macromolecules
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
a cell is
the smallest most basic biological unit of life
proteins
polymer of amino acids
variety of functions
catalyze
structural ex, filaments
20 different amino acids
nucleic acids
chemical molecule that carries genetic information
dna
vast amount of hereditary info
coiled and twisted into highly compact form
made of nucleotides
nitrogenous base
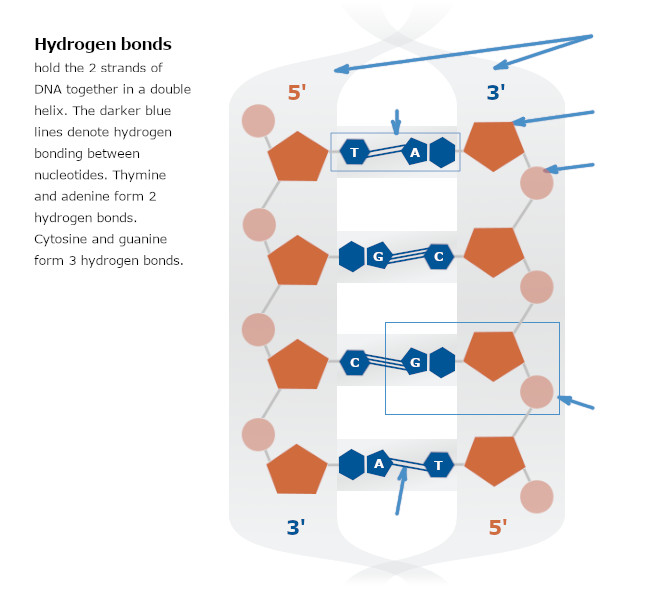
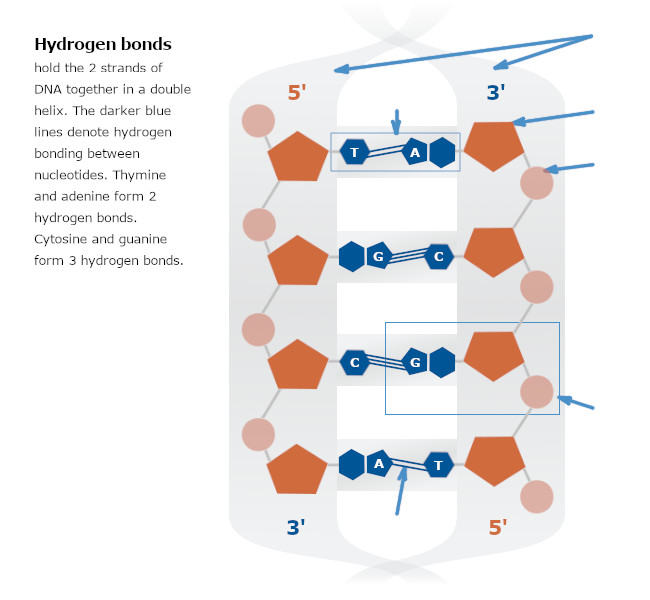
adenine, guanine (purine)
cytosine or thymine (pyridine)
a and t, c and g
deoxyribose
phosphate
rna
interprets the information, can leave nucleus
uracil instead of guanine
reads the opposite
lipids
mainly composed of hydrophobic hydrocarbons
foundation of plasma membrane
restricts movements of materials in or out the cell
carbohydrates
carbohydrate is watered carbon ch2o
monosaccharides
only one sugar unit
linear or ring
ring better for structure
disaccharides
two monosaccharides
sucrose is a disaccharide
lactose, maltose
polysaccharides
many saccharides
important for energy storage
plant poly = starch
cell walls
hydrogen bonds