Carbohydrate metabolism/Glycolysis
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Metabolism
Sum of all process by which living organisms acquire and utilize energy.
Ultimate source of energy=sun.
Chemotrophic (organisms that obtain their energy from biomolecules) and carbohydrates are the ultimate source
Regulation
Each metabolic pathway is controlled by rate limiting step. It may be via: Other cellular molecules, Acting on the enzymes catalyzing the reaction, Increasing/decreasing the amount of enzyme, Cellular conpartmentalization using cellular organelles.
Catabolic: generate energy. Breaking down of a molecule.
Anabolic: energy used. Forming of molecules.
Metabolic pathways
Located in different cell compartments and this compartmentalization mat assist in regulation of cellular metabolism
Dietary carbohydrates
Mouth: The enzyme salivary amalyase begins breaking down starch into shorter polysaccharides.
Stomach: Salivary amylase is inactivated and no further carbohydrate digestion occurs.
Small intestines: Majority of starch digestion and breakdown of disaccharide occurs here. The enzyme pancreatic amylase breaks down starch into mono-/di-/oligo-saccharide.
The digestion of carbohydrates is completed by the enzymes attached to the brush border of the small intestinal villi. Here, the disaccharide and oligosaccharide are broken down into monosaccharides
Large intestines: Fiber and other indigestable carbohydrates are partially broken down by bacteria to form short chain fatty acids and gas. The remaining fiber is excreted in the feces.
ą-amylase
Hydrolyzes ą(1-4) glycosidic bonds in amylose and amylopectin. Products are maltotriose, Maltose, glucose, and ą-dextrin.
Maltase, disaccharidase and ą-dextrinase complete the digestive process in the small intestine.
Maltase hydrolyzes Maltose to glucose and ą-dextrin hydrolyzes ą(1-6) glycosidic bonds in dextrin.
Monosaccharides like glucose then taken up by epithelial cells and taken to blood where they can be used as source of energy.
Glycolysis
Glucose broken to 2 pyruvate molecules. 1st process of glucose oxidation.
1st step in process serves to trap glucose in the cell since a phosphorylated molecule cannot leave the cell. Occurs in cytoplasm and doesnt require oxygen.
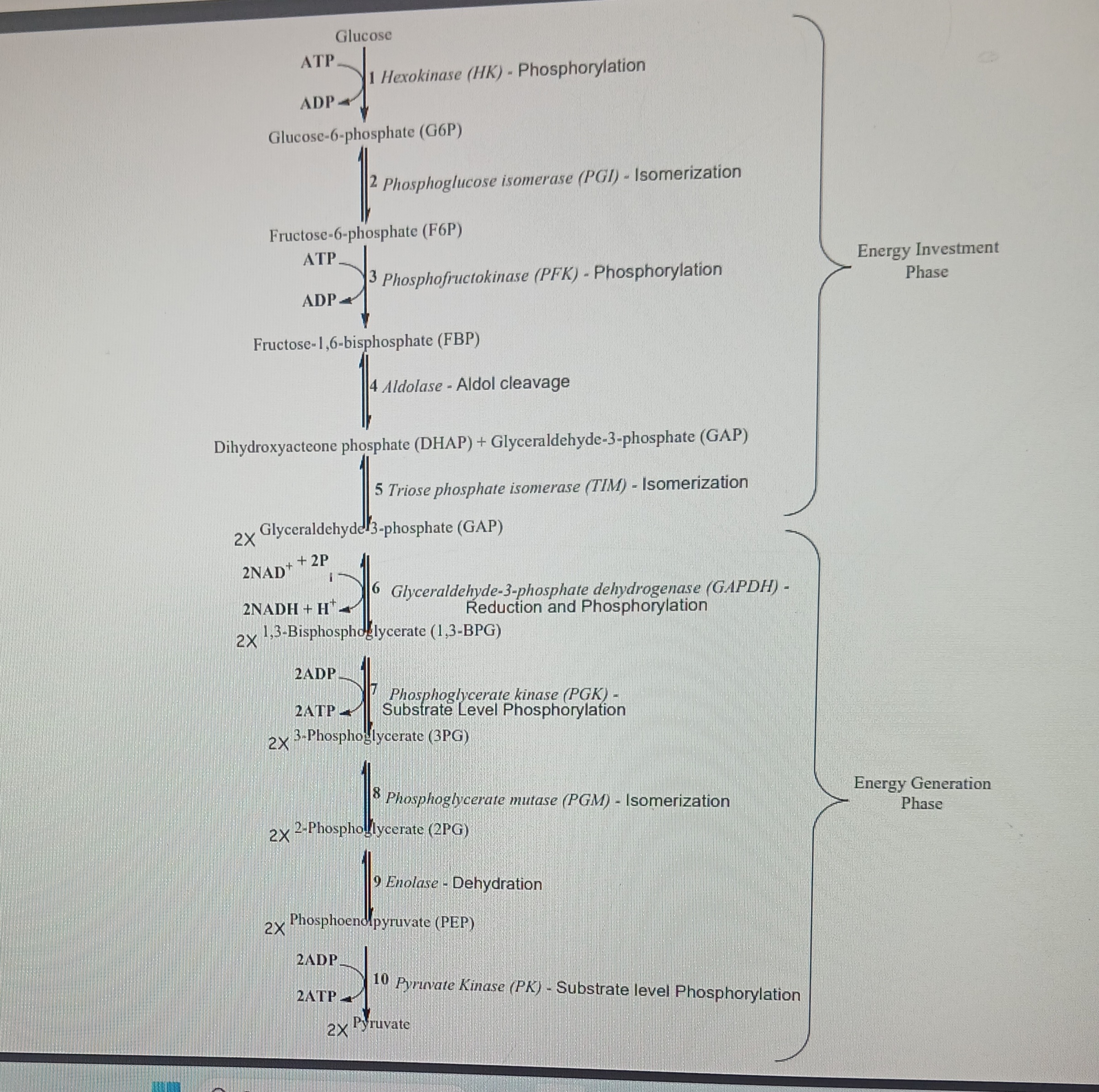
Glycolysis enzymes
Hexokinase
Phosphoglucose isomerism
Phosphofructokinase
Aldolase
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Phosphoglycerate kinase
Phosphoglyceromutase
Enolase
Pyruvate