AP Comparative Iran Terms
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Assembly of Religious Experts
86 man assembly of clerics elected directly by the people; broad constitutional interpretation responsibility; selects the Supreme Leader; has the right to dismiss Supreme Leader; must have a seminary degree
Ayatollah
Supreme leader of Iran; following the revolution, Khomeini became the country's Supreme Leader, a position created in the constitution as the highest ranking political and religious authority of the nation.
Dual society
a society and economy that are sharply divided into a traditional, usually poorer, and a modern, usually richer, sector
Faqih
an expert in Islamic Law; leading Islamic jurist to interpret the meaning of religious documents and sharia - HINT: think of this as the person who has jurist's guardianship
Farsi
the language and people group of Iran, also often called Persian
Fundamentalism
Religious beliefs of a literal nature that often lead to right-wing political views.
Guardian Council
This is the most powerful theological body in Iran. It consists of 12 members 6 clerics appointed by the Supreme Leader and 6 judges appointed by the Majils. The importance of them is they have to approve all candidates and all legislation.
Hezbollah
A radical Shiʿite Muslim organization in Lebanon engaged in guerrilla warfare against Israel; have strong ties to Iran
Hojjat al-Islam
literally "the proof of Islam." In Iran, it means a medium-ranking cleric.
Imam
Prayer leaders in mosques
Jihad
Literally "struggle"; although often used to mean armed struggle against unbelievers, most commonly means spiritual struggle for self-improvement.
Jurist's guardianship
Developed by Ayatollah Khomeini, supports the notion that senior clerics have the best capacity to rule in a Muslim society; Iranian clergy should rule on the grounds that they are the divinely appointed guardians of both the law and the people
Majles
Arabic term for "assembly"; used in Iran to describe the parliament.
Mosque
Muslim place of worship, equivalent to a church, temple, or synagogue.

OPEC
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries; Founded in 1960 by Iran, Venezuela, and Saudi Arabia, it now includes most oil-exporting states with the notable exceptions of Mexico and former members of the Soviet Union. It tries to regulate prices by regulating production.
Pahlavis
Leaders of the dynasty of the shahs, favored westernization
Pasdaran
Persian term for guards, used to refer to the army of Revolutionary Guards formed during Iran's Islamic Revolution.
People of the Book
The Muslim name for Jews and Christians for whom the Muslims had religious tolerance; called this because each religion had a holy book with teachings similar to that of the Qur'an
Qanun
Regular laws passed by the government. Are second to Shariah law
Qur'an
Muslim holy book, believed to be the word of God, given to prophet Muhammad

Rentier state
A country that obtains much of its revenue from the export of oil or other natural resources.
Shari'a
Islamic law derived mostly from the Qur'an and the examples set by the Prophet Muhammad.
Shi'ism (or Shiite)
Dominant branch of Islam in Iran, believe that the head of Islam should be a descendant of prophet Muhammad
Supreme Leader
Title given to the ayatollah who sits atop all Iranian political institutions.
Theocracy
A government ruled by religion; religious leaders are the head of the nation-state; rule on the grounds that they are the only interpreters of God's will and law.
Tudah Party
an Iranian communist party. Formed in 1941, with Soleiman Mohsen Eskandari as its head, it had considerable influence in its early years and played an important role duringMohammad Mosaddeq's campaign to nationalize the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company and his term as prime minister. Its influence waned in the crackdown that followed the 1953 coup against Mosaddeq. The party still exists, but is much weaker as a result of the banning of the party and mass arrests by the Islamic Republic in 1982 and the executions of political prisoners in 1988.
White Revolution
The term used by the shah to describe reforms in Iran between the end of World War II and the downfall of his regime in 1979
Zoroastrianism
Persian religion founded by Zoroaster; taught that humans had the freedom to choose between right and wrong, and that goodness would triumph in the end
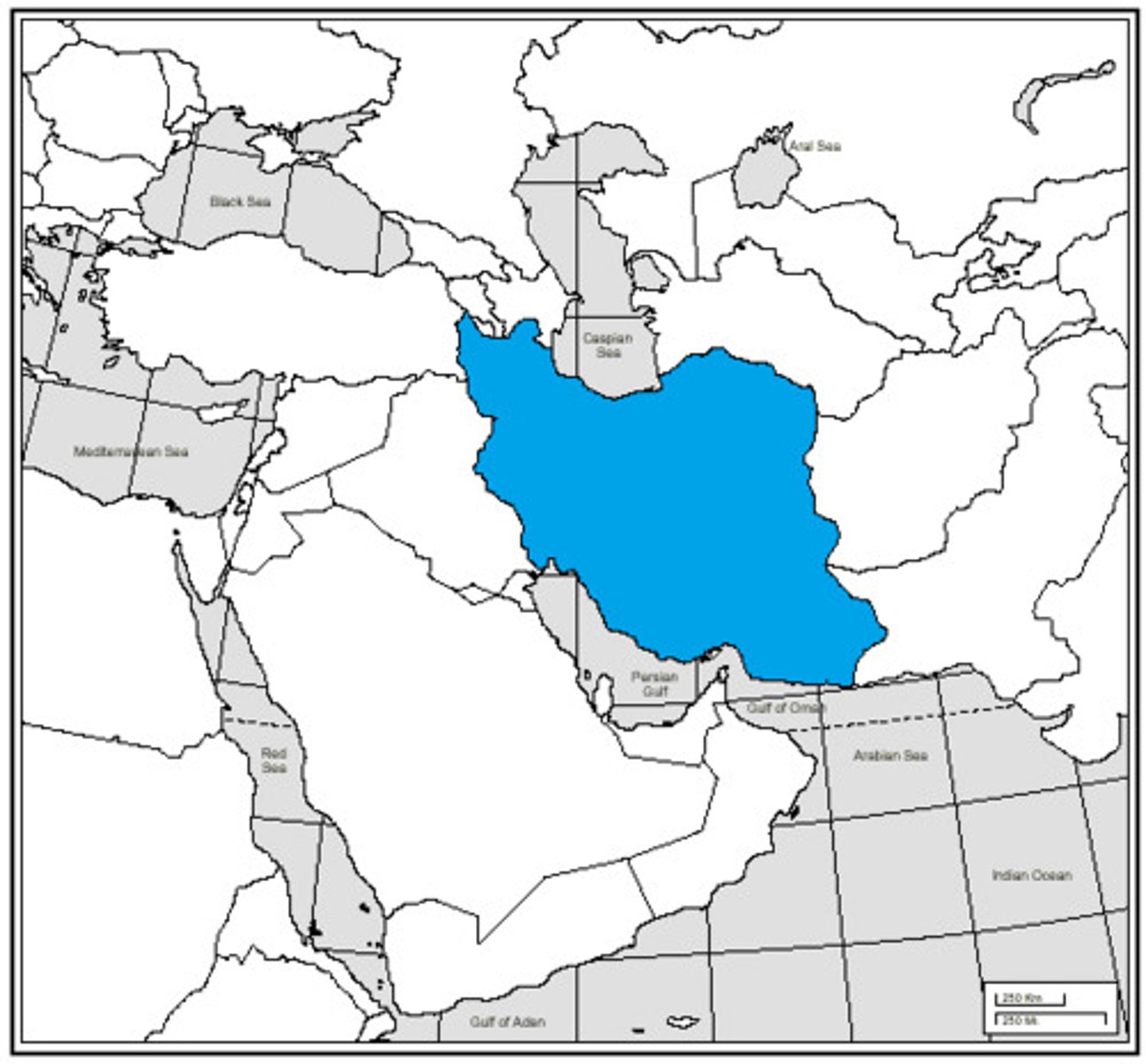
Iran
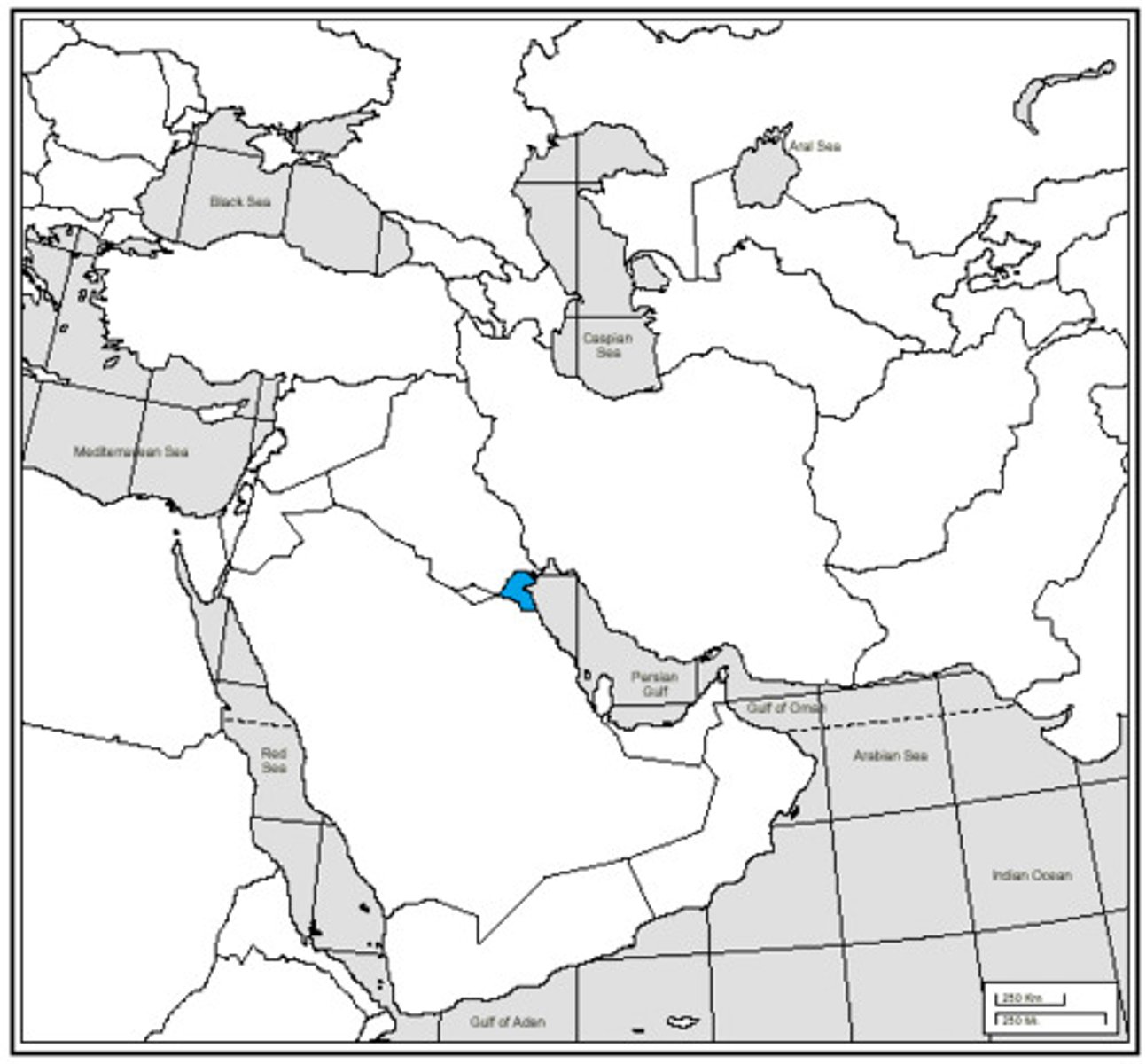
Iraq
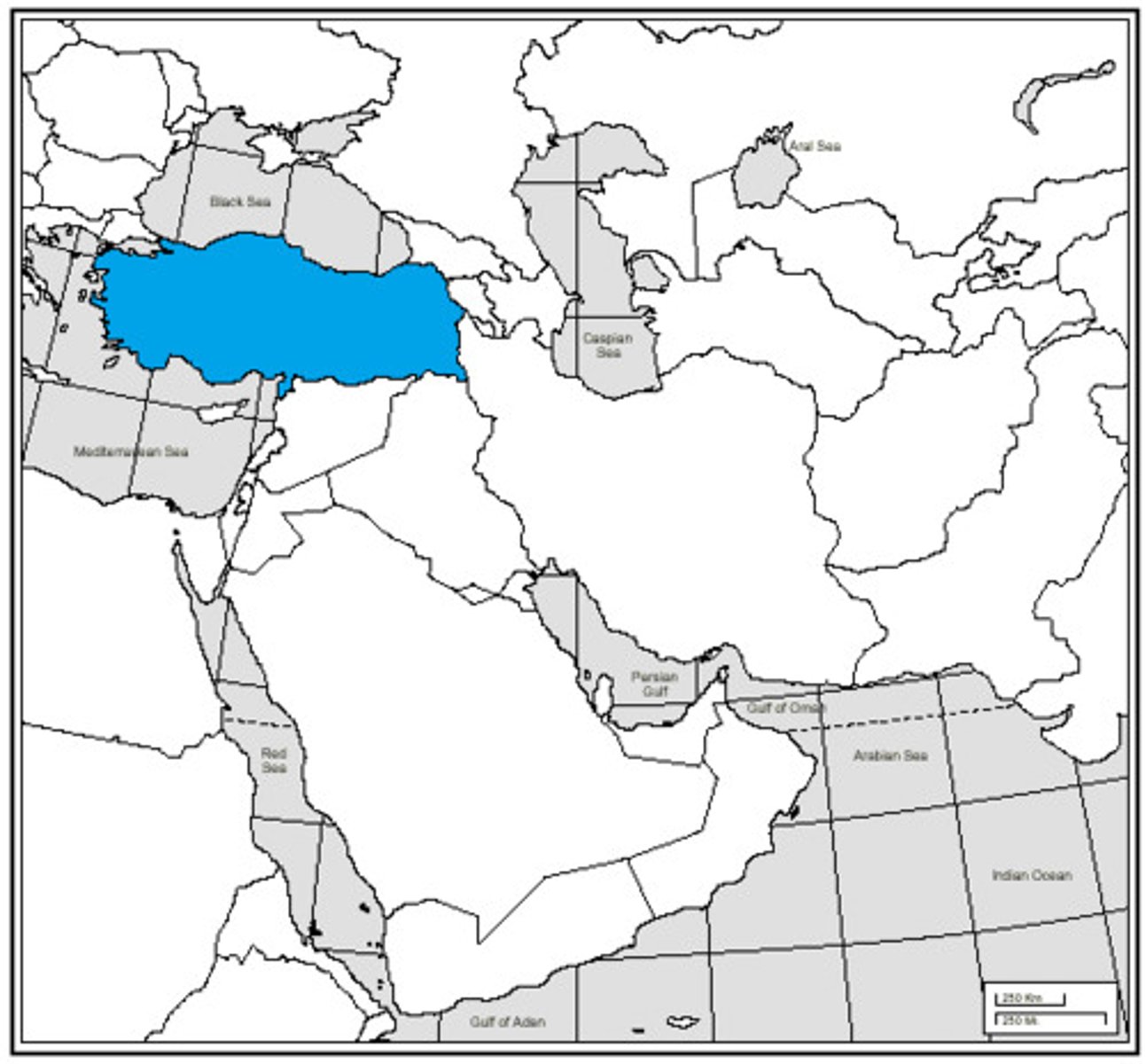
Turkey
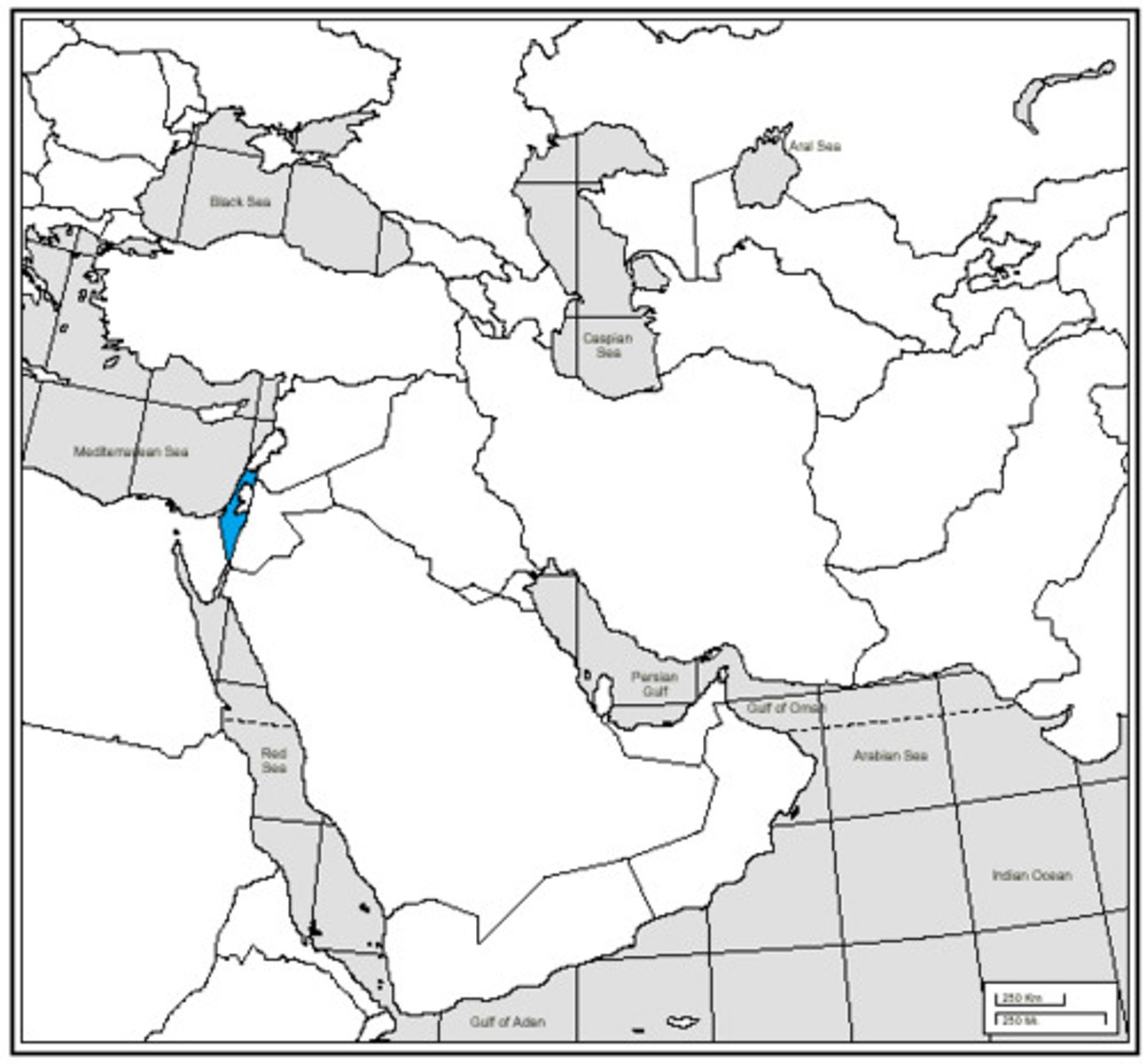
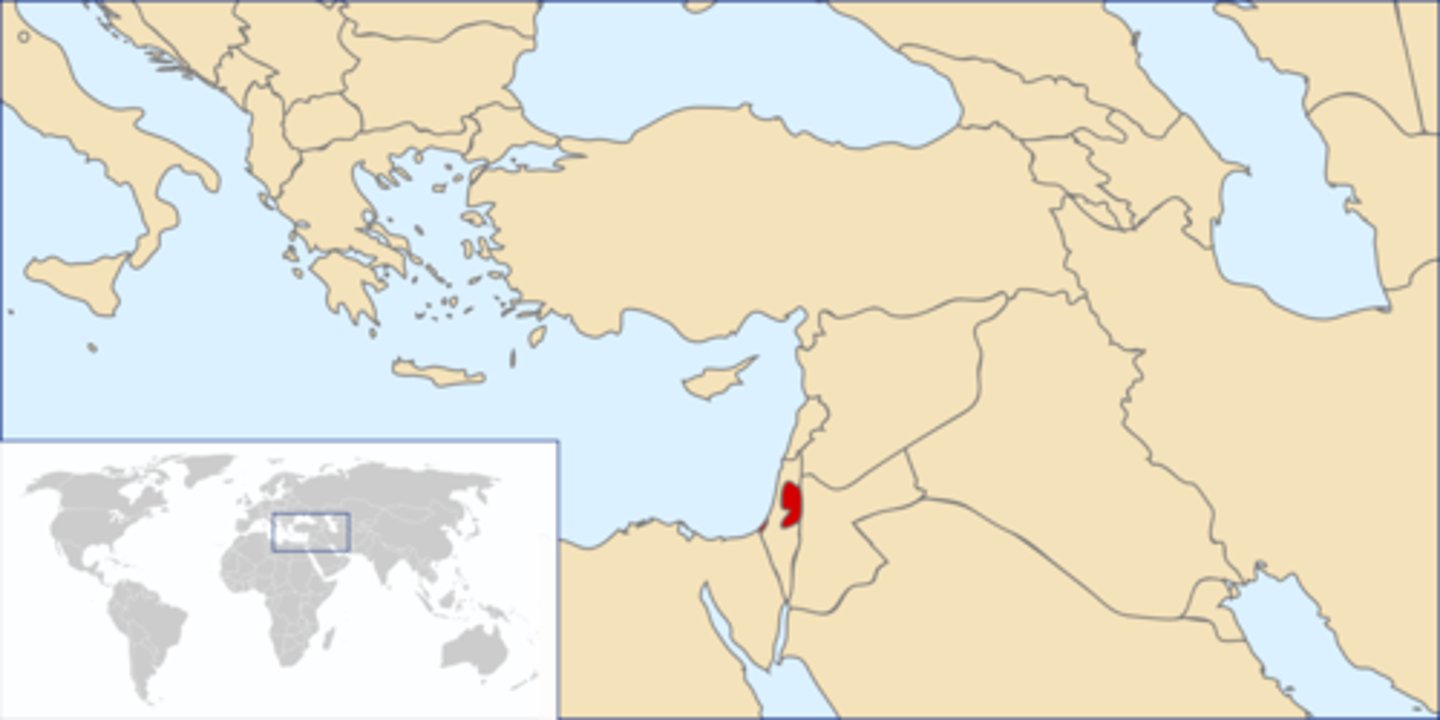
Israel
Palestine
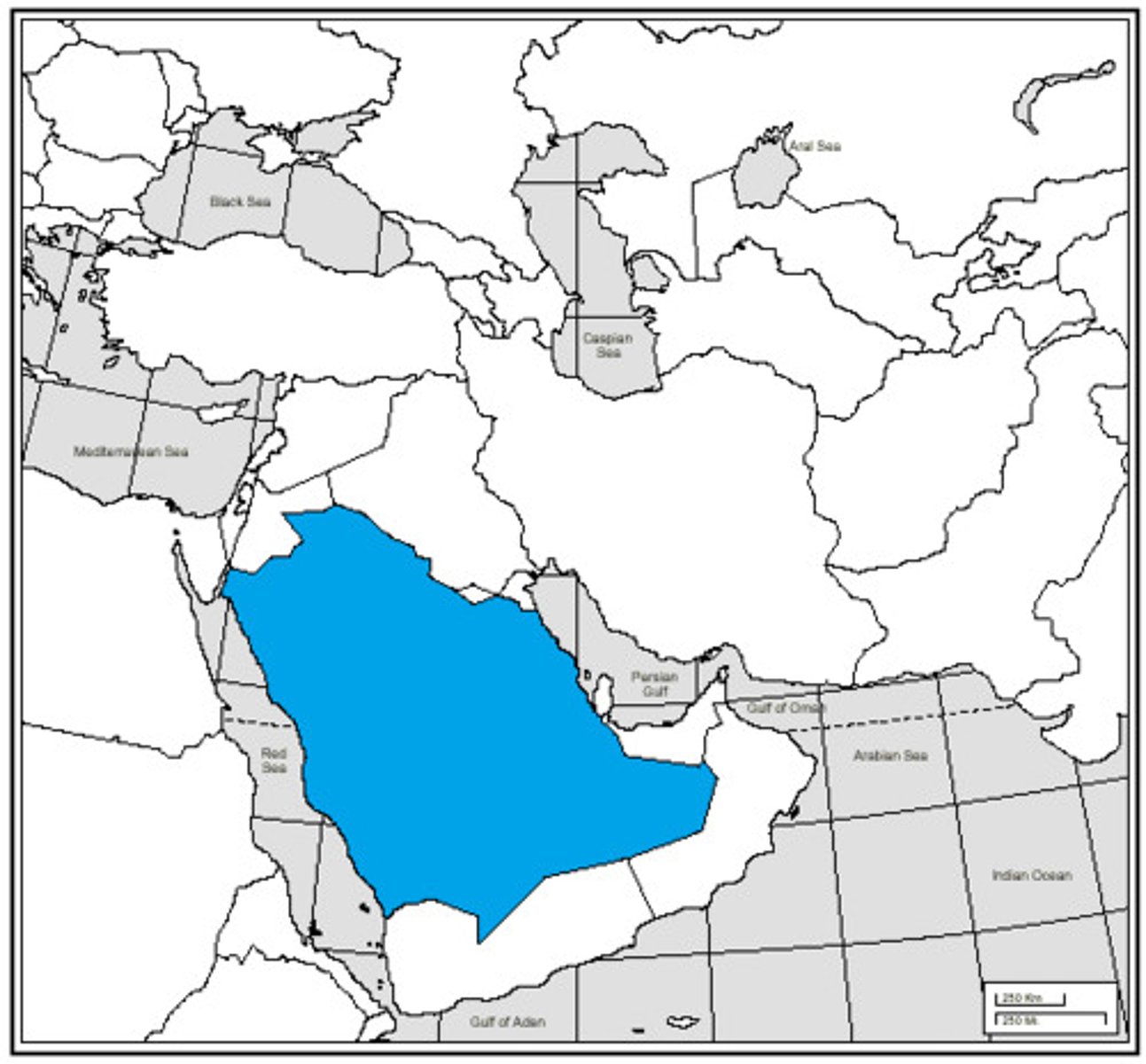
Saudi Arabia
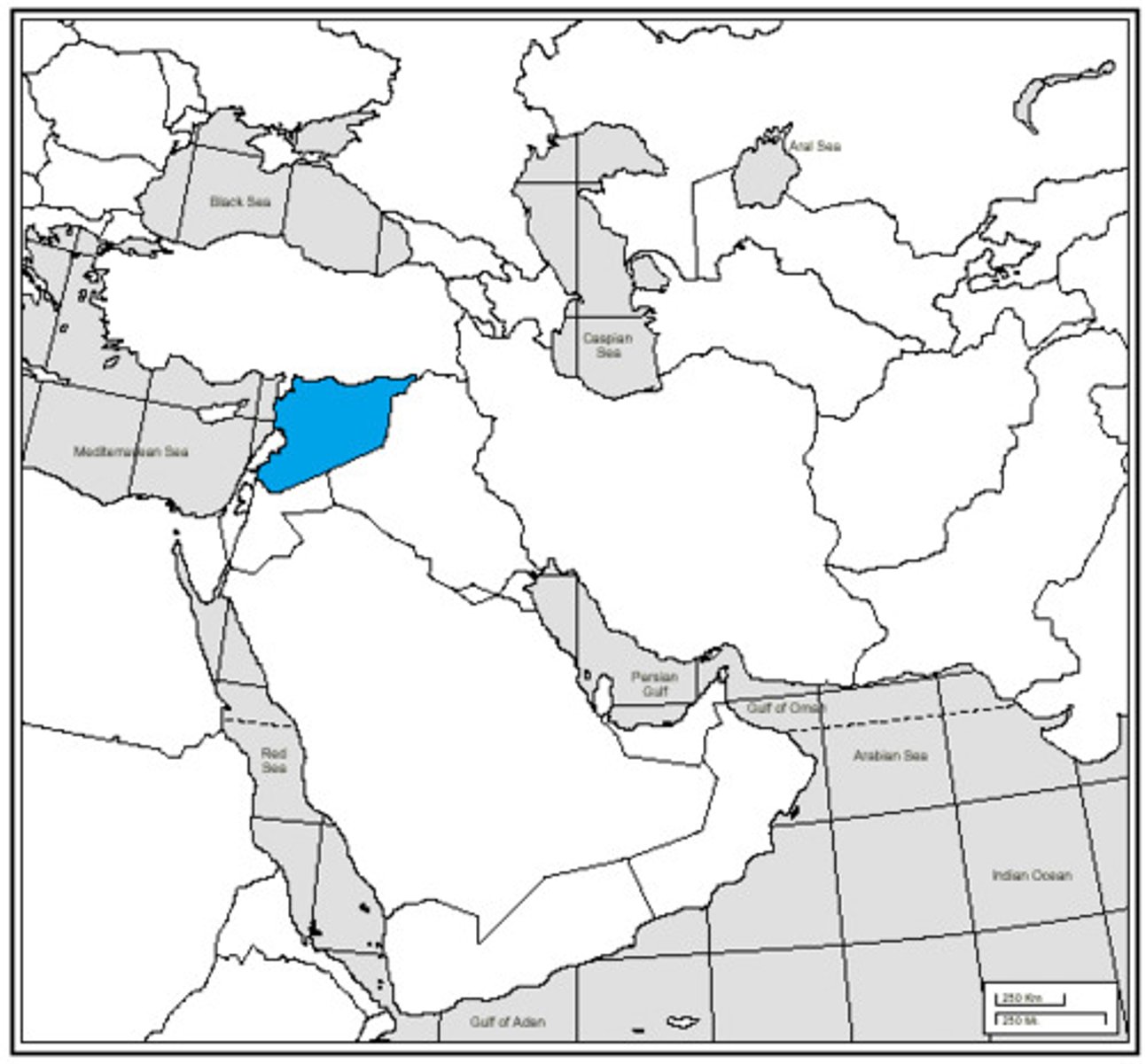
Syria
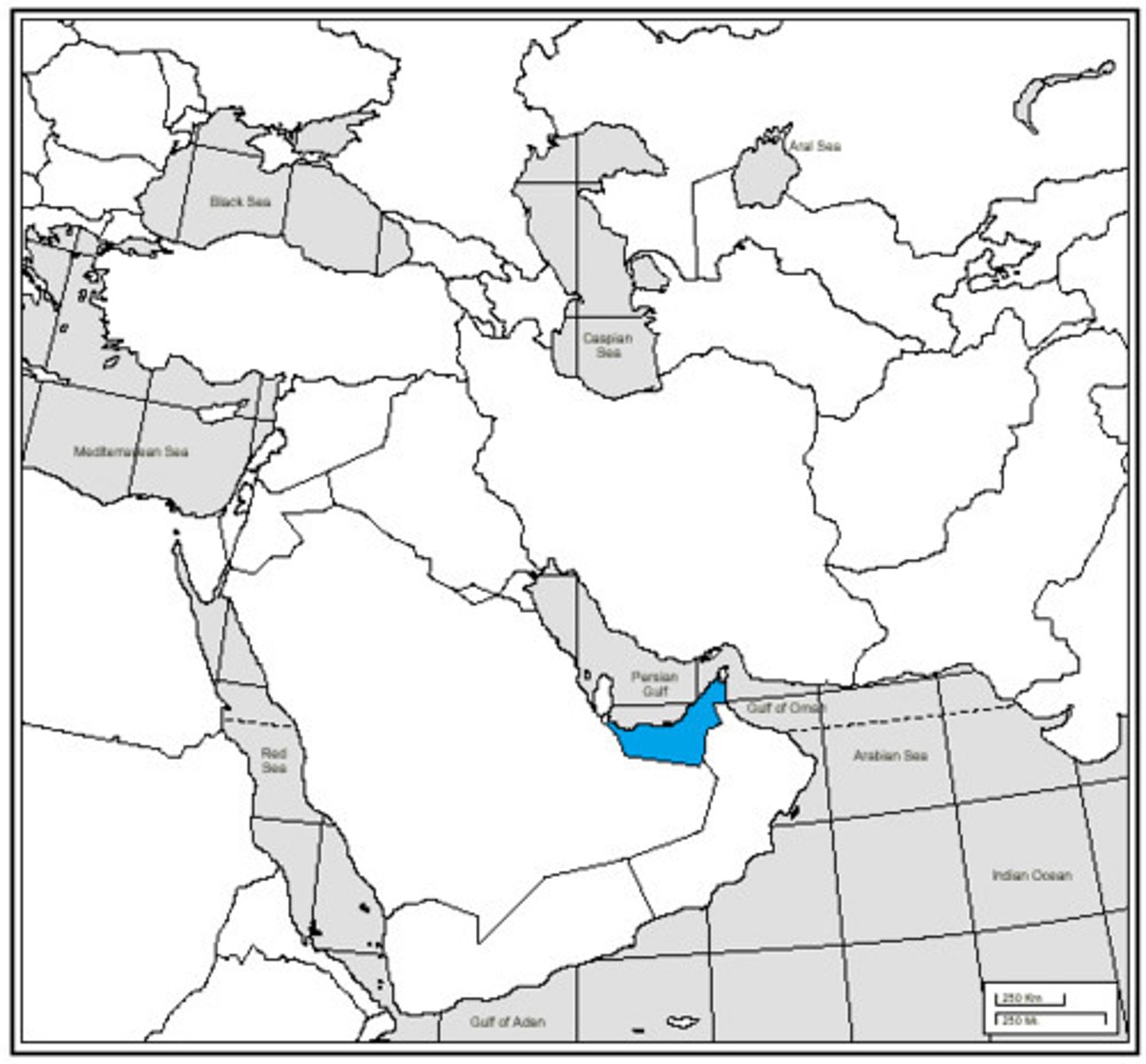
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Afghanistan
Kuwait