Bio Ch 3-4
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
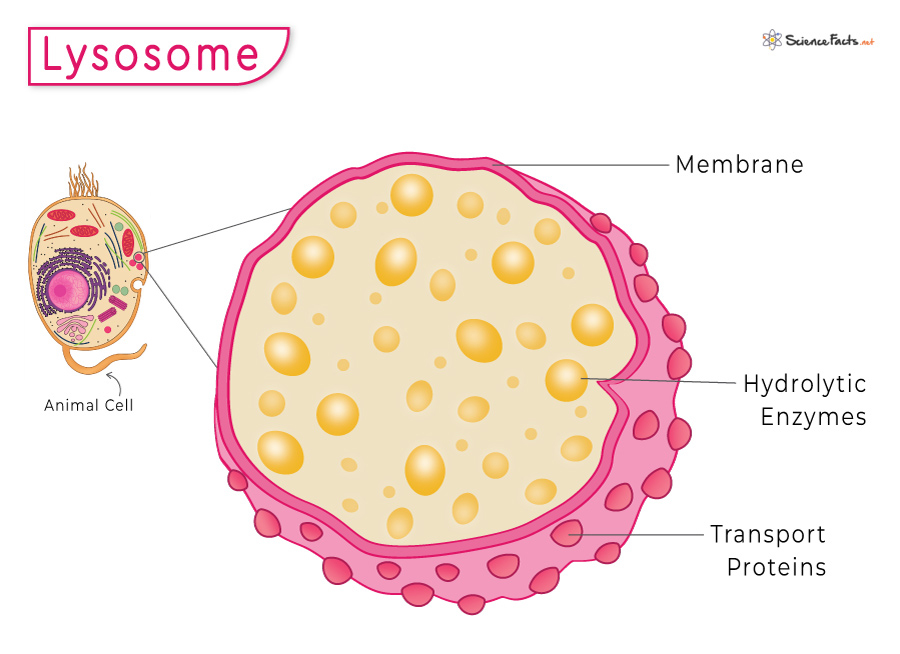
Lysosomes
Removing dead and damaged cells, and breaking up food molecules. The waste system of the cell.
Located all about the cytoplasm, but especially near the Smooth ER and Golgi.
Eukaryotic only
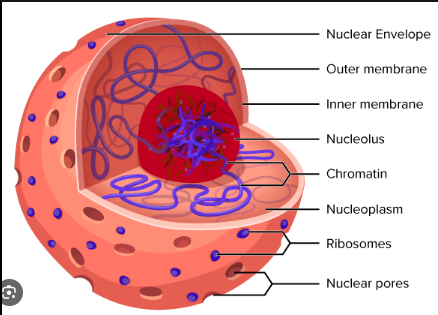
Nuclear Envelope
Separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Regulates transportation of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Also provides structural support.
Located around the Nucleus - Encases
Eukaryotes only
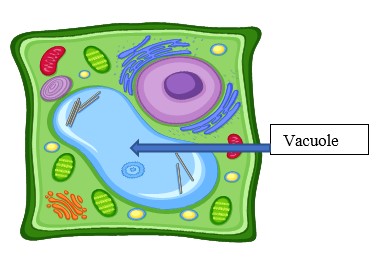
Central Vacuole
Stores water, nutrients, and waste - sap. Also helps make cells rigid.
Can take up 90% of the cell’s volume.
Only plant cells, but smaller ones can be found in animal and prokaryotes.
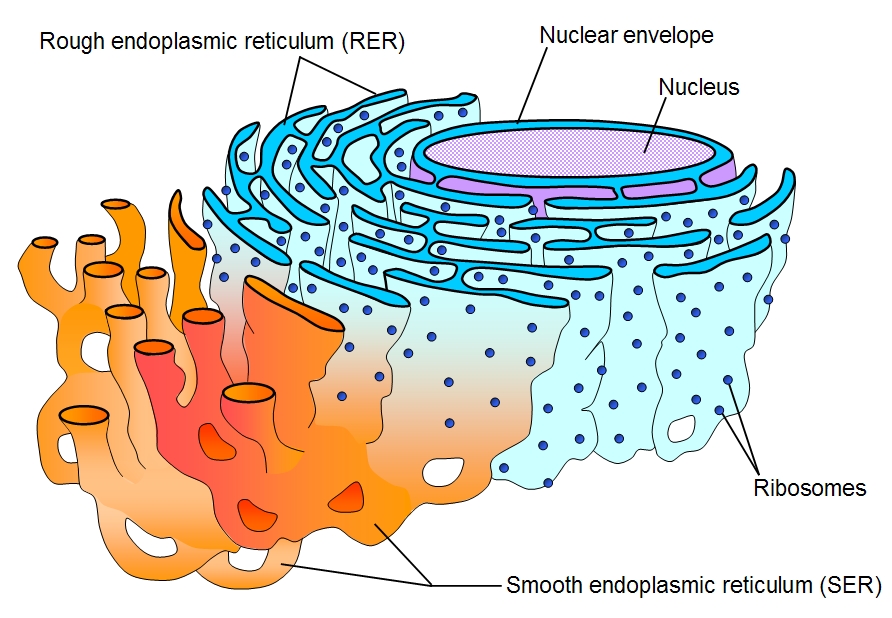
Smooth endoplasmic Reticulum
Creation and storage of lipids and steroids.
On the outside of the RER, around the Nucleus
Only Eukaryotes
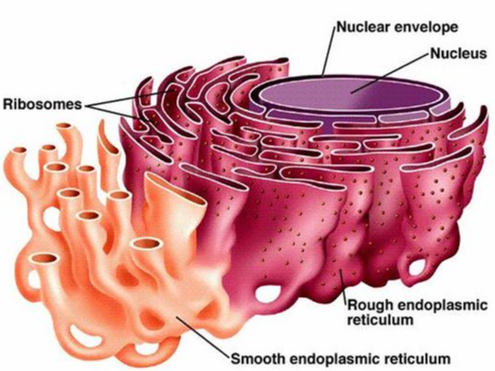
Rough endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesizes proteins. Involved in the production, folding, quality control, and dispatch of proteins. Utilized embedded ribosomes to do this.
Between the SER and nucleus.
Only Eukaryotes
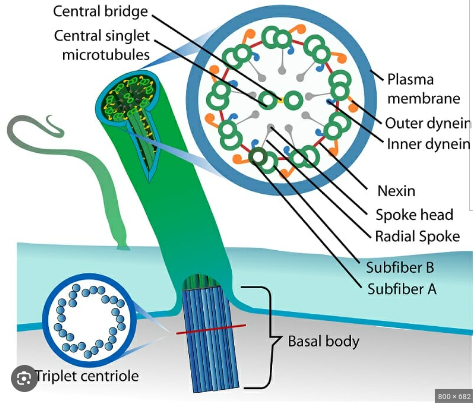
Cilia
Locomotion (movement) of the cell, and to help transport fluid materials past the cell. Work in unison to SWEEP. Can also detect and transmit extracellular ques.
On the outside of the cell. A protection embedded in the cell membrane.
Only Eukaryotes.
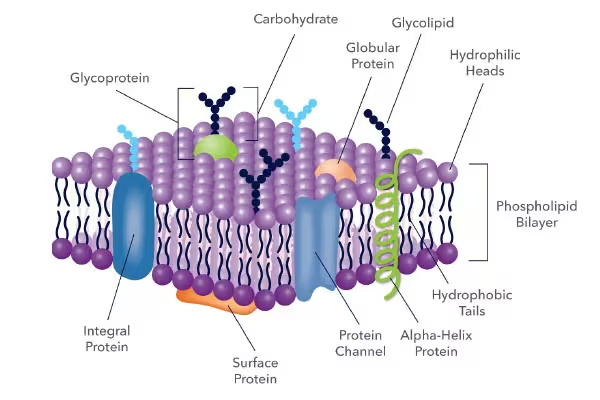
Plasma Membrane
Selective phospholipid barrier that allows passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products. It is also responsible for the isolation of the cytoplasm (and bound organelles) from the cell’s external environment - protection.
Located in between the cell wall and cytoplasm plant cells. In-between the cell’s external environment and cytoplasm in animal cells.
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
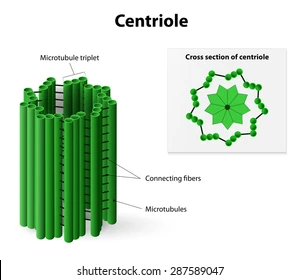
Centriole
Organizing microtubules that serve as the cell’s skeletal system. They promote cell division, helping in the production of spindle fibers that split the chromosomes (mitosis).
Located near the nucleus
Found mainly in animal cells. Some lower plant cells also have it. No prokaryotes.
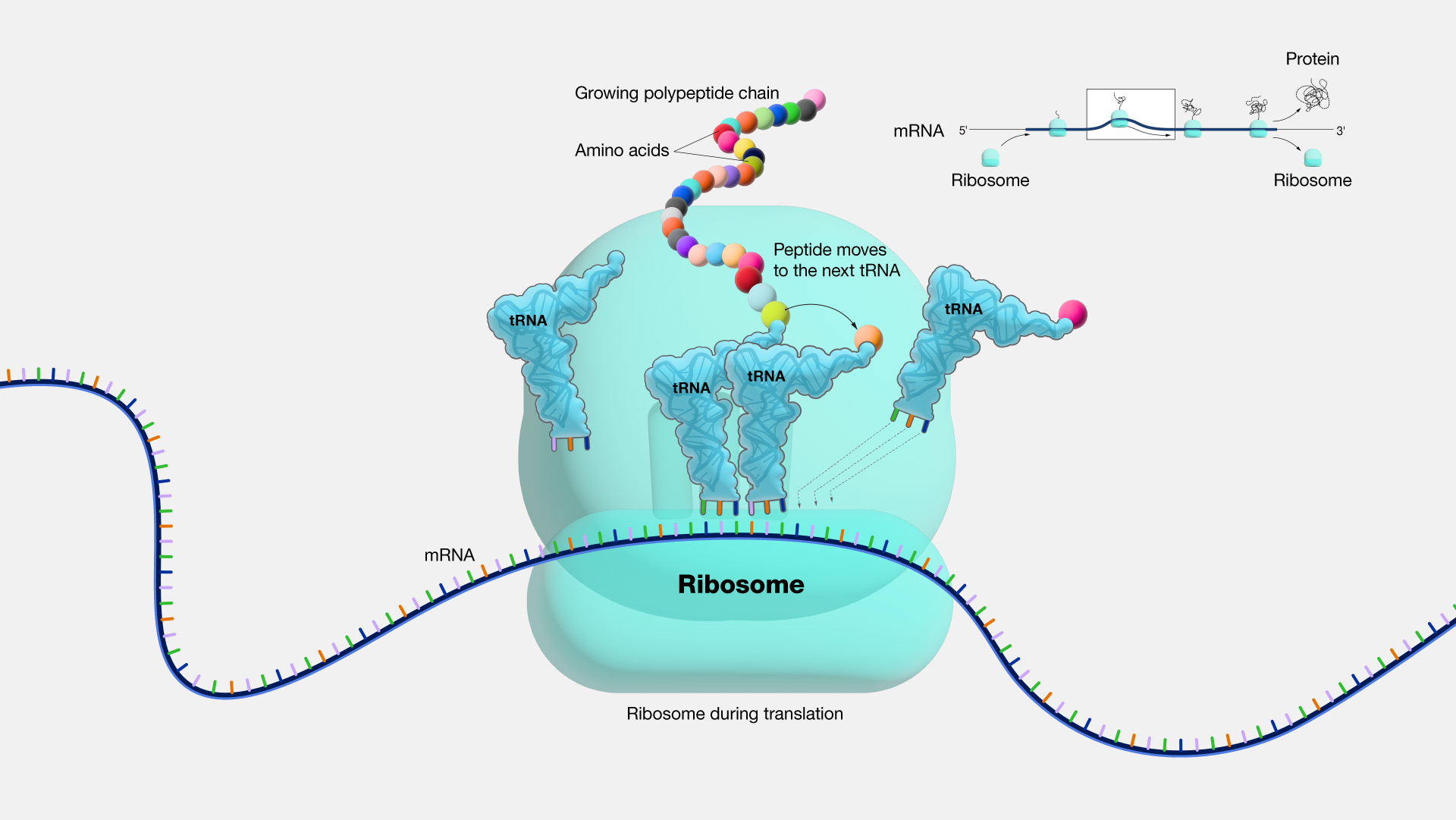
Ribosome
StrUses information provided by the nucleus to construct proteins. Gets info by decoding RNA message.
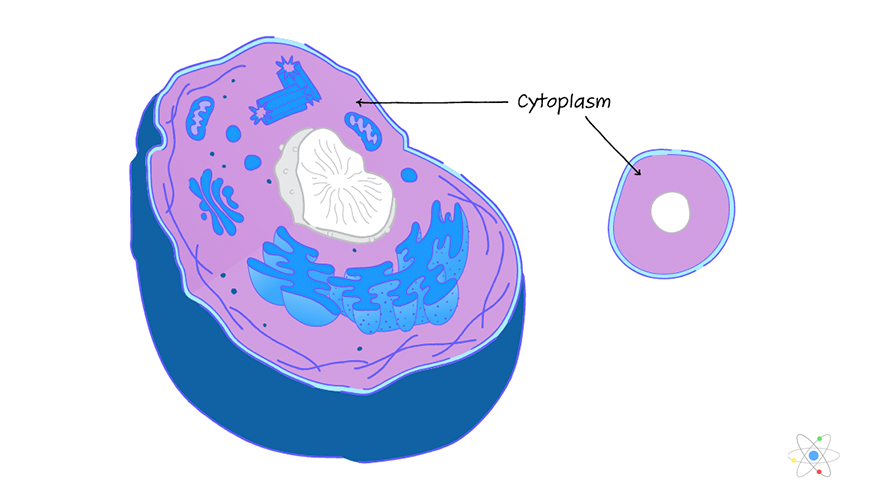
cytoplasm
Organelle responsible for holding all the components of the cell and protecting them. It is also responsible for maintaining cell shape and allowing transportation within the cell.
Fills the inside of the plasma membrane
Found in both prokaryotes an Eukaryotes
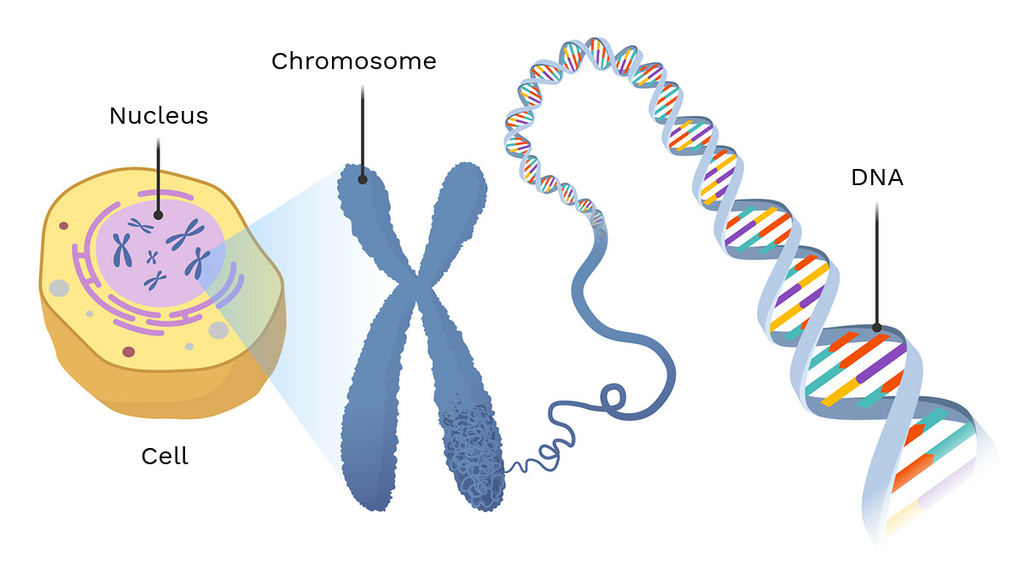
DNA
Contains genetic info needed for an org to develop, survive, and reproduce. Its unique sequences are converted into messages used to produce proteins.
Eukaryotes: Tightly packed into chromosomes, located in the nucleus
Also located in a single chromosome in mitochondrion and chloroplasts
Prokaryotes: In the nucleoid (not encased in a nuclear membrane)
In prokaryotes & eukaryotes
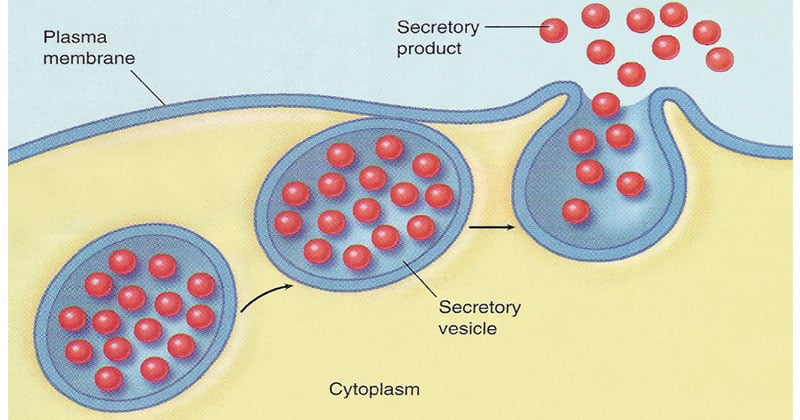
Vesicle
Transport materials throughout the cell, or to their destination outside the cell. They transport proteins, enzymes, hormones, and neurotransmitters.
All throughout the cell. Most are found close to the golgi and ER.
Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
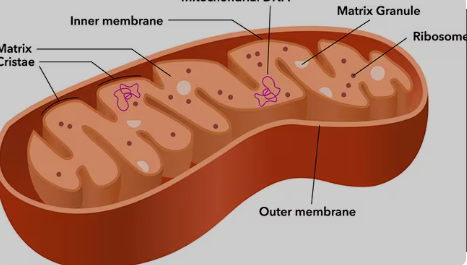
Mitochondria
Generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell’s biochemical reactions. It produces ATP through cellular respiration, which is the cell’s energy source.
All about the Cytoplasm
Eukaryotes (Both plant and animal cells), not in Prokaryotes
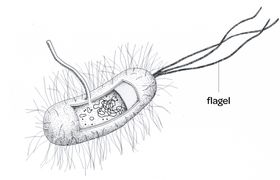
Flagella
Aide in movement of the cell or organism, and acts as a sensory organ. Can assume the motion of a fish’s tail or a propeller to swim the cell from one location to another
Located at 1 pole, both poles, or in large numbers along the lenth of the cell.
Mostly in prokaryotes, but some Eukaryotes.
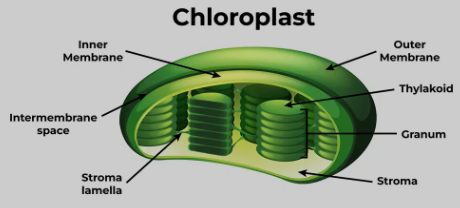
Chloroplast
Produce energy for the cell through photosynthesis
Located about the cytosol
Cells of all green tissues of plants and algae. Only in plant cells, no prokaryotic or animal
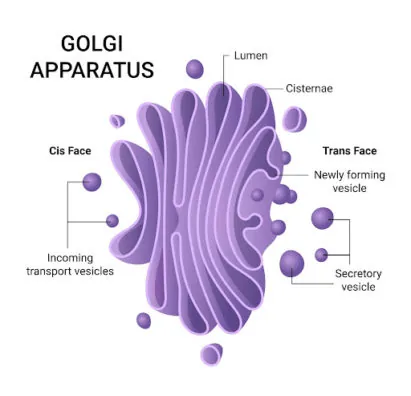
Golgi Apparatus
A factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and stored for transport to their destinations. It is responsible for transportation, modifying, and packaging of proteins and lips into vesicles for delivery.
Near the nucleus and ER
Only eukaryotic cells
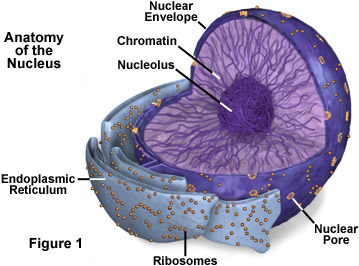
Nucleus
Repository of genetic information, and as the cells control center. It produces ribosomes, thus controls protein and enzyme synthesis. Also controls heredity, cell division, and cell growth.
Roughly in the middle of the cell. Sticks out the most in a picture. By the ER.
Only eukaryotes
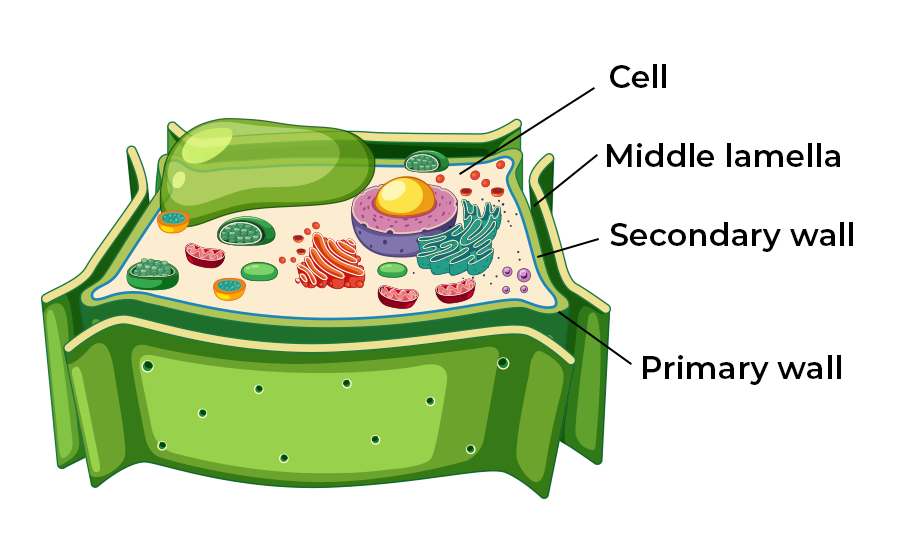
Cell Wall
Support and maintain cell’s shape
Between cell membrane and outside envi in plant cells, and between cell membrane and capsule In prokaryotes.
Only in plant cells and prokaryotes
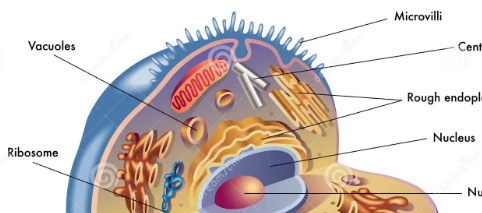
Microvilli
Increase the cell’s surface area and efficiency of absorption
Only Animal Cells
Projections on the outside of the cell.
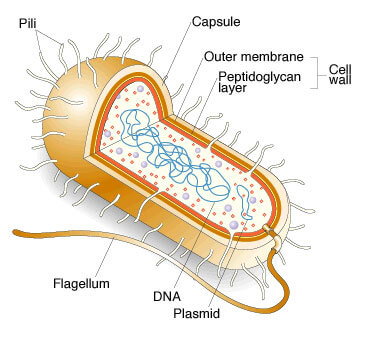
pili
Long, hair-like structures found on the surface of certain bacteria and archaea. They help in cell movement and attachment to surfaces.
Prokaryotes
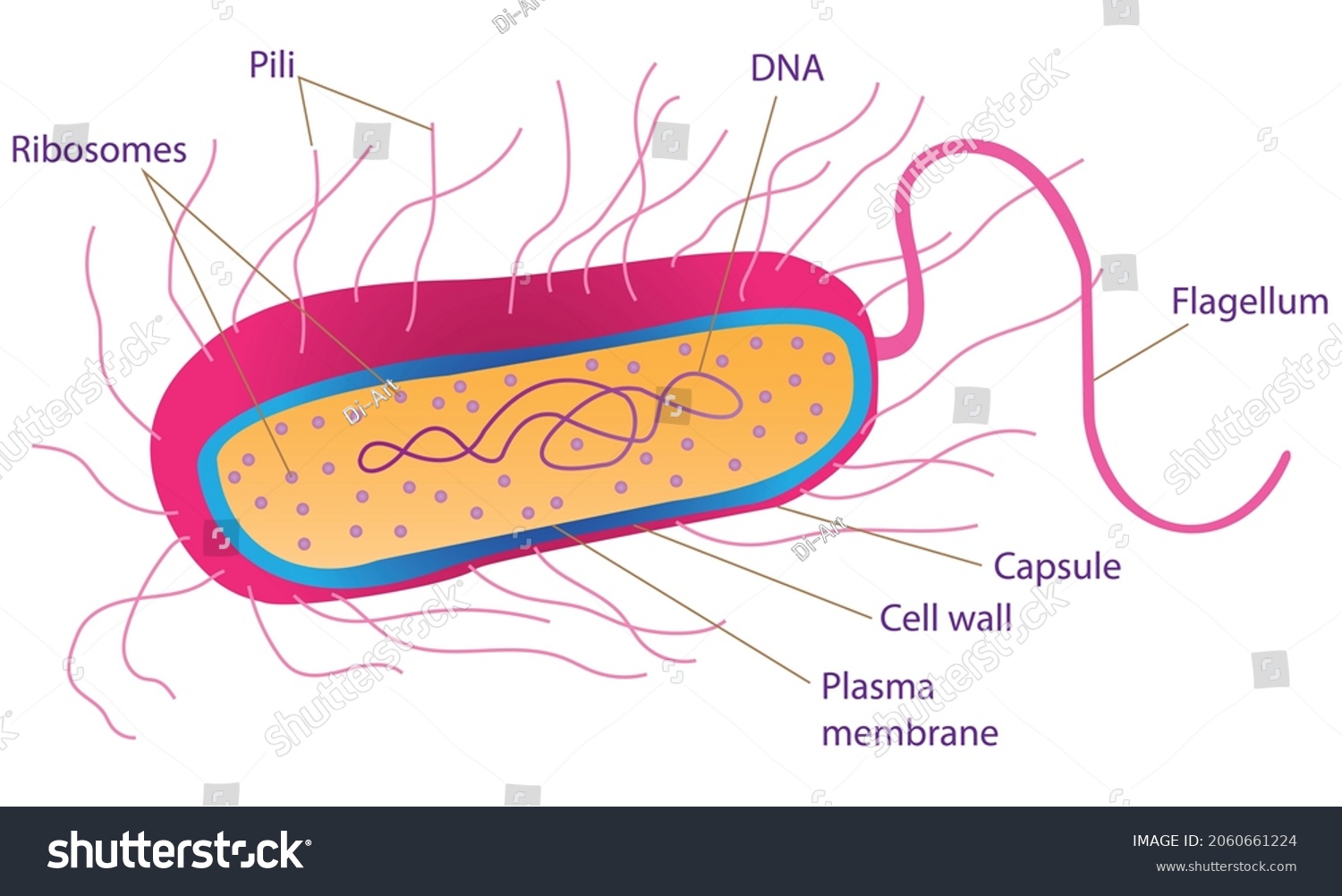
Capsule
Polysaccharide structure that provides protection to the bacteria by shielding them against sunlight, chemicals, and other harsh environmental factors.
Encases cell
Prokaryote
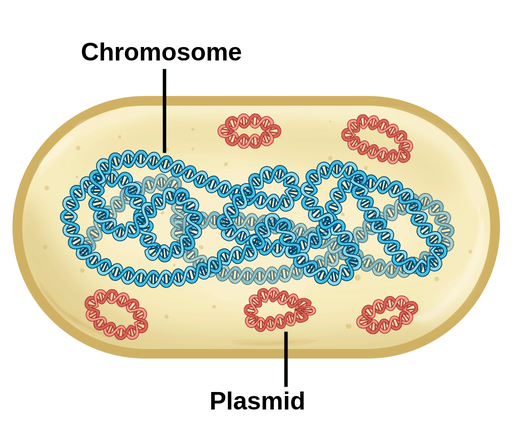
Closed loop chromosome
Their control centre, containing the genetic information
In cytoplasm, no nuclear membrane
Prokaryote only
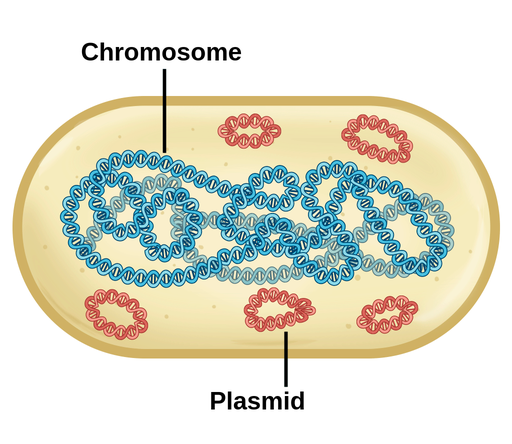
Plasmid
A small, circular DNA molecule that is separate from the chromosomal DNA in a cell. Often carry genes that provide advantages to the bacteria, such as antibiotic resistance or the ability to produce certain proteins.
In cytosol, separate from closed-loop chromosome
Prokaryote only
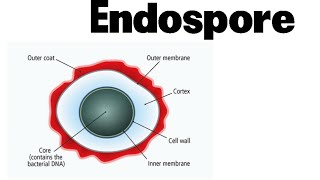
Endospore
Dormant non-reproductive structure formed by certain bacteria. It is a survival mechanism that allows bacteria to withstand harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, lack of nutrients, and exposure to chemicals or radiation. This structure enables the bacteria to remain viable for extended periods, even in unfavorable environments.
In cytosol
Prokaryotes only
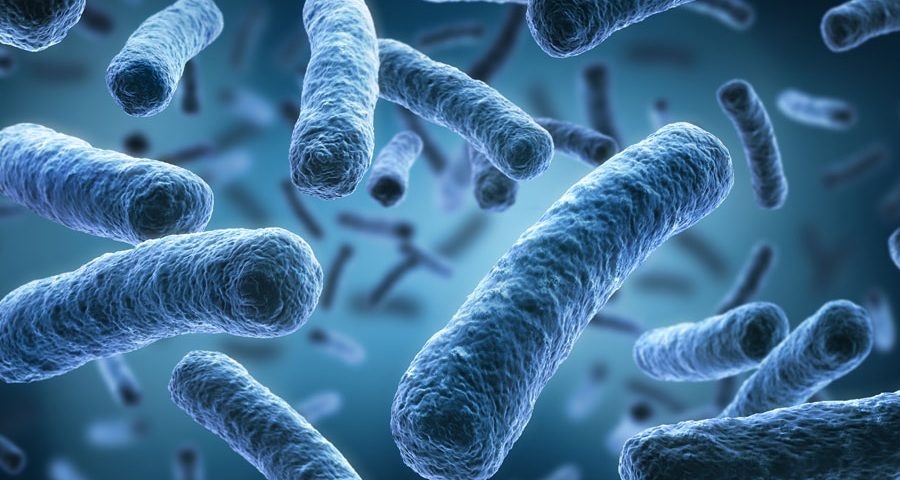
Bacillus
Rod shaped Bacteria Cell
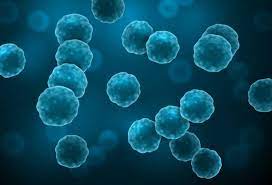
Coccus
Bacterial sphere
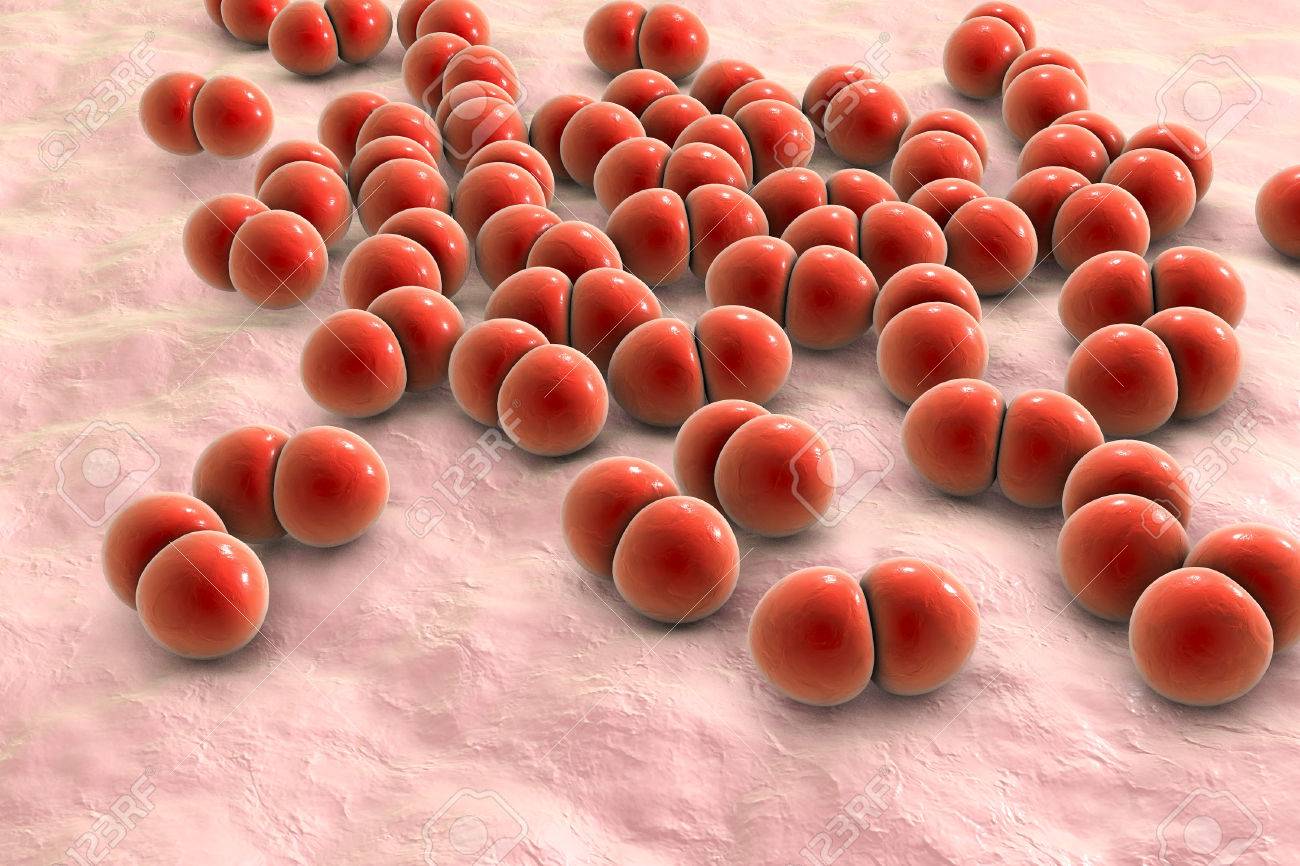
Diplococos
Pairs of cocci
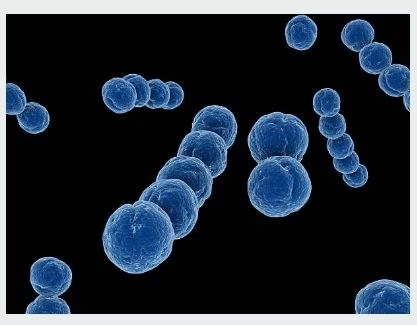
Streptococcus
Cocci in a chain
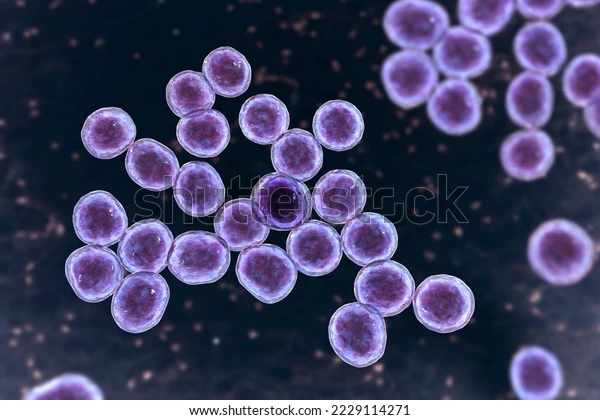
Staphylococcus
cluster of cocci
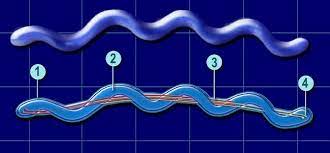
spirochete
spiral shaped Bacteria cell