Core Content
1/421
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
422 Terms
What does PVA stand for?
Polyvinyl acetate
What can PVA be used on?
Wood (widely used for the construction of furniture)
How strong is PVA?
Strong
How long does PVA take to dry?
4-24 hours
What can hot glue guns be used for?
Woods, plastics and metals
What strength joint does a hot glue gun give?
Medium strength
What form is the glue in hot glue guns?
Thermoplastic glue sticks
How long does hot glue take to dry?
30 seconds once cooled
What can all purpose adhesive be used on?
Wood, plastics and metals
What can UHU be used to glue?
Mixed materials, viable joints and transparent materials
What strength joint does UHU give?
High strength
What form does UHU come in?
liquid
What is the drying time of UHU?
10 minutes
What can araldite be used on?
wood, plastic, metal and as a filler to bridge/fill gap as it is waterproof
What strength joint does araldite give?
Strong
What form does araldite come in?
2 tubes - hardener and resin
What is the drying time for araldite?
1/2 - 6 hours
What can tensol be used on?
Thermoplastics
What is tensol used for?
Joining plastics?
How does tensol work?
Dissolves the surfaces, fusing them together
What strength joint does tensol give?
Medium
What is the drying time of tensol?
3-24 hours
What is one point perspective?
What is 2 point perspective?
What can 1 point perspective be used for?
What can 2 point perspective be used for?
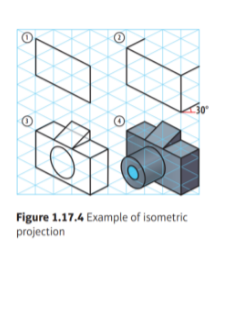
What are the 3 rules of isometric drawing?
- horizontal edges are drawn at 30 degrees
- vertical edges are drawn as vertical lines
- parallel edges appear as parallel lines
What are the benefits of isometric drawings?
What can isometric drawings be used for?
"
They are used by architects and engineers to communicate their ideas to the client and manufacturer, showing the product or design to scale
What are orthographic projections?
"Orthographic projections are working drawings in either a first or third angle projection and show each side of a design without perspective, ie a 2D drawing of a 3D object.
"
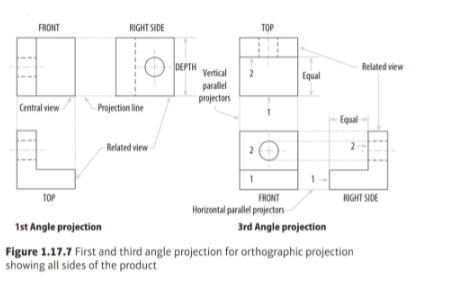
What can orthographic drawings be used for?
How do orthographic drawings work?
What does an oval represent?
Start/end
What does a parallelogram mean?
input/output
What does a diamond mean?
A decision/question
What does a rectangle mean?
A process/action
What is the main component of polymers?
Crude oil (usually made from oil-based petrochemicals), but coal and gas can also been used
What is environmentally unfriendly about crude oil and polymers?
What are the 2 types of plastics?
Thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics
What can thermoplastics be used for?
Milk bottles, food packaging
What can thermosetting plastics be used for?
Light switches, plug sockets
Which type of plastic is easier to recycle?
Thermoplastics
What is the difference between the 2 plastics?
Thermosetting plastics burn if heat is applied, but thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped multiple times
What is the iterative design process?
What is collaboration?
What are the advantages of collaboration?
innovative product.</div>
wouldn’t have thought of</div>"
What does SCAMPER stand for?
"

What is user centred design?
What are the advantages of user centred design?
What is systems thinking?
How can you use systems thinking to design products?
What is paper made of?
Fine cellulose fibres, usually from wood but also hemp, flax, cotton or bamboo, pressed together with water and then dried
How is the required texture and surface finish achieved?
What is paper and board measured in and what does it mean?
How is paper made?
What is paper?
A mixture of 2+ metals or elements, which has improved properties and characteristics
What is toughness?
Resistant to impact and water
What is board?
What is flexibility?
Amount material bends when a force is applied, determined by thickness and weight
What is flexural stiffness?
Resistance to an external bending force
What is handling stiffness?
The ability to support its own weight
What is printability?
What is printability affected by?
What is biodegradability?
Ability to be broken down by bacteria or other biological means
What does compostable mean?
Compostable means that a material can biodegrade in less than 12 weeks
Why are most uncoated paper products biodegradeable?
Most uncoated paper products are biodegradable because they are made from wood pulp
What is an electronic system?
It has input and output devices, with a controller between them
What does the electronic system do?
What is the input, controller and output of a computer?
Mouse or buttons on keyboard - input (give information to the computer) ----> computer controller reads inputs, and the program tells it what to do ----> Screen/printer/laser cutter/robot in a factory
What is a light dependant resistor (LDR)?
What is input signal?
Information given to the system by an input device
What is input device?
Something that can give an input signal to the system
What is an output signal?
An instruction the system gives to an output device
What is an output device?
Something that is controlled by the output signal from the system
What is a program?
A set of instructions the system controller has been given to make the electronic system do what it's supposed to do
What is resistance?
A measure of how easy it is for electricity to flow in a circuit
What is a sensor?
It is affected by the conditions around it.
What is a thermistor?
How does an electric thermometer use a thermistor?
As the temperature changes, the system measures the resistance of the thermistor and turns it into a number to display on a screen
What else can be used to give an input signal?
As well as sensors, there are some other components than can be used to give an input signal to an electronic circuit
What is a rocker switch?
What is a resistor?
What can resistors be used for?
What is a transistor?
A tiny electronic switch which has 3 connections
What are the 3 connections of a transistor?
Why are transistors useful?
In sensing circuits to amplify the small current you get from some sensors
What kind of conductor is a transistor?
A semi-conductor
How can transistors be made extremely small?
By etching them onto silicon wafers known as silicon chips
What are output devices controlled by?
What is a buzzer and how is it useful?
What is an LED and what is it used for?
What is a component?
An individual piece of a circuit
What is circuit
Individual components are joined up with a conductive material so electricity can flow through them and perform a task
What is voltage?
The amount of force available that could make electricity flow
What is current?
The amount of electricity that is flowing through a circuit
What is a semi-conductor?
A material that allows electricity to flow under certain conditions