Mammalogy lecture exam 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
what is measured as volume of oxygen consumed per unit time?
resting metabolic rate
what is measured as oxygen consumed per day?
total metabolic rate
how does metabolic rate increase?
total metabolic rate increases with size, larger animals need more food
what is oxygen consumed/per day/gram body mass, decreases with body mass, smaller mammals need more food per gram of body mass?
mass specific metabolic rate
what is the maintenance of body temperature by means of heat produced inside the body by chemical reactions?
endothermy
what maintain a relatively consistent body temperature?
homeothermy
what means the regulation of body temperature varies?
heterothermy
what means body temperature is regulated in different parts of the body?
regionally
what means temperature of body is regulated at different times?
temporally
why is body temperature maintained?
enhance chemical reactions, increases information processing, enhances neuromuscular system, allows animals to be active in almost any environment
what is the normal body temperature for eutherian “placental” mammals?
36 C to 38 C
what is the normal body temperature for monotremes and marsupials?
30 C to 33 C
what is Heat Production = Heat Loss?
thermodynamic equilibrium
what are properties which influence heat exchange (loss to environment)?
metabolic rate, moisture loss, insulation, absorption of radiation, size, shape and orientation of body, temperature difference of animal and environment
what measures the internal temperature of mammals?
hypothalamus
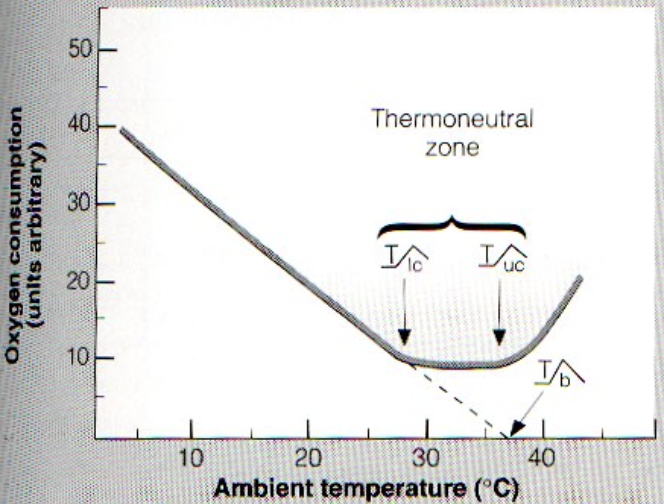
what means range of temperature within which the metabolic rate is minimal and does not change as ambient temperature increases or decreases?
thermal neutral zone
what means air movement?
convection
how is heat lost to the environment?
radiation, conduction, convection, evaporation
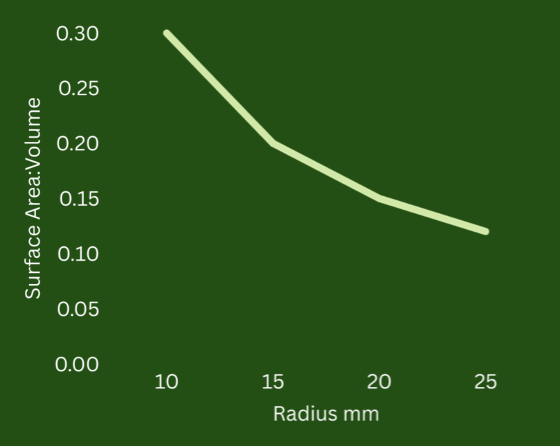
what does this graph show?
higher surface:volume equals more surface to lose heat relative to body size of mammal
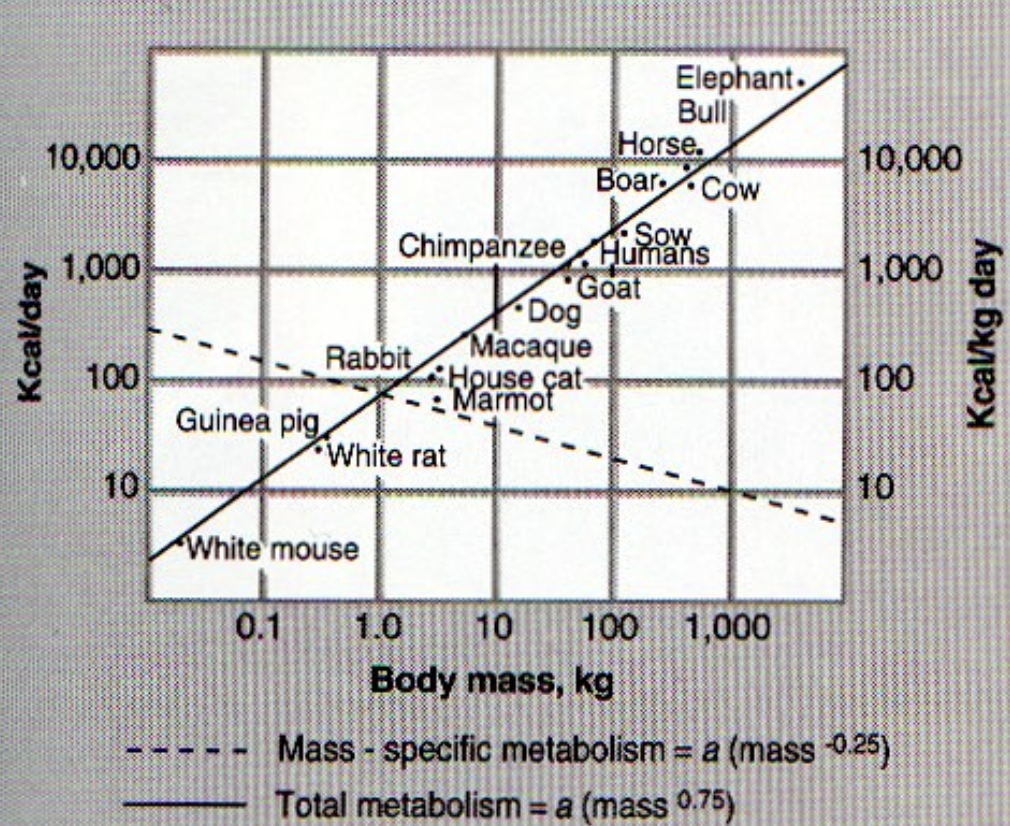
what does this graph show?
larger animals consume more per day, smaller animals need to consume more per their body mass
what means races from cooler climates tend to be larger than members of same species in warmer climates, because of the energetic advantage of decreasing surface area:volume, larger mammals have less surface area per volume and benefit from reduced rates of cooling?
bergman’s rule
what reduces thermal conductance using fur or fat, and effectively reduces lower critical temperature?
insulation
what insulates by trapping a layer of air near skin, works well for terrestrial and amphibious mammals, and is not effective if water displaces layer of air?
fur
what means marine and aquatic mammals have blubber, blubber is a thick layer of adipose tissue, up to 40% of mass of ring seals, also insulation?
fat
what means appendages of endotherms in colder climates tend to be shorter than those in warmer climates?
Allen’s rule
what means arteries and veins in extremities are close together, blood from the core warms blood returning from extremities, lower temperature in extremities reduces the difference in temperature between appendage and environment, lower heat loss in environment?
countercurrent heat exchange
what is used by many small mammals to combat cold, effectively decreases surface:volume ratio?
huddling
what means many small mammals forage in tunnels covered by leaves or snow?
foraging zones
what means move to a milder climate?
migration
what means stay in sheltered location?
reduced activity levels
what means period of inactivity characterized by a reduced metabolic rate and lowering of body temperature?
dormancy
what is generally short term, body temperature 10-22 C, common in bats and shrews?
torpor
what is profound dormancy, lasts weeks, body temperature 2-5 C?
hibernation
what is the cost of hibernation?
large mass loss
which lost the most mass in Wyoming ground squirrels?
adult and yearling males
how much of earth is desert?
35%
how much of body mass of mammals is water?
70%
what is the maintenance of proper internal salt concentrations?
osmoregulation
what are primarily responsible for osmoregulation, rid body of nitrogenous waste?
kidneys
what are the three types of nitrogenous wastes in vertebrates?
ammonia, urea, uric acid
what is very toxic, requires a lot of water to dilute and dispose of, no energy cost, and found in fish and amphibians?
ammonia
what is not as toxic, water soluble, can be concentrated more than ammonia, requires energy to produce, primary product in mammals?
urea
what is not as toxic, not very soluble in water, requires very little water to expel, energetically costly, used by birds and reptiles?
uric acid
what produce feces 2.5 times drier and rats and also assimilate 90% of digested food?
heteromyids
what produce concentrated milk?
desert mammals
what does carbohydrates + O2 = CO2 +H2O mean about animals?
use metabolic water
what are most water requirements met by in desert living mammals?
prey
what is a major mechanism employed by mammals to reduce body temperature, water absorbs a great deal of heat when it changes state, water may be scarce so this may be limited?
evaporative cooling
what is the loss of water and salts from eccrine glands (not in rodents and lagomorphs)?
sweating
what is rapid shallow breathing that increases evaporation from respiratory tract, do not lose salts, cools brain, may cause respiratory alkalosis?
panting
what is the spreading of saliva on limbs, tails, chest etc (common in rodents and lagomorphs)?
saliva spreading
what prevents water loss through respiration, inhaled air passes over moist tissue and is warmed and humidified, nasal tissues are cooled by this evaporation, during exhalation, moisture in returning warm, saturated air from lungs condenses in nasal passages, water is conserved?
respiratory heat exchange
what is an almost hairless region that allows heat loss?
thermal windows
what is a period of dormancy in response to hot or dry conditions (common in rodents and also occurs in marsupials and others)?
estivation
to avoid high temperature almost all rodents of North American deserts (except sciurids) are what?
nocturnal and fossorial
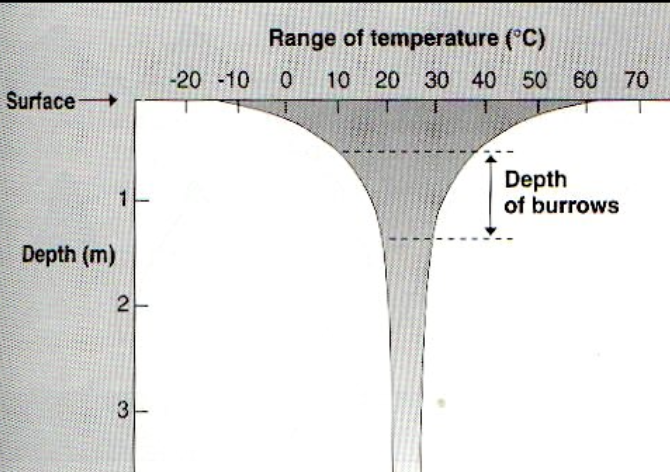
what does this graph show?
subsurface temperature in deserts
what have small daily fluctuations in body temperature, 36 C in early morning and 39 C by midafternoon?
hydrated camels
what has their daily variation in temperature triple, 34.5 C at night and 40.5 C during the day, enables them to lose heat at night when cool, does not require sweating, saves 4.5 L water a day?
dehydrated camels
what can tolerate a water loss of 30% (most other mammals die at 15%), and rehydrate quickly, concentrate urine and reabsorb water from feces, fur insulates and thermal windows allow heat loss, have numerous sweat glands?
camels
what detect radiant energy in form of light, is the primary sense in humans?
photoreceptors
what is the reflective layer in the eye that reflects light back to the retina, improves night vision, and is responsible for eye shine (nocturnal mammals)?
tapetum lucidum
what are light sensitive in the eye?
rods
what are color sensitive in the eye?
cones
which animals have more rods?
nocturnal
which animals have more cones?
diurnal
what is hearing by?
mechanoreceptors
what are the external ears that are unique to mammals called?
pinnae
what kind of sound is used by elephants and is too low for humans (< 20 Hz)?
infrasound
what kind of sound is used by bats and is too high for humans (> 20 kHz)?
ultrasound
where do bats form their sound for echolocation, notice when pulse is altered, can detect size, shape, distance, texture and movement, can discriminate echo delays as short as 70 millionths of a second, and resolve objects as small as the width of human hair?
larynx
where does the echolocation pulse originate in toothed whales, is directed by disc shaped skull and focused by fluid filled melon, and is received via lower jaw and channeled through fluid filled sinus to inner ear?
nasal sac in forehead
what type of receptors are taste and smell?
chemoreceptors
what is generally not a primary sense, important in diet selection?
taste
what is well developed in most mammals, important in locating danger, finding food and mates, communication, etc, reduced in whales and some higher primates?
olfaction
what is through mechanoreceptors, includes vibrissae, many have specialized receptors in snouts and lips, highly evolved tactile receptors in digits(especially primates), tactile systems highly developed in mammals that burrow?
touch
what are used to detect small electrical fields produced by prey, can be found in star nosed mole and platypus?
electroreceptors