vector borne
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
VECTOR-BORNE DISEASES
Chikungunya Virus Disease
Dengue Fever
Lymphatic Filariasis (Elephantiasis)
Malaria
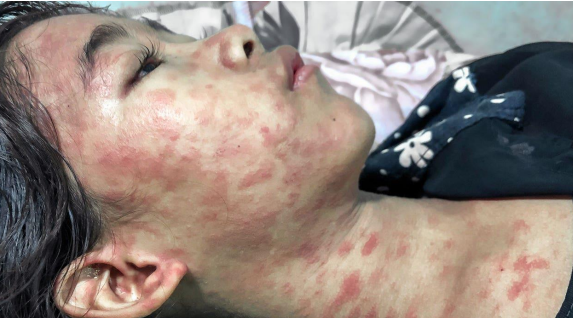
Chikungunya Virus Disease
Chikungunya, a viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes, causes joint pain and is rarely fatal. Symptoms last two to three days, with the virus remaining in the body for five to seven days.
Chikungunya Infectious agent
• CHIKV- chikungunya virus • An alphavirus genus of the Togaviridae family
Chikungunya Incubation Period
• 4-8 days
Mode of transmission Chikungunya
• Bite from an infected female mosquito (Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti)
• Aedes albopictus and aedes aegypti Chikungunya
• Day-biting (2 hours after sunrise and 2 hours before sunset)
• Low-flying
• Stagnant and clear water
• Urban communities
Clinical Manifestations Chikungunya
fever
Headache, nausea with occasional vomiting
petechial rash
joint pain
Diagnostic procedures Chikungunya
• Serology (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [ELISA])
Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Medical and Nursing Management Chikungunya
• No specific antiviral treatment
• Treatment is directed primarily at relieving symptoms (symptomatic treatment)
• There is no commercially available vaccine for chikungunya.
Dengue Fever
bite of an infected Aedes mosquito characterized by flu-like symptoms, but can progress to a more severe, potentially life-threatening form called dengue hemorrhagic fever. Benign form of disease with systemic symptoms, fever and often rash associated with pain behind the eyes, joints and bones.
Severe Dengue
sometimes fatal manifestation of dengue virus infection characterized by bleeding and hypovolemic shock.
Infectious Agent dengue
• Flaviviruses 1,2,3,4 from family of Togaviridae
• Arboviruses group B
Incubation period dengue
• 3-14 days, frequent in rainy season
Mode of Transmission dengue
Bite of an infected mosquito, principally by the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
Phases of Dengue
1. Febrile Phase
2. Critical Phase
3. Recovery Phase
Febrile Phase
• 2-7 days
• High fever (40°C)
• Rash (Herman’s rash)
• Mild hemorrhagic manifestations (petechiae, bleeding gums)
• Leukopenia and Thrombocytopenia
Critical Phase
Around the 3rd to 7th day of illness (DEFERVESCENCE STAGE- fever starts to subside)
• Warning signs: Severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, difficulty breathing, bleeding
• Severe dengue: Shock, organ failure, death
Recovery Phase
• 2-3 days
Diagnostic Procedures dengue
• Dengue NS1 antigen test (Requested 1-5 days of illness)
• Dengue IgM/IgG antibody test (Dengue Dot) (beyond 5 days)
• Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Torniquet test
Requested 1-5 days of illness during the early phase of acute dengue infection.
• Dengue NS1 antigen test
• Requested beyond 5 days
• IgM- acute, late infection
• IgG- previous infection
• May give false positive result due to antibodies induced by dengue vaccine.
• Dengue IgM/IgG antibody test (Dengue Dot)
One of gold standard lab test to confirm dengue virus.
• Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
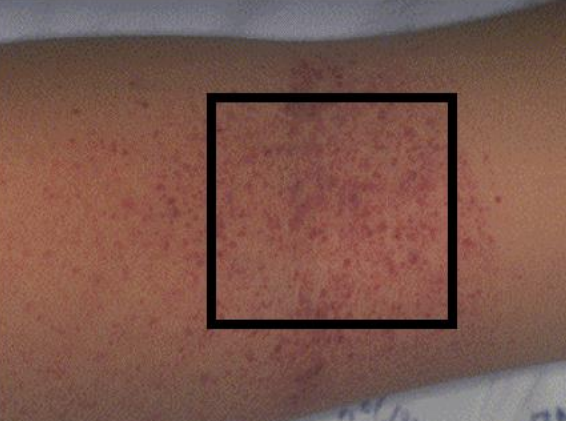
Torniquet test
(Rumpel Leade’s test/capillary fragility test)- screening test • Presumptive positive: >20 petechiae in 1 in square.
Medical Management dengue
• Priority: FLUID REPLACEMENT
• Symptomatic and supportive treatment
• Analgesic medications (Avoid: Aspirin)
• Paracetamol for fever
Nursing management dengue
• Encourage oral fluid intake
• Diet: avoid dark colored food
Lymphatic Filariasis (Elephantiasis)
A parasitic disease caused by several species of microscopic thread-like worms that only lives in human lymphatic system which causes extensive disability, gross disfigurement, and untold suffering.
Infectious Agents Lymphatic Filariasis
• Wuchereria bancrofti (Responsible for 90% of cases)
• Brugia malayi
• Brugia timori
Incubation Period Lymphatic Filariasis
• 8-16 months
Mode of transmission Lymphatic Filariasis
Person to person from bite of mosquitoes that harbor the parasite in their mouthparts.
Clinical Manifestations Lymphatic Filariasis
• Asymptomatic stage:
• Acute stage:
• Chronic stage: (10-15 years from onset of 1st attack)
Asymptomatic stage:
• 50% of all infected person
Acute stage:
• Fever, headache, and chills
• Swelling, redness and pain in the arms, legs or scrotum (lymphadenitis)
• Abscesses may appear as a result of dying worms or a secondary bacterial infection.
Chronic stage: (10-15 years from onset of 1st attack)
• Hydrocele, orchitis, spermatic cord inflammation, epididymitis
• Obstruction of lymph and serous fluid resulting in permanent and disabling elephantiasis of the lower extremities or testes.
Diagnostic Procedures Lymphatic Filariasis
• Circulating filarial antigen (CFA) test (immunochromatographic test)- done anytime of the day.
• Nocturnal Blood Exam (NBE)- blood test done after 8 pm (larvae is active at 10pm-2am)
Nursing management Lymphatic Filariasis
• Elevate affected leg and apply elastic bandage.
Medical Management Lymphatic Filariasis
Diethylcarbamazine citrate (DEC) or Hetrazan – kills larvae and adult worms.
Malaria
An acute and chronic parasitic disease transmitted by the bite of an anopheles mosquitoes and is confined mainly to tropical and sub-tropical areas
Malaria infectious agent
• Plasmodium Falciparum (• Most fatal; common in the Philippines)
• Anopheles mosquito malaria
• Night-time biting
• High-flying
• Rural areas
• Clear, flowing water and shaded streams
Clinical Manifestations (malaria)
• COLD Stage: severe, recurrent chills (30min-2hours)
• HOT Stage: Fever, headache and vomiting, seizure (4-6 hours)
• WET Stage: profuse sweating
Return to normal temperature with tiredness or malaise
Diagnostic Procedures malaria
• Malarial smear - Gold standard for diagnosis
Medical management malaria
• Artemeter-Lumifantine (Co-artem)
Nursing management malaria
• Cold stage- apply external heat and offer hot drinks.
• Hot stage- TSB, alcohol rubs, ice cap on forehead, antipyretic as ordered
• Wet stage- warm sponge bath • Provide comfort measures and increase fluid intake
• Cold stage- apply external heat and offer hot drinks.
Nursing management malaria
• Hot stage- TSB, alcohol rubs, ice cap on forehead, antipyretic as ordered
Nursing management malaria
• Wet stage- warm sponge bath • Provide comfort measures and increase fluid intake
Nursing management malaria
Prevention and Control of Vector-borne Diseases
• Search and destroy (breeding sites and elimination of vectors)
• Seek early consultation (early detection and treatment of cases)
• Self-protection measures (wear long sleeves, pants and socks, avoid hanging too many clothes inside the house, use of chemically treated mosquito nets)
• Say Yes to fogging (only during outbreaks) and house spraying.
• Environmental sanitation
• Search and destroy (breeding sites and elimination of vectors)
Prevention and Control of Vector-borne Diseases
• Self-protection measures (wear long sleeves, pants and socks, avoid hanging too many clothes inside the house, use of chemically treated mosquito nets)
Prevention and Control of Vector-borne Diseases
• Say Yes to fogging (only during outbreaks) and house spraying.
Prevention and Control of Vector-borne Diseases
• Environmental sanitation
Prevention and Control of Vector-borne Diseases