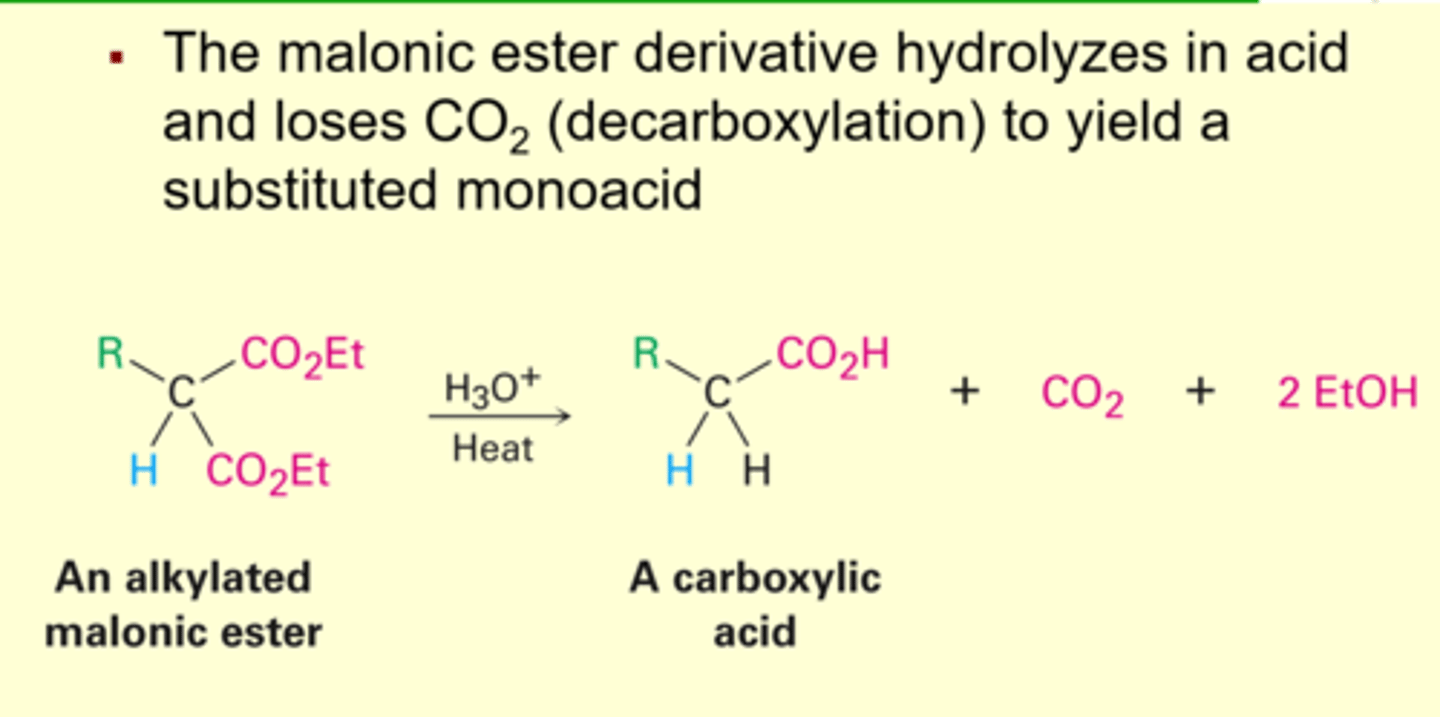
Decarboxylation of -Ketoacids
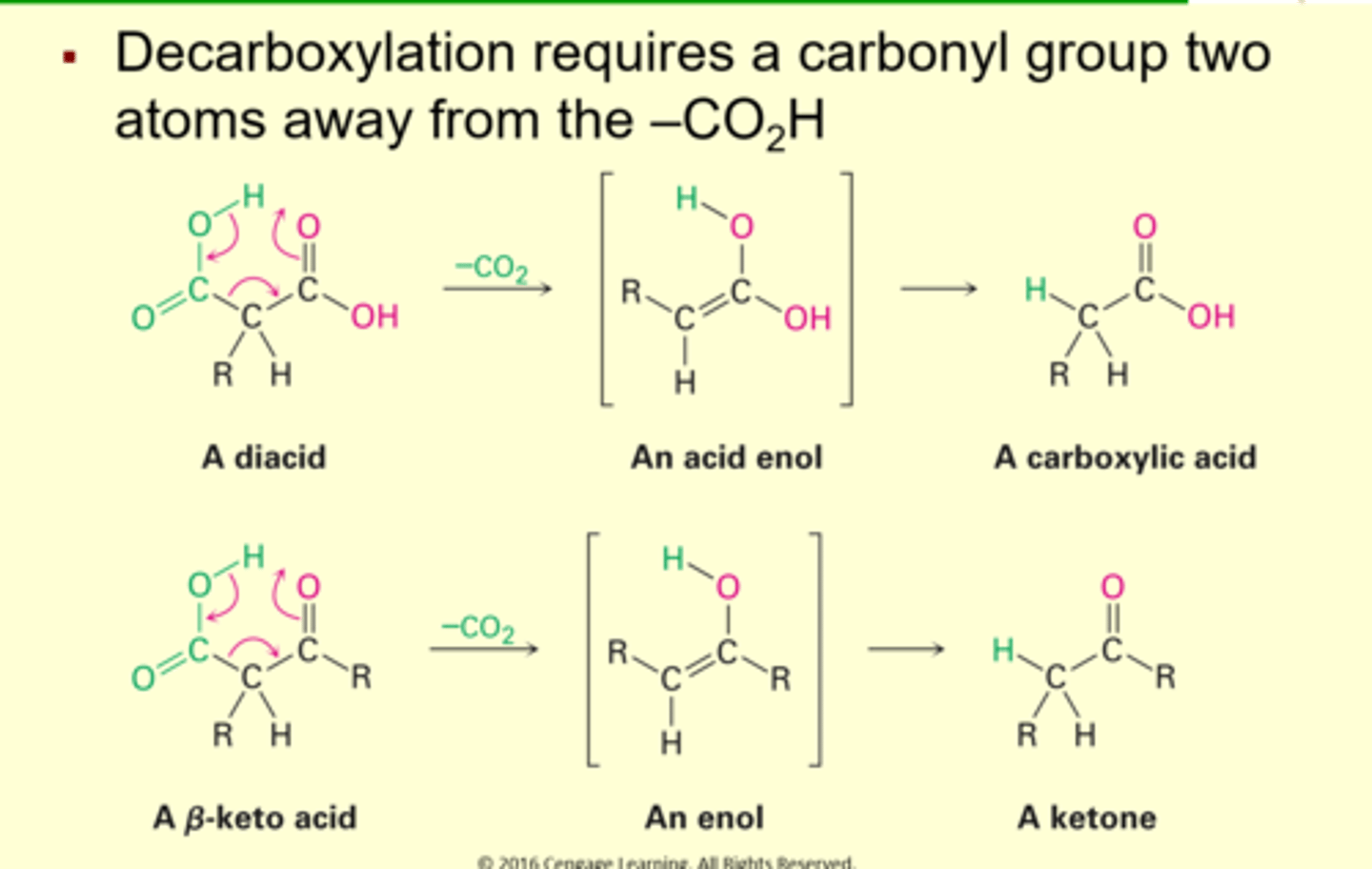
Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
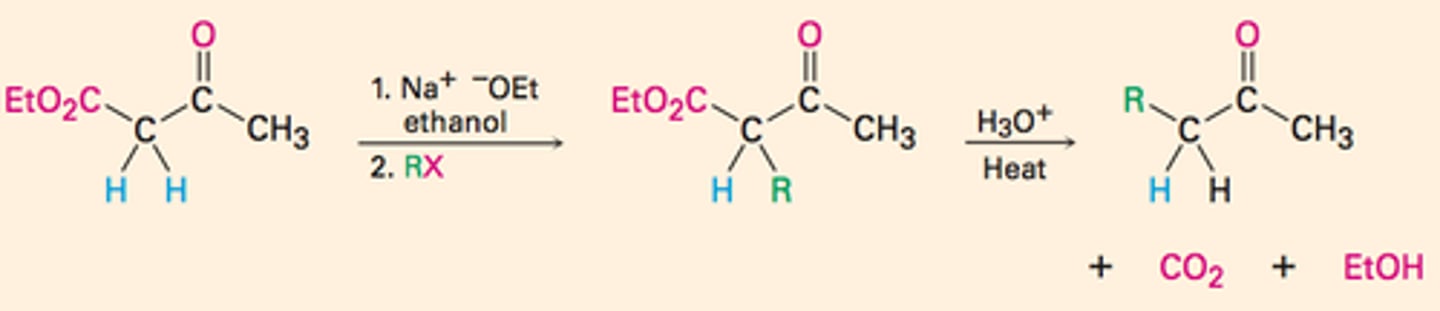
Direct Alkylation of Ketones,Esters, and Nitriles
Alkylation of enolate ions
- just replacing an h with a r
- tertiary halides don't react at all because of competing elimination
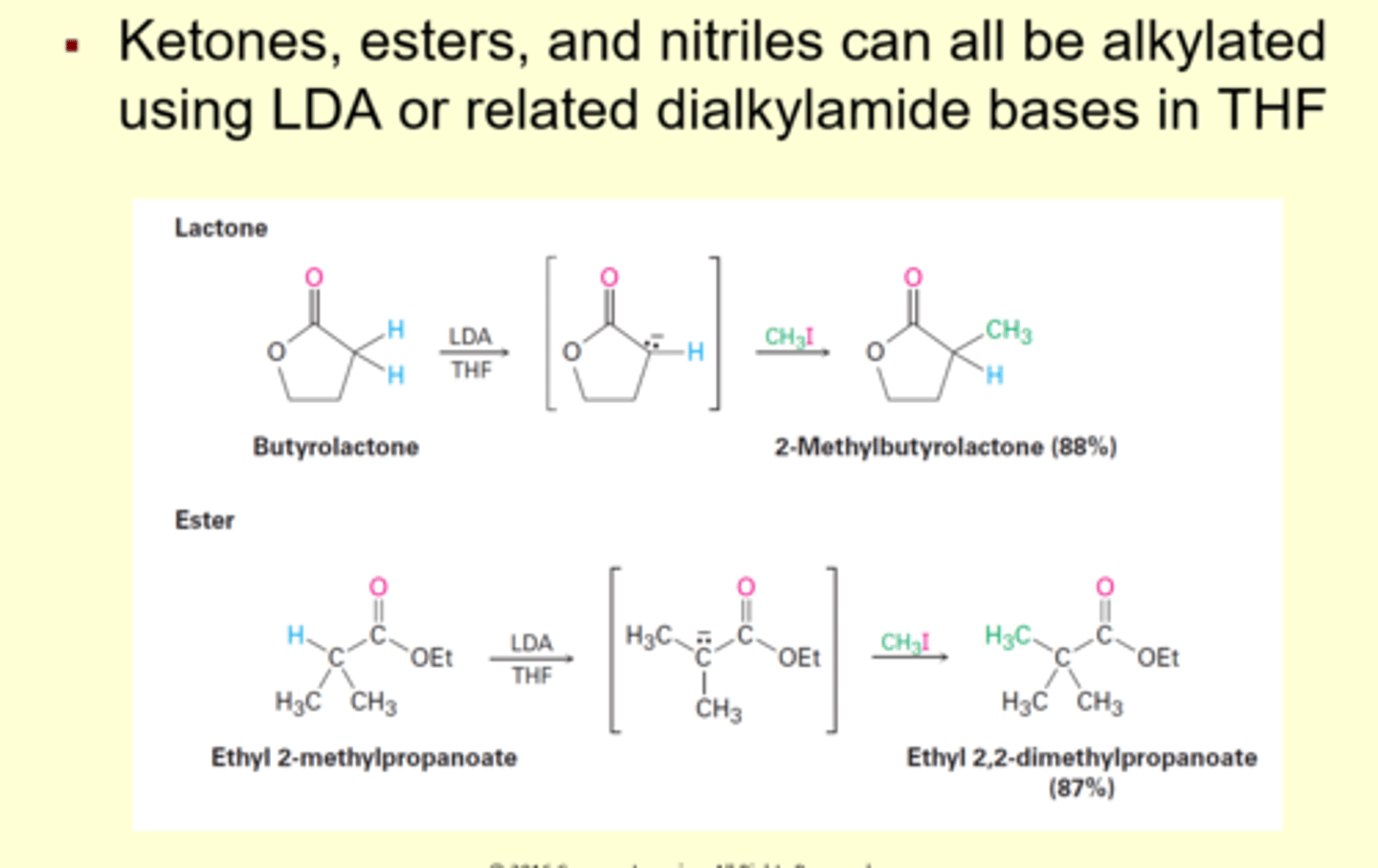
phenyl benzoate
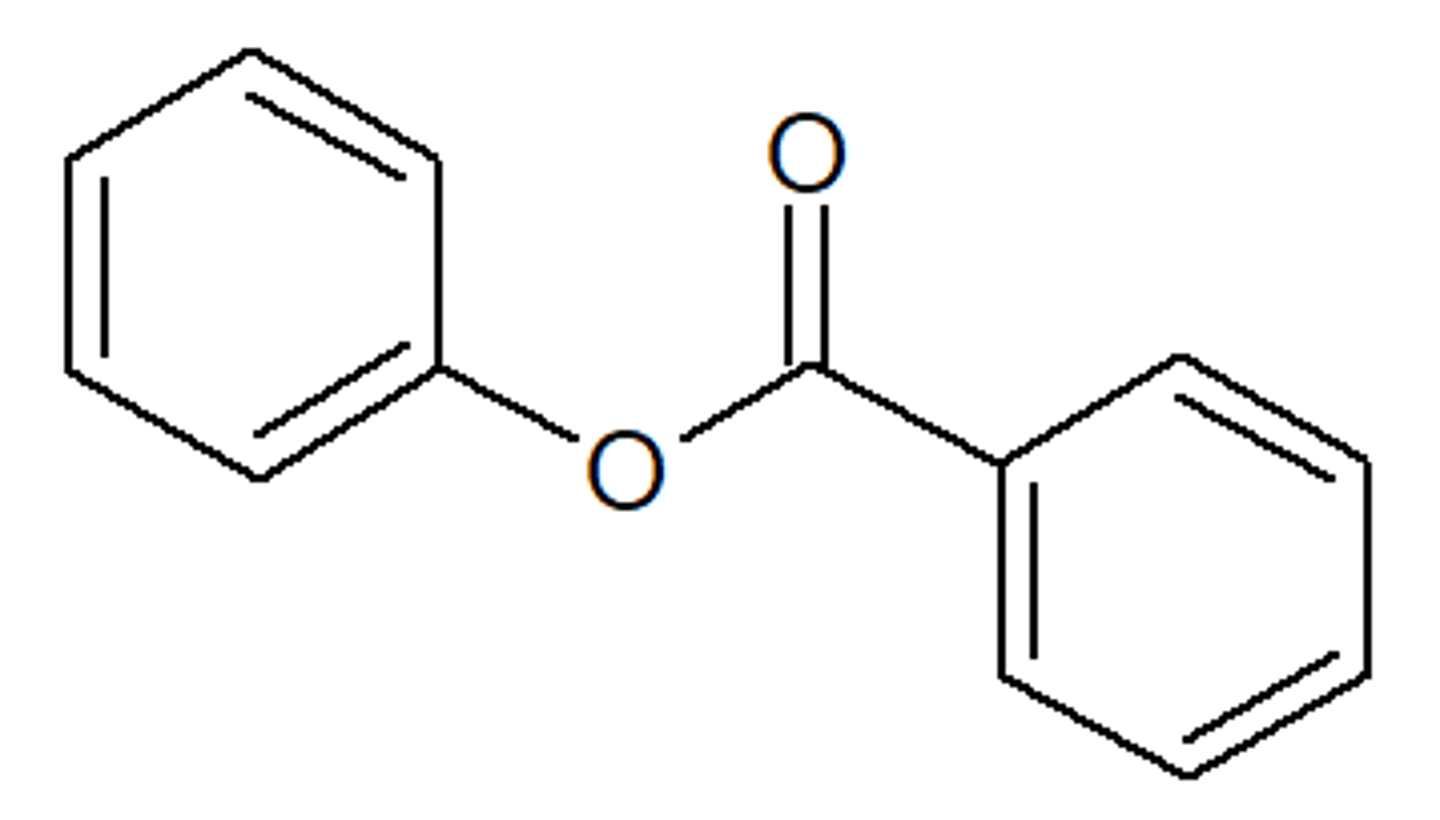
isopropyl thiobenzoate
beneze group with thioester and a isopropyl group on the S
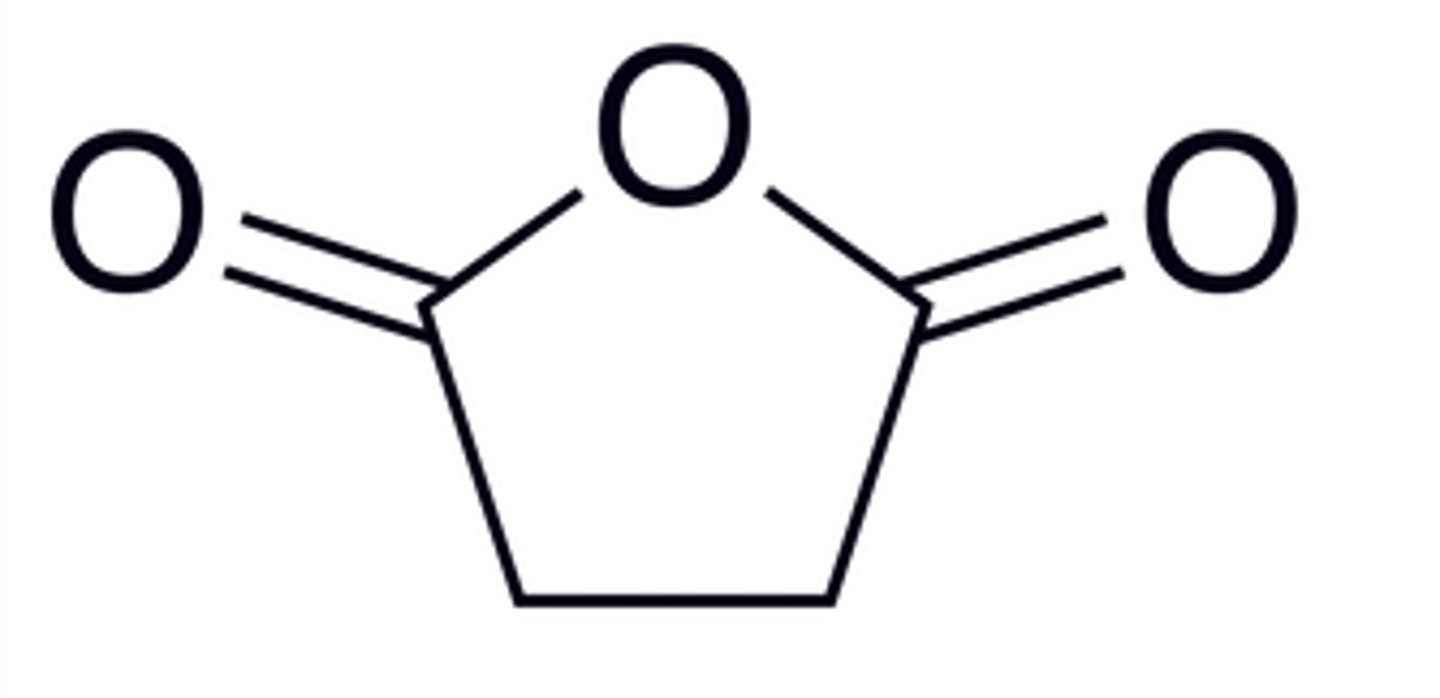
Succinic anhydride
Substitution rxns with amides do not react with
- CH3CO2 - Na+
- Direct nucleophilic substitution reactions do not react because amine group are unreactice, so like cyclohexanol, etc.
Cyclohexanol + CH3CO2COCH3/pyridine (also (CH3CO)2O )
removes the h from the alcohol and makes a carbonyl group with methyl so its cyclohexyl ethanoate
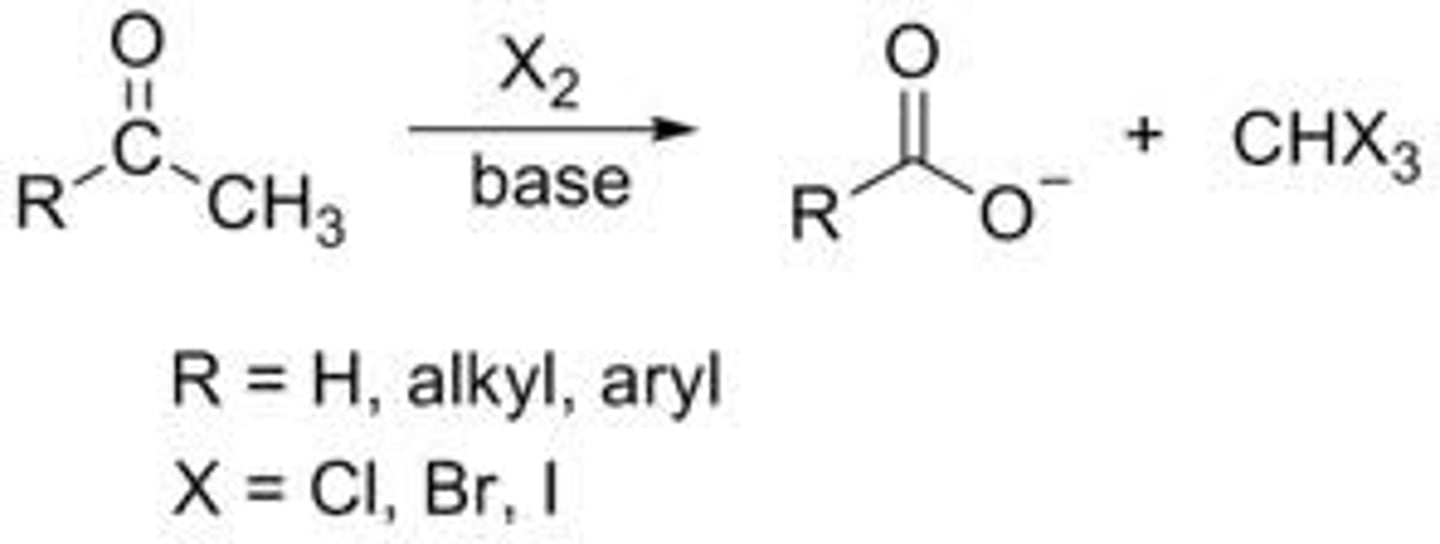
Haloform reaction
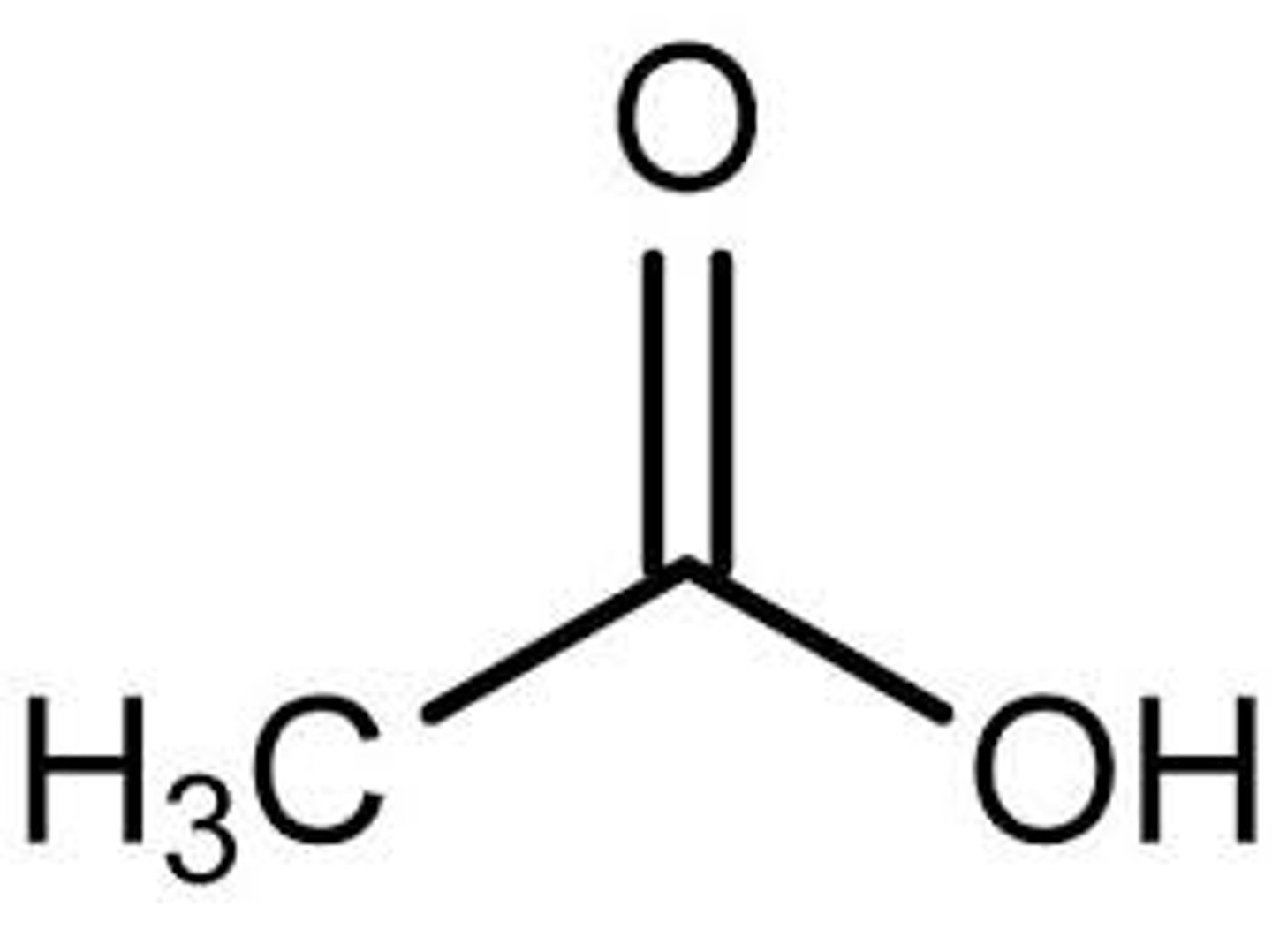
Acetic acid
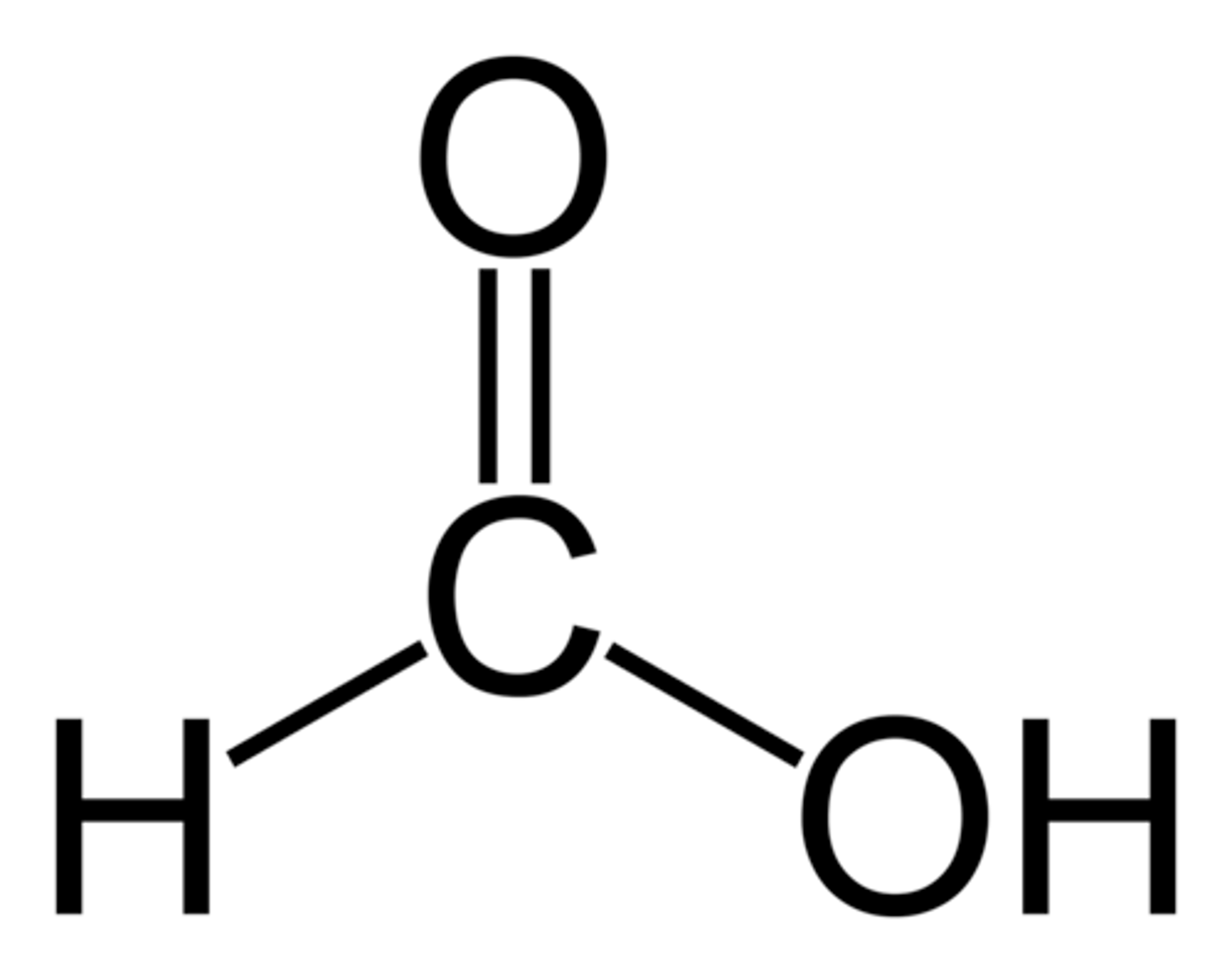
formic acid
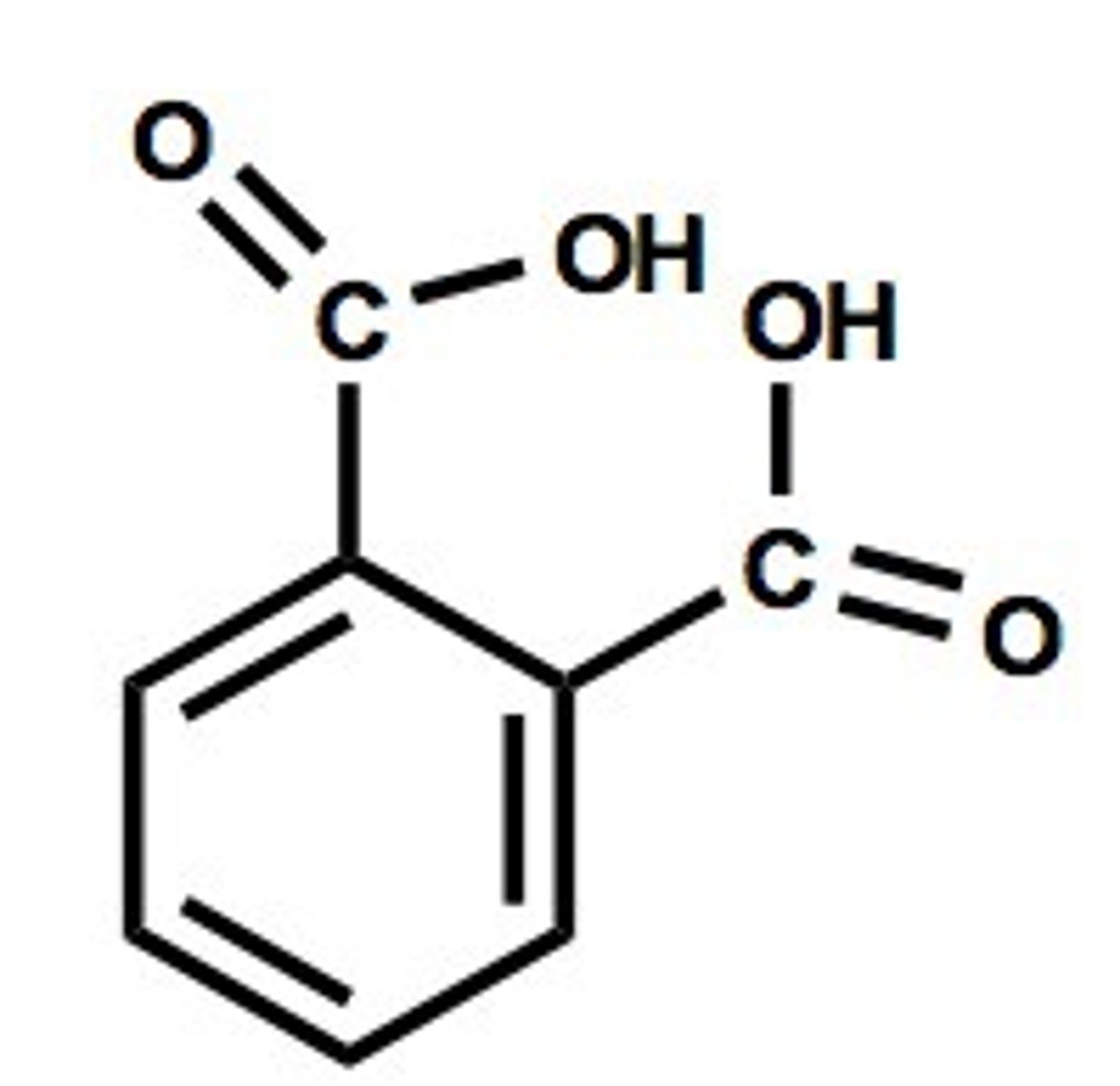
Phthalic Acid
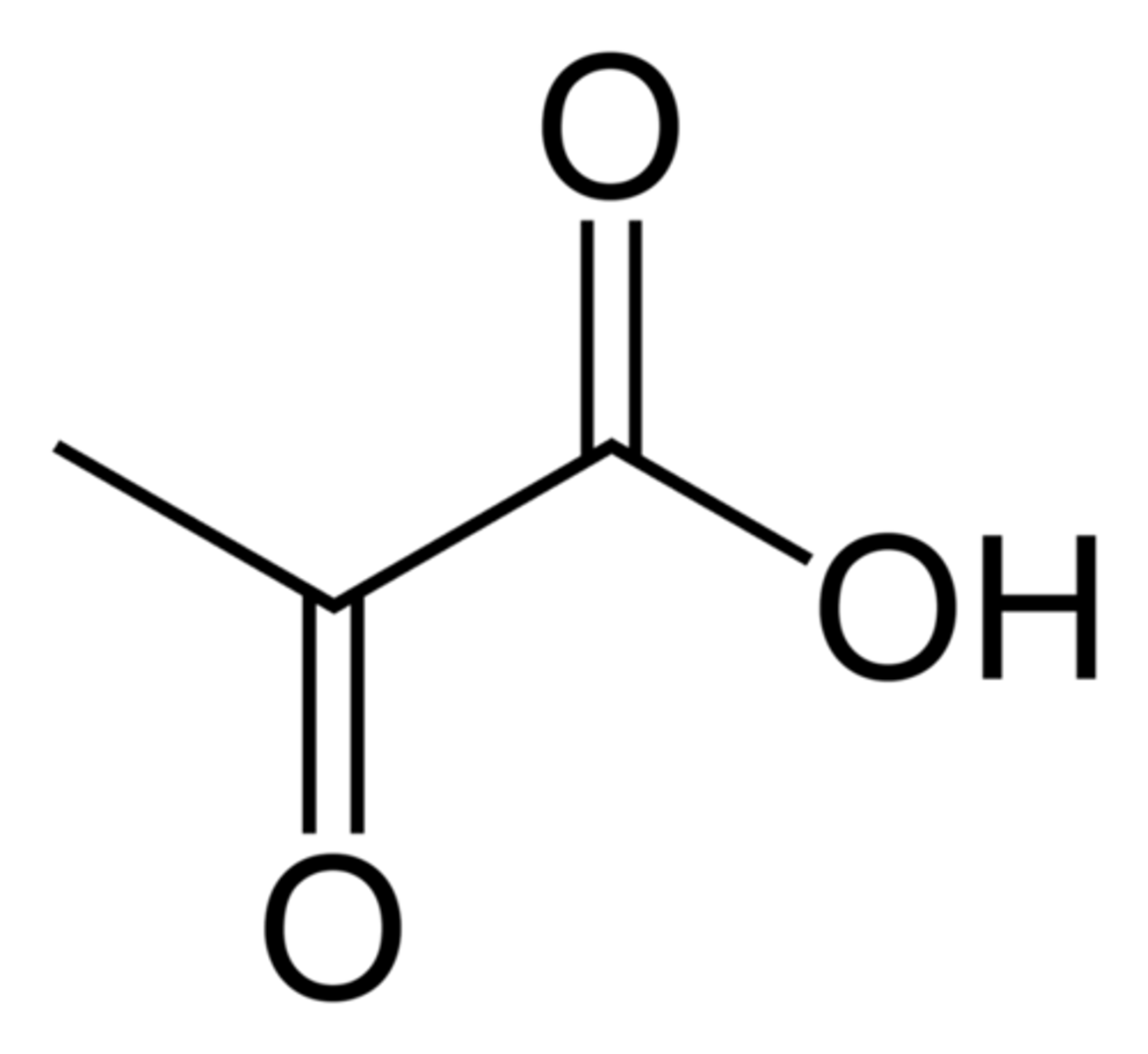
pyruvic acid
glyceric acid
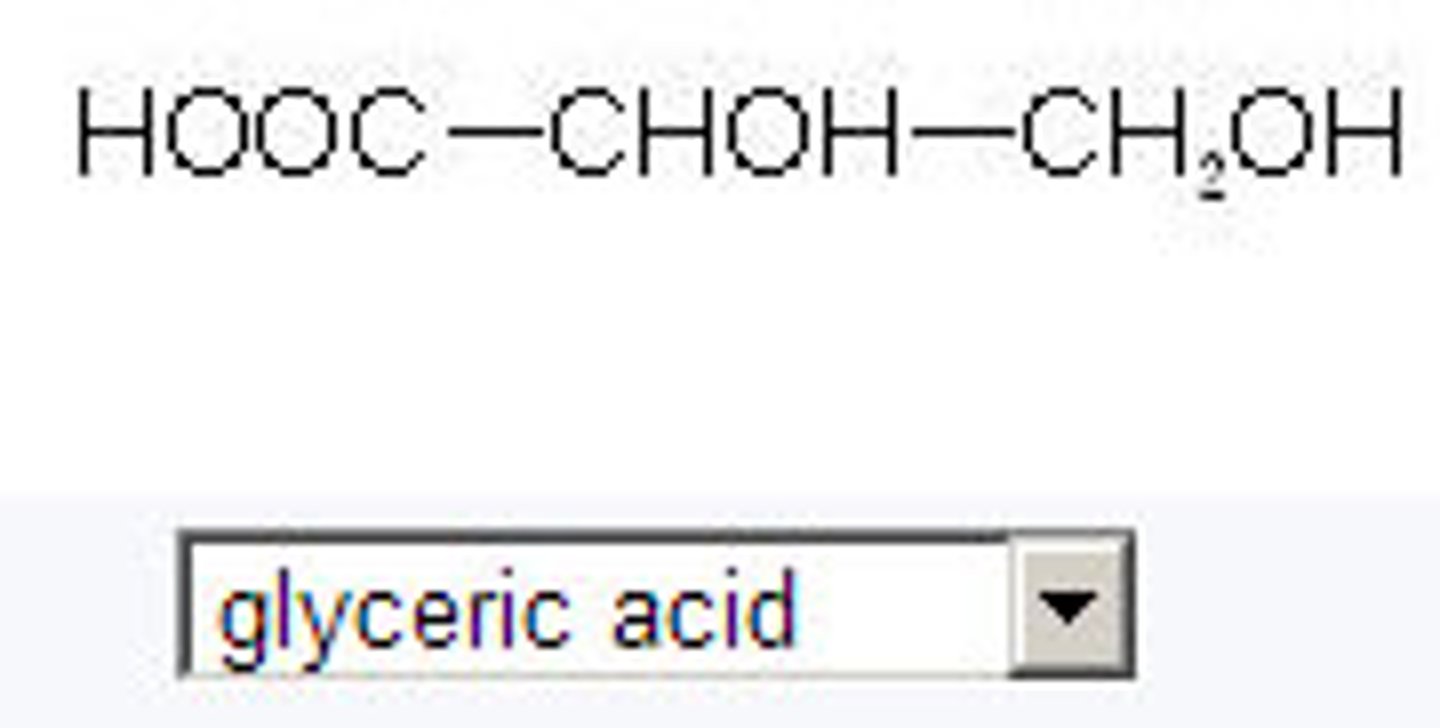
malic acid
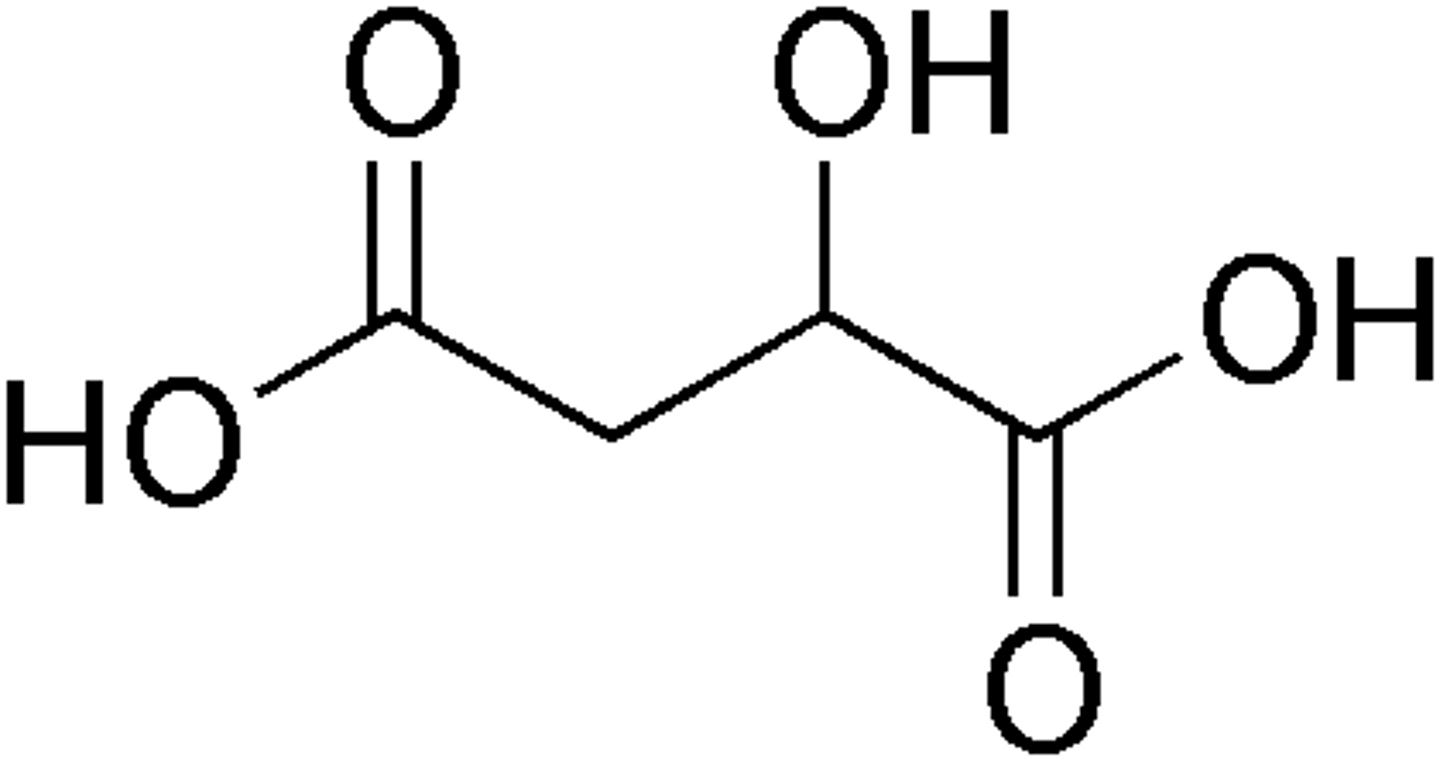
oxaloacetic acid
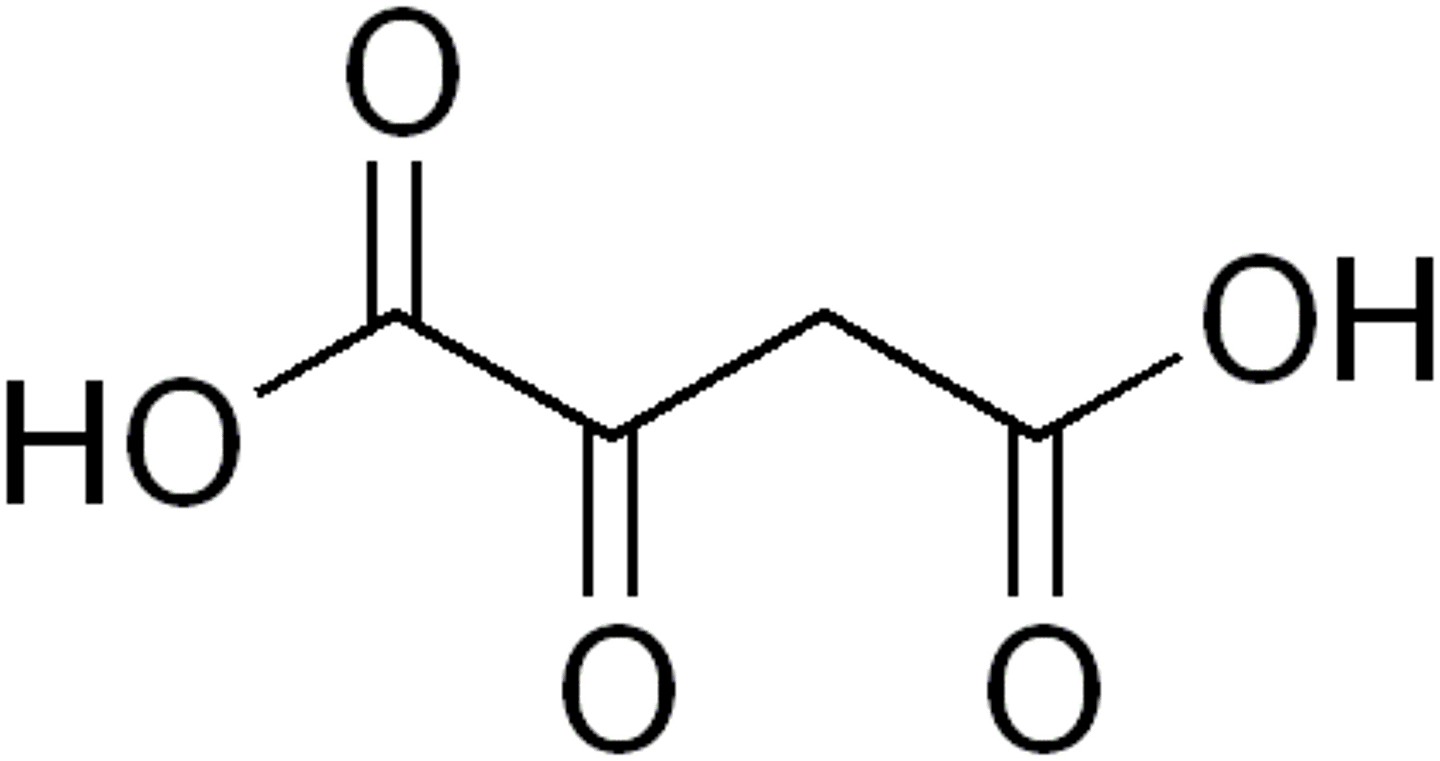
benzonitrile
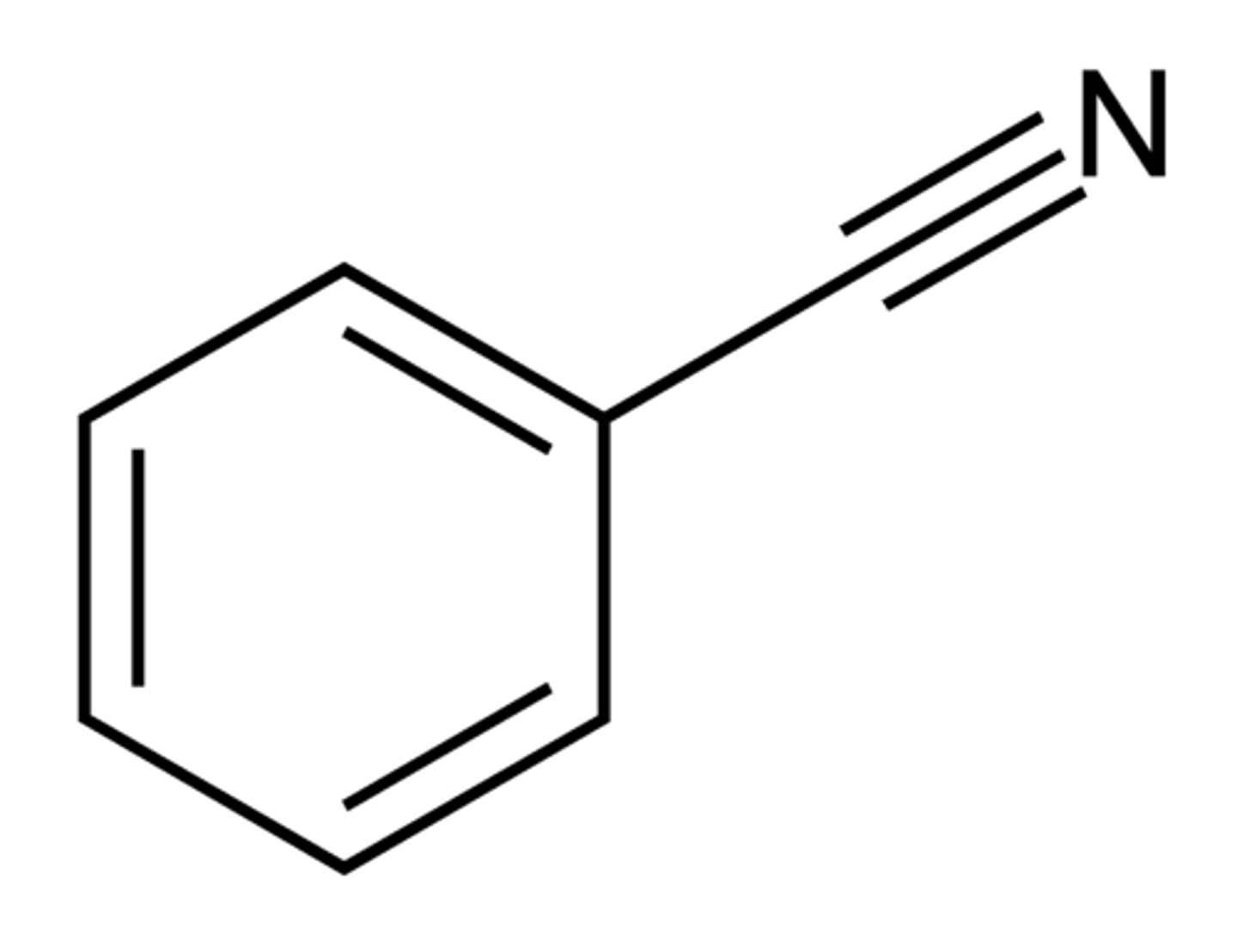
acetonitrile
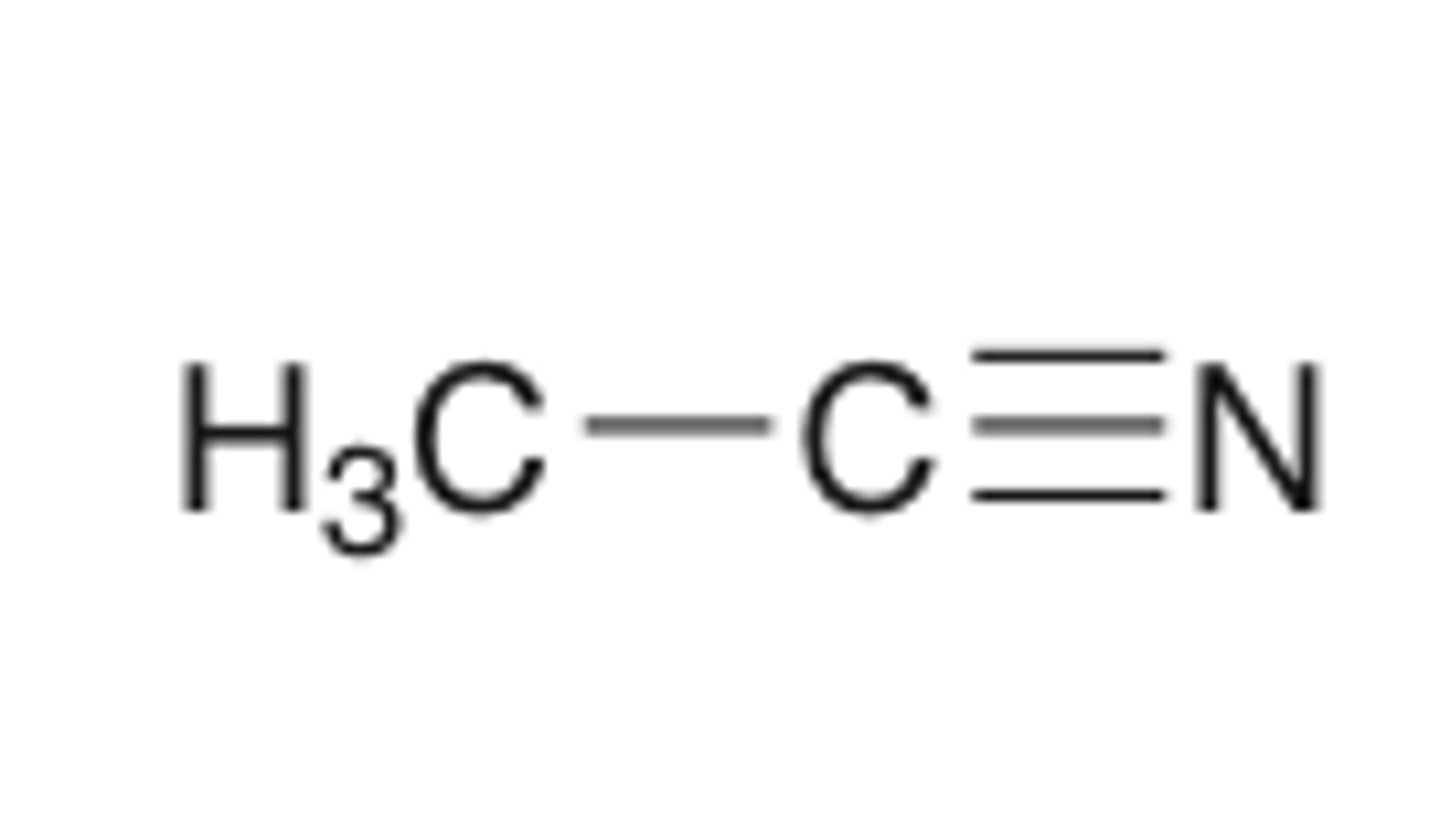
KMnO4/H2O (or Na2Cr2O7 or H2Cr2O7)
substituents in to CA's preferable methyls
can break rings too and make di CA's
CrO3/H3O+
turns alcohols and aldehydes into CA's
1. Mg, ether
2. CO2, ether + R-X
3. H3O+
Or 1. NaCN/2.H30+
R-CO2H
NaOH/H3O+
or
H+/H2O
can turn cyano/nitriles into ?
can turn cyano/nitriles into CA's
OsO4/Zn,H3O+
can turn db into one alcohol and the other CA's
SOCl2, benzene/80oC + CH3CH2CH2CH(CH3)CONH2
CH3CH2CH2CH(CH3)CN
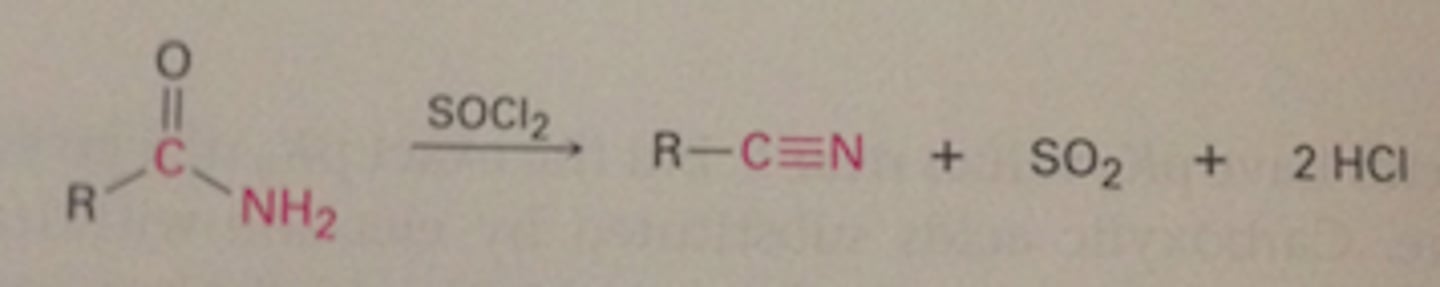
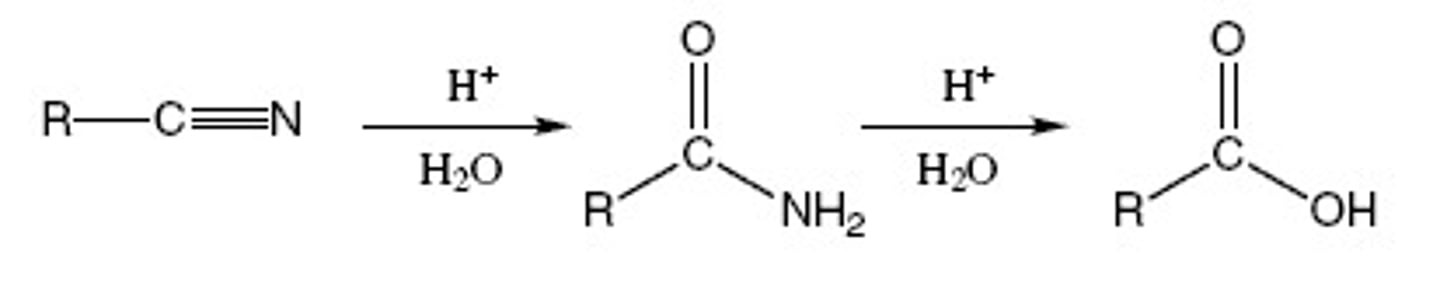
R-CN -) H3O+ (or NaOH,H2O)
R-CNH2
R-CN + LiAlH4,ether/H2O
R-CNH2
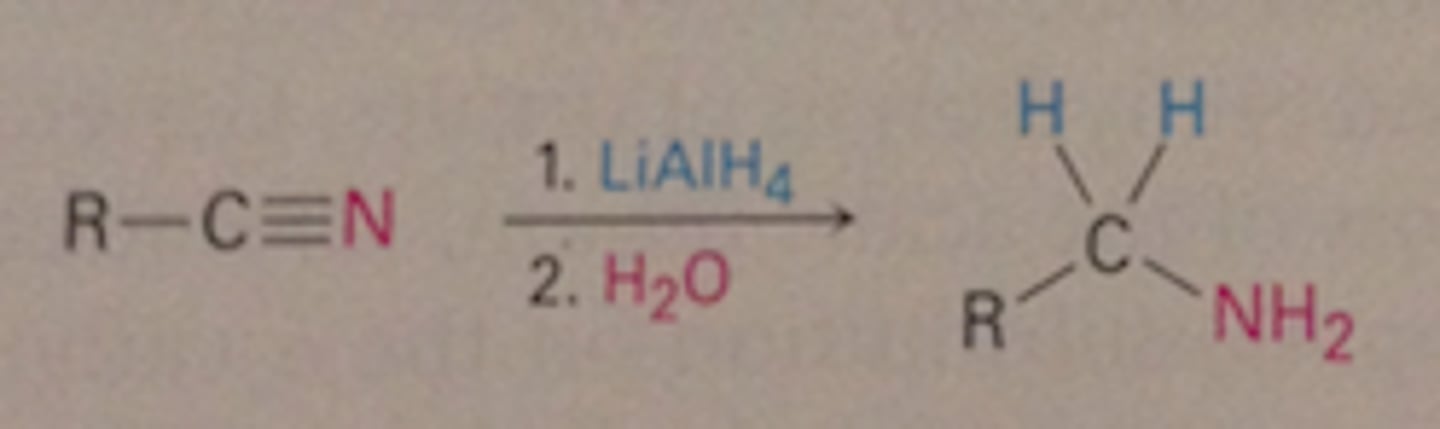
R-CN + RMGX/H2O

R-BR + NaCN
R-CN
Can only work if there are no tertiary carbons
PCC does NOT work on aldehydes because
it oxidizes alcohols into aldehydes not reverse
NMR chart
H NMR (Proton)
Alcohol (-OH): 1-5 ppm
Aldehyde (-CHO): 9-10 ppm
Ketone (α-CH): 2.1-2.5 ppm
Carboxylic acid (-COOH): 10-13 ppm
Ether (-O-CH₂-): 3.3-4.0 ppm
Ester (-COOCH₃ / -COOCH₂-): 2.0-4.5 ppm
Nitrile (-CH₂-C≡N): 2.1-2.5 ppm
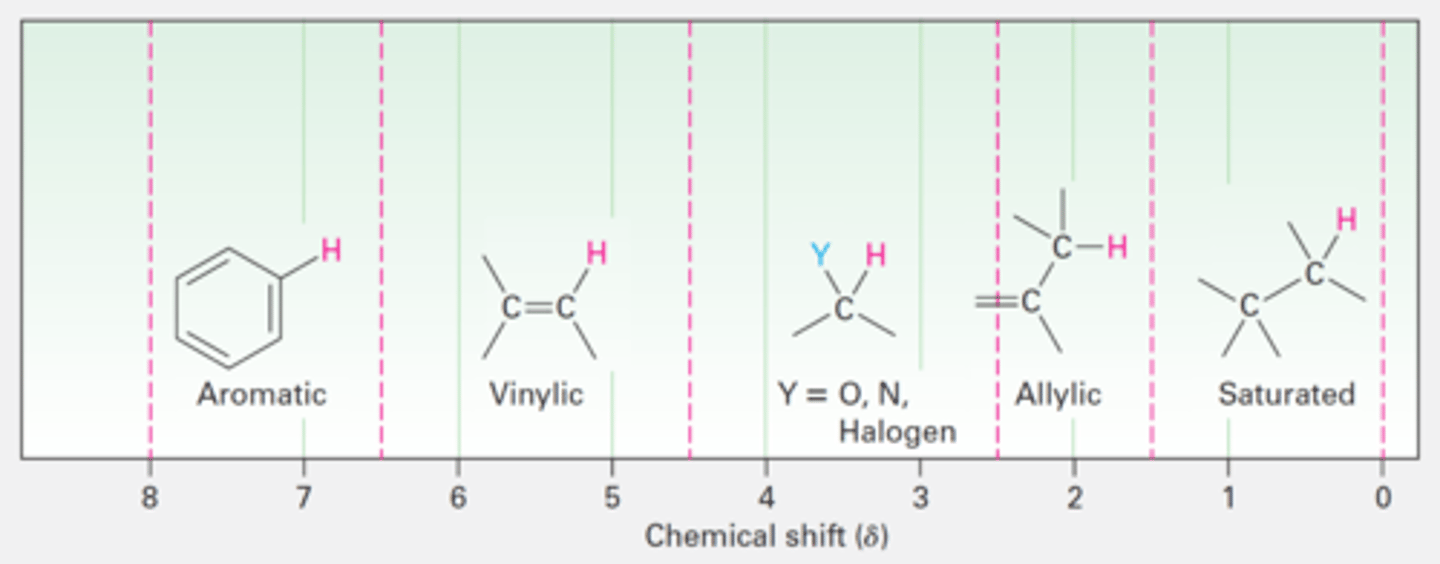
formaldehyde
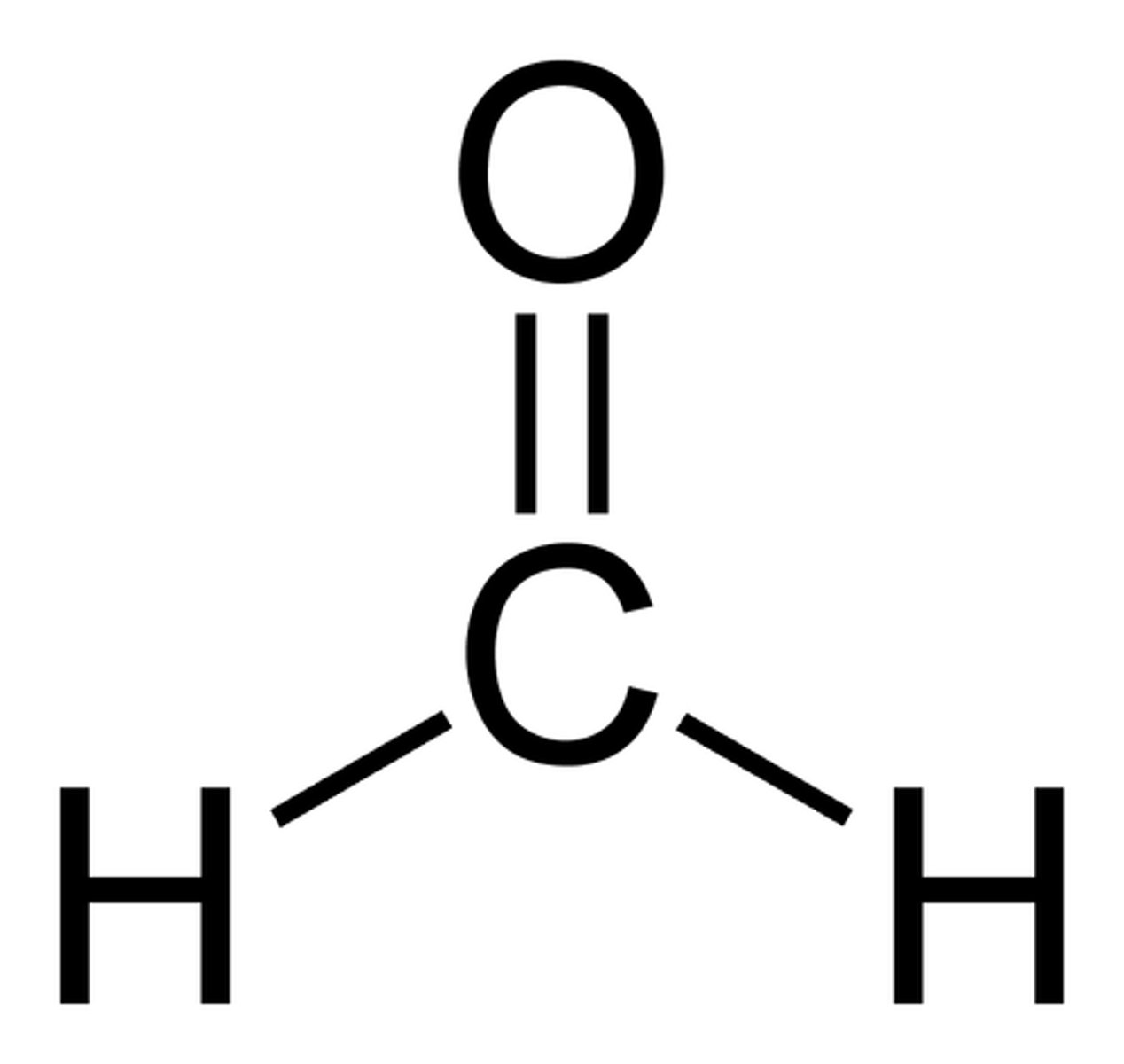
acetaldehyde/ ethanal
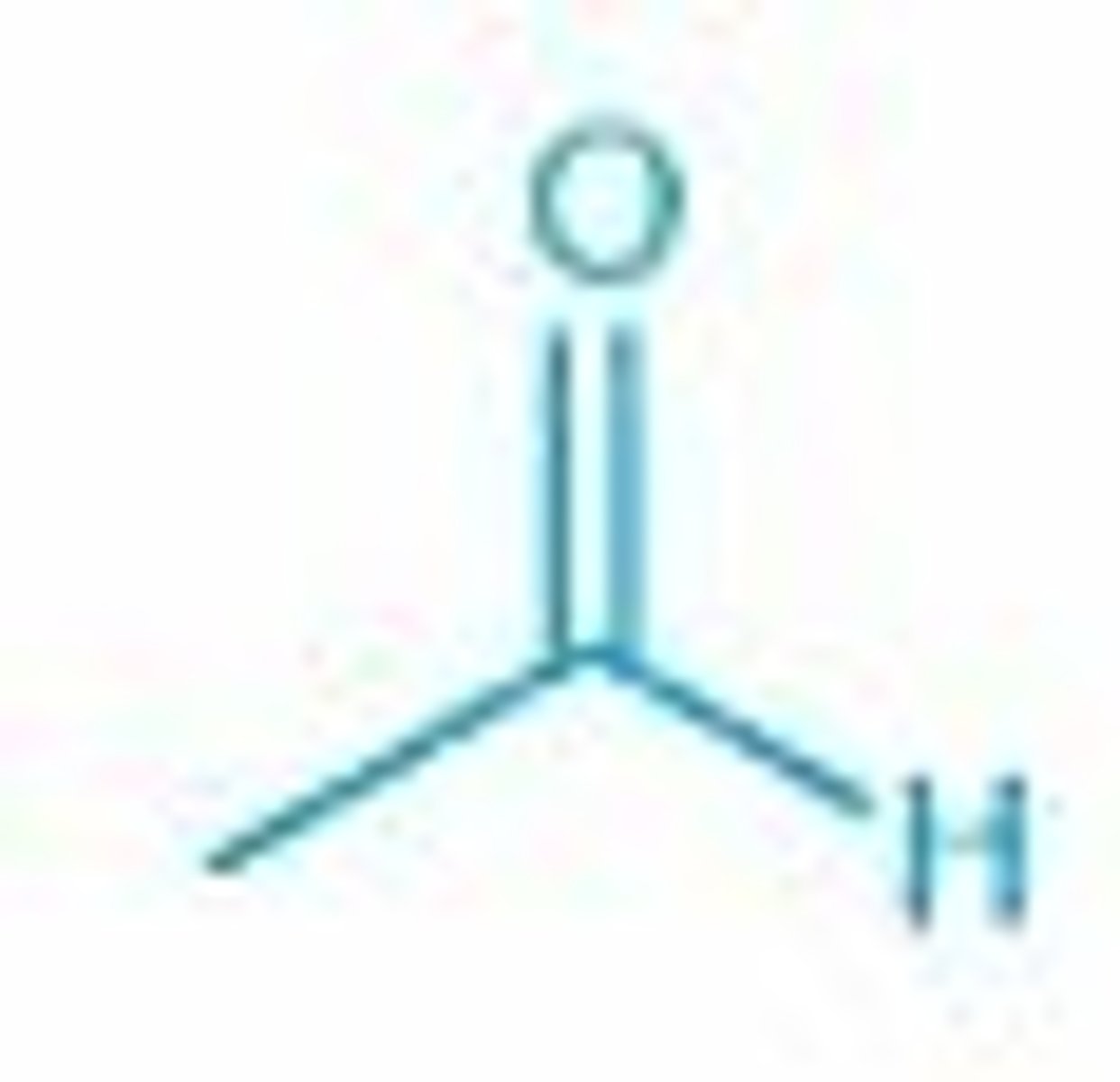
acrolein / propenal
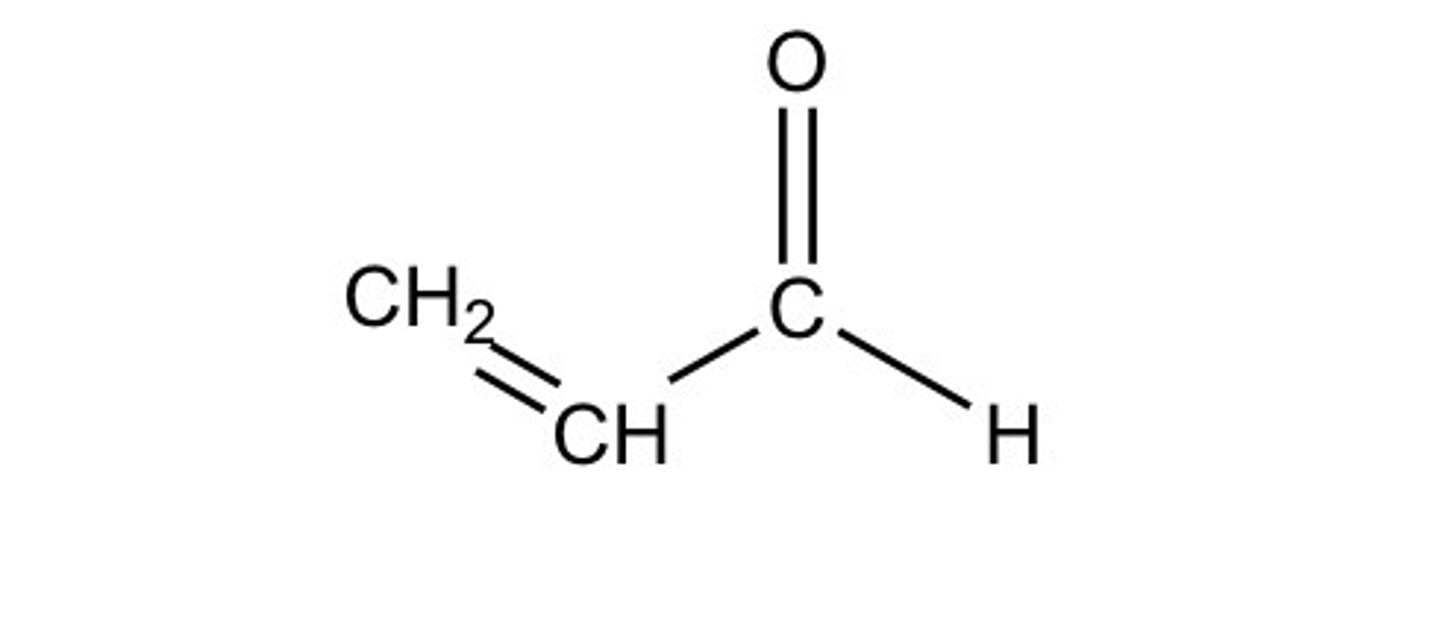
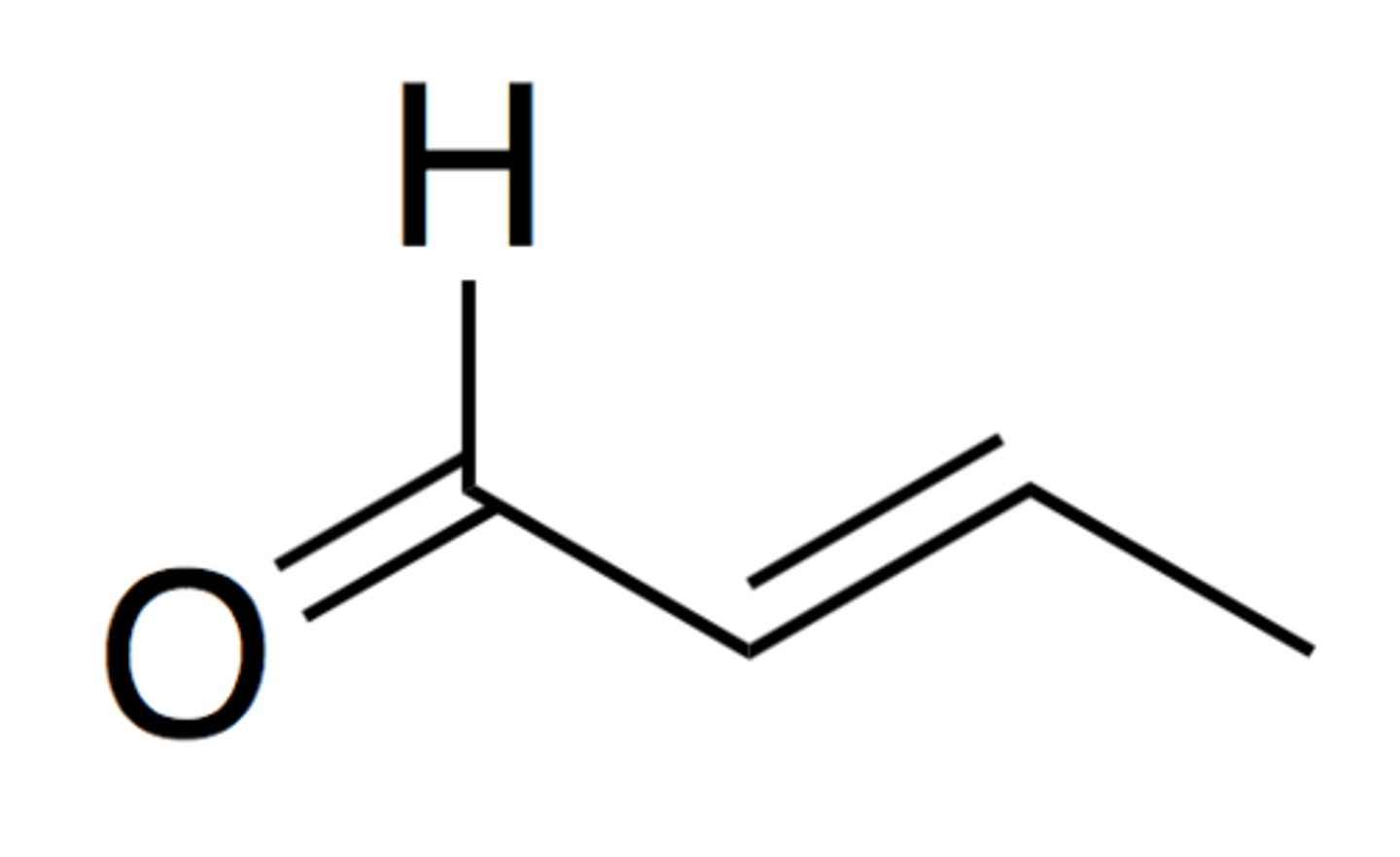
crotonaldehyde / 2 butenal
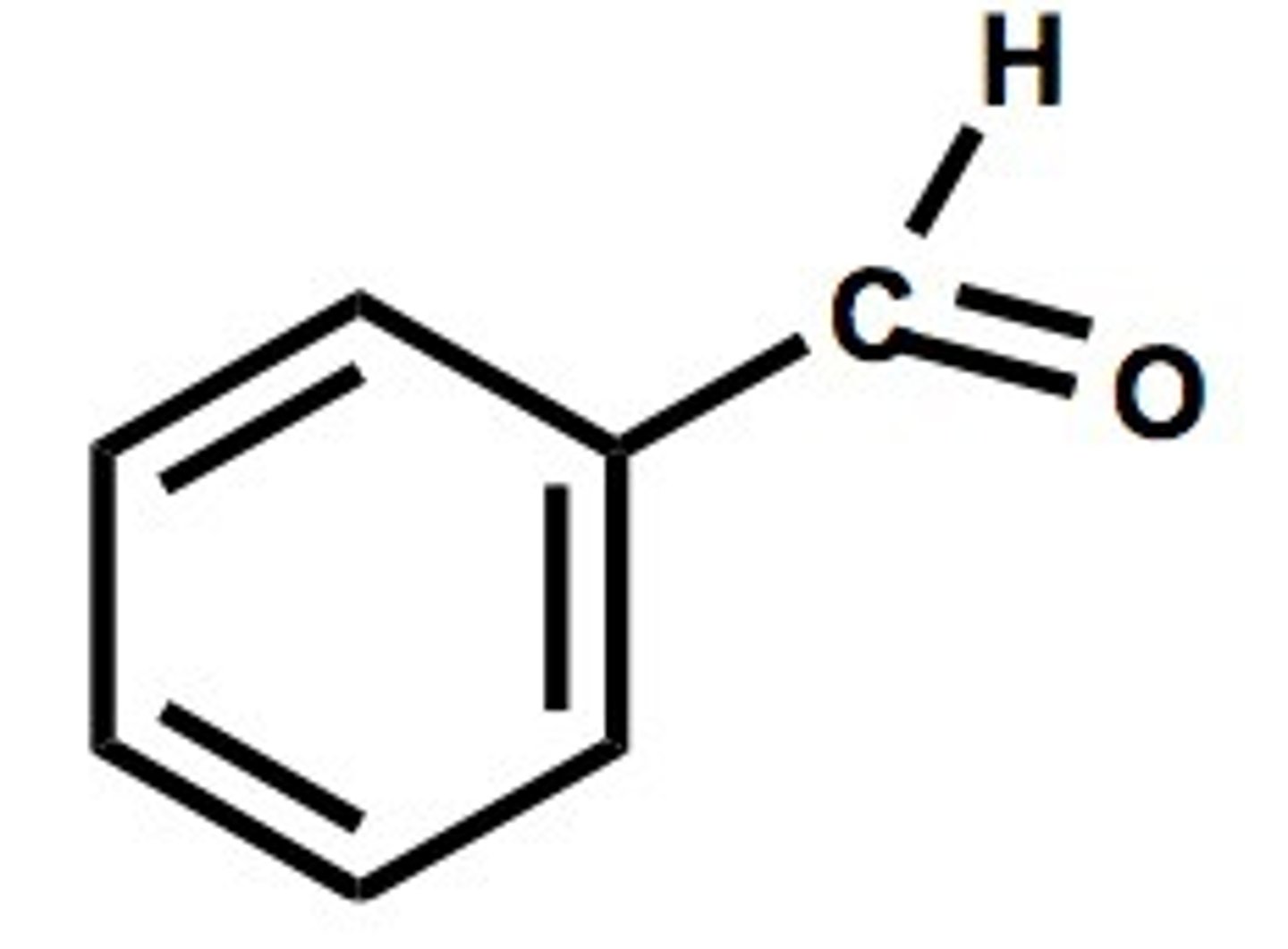
benzaldehyde
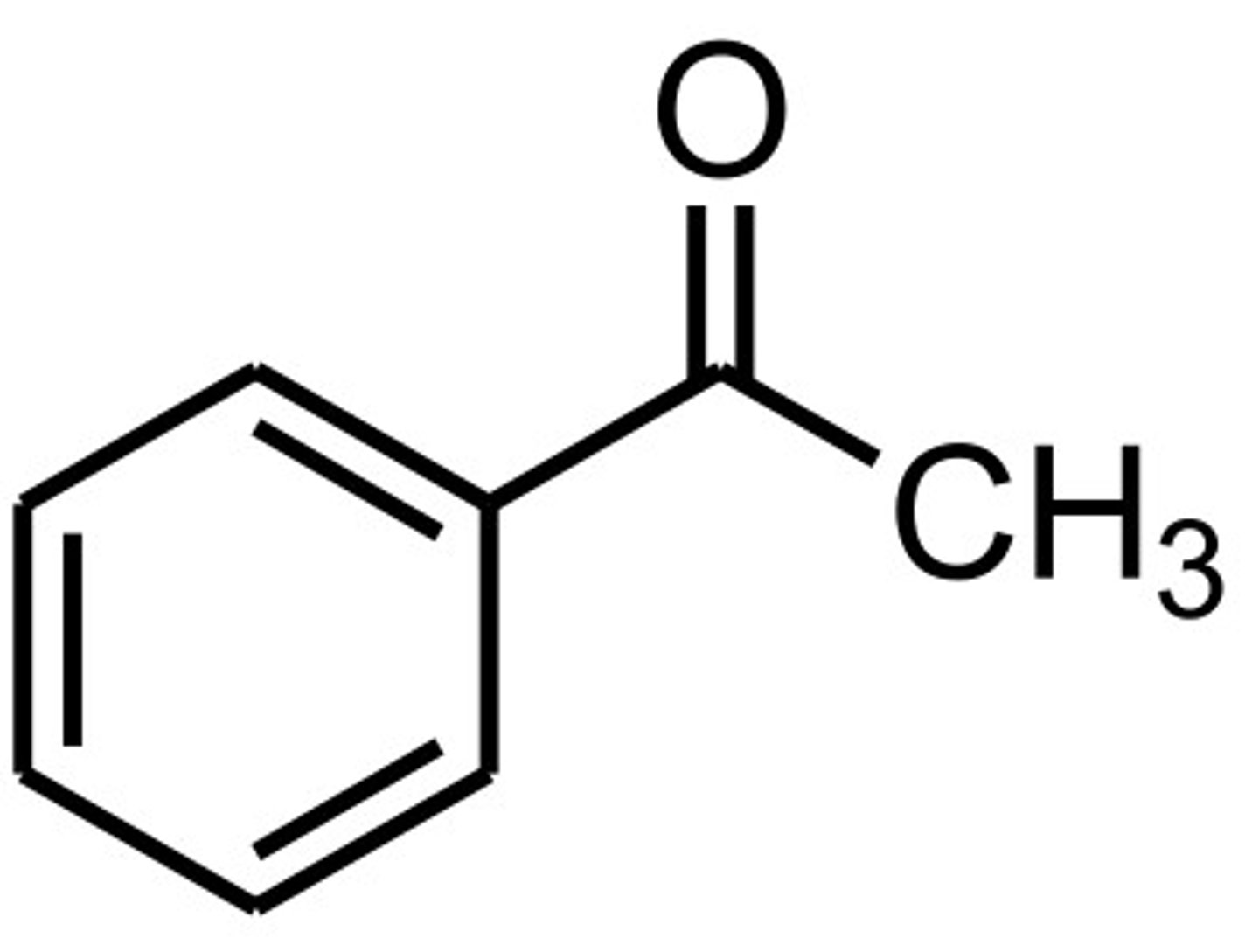
acetophenone
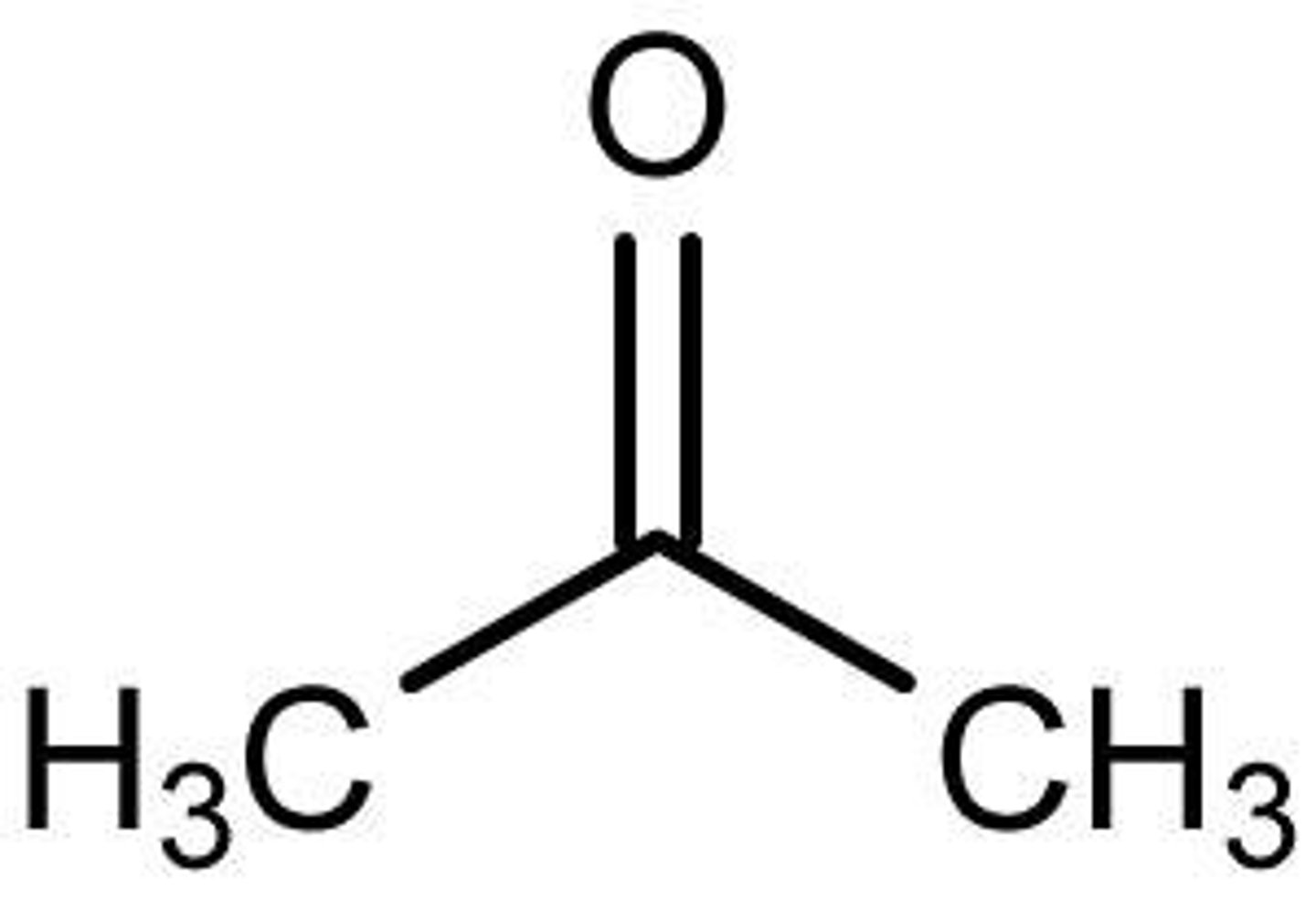
acetone
oxo is used when?
other functional groups are present
Oxidation of primary alcohols to get aldehydes
1. DMP/CH2Cl2
or PCC
Oxidation of esters to get aldehydes
2. DIBAH, toulene/H3O+
Oxidation of db to get aldehydes
3. O3/Zn,H3O+ (from double bonds)
Ketones prep from secondary alcohols
1. Periodinane or CrO3
Ketones prep
2. O3/Zn,H3O+ (from double bonds)
3. H3CCOCl, AlCl3/heat (friedal crafts j addition)
4. H30+/HgSO4 (from triple bonds)
oxidation OF aldehydes and Ketones
A: CrO3,H3O+/Acetone
K: 1.KMNO4/H2O 2. NaOH/H3O+ (gives di)
gives carboxylic acids
Nucleophilic Addition to aldehydes or ketones
can be addition ( Nu-/H2O) or substitutive ( NUH/H2O)
how cyanohydrins are formed too
Aldehydes and ketones react with water to form
diols
Aldehyde/ ketone + H-Y
reactive when y= -OCH3, -OH, -Br, -Cl, - HSO4-
NaBH4=
LiAlH4=
Formaldehydes/Aldehydes/Ketones/Esters + grignard (CH3MgBr, ether/ H3O+ )=
- only works on aldehydes and ketones
- works on everything including esters and carboxylic acids
- makes 1, 2, 3, 1 alcohols, DOES NOT WORK ON CA's
all makes alcohols
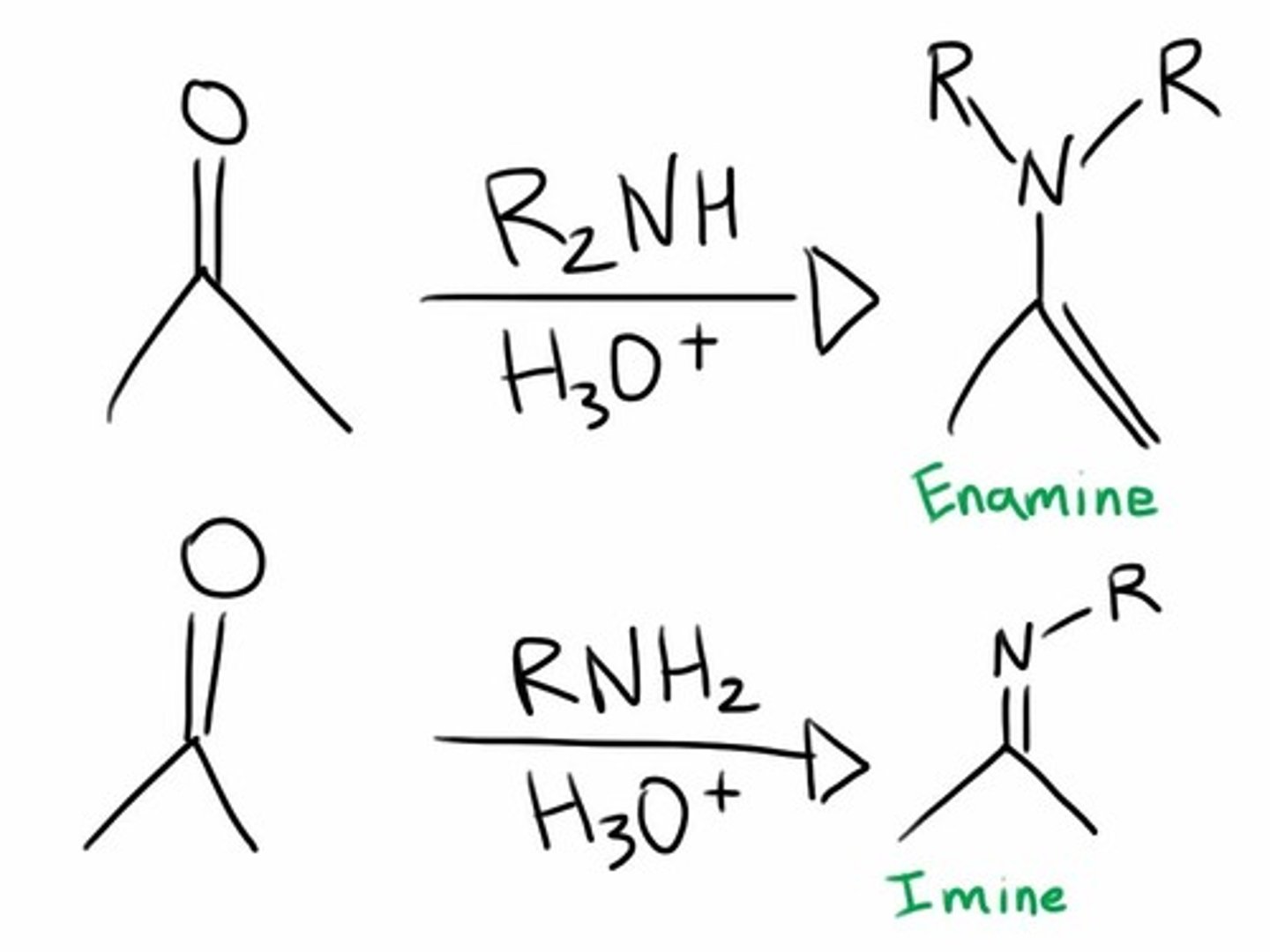
imine and enamine formation
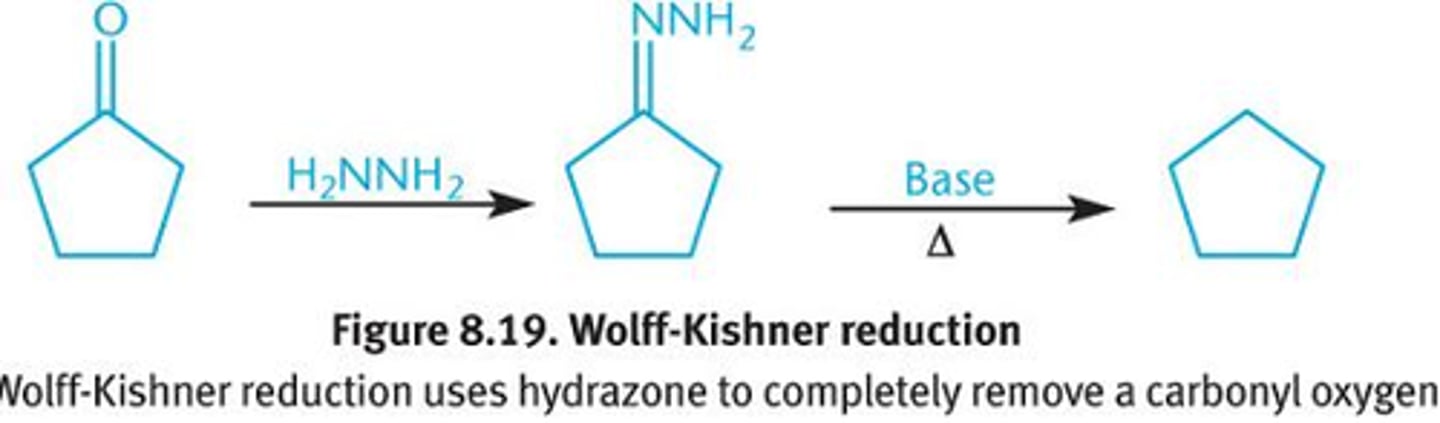
Wolf Kishner rxn (Aldehyde/ Ketone -) alkane)
H2NNH2/KOH
Aldehydes/ Ketones + 2 equiv Alcohols (2ROH)
Acetals
di ethers
can serve as protecting groups