O-Chem Ch. 6
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What reaction is a Polar Protic Solvent better for?
SN1
What reaction is a Polar Aprotic Solvent better for?
SN2
What does an Aprotic Solvent do?
Solvates carbocations, but not the anions (nucleophiles)
SN2 Reaction Rate Equation
rate = [sub][nuc]
If in the SN2 reaction the substrate is doubled, what happens to the rate?
If the substrate is doubled, the rate doubles as well.
If in the SN2 reaction the substrate is doubled and the nucleophile is tripled, what happens to the rate?
If the substrate is doubled and the nucleophile is tripled, the rate will increase by a factor of 6. (2×3=6)
SN1 Reaction Rate Equation
rate = [sub]
If in the SN1 reaction the substrate is doubled and the nucleophile is tripled, what happens to the rate?
If the substrate is doubled and the nucleophile is tripled, the rate will double, since in an SN1 reaction, the nucleophile concentration doesn’t affect the rate.
What happens if you increase the strength of the Nucleophile in an SN2 reaction?
The rate of the SN2 reaction increases
What happens if you decrease the strength of the Nucleophile in an SN2 reaction? (Aka you used a Protic Solvent for an SN2 reaction)
The rate of the SN2 reaction decreases
What happens if you increase the strength of the Nucleophile in an SN1 reaction?
The rate isn’t affected by the Nucleophile in an SN1 reaction
If the leaving group [ex. Br] was on a wedge, would the Nucleophile that attaches (backside attack) be on a wedge (toward you) or dashed (away from you)?
The nucleophile will be on the dashed line, since after the Br (that was on the wedge) is disconnected, the H will move from the dashed to the wedge and the Nu. will attach to the dashed.
How many steps are involved in an SN2 reaction?
The SN2 reaction mechanism is a ONE step reaction mechanism. All the bond breaking and making happen in one step.
What is the correct order of reactivity for an SN2 reaction of alkyl halides? Most reactive to least reactive.
methyl > 1° > 2° > 3°
Why is a primary carbon (1o) the best for an SN2 reaction?
Because during the backside attack, the nucleophile will have an easier time getting past the one group. In other words, the 1o carbon isn’t as sterically hindered as the rest.
Why is a tertiary carbon (3o) bad for an SN2 reaction?
Because during the backside attack, the nucleophile will have a hard time getting past the bulky groups. In other words, the 3o carbon is too sterically hindered.
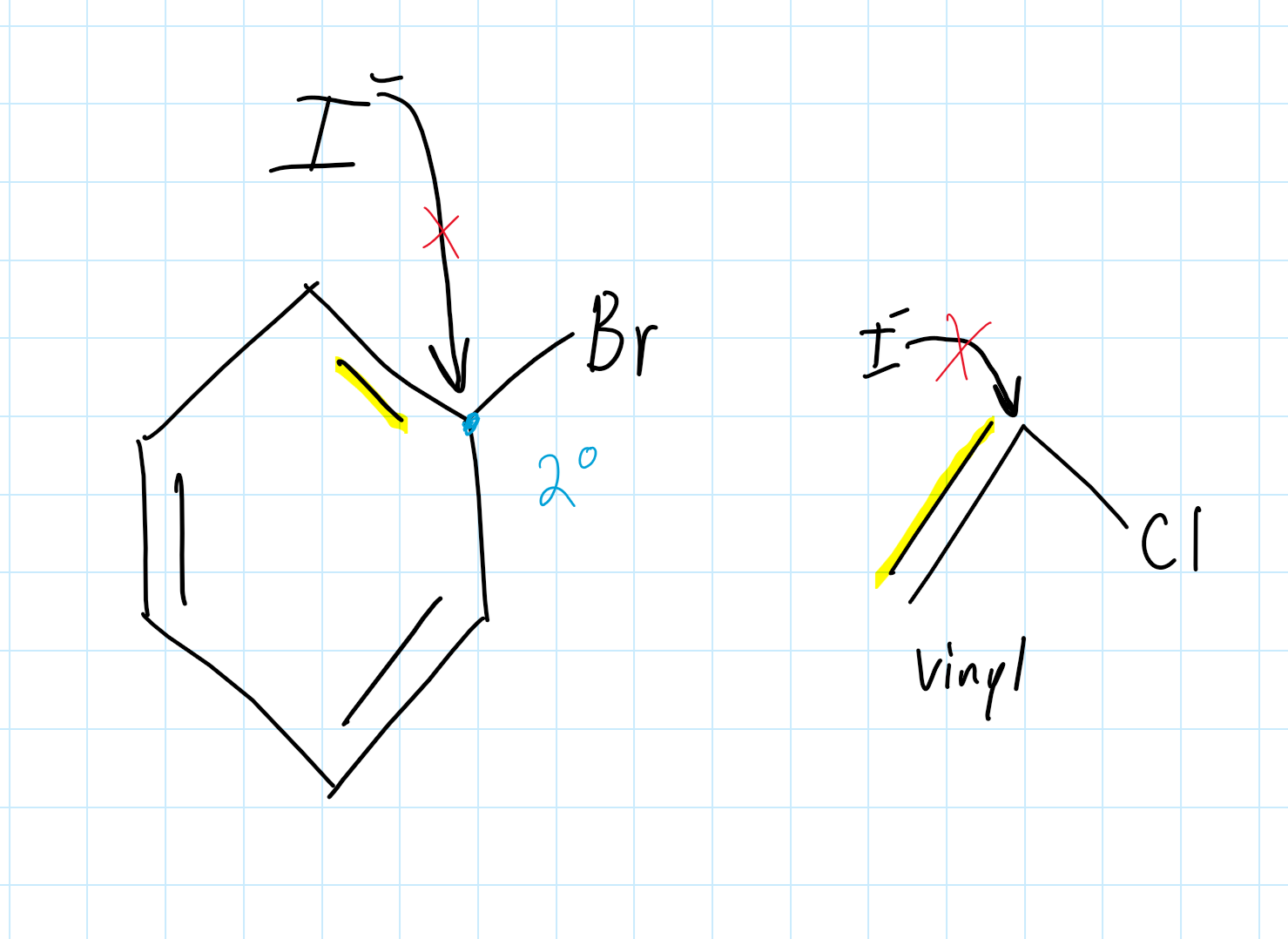
Can an Aryl Halide participate in an SN2 reaction?
No, an Aryl Halide can’t participate in SN1 or SN2 reactions. This is because the Nucleophile is unable to do a backside attack, due to the π bond electron cloud that repels the Nucleophile.
Which of these nucleophiles be faster in an SN2 reaction? Is it the OH- or H2O?
The OH- is faster due to the OH having that negative sign. Making it a stronger nucleophile, therefore increasing the reaction speed.
Does Nucleophility decrease or increase going right or left on the periodic table?
Going right to left on the periodic table will increase the nucleophility.
(SN2) In a PROTIC solvent, will the nucleophility increase going down or up?
It will increase going down, because F- is more reactive, attracting all the partially positive H, therefore trapping our nucleophile, but I- is also reactive, but due to a bigger electron cloud, it’s better at dispersing the H, still relatively trapped, but can escape.
(SN2) In an APROTIC solvent, will the nucleophility increase going down or up?
It will increase going up, because F- is more reactive than I-, due to F- having a tighter electron cloud.
When H2O attacks the carbon in an SN2 reaction, is it behaving as a Nucleophile or a Base?
It is behaving as a Nucleophile.