Biology IGCSE - Diseases and Immunity
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Pathogen
disease-causing organism
Transmissible disease
A disease that can be passed from one host to another → transmissible diseases are caused by pathogens
Transmission
movement of a pathogen from one host to another
Features of viruses
Protein coat → protects virus
Genetic material (DNA or RNA) → carries instructions for making new viruses
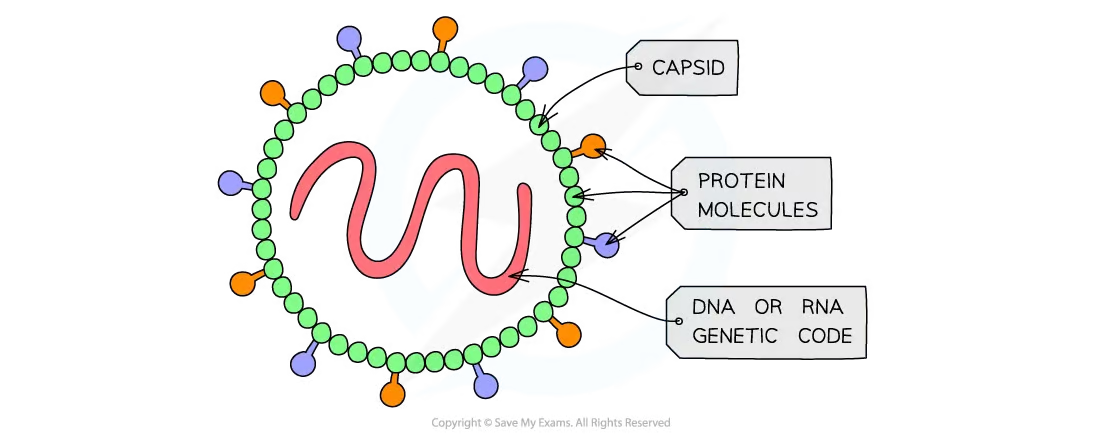
How pathogen are transmitted
by direct contact → e.g. through blood + other body fluids
indirectly → e.g. contaminated surfaces, food, animals + air
Body defences against pathogens → skin (physical barrier)
prevents pathogens from entering body
Body defences against pathogens → hairs in the nose (physical barrier)
Trap dust + microbes → stopps them from entering lungs
Body defences against pathogens → mucus (chemical barrier)
Sticky substance in airways that traps pathogens → moved out by cilia
Body defences against pathogens → stomach acid (chemical barrier)
Kills bacteria + pathogens swallowed in food or mucus
Body defences against pathogens → white blood cells (chemical barrier)
Part of immune system → destroy pathogens by ingesting them (phagocytosis) or producing antibodies
Importance of a clean water supply in controlling the spread of disease
prevents spread of waterborne diseases → e.g. cholera, typhoid → ensures people drink + use safe, uncontaminated water.
Importance of hygienic food preparation in controlling the spread of disease
stops bacteria from entering body through contaminated or undercooked food → prevents food poisoning + other infections
Importance of good personal hygiene in controlling the spread of disease
regular handwashing + cleanliness remove harmful microbes → reduces risk of spreading germs through touch, coughing, or sneezing
Importance of waste disposal in controlling the spread of disease
proper disposal of rubbish + waste prevents growth of bacteria + breeding of pests → e.g. flies, rats → helps avoid contamination of food + water sources
Importance of sewage treatment in controlling the spread of disease
removes harmful microbes + waste from human sewage → prevents pollution of water bodies → reduces risk of disease spreading through water
Active immunity
Defence against a pathogen by antibody production in the body
Host
An organism in which a pathogen lives and reproduces
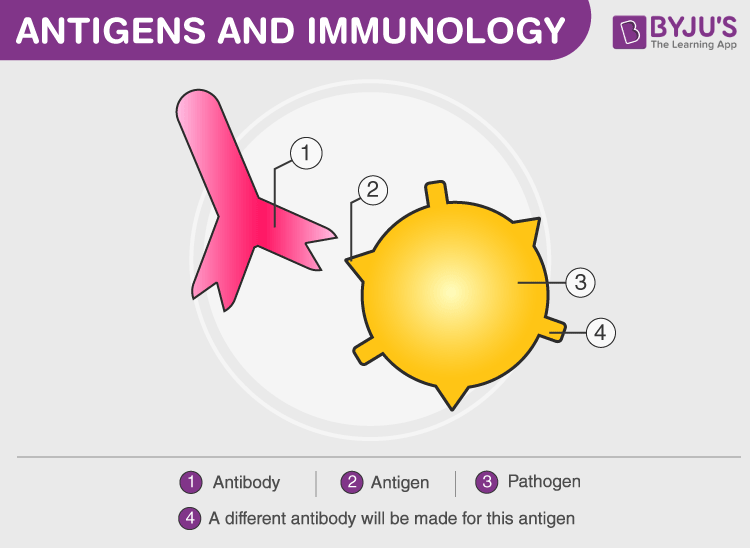
Antibody
Proteins that bind to antigens leading to direct destruction of pathogens or marking of pathogens for destruction by phagocytes
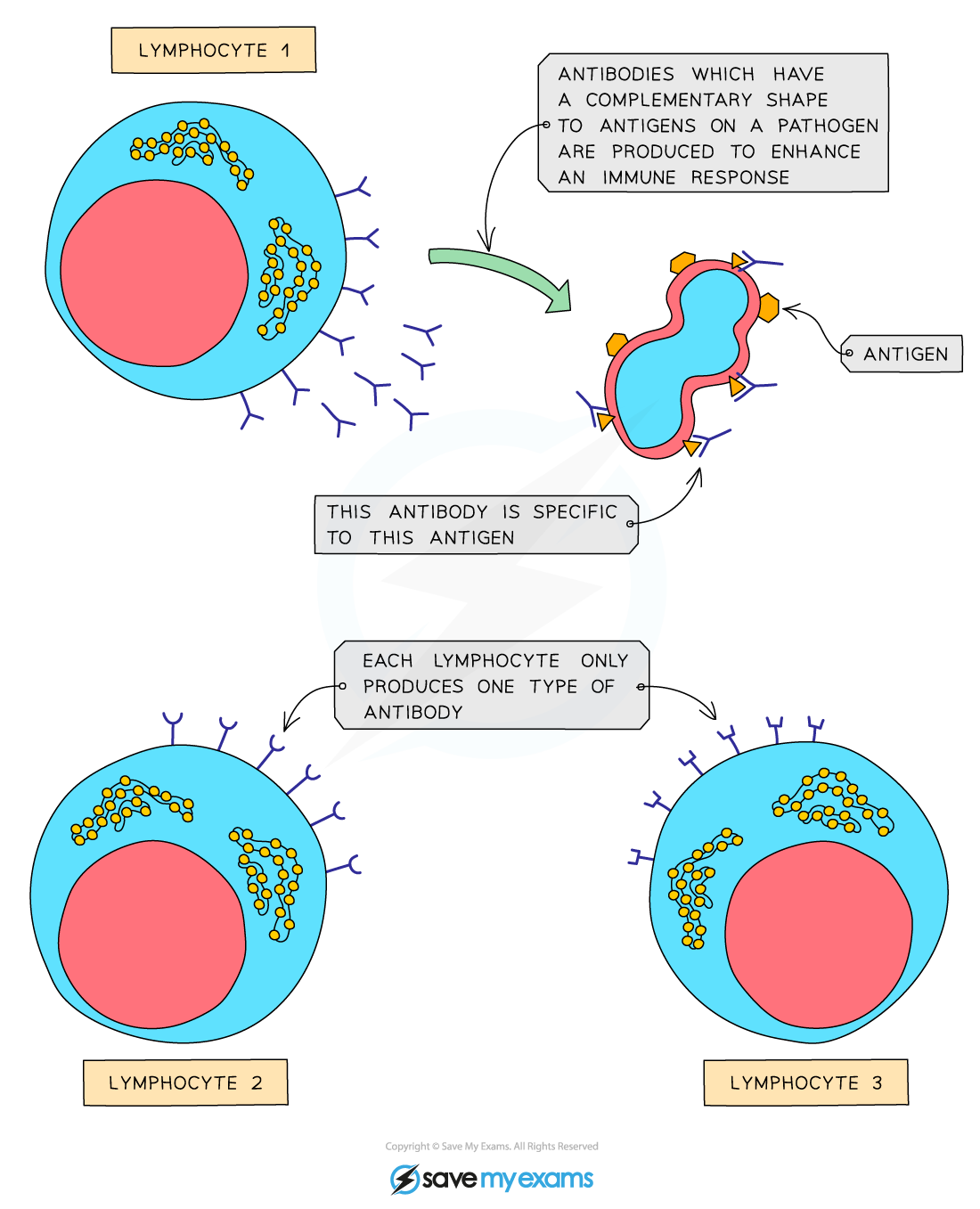
Antigen
chemical that is recognised by the body as being ‘foreign’ and stimulates an immune response
Immune response
reaction of the body to the presence of an antigen; it involves the production of antibodies
each pathogen has its own antigens → have specific shapes
specific antibodies have complementary shapes → fit specific antigens
How does immune system know what to attack
→ all cells have a specific antigen on their surface (special protein)
→ each human has their own specific shape of antigen on their surface of their cells → these are self antigen
→ pathogen, including viruses, also have their own specific antigen → non - self antigen
→ antibodies are protein produced by lymphocytes that bind specific antigens
Why are antibodies unable to kill viruses
viruses inject themselves into host body cells
antibodies don’t affect body cells
antibodies affect bacteria cell walls → viruses don’t have a cell wall
Why bacteria has become more resistant
Not finishing a course of antibiotics according to doctor’s instruction
Taking antibiotics when not needed
Mass use of antibiotics on farm animals
Vaccine
harmless preparation of dead or inactivated pathogens that is injected into the body to induce an immune response
Explain that active immunity is gained after an infection by a pathogen or by vaccination
It can happen naturally after an infection
It can also happen artificially through vaccination → weakened or inactive form of the pathogen is introduced to trigger the immune response
Process of vaccination
weakened pathogens or their antigens are put into body
antigens stimulate an immune response by lymphocytes → produce antibodies
memory cells are produced → give long-term immunity
Vaccinations are available for some pathogens → help control spread of diseases
role of vaccination in controlling spread of diseases
Stimulating immune system → produce antibodies without causing illness
Protecting individuals from getting infected
Reducing no. of infected people → lowers chance of transmission
Helping create herd immunity → unvaccinated people are protected because disease can’t spread easily