2Chromosomes and Cellular Reproduction
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
unicellular/no membrane bound organelles
its DNA does not exist in highly ordered and packed arrangement; typically no histones
circular DNA/typically only one chromosome/small amount of DNA/double stranded
made of eubacteria and arachaea
Nucleus absent
membrane bound organelles absent
Prokaryote
can be unicellular and multicellular with membrane bound organelles
DNA is surrounded in a nuclear envelope to make nucleus
DNA is closely associated with histones to form tightly packed chromosomes
Eukaryote
What is the role of histone proteins in eukaryotic chromosomes?
helps regulate accessibility of DNA to enzymes and other proteins that copy and read the DNA
enables the DNA to fit in to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell
Why do Eukaryotic cells require mechanisms to ensure that a copy of each chromosome is faithfully transmitted to each new cell?
Because unlike prokaryotes, eukaryotes have MULTIPLE linear DNA molecules (chromosomes) which can result in many errors if copying is not done correctly
do not posses the structure of a cell
composed of an outer protein coat surrounding DNA or RNA
can only survive with a host cell
Viruses
What are the 3 fundamental events that must take place for a cell to reproduce successfully?
genetic info must be copied
copies must be separate from each other
the cell must divide
What is the process that occurs when a prokaryotic cell reproduces?
Binary Fission
In binary fission, the specific place on a circular chromosome where replication begins
Origin of Replication
In binary fission how many origins of replication are there?
only one
First step of binary fission
replication of the circular chromosome begins at the origin of replication making two newly replicated chromosomes
Second step of binary fission
Origins of the two newly replicated chromosomes move away from each other and toward opposite ends of the cell.
Third step of binary fission
A new cell wall forms between the two chromosomes, producing two cells, each with an identical copy of the chromosome
Proteins that encircle the DNA and help keep the two newly synthesized chromosomes from getting tangled as they are replicated
Structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) complexes
Maintains precise spatial relations among the components of the nucleus and takes part in DNA replication, the expression of genes, and the modification of gene products before they leave the nucleus.
Nuclear Matrix
Explain a homologous pair
a set of chromosomes (one from each parent) in which they are alike in size and structure and carry information. the genes on each chromosome are in the same order, but these genes from both chromosomes can have different alleles based on the parent.
THEY ARE NOT IDENTICAL ONLY THE ORDER OF THE GENES ARE THE SAME
How many chromosomes does a human have? How many pairs? How many sets?
46 total chromosomes
23 pairs (23 from one parent and 23 from the other)
2 sets of chromosomes from each parent
Cells that carry two sets of genetic information/chromosomes (2n n=number of chromosomes)
Diploid
A single set of chromosomes (n) typically found in gametes
Haploid
Cells of some other eukaryotes contain more than two sets of genetic information
Polyploid
Diploid cells have ____
a. 2 chromosomes
b. 2 sets of chromosomes
c. one set of chromosomes
d. two pairs of homologous chromosomes
b (2 sets meaning a set from each parent)
True or False: Each chromosome is a single molecule of DNA
True
What three elements consider a chromosome functional?
centromere
pair of telomeres
origins of replication
Serves as the attachment point for spindle microtubules
Centromere
A multiprotein complex that assembles on the centromere and later attaches to spindle microtubules
Kinetochore
Chromosomes lacking a _______ cannot be drawn into the newly formed nuclei
Centromere
Submentacentric centromere

Metacentric centromere

Telocentric centromere

Acrocentric centromere
The specific DNA sequences and associated proteins located at the tips of whole linear chromosomes
Telomeres
What is the purpose of telomeres?
Protect and stabilize the chromosome ends. If a chromosome end breaks it will be degraded
In preparation for cell division, each chromosome replicates, making an IDENTICAL (same exact alleles) copy of itself called
Sister chromatids (2 molecules of DNA)
What would happen if a chromosome did not have a kinetochore?
Kinetochores are needed for spindle fibers to attach to the centromere and separate chromosomes. Without kinetochore, there would be no separation and there would be a missing chromosome in daughter cells.
The cell cycle consists of what?
Interphase (G1, S, G2) and m phase (mitosis and cytokinesis)
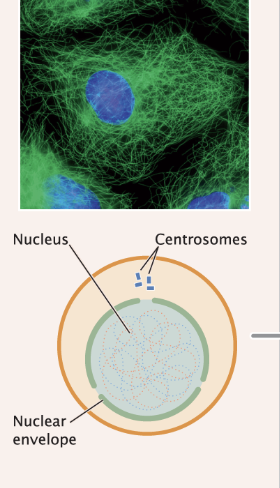
Phase in the cell cycle undergoing a period of growth, development between cell divisions as well as protein/biochemical reactions. Chromosomes are relaxed but never uncoiled
nuclear membrane is present and chromosomes are relaxed
Interphase
The cell grows and proteins necessary for cell division are synthesized. This stage typically lasts several hours.
G1 (Gap 1)
A phase during interphase that a cell can choose to go into before the G1/S checkpoint. Cells exit the active cell cycle in response to regulatory signals and pass into a nondividing phase. Cells usually maintain in size and can stay in this phase for a while.
G0
A checkpoint that holds the cell in G1 until the cell has all the enzymes and proteins necessary for the replication of DNA. After this checkpoint is passed then the cell is committed to divide.
G1/S checkpoint
The phase in during interphase where each chromosome is duplicated
S Phase
Before: each chromosome is unreplicated
After: each chromosome is replicated making 2 sister chromatids and are connected by a centromere
True or False: DNA synthesis must take place before the cell can proceed to mitosis
True
If DNA synthesis is blocked (by drugs or by a mutation), the cell will not normally be able to undergo mitosis
The stage in interphase where several additional biochemical events necessary for cell division take place
G2
A checkpoint near the end of G2 that makes sure all of the cell’s DNA is replicated and undamaged. If cell does not pass, then some additional proteins may be activated in order to pass so that it can divide and enter the M phase
G2/M checkpoint
Part of the cell cycle in which the copies of the cell’s chromosomes (sister chromatids) separate and the cell undergoes division
M Phase
State the 5 stages of mitosis and the last part of the M phase
prophase
prometaphase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
cytokinesis
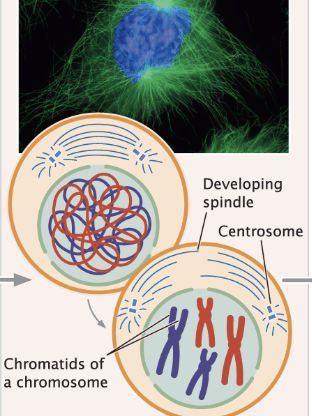
chromosomes condense forming chromosomes
each chromosome has 2 sister chromatids that have identical alleles
mitotic spindle forms
Prophase
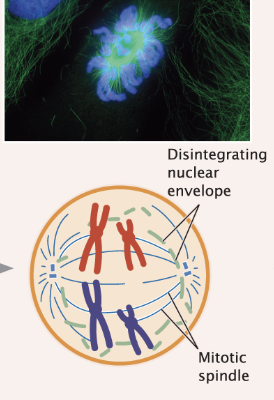
nuclear membrane disintegrates
spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores on centromeres of chromosomes/sister chromatids
Prometaphase
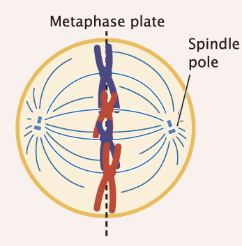
chromosomes line up on the plate
spindle fibers extend from the centromeres to the centrosomes
Metaphase
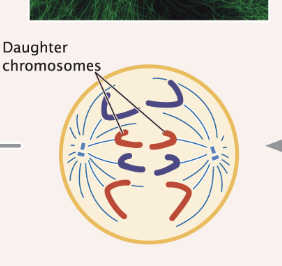
the sister chromatids move towards opposite poles
previously known 2 sister chromatids are now known as 2 individual unreplicated chromosomes
Anaphase
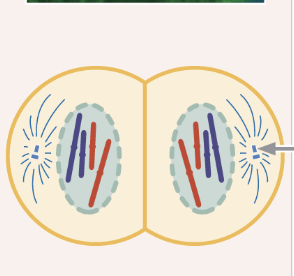
chromosomes arrive at spindle poles
centrosomes are at the poles with few remaining spindle fibers
nuclear membrane re-forms
chromosomes relax
Telophase
Encircle DNA within chromosomes and bring about condensation. A type of structural maintenance of chromosomes complex that plays a role in chromosome segregation
Condensins
During prometaphase, ______ molecules are added to and removed from the microtubules, causing them to undergo repeated cycles of growth and shrinkage
Tubulins
cytoplasm divides
Cytokinesis
True or False: Mitosis ensures that one of the two sister chromatids from each replicated chromosome passes into each new cell.
True
True or False: Each of the cells produced contains a full complement of chromosomes: there is no net reduction or increase in chromosome number.
True
What process produces genetically variable cells?
Meiosis
What process causes the chromosome number in the newly formed cells to be reduced by half?
Meiosis
Process that comes at the end of meiosis I resulting in the number of chromosomes per cell to be reduced by half
Reduction Division
Process that comes at the end of meiosis II
Equational Division
What are the substages of Prophase I?
leptotene
zygotene
pachytene
diplotene
diakinesis
What are the stages of meiosis I?
Prophase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
What are the stages of meiosis II?
prophase II
metaphase II
anaphase II
telophase II
Stage of prophase I: chromosomes condense and become visible.
Leptotene
Stage of prophase I: chromosomes continue to condense; homologous chromosomes pair up and begin synapsis
Zygotene
Close pairing of chromosomes
Synapsis

A homologous pair of synapsed chromosomes consisting of 4 chromatids
Bivalent/Tetrads
Stage of Prophase I: Chromosomes become shorter and thicker, and a three-part synaptonemal complex develops between homologous chromosomes
Pachytene
Crossing over where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic information occurs when? Are these diploid or haploid?
Prophase I and diploid (92)
Stage of Prophase I: Centromeres of the paired chromosomes move apart, but the two homologs remain attached at each chiasma.
Diplotene
Stage of Prophase I: chromosome condensation continues, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle forms, setting the stage for metaphase I
Diakinesis
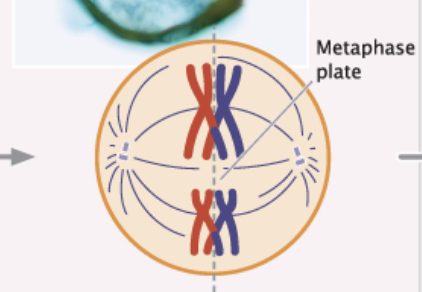
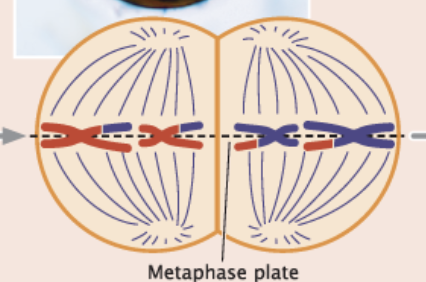
Initiated when homologous pairs of chromosomes align along the plate.
A microtubule from one spindle pole attaches to one chromosome of a homologous pair, and a microtubule from the other pole attaches to the other member of the pair
diploid 92
Metaphase I
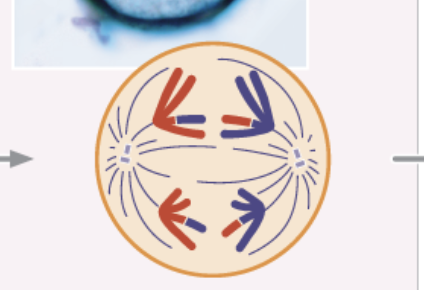
homologous chromosomes separate and move toward opposite poles
sister chromatids remain attached and travel together
Anaphase I
chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles
homologous chromosomes are now considered sister chromatids
cytoplasm divides
haploid (n) 46
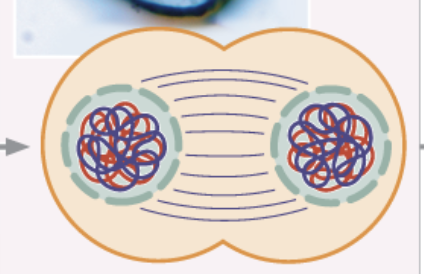
Telophase I
chromosomes recondense and the events of interkinesis are reversed
sister chromatids form
spindle re-forms
nuclear membrane once again breaks down
haploid 46
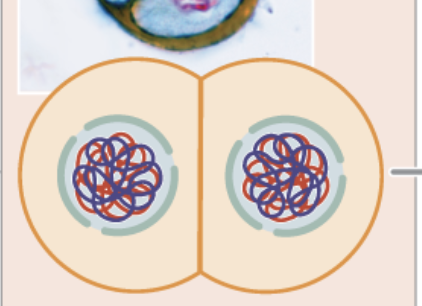
Prophase II
individual chromosomes/sister chromatids line up on the equatorial plate (horizontal)
haploid 46
Metaphase II
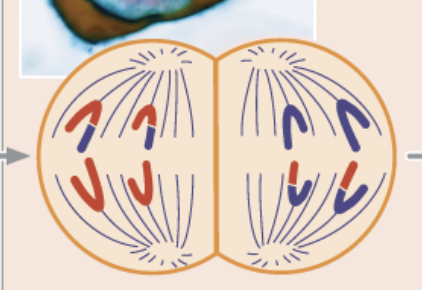
sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles
each chromatid is now considered a chromosome
haploid 46
Anaphase II
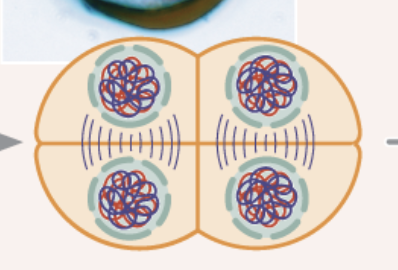
chromosomes arrives at the spindle poles
cytoplasm divides again
nuclear membrane reforms around chromosomes
4 genetically non-identical haploid gametes form
haploid 23
Telophase II
The period between meiosis i and meiosis II in which the nuclear membrane re-forms around the chromosomes clustered at each pole, the spindle breaks down, and the chromosomes relax
Interkinesis
Which of the following events take place in metaphase I?
a. crossing over
b. chromosomes condense
c. homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate
d. individual chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate
C
What two processes result in genetic differences that are unique to meiosis?
crossing over (occurs in Prophase I)
separation of homologous chromosomes (In anaphase I)
After crossing over, will the sister chromatids be identical still?
No
The creation of new combinations of alleles on a chromatid
Recombination
A protein that holds chromatids together and is another type of structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) complex
Cohesin
During anaphase of mitosis, where does cohesin lie?
Along the entire length of the chromosome
What breaks down cohesin in mitosis that allows the sister chromatids to separate?
Separase
During anaphase I of meiosis how does cohesin lie?
Along the length of the chromosome but at the centromere they are protected by shugoshin
What is the role of shugoshin?
Prevents the separation of the two sister chromatids during anaphase I. It is broken down by the end of metaphase II, allowing cohesin to be broken down
Production of gametes in a male animal and takes place in the testes
Spermatogenesis
diploid primordial germ cells that divide mitotically to produce diploid cells
can undergo repeated rounds of mitosis
can also initiate meiosis and enter prophase I and make a primary spermatocyte
Spermatogonia
formerly a spermatogonia
cell is still diploid since chromosomes have not yet separated
completes meiosis I and becomes secondary spermatocyte
Primary spermatocyte
formerly primary spermatocyte
undergo meiosis II making two haploid spermatids
Secondary spermatocyte
a secondary spermatocyte that underwent meiosis II
Spermatids
How many haploid spermatids does each primary spermatocyte produce?
4
Production of gametes in a female animal
Oogenesis
Is produced when diploid primordial germ cells divide mitotically in the ovaries
can undergo rounds of mitosis or can also go through meiosis
If undergoes meiosis, turns into primary oocytes in prophase I
diploid
Oogonia
formerly oogonia
completes meiosis I
still diploid
produces 2 products
Primary oocytes
the name when most of the cytoplasm is allocated to the chosen haploid cell out of the two primary oocytes/cell
now haploid and completed meiosis II
cytokinesis is unequal
produces two products
Secondary Oocyte
The smaller cell, which contains half of the chromosomes but only a small part of the cytoplasm
doesn’t have a purpose and disintegrates
First polar body
one of the products from the secondary oocyte
cytokinesis is unequal again
acquires most of the cytoplasm
capable of being fertilized
Ovum
the smaller cell after production of the ovum
disintegrates
Second polar body
How many gametes are produced form each primary oocyte?
One