Special Senses - Eye
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
eyeball contains ______ layers of tissue
3
What are the 3 layers of tissue in the eyeball
1. Fibrous
2. Vascular
3. Inner
___________ separates internal cavity into anterior and posterior segments
lens
Is fibrous layer vascular or avascular?
avascular
What type of connective tissue makes up the fibrous layer?
dense connective tissue
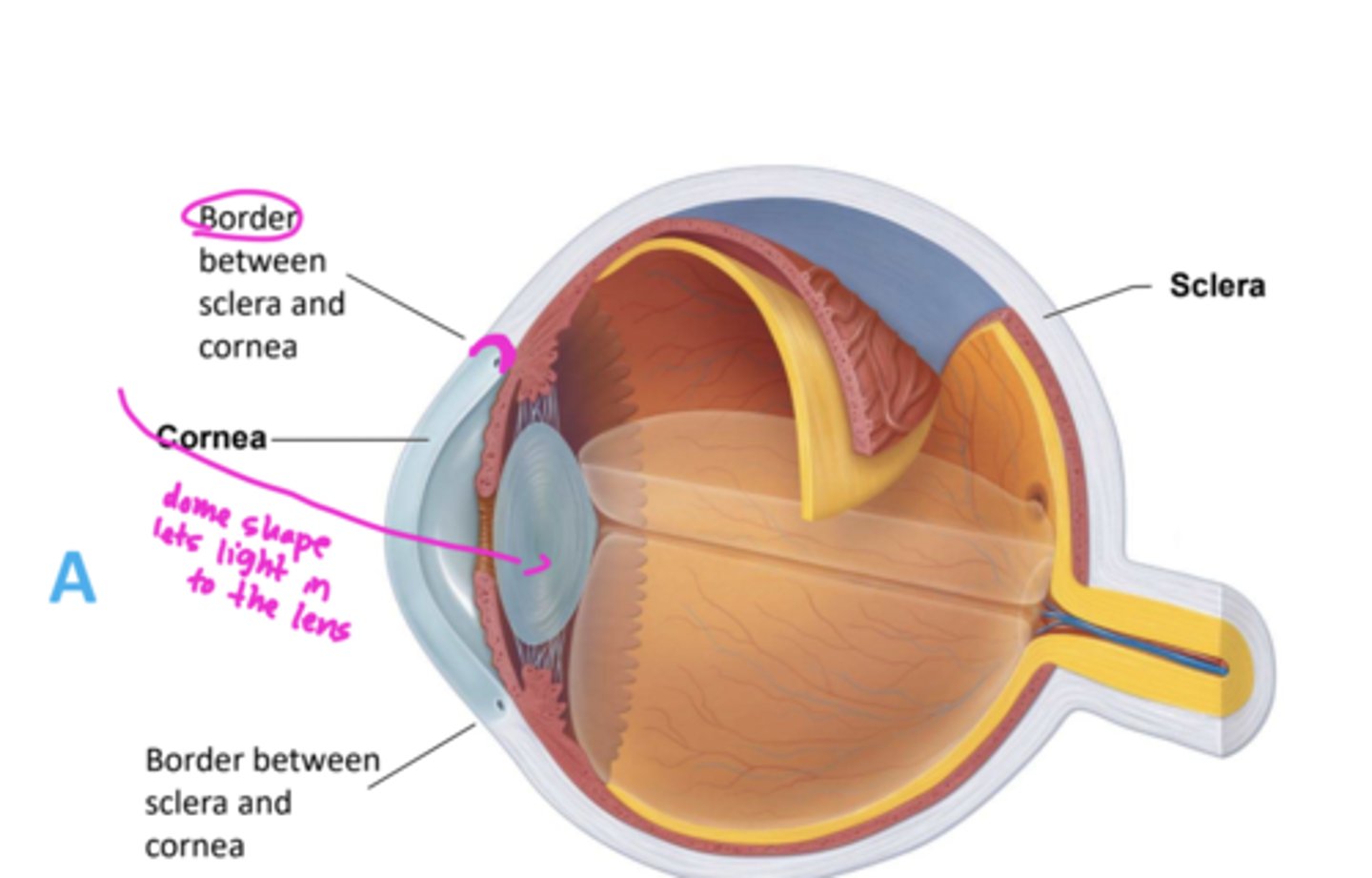
two regions of the fibrous layer of the eye
sclera and cornea
opaque posterior region in fibrous layer
sclera
transparent anterior 1/6 of fibrous layer
cornea
what anchors eye muscles to the eye
sclera
what bends light as it enters the eye?
cornea
dome shape lets light in to the lens
the cornea has numerious _______ receptors
pain
what do the cornea pain receptors contribute to
blinking and tearing reflexes
middle layer of eye
vascular layer
the vascular layer of the eye is also known as the
uvea
three regions of the vascular layer
choroid, ciliary body, and iris
which region is underneath the sclera in the posterior eye
choroid region
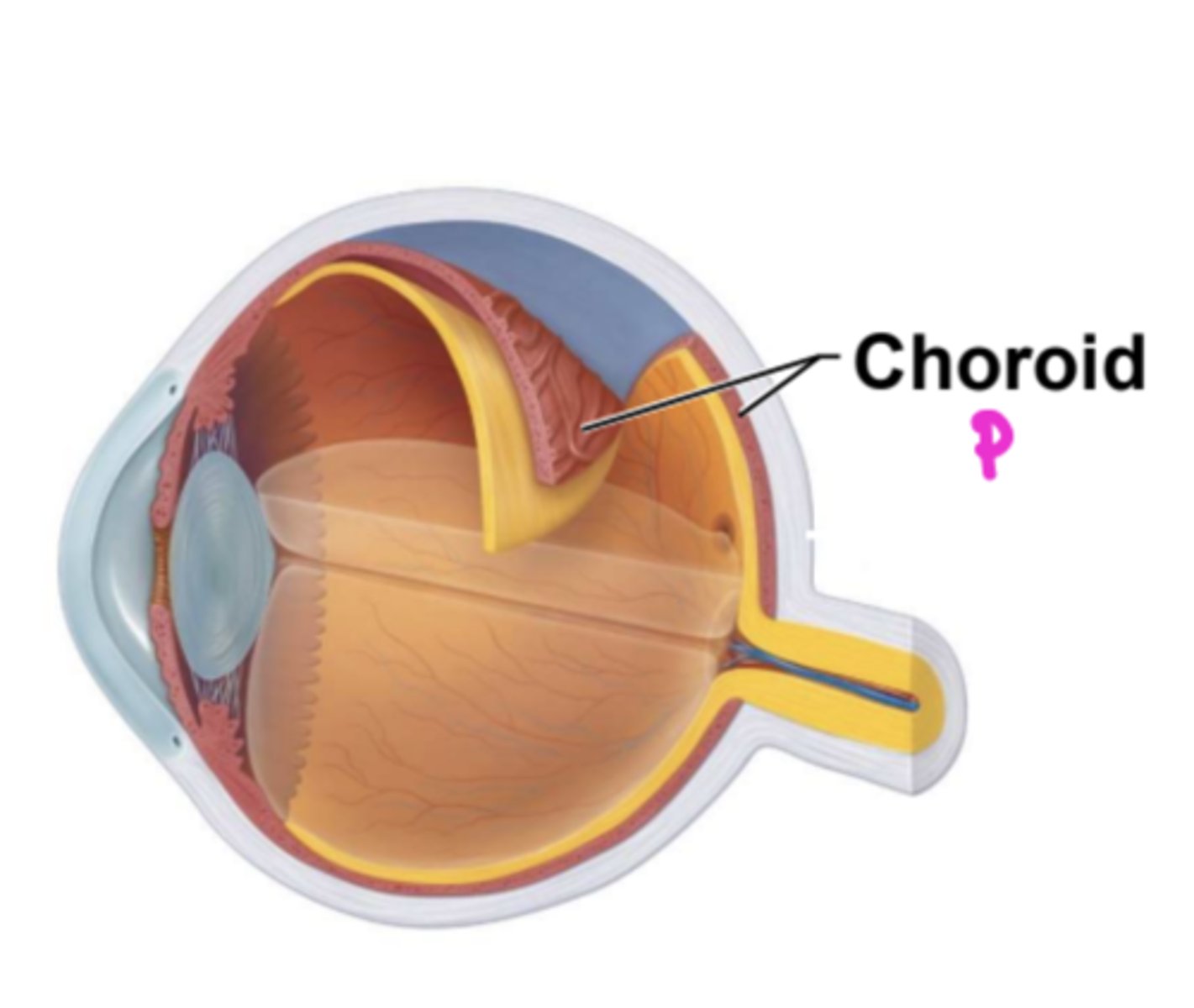
which region supplies blood to all layers of eyeball
choroid region
purpose of brown pigments in choroid region
absorbs light to prevent light scattering and visual
confusion
Ring of tissue surrounding lens
ciliary body
ciliary muscles are made out of _____ muscle
smooth
miliary muscles control ________ shape
lens
_________ holds lens in position
Ciliary zonule (suspensory ligament)
Colored part of eye
Iris
Central opening that regulates amount of light entering eye
Pupil
________ is the opening in the center of the iris
pupil
two muscles of the iris
circular (inner)
radial (outer)
circular muscles contract = _______ pupils
constrict
radial muscles contract = _______ pupils
dilate
constriction of circular muscles
Close vision and bright light
constriction of radial muscles
Distant vision and dim light
Inner layer of the eye is called the __________
retina
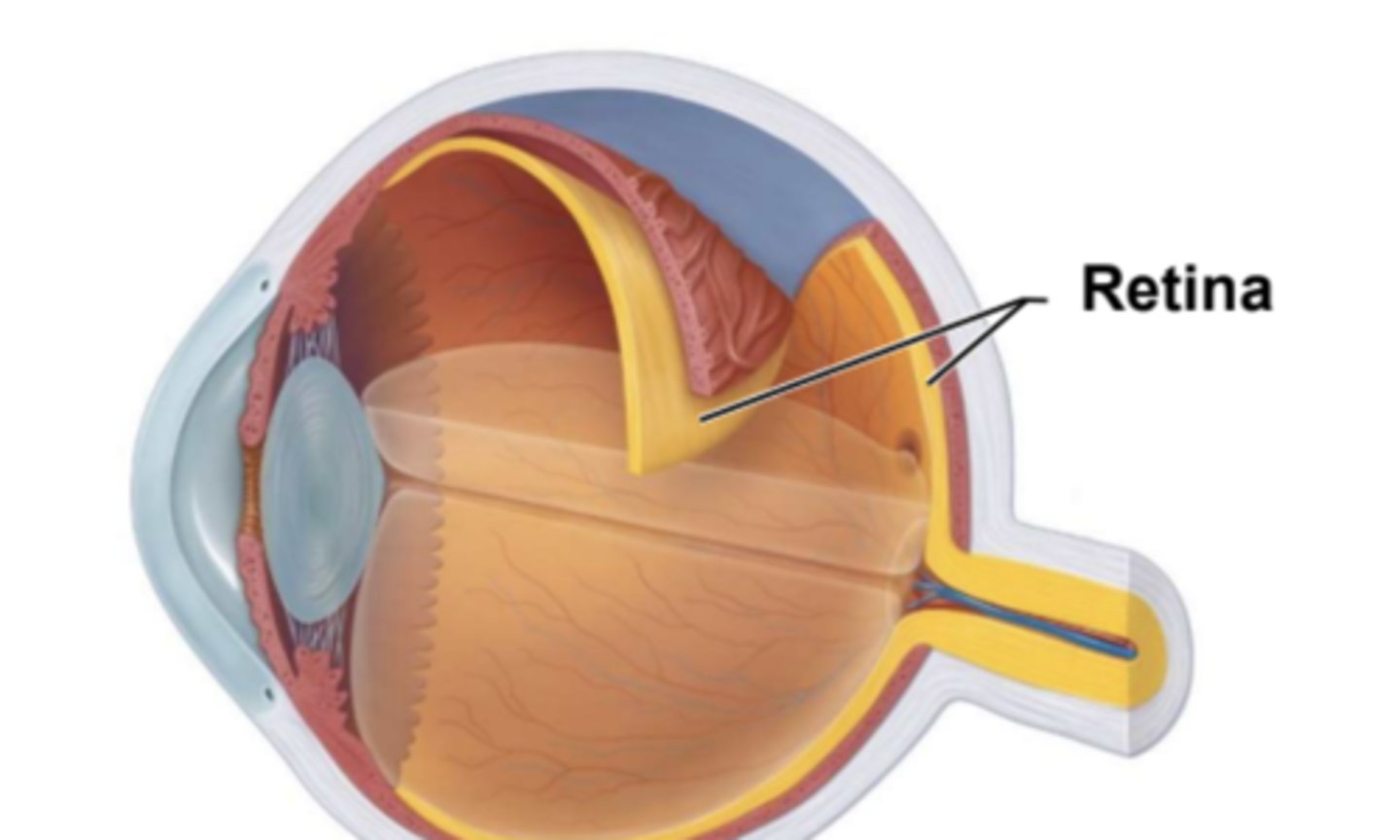
what are the layers of the retina
outer pigmented layer
inner neural layer
pigmented layer has _____ cell-thick lining
single
function of the pigmented layer
absorbs light and prevents scattering
stores vitamin A
cells of the neural layer
photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells
order of light entering the eye
cornea, lens, retina, photoreceptors
Order of information processing in vision
photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, optic nerve, brain
2 types of photoreceptors
rods and cones
site where optic nerve leave eye
Optic disc (blind spot) because it lacks photoreceptors
peripheral vision receptors for dim light
rods
vision receptor for bright light
cones
color vision
cones
where are cones localized
Macula lutea, an oval region exactly at posterior pole
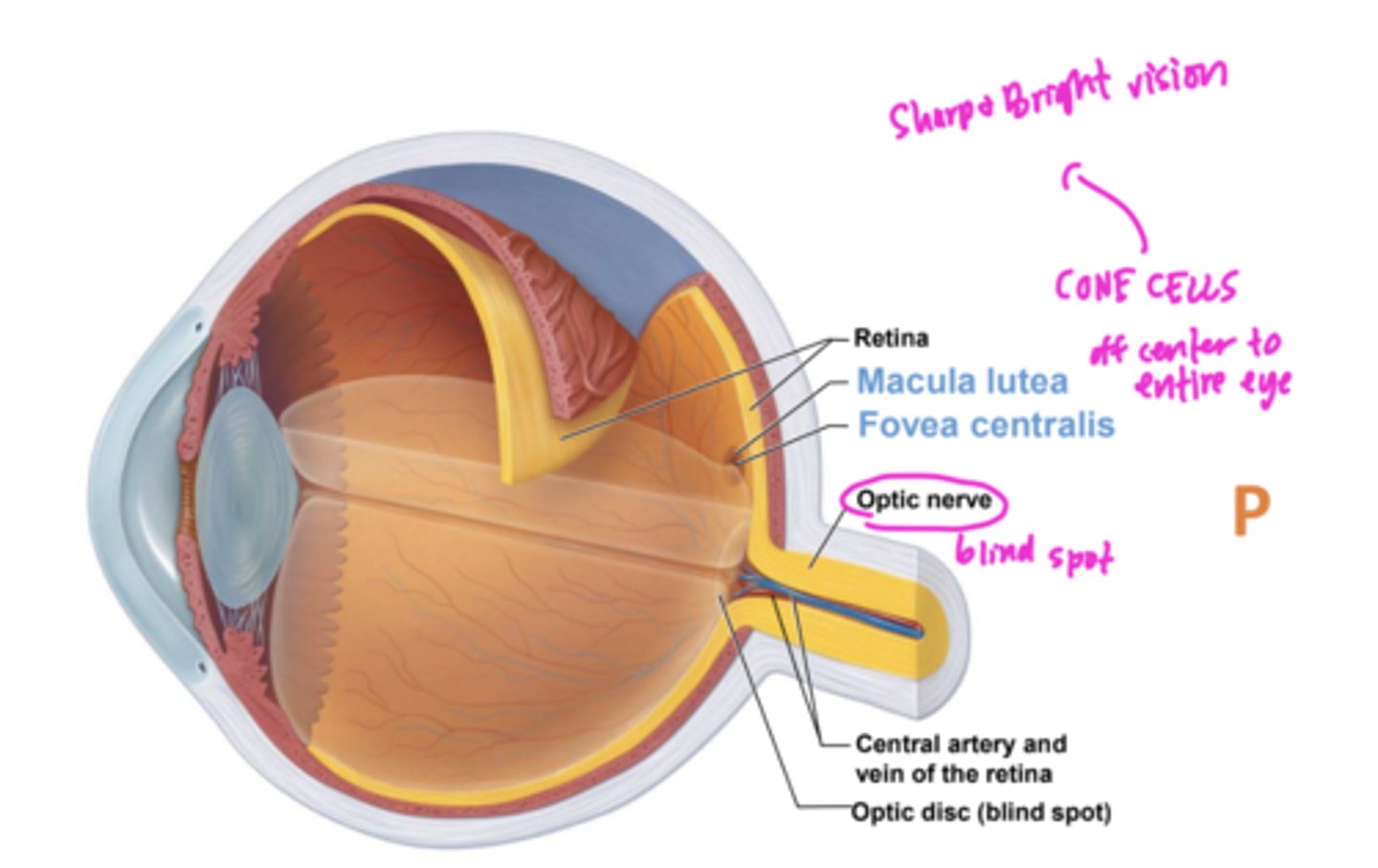
Tiny pit in center of macula with all cones
Fovea centralis
Macular Degeneration
Loss of vision in the center of the visual field due to damage of the macular lutea/fovea centralis (age related)
are rods affected in macular degernation?
no, Peripheral vision remains
dry macular degeneration
age related caused by deposits of lipids/proteins
fuzzy/distorted vision
wet macular degeneration
blood vessels growing in vision areas = damage rods and cones
blind spot in center of field of vision
What separates the eye into two segments
lens and ciliary zonule
fluid in the anterior segment of eye
aqueous humor
fluid in the posterior segment of eye
vitreous humor
both humor function to ....
transmit light and contribute to intraocular pressure
how does vitreous humor hold neural layer of retina firmly against pigmented layer
intraocular pressure
where does aqueous humor drain
sclera-cornea junction
which humor forms in embryo and lasts lifetime
vitreous humor
forms by filtration from the
capillaries in the ciliary processes
aqueous humor
Aqueous humor flows from the posterior chamber through the _______ into the anterior chamber.
pupil
how does the lens process information
changing shape to precisely focus light on retina
changes in lens with age
more dense
covex
less elastic
disease caused by clouding of lens
cataracts (more light needed to see)
Pinkeye is an injection of the
conjunctiva
The cornea is part of the
fibrous layer (outer)