2(e) Nutrition in plants
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Photosynthesis
The process of making glucose using sunlight. It converts light energy into chemical energy.
Word equation for photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Balanced chemical symbol equation for photosynthesis

Limiting Factor
The factor at the lowest level limiting the rate of reaction.
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide
Light intensity
Temperature
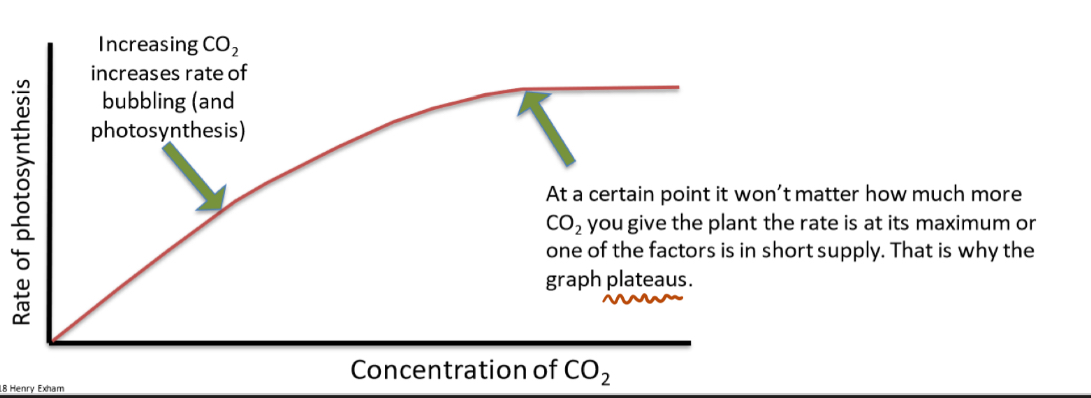
Carbon dioxide and rate of photosynthesis
Increased carbon dioxide concentration increases rate of photosynthesis, but up until a certain point. The rate is at its maximum because one of the other two factors becomes the limiting factor and is in short supply. The graph plateaus.
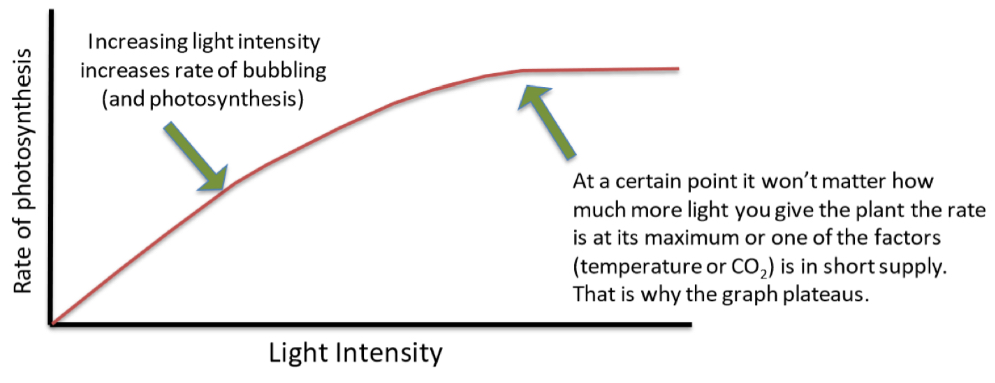
Light intensity and rate of photosynthesis
Increased light intensity increases rate of photosynthesis, but up until a certain point. The rate is at its maximum because one of the other two factors becomes the limiting factor and is in short supply. The graph plateaus.
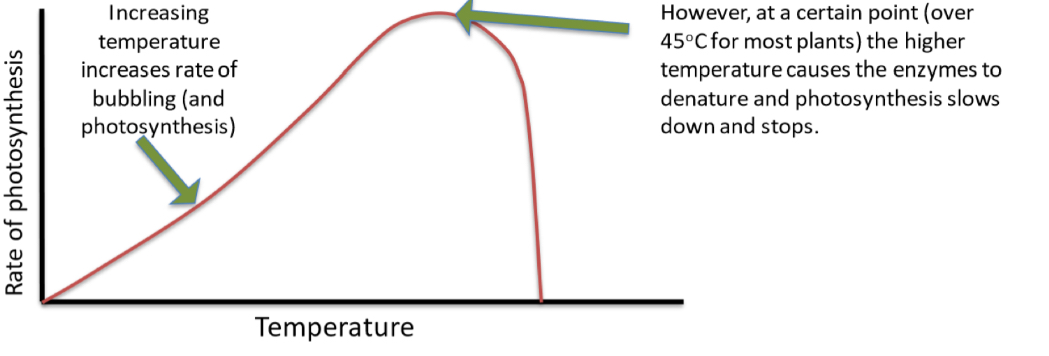
Temperature and rate of photosynthesis
Increased temperature increases rate of photosynthesis, but up until a certain point. The temperature exceeds the optimum temperature, causing the enzymes to denature. Therefore the rate of photosynthesis rapidly decreases and stops.
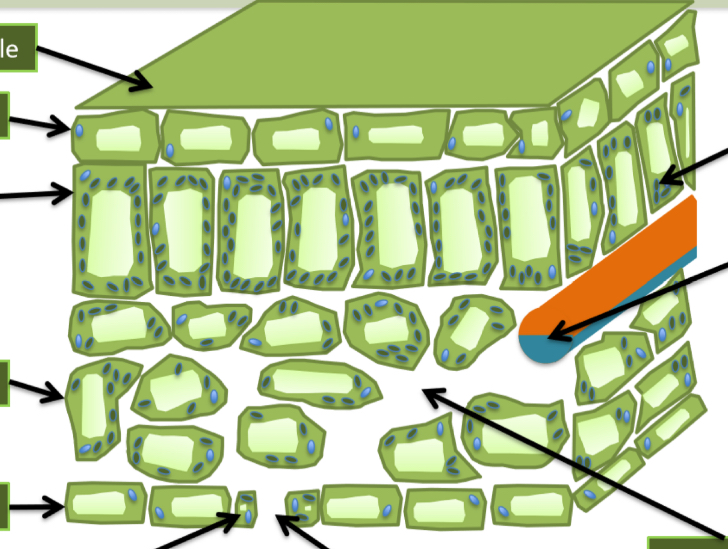
Label the parts of the leaf in the diagram.
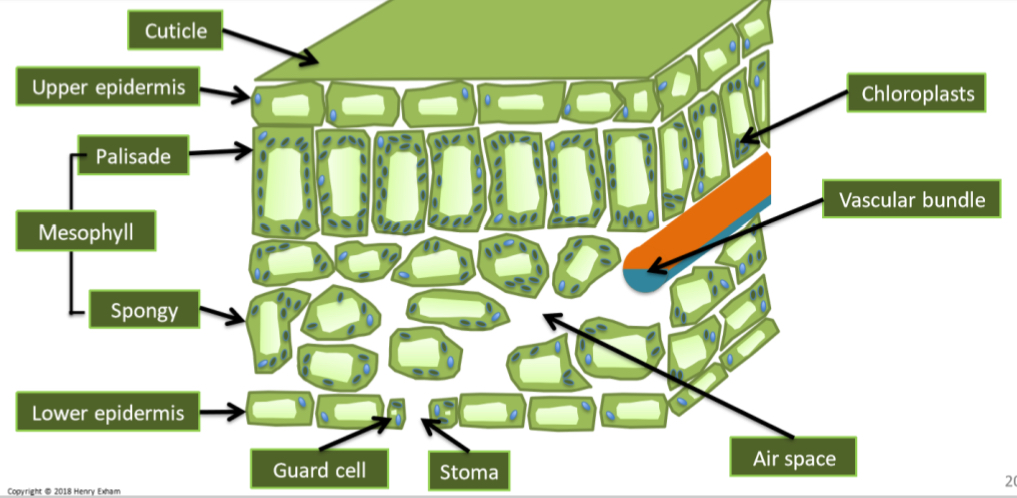
How does the waxy cuticle help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
Waxy cuticle is a water proof layer which helps prevent water loss by evaporation.
How does the upper epidermis help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
It is transparent and thin to allow more light through to the palisade mesophyll layer, to the chloroplasts.
How does the palisade mesophyll layer help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
Cells in palisade mesophyll layer are tightly packed, close to light and contain lots of chloroplasts to absorb more light.
How does the spongy mesophyll layer help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
It contains air spaces to allow for gaseous exchange.
How does the lower epidermis layer help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
It contains a lot of stomata to allow for gaseous exchange.
How do the guard cells help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
Guard cells control if the stomata are open or closed. They prevent water loss when closing stomata.
How do Xylem cells help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
Xylem cell transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves.
How do Phloem cells help the plant photosynthesise efficiently?
Phloem cell carries the sugar produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
How is the shape of leaves adapted for pbotosynthesis?
Leaves have a broad shape, this increases surface area to catch more light to maximise photosynthesis.
Leaves are flat and thin, this decreases the distance for diffusion. Diffusion can happen faster for gaseous exchange.
What are the minerals required by plants?
Magnesium
Nitrate
Potassium
Phosphate
Magnesium ions
Required to make chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis.
Deficiency leads to yellow leaves and stunted growth.
Nitrate ions
To make amino acids hence protein for growth
Deficiency leads to yellow leaves and stunted growth
Potassium ions
Required for enzymes needed for photosynthesis and respiration
Defieciency leads to poor flower/fruit growth, discoloured leaves
Phosphates
To make DNA and cell membranes for respiration and growth
Deficiency leads to poor root growth and purple leaves
Practical: effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis(CORMMSS)
I will use the same species of pondweed in this investigation.(O)
I will put pondweed in a container with water and place a lamp at a specific distance measured with a ruler e.g. 30cm.
I would leave the pondweed to photosynthesise for 5 minutes(M) and count the bubbles produced to help calculate the rate of photosynthesis.(M)
I will then repeat this 5 more times, moving the lamp backwards by 10cm each time.(C)
During the practical, i will control the temperaturevand the concentration of water by adding a certain volume of sodium hydrogen carbonate.
I will repeat the experiment at least 3 times to make it more reliable. (R)
How can starch show that photosynthesis has taken place?
Glucose is a product of photosynthesis. Excess glucose is rapidly converted to insoluble starch and stored in a leaf.
Practical: Test for starch production
Take a leaf from a plant.
Boil it in some hot water for about 30 seconds to kill the leaf.
Put a boiling tube of ethanol into the beaker with hot water. The ethanol will boil.
Put the leaf in the boiling ethanol to remove the green colour(chlorophyll)from the leaf so it becomes easier to see the colour change.
Remove the leaf from the boiling tube and rinse the leaf in cold water to rehydrate it.
Dry the leaf and spread it out on a white tile.
Add some drops of iodine and record the colour after a few minutes.
Explain safety precautiond that should be taken when carrying out the test for starch.
Use water bath/ turn off bunsen burner because ethanol is highly flammable.
Wear goggles to protect eyes.
Use forceps to protect fingers/skin.
Why is the leaf hold in boiling water?
It kills the leaf, denaturing the enzymes and stopping any chemical reactions including digestion and photosynthesis so no more starch is produced.
Why is the leaf put in boiling ethanol?
It removes the chlorophyll / the green colour/pigment of the leaf so that the colour of the test result becomes more visible.
Test if chlorophyll is required
Use a variegated lead that has white area without chlorophyll. Test both white and green parts of leaf and draw/record the results.When tested for starch, only the green parts containing chlorophyll should show a positive result(blue-black) and the white parts will remain orange.
Test if light is required
Use a destarched plant(a plant that has not been able to photpsynthesise and has therefore used up its store of starch for energy instead.)
Use aluminium foil to cover part of the leaf on both sides.
Leave it in sunlight to photosynthesise for 24h.
Test the leaf for starch.
Test if CO₂ is required
Set up a destarched plant next to a container of soda lime within a sealed glass bell jar. The soda lime will absorb all the carbon dioxide in the bell jar.
Set up a control apparatus without soda lime.
Leave both in sunlight for 24h.
Test for starch